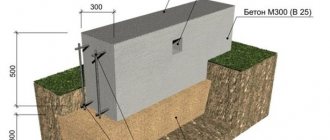
This type of building foundation is resistant to tension and compression, which gives the foundation high strength.
Optimal calculation of the number of profile and smooth rods of certain diameters connected in a single frame ensures the load-bearing capacity and reliability of the foundation of a building or structure.
We will tell you in the article how to calculate the amount of reinforcement for a strip foundation.
Standards
As a result of many years of research and testing, methods for calculating the reinforcement of poured strip foundations were developed.
During the Soviet era, regulatory documentation was developed regarding calculations of reinforcement for strip foundations.
Back in 1989, the USSR State Construction Committee approved SNiP 2.03.01-84 “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures” , the standards of which are still valid. It specified the rules for generating initial data for calculating reinforcement.
SNiP sets out the procedure for calculating the quantity and diameters of longitudinal, vertical and transverse reinforcement, how to make welded connections of rods and install embedded parts in a concrete monolith. A separate chapter provides instructions for the design of prestressed elements.
Earlier in 1978, the “Guidelines for the design of concrete and reinforced concrete structures made of heavy concrete (without prestressing)” were developed and adopted for mandatory execution. Based on these two documents, design organizations developed methods for calculating the reinforcement of strip foundations.
Calculation of formwork for strip foundations
The main task of the formwork is to hold the liquid concrete mass in the desired shape until the monolith completely hardens. Calculation of formwork is an integral part of the economic analysis of the costs of building a facility. How accurate the enclosing structures will be depends on their reliability. At the same time, correctly selected dimensions of formwork elements will prevent the occurrence of emergency situations. Every developer is interested in how to calculate the formwork for floors, walls, vertical supports and strip foundations. There are many different designs for pouring concrete.
How to calculate how much is needed?
The cornerstone of the methodology for calculating the reinforcement of strip foundations is the principle of the predominance of the resistance of the soil foundation over the specific load from the weight of the building or structure.
Compliance with this ratio is the basis for calculating the width of the tape. Together with the laying depth, this parameter determines the cross-sectional size of the poured foundation.
After this, the load-bearing capacity of the belt is calculated, the value of which depends on the full load of the ground part of the structure. At this stage, the number and assortment of reinforcing bars and their form of connection into a single frame are determined.
If you press on any soft object, it will bend . The upper plane will compress, and the material below will stretch. So in a strip foundation, its upper part will experience compression, and the lower layer will be affected by tensile forces.
This physical phenomenon is taken into account when calculating a monolithic tape. That is, reinforcement is laid in the upper and lower belts, which withstands compression, and the concrete below resists tension.
Based on this provision, the “Guidelines for the design of concrete and reinforced concrete structures made of heavy concrete (without prestressing)” was developed.
Heavy concrete is prepared from:
- cement M 300 – M 800,
- crushed granite rocks,
- medium-fraction sand,
- water of medium hardness with the addition of various types of plasticizers.
It is used for the construction of poured foundation strips.
In addition, they use the Code of Rules SP 52-101-2003, which contains recommendations for calculation and design related to the manufacture and installation of LF reinforced frames. The rules are consistent with the requirements of SNiP 52-01-2003.
Determining the laying depth and height of the tape
When calculating the depth of the base of a strip foundation, two factors are included:
Ground water level
The groundwater level is easy to determine if there is a well near the construction site . The distance from the ground level to the surface of the water in it will be equal to the desired parameter.
In the department of architecture and land management of the local administration, you can get a copy of the vertical survey linked to the construction site, where the groundwater level will be indicated. If there is neither one nor the other, then this indicator is determined by taking soil samples using soil drilling.
To prevent deep water from affecting the foundation, the base of the filler tape is placed above this mark.
Freezing depth
It is necessary to know it because exposure to wet soil at sub-zero temperatures in winter causes water in it to freeze . This process causes soil heaving because at this time it sharply increases in volume.
Heaving forces can easily push up the foundation of a house. To prevent this from happening, the sole of the tape should be below the frost heave zone. The freezing depth is determined by reference or in the same way as when establishing the groundwater level.
The depth of the foundation strip should be above the groundwater level and below the soil freezing level. The number of longitudinal rows depends on the height of the base. According to SNiP, the distance between structural rows of reinforcement should not be more than 40 cm.
How many rows of reinforcement are needed to reinforce a strip foundation 1 meter high? Number of rows depending on the height of the base:
- up to 70 cm – without longitudinal reinforcement;
- from 71 to 90 cm – one row;
- from 91 to 130 cm – two rows;
- from 131 to 170 cm – three rows;
- from 171 to 210 cm - four rows.
It has been established that at the construction site, groundwater lies at a depth of 1200 mm, and the level of soil freezing is 800 mm. In this case, the depth of the LF is taken to be 1 meter. The height of the tape, taking into account the standard height of the plinth of 150 -200 mm (the distance from the top of the foundation to the ground level), will be equal to 1150 - 1200 mm.
Load collection
The maximum structure weight includes the following:
- The weight of all house structures, including the foundation.
- Snow load on the roof (SNiP 2.01.07-85).
- Weight of equipment: stove, boiler, piping system, plumbing fixtures, furnishings, etc.
- Approximate weight of the maximum number of people staying in the house at the same time.
The total weight is multiplied by the safety factor - 1.1. This parameter - P will be the main determining factor in calculating the width of the foundation.
Outsole width
The width of the strip foundation is calculated using the formula Tхk/S ≤ R, where:
- T - specific load from the maximum weight of the structure (see above);
- k – safety factor (1.1);
- S – sole area (S = P/T);
- R – soil resistance.
R = 1.88 kg/cm2 (soil - loam), P = 15000 kg, T = 1.8 kg/cm2, L – tape length 24 m. S = P/T = 8333 cm2. The optimal width of the tape will be equal to: S/L = 8333/2400 = 3.47 cm. Therefore, the width of the LF can be taken based on the thickness of the masonry + tape protrusions on both sides of the wall (25 mm x 2 = 50 mm).
When constructing an external fence of 1 brick (250 mm), the width of the LF will be 250 +50 = 300 mm = 30 cm. If the walls are erected from cinder blocks, then the transverse dimension of the tape is 40 cm. For walls 1.5 masonry elements thick, the foundation is made wide 50 cm or more.
Quantity of reinforcement for slab foundation
How to calculate for this type of basis. Most often it is used for the construction of small cottages, holiday villages, and other buildings without basements or semi-basements. Externally it looks like a solid plate with a metal base. The average S of the base is no more than 20 - 25 cm.
Before starting, you need to clearly determine the diameter of the rod that will be used. In accordance with GOSTs and SNiPs, on most soils with a non-flowing surface, a ribbed rod of class AI, the diameter of which is one centimeter, is used. If the earthen base has high flowability, then you also have to use a ribbed rod, but only with a diameter of 1.5 cm. Vertical foundations can be constructed using AI class rods, but the diameter is much smaller and is 0.5 cm.
In the case of load-bearing structures, you need to be extremely careful and calculate the load correctly. The material from which the wall will be made plays an important role, since the mass of the entire structure as a whole depends on it. Building codes indicate that small permanent structures can be constructed with rods up to 1.0 cm in diameter. Massive buildings require the installation of reinforcement 1.5 cm in diameter.
The average distance between the rods should not exceed 20.0 cm, both in the longitudinal and transverse directions. The calculation per square meter of rods is 5, which are connected to each other with a special wire. Knitting occurs both with crochet and with automatic equipment - a gun, depending on the availability and area of knitting.
Dependence of the number of rods on the reinforced frame diagram
The tape experiences two main forces . One of them presses from above (load from the house), the other force vector pushes the tape upward (soil resistance + soil heaving). To balance this phenomenon, two horizontal belts of reinforcing bars are made in the monolith mass.
Double-layer reinforcement at the top and bottom inside the concrete is relevant for shallow and medium-depth foundations. For deeply buried belts you need to install 3 belts. To fix the rods in space, they are fastened with knitting wire. This type of reinforcement frame formation is called the structural type.
Longitudinal (working) rods are tied with transverse and vertical rods that do not bear load . According to SNiP 52-01-2003 and the Manual (see above), longitudinal rods are located along the entire length of the tape with a gap between the reinforcement and the formwork of at least 30 mm and 50–70 mm from the bottom.
Vertical sections are located along the belts, alternating every 100 - 300 mm from each other. The transverse sections correspond to the size of the belt width from 300 mm.
When calculating the lengths of the rods, you need to add allowances - at least 30 ø of the rod for tying the reinforcement unit. The reinforcement is extended with an overlap with the ends inserted by 150 mm.
Now, knowing these standards, it is easy to determine the number of rods in all directions. After this, it remains to determine their diameters.
Diameter and location
According to the above regulatory documents, the total cross-sectional area of the longitudinal reinforcement should be equal to 0.1% of the cross-sectional area of the tape .
For example, the width of the foundation is 400 mm, and its height is 1000 mm. Then the transverse area of the rods will be 4000 cm2.
You will need 4 bars of periodic reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm . Smooth sections of vertical reinforcement are prepared from rods ø 6 mm, and for crossbars smooth sections ø 8 mm are used. Read about choosing and calculating the diameter of reinforcement in this article.
Calculation rules and parameters
Calculation of reinforcing bars consists of two parts: calculation of longitudinal and calculation of vertical and transverse reinforcement.
Longitudinal sections
To form double-belt reinforcement, 4 longitudinal rods of a periodic profile are installed along the entire perimeter of the foundation. With a tape length of 24 m, the reinforcement will require 24 x 4 = 96 m, with allowances this will be 100 m.
Vertical and transverse bars
The interconnected segments form a frame, in the corners of which there are longitudinal rods . Their calculation depends on the width and height of the tape. With a height of 100 cm and a width of 40 cm, the tape will require transverse sections 30 cm long and vertical connections 92 cm high (subtract the lower gap of 50 mm and the upper protective layer of concrete 30 mm from 1000 mm).
For a perimeter with a length of 24 m and alternating frames with an interval of 300 mm, it is easy to calculate that for vertical bars you will need smooth rods ø 8 mm with a total length of (24000/300) x 2 x 0.92 m = 147.2 m. The need for transverse reinforcement will be (24000/300) x 2 x 0.3 = 48 m.
Bottom line
Based on the previous, we can summarize the need for reinforcement for a foundation 24 m long:
- vertical rods ø 8 mm – 150 m;
- cross rods ø 6 mm – 50 m;
- longitudinal periodic reinforcement ø 12 mm – 100 m.
According to the standards, the consumption of tying wire is 50 cm for each connection point of reinforcing bars. For strip poured foundations, steel thread ø 0.8 – 1.2 mm is used.
Calculation of wooden formwork
At the beginning of the calculation, we measure the perimeter of the foundation. Multiply the result by 2, since the concrete is poured between two boards of the erected structure
The height of the structure being erected is equal to the height of the foundation + 20 cm of margin. Additional height, when calculating, is necessary, since the entire structure must be higher than the level of the poured concrete mixture.
To calculate the required number of cubic meters of boards for installing the formwork, it is necessary to multiply the resulting perimeter length by the height of the board and multiply by the thickness of the board.
Let's look at an example of calculating wooden formwork:
- house perimeter -100 m;
- foundation height = 0.5 m boards + 0.2 m stock = 0.7 m;
- board thickness -0.05 m.
Using simple mathematical calculations, we calculate: (100*2)*0.7*0.05=7 m3.
Using calculators
Not all developers are able to tinker with calculations of the need for reinforcement. There is also a risk of mistakes made during foundation design. Online calculators help you accurately calculate how many and what type of steel rods need to be prepared to form the reinforced frames of a poured foundation.
Services request initial parameters such as:
Base length.
- Tape width.
- Sole depth.
- Diameters of longitudinal, vertical and transverse reinforcement.
- The number of longitudinal rods in the cross section.
- The number of rows of vertical and transverse rods and the pitch between them.
- Soil resistance.
This data is entered into the service windows. After this, you need to click on the “Calculate” field. After this, the calculator will show the linear molding of each type of reinforcement and its weight.
On the Internet you can find several types of LF calculation calculators , which will provide not only reinforcement data, but also suggest the best location of the tape branches, its width and height. You can find popular calculators here and here.
You will find all the most important things about strip foundation reinforcement in this section of the site.
Calculation of the amount of concrete for the foundation
Calculating the required amount of concrete for the foundation is an important stage in which mistakes should never be made. If mistakes are made, first of all, the material will be used and left in the end. In the future, you will no longer be able to use it, and the material will be damaged and remain unused. In order to avoid errors and in order to save material, as well as reduce financial costs, you need to make the calculations correctly.
How to calculate the amount of concrete for the foundation? As noted earlier, each calculation depends, first of all, on what type of foundation is used.
Let's look at each type separately.
For pouring a slab foundation
The calculation of a slab foundation is the simplest among all other calculations.
So, the formula is this: Volume of the slab = length of the base of the parallelepiped multiplied by the width of our base, and then multiplied by the height of the parallelepiped. So, we find out the volume of the slab.
Next, we need to find out the volume of reinforcement.
Reinforcement volume = number of rods multiplied by P (constant value 3.14), and then multiplied by the radius of the reinforcement (squared), and then multiplied by the length of the rods.
Next, we need to find out the volume of concrete. To do this, we subtract the volume of the reinforcement from the volume of the slab.
For pouring a columnar foundation
What formula is needed to calculate the pouring of a columnar foundation? Volume of concrete = number of piles multiplied by P (constant value 3.14), then multiplied by the diameter of the pile (squared) and multiplied by the height of the existing piles. Next, we divide all this by 4.
For pouring a strip foundation
Volume of concrete = total area multiplied by the height of the tape.
Today we have discussed how to determine and find the amount of concrete required for pouring various types of foundations. Now you know how to make calculations correctly and competently.
Before substituting values into formulas, make sure once again that these values are really the same, without changes.
After all, as noted earlier, the structure can be deformed and also change in size and volume. Take this factor into account and take measurements again if necessary. Happy construction.