The basement foundation is an additional room that is not considered a floor by law. The structure, half immersed in the ground, is an excellent insulating layer that protects the house from cold and dampness. A foundation with a plinth can be used to build a cellar, workshop, garage, and even a guest room if there is effective ventilation. A good solution is to place equipment in the underground level that ensures the vital functions of the building - a heating boiler, a storage tank, an electrical panel, a generator, a gas distribution box.
Reasons for protecting the basement from moisture
The foundation is the main barrier between groundwater and the basement. Lack of protection from moisture or an ill-conceived option contributes to the formation of mold, mildew and dampness. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out external waterproofing of the basement. The porous structure of concrete is well saturated with water, and subsequently:
- formation of cracks;
- the appearance of fungus and mold;
- the basement may be filled with water.
loss of room heat;
Therefore, it is necessary to provide reliable protection of the foundation from groundwater and dampness. Work should be carried out at the initial stage of construction.
Possible protection options
There are several technologies to protect the foundation from destruction:
- Removing excess moisture from the soil using a drainage system.
- Creation of a waterproofing layer.
The possible methods do not cancel each other out; in certain cases they are used together. At high humidity, enhanced protection is required.
Anti-corrosion measures are provided for by technological standards at the production stage of structures. During the manufacturing process, chemical components are added to the working composition. Under actual operating conditions, the anti-corrosion protection indicators are adjusted downwards. Therefore, at the zero construction cycle, all necessary methods are considered.
Possible types of anti-corrosion measures (two levels of protection are determined) are set out in SP 28.13330.2012.
Drainage of rain and melt water from the construction site is mandatory to avoid waterlogging of the soil. A vertical layout of the site is carried out, giving a special slope.
The method of protecting the foundation from water is selected after hydrogeological studies.
Waterproofing materials
To protect the foundation base from moisture, waterproofing work is carried out. The material varies in reliability, complexity of the device and cost. There are several types of foundation waterproofing:
- locking mastic (combined, polymer, bitumen compositions);
- coloring mixture (special paints);
- rolled products (roof felt, roofing felt).
A protective barrier is created outside and inside the building. The materials used must have good adhesion, fit tightly to the surface, and form a layer of uniform thickness. In this case, you will get reliable protection against excess moisture, dampness, and the formation of fungus and mold.
External waterproofing
How to protect the foundation from moisture from outside the building, what material is better to use? To perform construction operations the following is used:
- bitumen mastic;
- roll waterproofing;
- polyurea (resin and isocyanate);
- PVC membranes with pimples.
The protective layer will be covered with earth and subjected to high pressure. Therefore, the hydraulic protection must have a good margin of safety. For exterior work, it is not recommended to use thin polymer films, solutions based on liquid rubber, or acrylic.
Bitumen mastic is used to prepare the base surface. Rolled waterproofing is fused as a second layer. It is recommended to lay the rolls with overlapping seams in several rows.
Polyurea is applied to a surface cleaned of dust and dirt using a sprayer. The composition of resin and isocyanate creates a durable film that does not allow water to pass through. The product adheres well to concrete. Spraying is performed several times.
A polyvinyl chloride membrane (with pimples) is attached to the surface using special pins. The material is durable and does not allow moisture to pass through.
How to strengthen the old foundation of a private house with reinforced concrete
The restoration technology involves the construction of a reinforced concrete strip along the perimeter of the building, increasing the contact area between the base and the soil and reducing the reaction of the soil.
This strengthening can be carried out along the boundaries of the entire base
Sequence of operations:
- Prepare a pit enclosing the structure.
- Clean the concrete surface.
- Place a cushion of sand at the bottom.
- Make holes for installing fittings.
- Drive in the metal rods.
- Connect them with a reinforcement cage.
- Assemble the wooden formwork.
Then pour cement mortar or concrete. After hardening, fill the reinforced concrete strip with soil.
Waterproofing inside the facility
For interior work, penetrating compounds are used. The impregnation penetrates the concrete structure and makes it waterproof. This makes it easier to protect the foundation from moisture from the inside. For work used:
- liquid rubber;
- penetrating waterproofing;
- polyurea.
The technology for applying a waterproofing solution is carried out in the following order:
- The wall is wetted with water.
- A penetrating compound is applied.
- The treated surface is kept moist for three days. To achieve good polymerization of the composition. Otherwise, the waterproofing will be of poor quality.
Drainage system
On wet soils, additional work must be done to drain water. To prevent the basement from flooding, a drainage system is installed around the building.
To drain water around the perimeter of the house, drainage pipes and gutters are installed and wellpoints are used. The structure is mounted on clay soils that are susceptible to heaving in winter. Drainage is laid at the stage of digging a pit under the foundation of the house. There are several types of design:
To complete the system, perforated drainage pipes are often used. There are no technical restrictions when laying the material, and installation is easy. It’s easy to protect the foundation from moisture with your own hands. To drain water, special wells and sumps are built.
Water intake devices (wellpoints, vacuum pumps) are installed to seasonally lower the water level. Gutters are installed to drain the soil and protect the foundation from rain.
The permissible depth for laying drainage pipes is from 4 to 5 meters. Be sure to top it with sand and gravel.
Is it necessary to cover the foundation for the winter?
If you meet such a deadline, then already in the process of building the foundation, you need to take a number of measures so that in winter it does not collapse under the influence of the external environment. Preserving the foundation for the winter is to protect the construction site as much as possible from rain, snow and groundwater. In addition, reinforced concrete structures without load can be pushed out due to the swelling of unevenly frozen ground.
Already at the stage of excavation and formwork you need to take care of drainage, insulation and waterproofing. Hanging piles from grillages may not need to be insulated. But separate pillars, left unloaded for the winter, will definitely move in different directions. Any monolithic foundation is subject to the forces of earth heaving. These processes are especially noticeable in clayey, moist and deeply frozen soil. If you get rid of the influence of at least one of these components, the deformations can be significantly reduced. We need to seal off the space surrounding the foundation from moisture, insulate the concrete, and pour sand, screenings, or other non-metallic compounds into the larger pit.
Groundwater drainage scheme
Construction of the blind area
How else can you protect the foundation from external influences? At the very base of the construction site, a kind of drainage system is performed. The blind area is made from various materials:
- paving slabs;
- asphalt concrete;
- cement-concrete mixture
The strip width is 0.6-1.2 meters. The purpose of the structure is to drain rain and melt water from the external walls of the building. In addition, it is a wonderful decorative element of landscaping. The blind area should be combined with the architecture of the facility and complement the landscape design of the surrounding area.
The technology for performing the work involves a bedding layer (crushed stone, sand, clay) and a decorative coating.
The structure must not be washed away by water and not allow it to pass through.
Protection of the base from freezing
So how to protect the foundation from freezing, and is it necessary to take additional actions? Insulation of the base of a construction site is necessary. If the process is not followed, the walls will become moldy and cracks will form. The resulting defects are good conductors of cold, and as a result, lead to the destruction of the base of the structure.
The base, unprotected by special materials, will crack from low temperature and moisture.
Insulation is carried out outside the building using several methods:
- Thermal insulation material is placed in the formwork when pouring the foundation. During the work process, fewer cracks are formed.
- The insulation is laid on the base of the constructed object.
They often resort to insulation inside the building. Additionally, a diffuse film is used with the main material. It helps to delay the penetration of moisture and condensation. Work is carried out in the following cases:
- The house is built on an uninsulated foundation.
- The basement is being converted into a living room.
- Strong exposure to moisture.
- The insulation material becomes damp.
Insulation is one of the ways to protect the foundation from moisture of an already built house.
It is not recommended to use mineral wool as base insulation. The material becomes saturated with water and ceases to perform its functions.
The insulation for the base of the building must have:
- Low heat transfer rates.
- Durability.
- Resistant to temperature changes.
- Lack of ability to pass water.
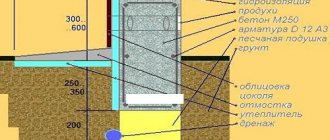
A reliable option for protecting the base of a building is laying bitumen rolls. The next option: treat the inside of the object with penetrating impregnation, and perform a blind area outside. At the junction of the wall and the foundation, roofing material is laid. Otherwise, dampness in the building is guaranteed.
Insulation of the basement floors of houses without basements
For seasonal homes, the thickness of insulation is calculated according to current standards based on comfort, and for permanent homes - based on energy saving. The calculations below were performed for the climatic conditions of the Moscow region. The required minimum value of the total resistance to heat transfer of the basement floor of a country house based on the comfort condition is 1.52, and from the energy saving condition - 2.8 m² ⋅ C/W. Knowing the design of the basement floor and the thermal conductivity coefficients of the materials, you can determine the required thickness of the insulation. Table 1 shows the results of calculations of some insulation materials with the following initial data:
- basement floor - monolithic reinforced concrete slab 150 mm thick;
- floor - made of tongue and groove boards (35 mm);
- underground - either ventilated or a non-heaving sand cushion 0.8 m thick.
Insulation dimensions
What thickness of insulation is required for effective soil insulation? According to the recommendations of specialists who carried out thermal calculations and based on the experience of operating insulated blind areas near houses, the minimum thickness of extruded polystyrene foam insulation is 50 mm. But around the corners of the building (within 2 m from the corner), where the cold accumulates, double thickness is needed.
It is recommended that the width of the insulation at the level of the soil surface be no less than the freezing depth. This will ensure sufficient band width with a positive temperature. But typical designs of shallow insulated foundations provide for the laying of horizontal thermal insulation at the level of the base of the foundation - 0.4 - 0.5 meters of depth, while the width of the insulation strip is much narrower and is determined by calculation. The wide pit is backfilled on top with non-heaving fine material.
Thermal insulation design
Sheets of extruded polystyrene foam insulation must be connected to each other in a groove; they must be laid close to the foundation insulation.
The strip is laid with a slope of 2 - 3% from the foundation to ensure water drainage from the house. Often, drainage is laid in the ground along the edge of the insulation, which removes water from the foundation.
A trench is made 0.5 - 0.6 meters deep. The bottom of the trench is filled with sand 10–20 cm thick, which also forms a slope away from the house.
Sheets of extruded polystyrene foam are laid on the sand and covered with waterproofing. The insulation is covered with a sand cushion at least 20 cm thick. Piece material for paths is laid on top of the cushion, which forms the blind area around the house. It is not recommended to concrete the blind area due to the unreliability of such finishing.
Insulation of soil under light buildings and roads
Very often it is necessary to insulate the soil under all kinds of extensions to the house - a veranda, a terrace, a staircase with a porch, a driveway to a garage, etc. All these buildings need protection from frost heaving. Soil insulation is carried out in the same way as near the foundation. But in this case, the buildings are not heated and freeze in winter, so the soil needs to be insulated under their entire area.
A pit is made to a depth of up to 0.6 meters from the base of the structure and wider to the depth of freezing in each direction (calculated widening).
A sand bedding is placed at the bottom of the pit, which forms the flow of water in the desired direction (usually from the center of the structure). Sheets of insulation are laid on the bedding, covered with waterproofing material, and a sand and gravel bedding with a thickness of 300 mm or more is made on top, which forms a cushion to redistribute point pressures. Sometimes, for this purpose, ready-made reinforced concrete blocks are laid, or a light foundation is poured.
Thermal insulation of pipelines
Typically, pipelines are insulated with a shell made of extruded polystyrene foam. But this method is bad because if warm water (energy) stops flowing into the pipeline, it will still freeze in frozen soil, no matter how thick the shell is.
Is it necessary to insulate the foundation of a house without a basement?
There are several reasons why it is necessary to pay attention to foundation insulation. Among them are:
- The first and most important reason is weather conditions, because due to constant temperature fluctuations, various forces act on the foundation, which will undoubtedly lead to the occurrence of cracks and subsequent destruction of the foundation.
- The second most important reason is to preserve heat in the house, and, accordingly, reduce costs during the heating season.
- The third reason for the need for insulation is to protect interior spaces from low temperatures and protect communications from moisture and cold.
Even if you note 3 important reasons, you can calmly answer the question: is it necessary to insulate the foundation of a house, especially without a basement? We think you will answer “Yes,” so let’s figure out what materials can be used and how to insulate this or that type of foundation.
Types of foundations for the basement
the ground floor must be at least half buried
The construction of a high foundation plinth for a private house is much more expensive than the installation of a shallow strip, a monolithic slab, not to mention a pile foundation. However, the costs incurred immediately begin to pay off with a healthy microclimate in the house, practicality and functionality of the underground structure. In addition to convenience, buried support systems have a high load-bearing capacity. You can even build a two-story brick mansion on them without any fear.
Before constructing the basement level, it is necessary to determine the level of its depth and its location relative to the floor slab of the first floor.
There are these types of foundations for a house with a basement:
- Recessed (recessed). In terms of its dimensions, it is 3-10 cm narrower than the first level of the house, which is very convenient in terms of waterproofing, since the penetration of water between the two structures is completely eliminated. At the same time, the bearing capacity of the base remains unchanged.
- Speaker. Such foundations are distinguished by powerful and thick walls, larger than those of the building on top. A set of expensive measures is required to protect the joint from moisture.
- Smooth. The outer walls of the house and the base coincide in level, which is not bad from an aesthetic point of view. But you need good waterproofing of the joint.
In accordance with current standards, the foundation with a basement must be buried in the ground to at least half its height.
How to insulate the foundation of a house from the inside and outside?
Today there is a large selection of materials for insulation, but the most popular for foundations are:
- Mineral or ecowool.
- Styrofoam.
- Polyurethane foam.
- Expanded clay.
- Earth.
It is up to the developer to decide which of the listed materials to use for insulating the foundation; however, the choice of one or another material should also be based on the characteristics of the future home, thermal characteristics and financial capabilities.
Features of external and internal insulation
There are two types of insulation, external and internal. External insulation of the foundation is carried out even before the construction of the floor and walls of the house, that is, at the very beginning of construction. As for internal insulation, it is carried out if it is not possible to do external insulation, that is, the house has already been completely built.
In addition to this, there is also external insulation of the foundation, that is, after the foundation and walls of the house have been erected. The outer layer of thermal insulation allows you to increase the service life of the foundation even in the presence of frequent low temperatures.
Choosing a foundation design with a basement and terrace
Monolithic slab for the ground floor
The foundation for a house with a basement and a terrace is a rather complex structure. To equip it, you need to choose the right material from which the walls of the support system will be built.
There are the following options for constructing a basement level:
- Tape block. It is assembled from powerful reinforced concrete blocks of 240×60×40 cm format. The fragments can be connected to each other by welding; in all cases, cement mortar is used. The advantage of this method is the high speed of construction, but you will have to spend money on delivery and installation.
- Monolithic. It is considered the most labor-intensive, but at the same time the most reliable type of basement floor. Thanks to the solid structure, leaks, shifts and cracks are practically eliminated. The structure is a closed form with an internal steel frame, filled with concrete.
- Brick. Refers to budget options, since the only serious expenses go to the delivery of material and excavation of the pit. Next comes manual work, where there is no need to make formwork and reinforcement. The downside is that brickwork is not resistant to high loads and dampness. You can choose this technology when building on dry and stable soil.
The strip foundation is strong, but needs additional protection from external and internal factors.
Insulation of various types of foundations
Since today there are several types of foundations that differ from each other in their designs, the insulation technology will be different for each of them, but its essence will come down to one thing - to protect the entire surface.
– insulation of strip foundation
As a rule, insulation of a house or foundation should be carried out evenly along the entire length of the strip base. To do this, the structure must first be prepared:
- Along the entire perimeter it is necessary to dig a trench about 1 m wide and a depth equal to the depth of the foundation.
- After this, the monolithic structure must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt and soil. This is necessary in order to obtain good adhesion between the material and the foundation surface. If necessary, the surface of the foundation is leveled using a cement screed.
- Before insulating the foundation, you need to take care of waterproofing. To do this, the surface of the foundation is coated with mastic or any other waterproofing material.
- Next, you can begin laying the insulation boards. Usually it is laid on special adhesive compounds. To achieve the best protection from cold and moisture, it is recommended to lay the insulation in two layers.
Such procedures must be performed along the entire perimeter of the foundation, trying to avoid gaps between the insulation, as this will lead to the formation of cold bridges. When the foundation is completely insulated, it is backfilled with soil.
– insulation of columnar foundation
How to insulate such a foundation of a house? To insulate a columnar foundation, you must first make a back-up (the so-called base). Its main function is that it protects the space between the soil and the foundation from moisture and low temperatures.
In order to make a pick-up, you must do the following:
- It is necessary to dig a small trench under the house, the depth of which will be about 20-40 cm.
- Next, sand or crushed stone layers of 15-30 cm are poured into it.
- Special bars with grooves are attached to the foundation pillars for further securing the boards to them. Thin boards are inserted into the grooves of the bars along the entire perimeter.
- Finally, the lower part of the structure is covered with expanded clay.
Having completed all these procedures, we can say with confidence that the foundation will be protected from moisture and low temperatures.
– insulation of slab foundations
Insulating a slab foundation is probably the most expensive of all types of foundations, but the costs will be fully recouped. In most cases, the base of a slab foundation is insulated with polyurethane foam. It is applied from a special device to the walls of the base.
Also, most often, they try to insulate a slab foundation even before it is poured, that is, they perform waterproofing from any material (most often roofing felt), after which foam plastic is laid in the foundation pit, on top of which a small screed is made. Next, reinforcement and pouring of concrete is done. You can also insulate a slab foundation on top of an already finished slab. This is recommended to be done in residential buildings for floor insulation.
– Insulation of pile foundations
A pile foundation most often has such a feature as an open space between the foundation and the ground. This indicates too much heat loss, so it is simply necessary to insulate this type of foundation, otherwise the house will be cold and damp.
Foam plastic is used as insulation for a pile foundation, and the insulation technology is carried out in several stages:
- Waterproofing foundation grillage.
- Laying insulation.
- Finishing work.
Protection of foundations and basement walls from frost heaving deformations
Protection of foundations and underground communications from frost heaving deformations
https://www.maxmir.com/publish/p_tech6.html
Alexander Matvievsky, Nina Umnyakova
Causes of frost heaving of soils
Quite often, after the end of the winter season, cracks appear on the facades and plinths of cottages, door frames warp, or cracks appear in window frames. The cause of these troubles in most cases is the movement of foundation foundations caused by the forces of frost heaving of the soil, which arise as a result of an increase in the volume of soil when it freezes.
Almost all soils (except rocky ones) can be subject to frost heaving, but to the greatest extent this disadvantage is inherent in clayey soils (loams, clays, sandy loams, fine and silty sands), as well as sands containing silty clay particles. Gravelly, coarse and medium-sized sands that do not contain silt-clay particles are considered non-heaving.
As already noted, soils containing tiny dust and clay particles are subject to frost heaving. Compared to coarse and medium sands, these particles bind water very well. When freezing, the water-saturated mass increases significantly in volume and begins to put pressure on structures located in the ground and push them out of the ground.
Frost heaving deformations are the result of the influence of so-called normal and tangential forces on the structure. The former arise under the base of the foundation as a result of freezing and an increase in the volume of heaving soil, the latter - due to the vertical displacement of soil frozen to the side surfaces of the foundation or to the basement walls. In addition, the frozen soil, which has increased in volume, begins to press perpendicular to the surface of the basement walls, causing deformation of the foundations in the horizontal direction.
The heaving process intensifies with an increase in the humidity of heaving soils as a result of precipitation (in particular, heavy autumn rains), with capillary rise of moisture and an increase in groundwater levels.
In the Moscow region, 80% of all soils are classified as heaving, and their freezing depth in winter can reach 1.4 m. Therefore, protecting foundations, pipes laid underground, areas covered with asphalt or tiles, as well as entrances to garages from deformation, caused by the forces of frost heaving is an urgent need.
To reduce the impact of frost heaving forces on underground structures during the construction and renovation of a house, it is recommended to take the following measures (Table 1).
| Table 1. | ||
| Reasons causing deformation of structures | Constructive solution | |
| The impact of normal forces of frost heaving on the base of the foundation | Installation of backfill (1) 100-200 mm thick under the base of the foundation from non-heaving soil: gravelly, coarse or medium-sized sand, gravel, crushed stone or sand-crushed stone mixture (sand 40%, crushed stone 60%) | |
| Impact of tangential forces of frost heaving on the side surfaces of foundations and basement walls | installation of coating (2) on the side surface of foundations and basement walls, reducing their roughness and adhesion forces with frozen heaving soil to the freezing depth; backfilling (3) of the foundation cavities to the entire freezing depth with non-heaving soil; The width of the backfill at the bottom of the excavation must be at least 0.5 m. | |
| Moistening heaving soil with precipitation | Construction of a blind area (4) with a slope of 3-5% away from the house, the width of which exceeds the width of the excavation for backfilling | |
| Increase in the moisture content of heaving soil due to rising groundwater levels | Drainage device (5) to lower the groundwater level and drain it from the foundation | |
| Siltation of non-heaving soils with silt-clay particles | Protection of sand bedding from the penetration of heaving soil particles into it using special filter materials (6) | |
When constructing buildings on heaving soils, it is necessary to place a cushion of washed sand, gravel or gravel-crushed stone under the base of the foundation. A base made of these non-heaving materials will prevent the normal (pushing) forces of frost heave from affecting the base of the foundation. It should be noted that when the groundwater level rises (in autumn, as well as during the melting of the snow cover), the backfill becomes surrounded by water saturated with particles of silty-clay soil. Migrating along with water, these particles penetrate into the bedding and clog it, gradually turning non-heaving soil into heaving one. As a result, after several years of operation, the foundation again finds itself standing on soil that deforms when it freezes. The use of special filter materials (fiberglass, "Taipar", etc.), which allow water to pass through well, but prevent the penetration of the smallest dusty-clay particles into the sand bed, allows you to prevent siltation of the bedding.
| Rice. 1 |
| 1 - foundation; 2 - backfill from non-heaving soil; 3 - filter material; 4 - existing heaving soil |
To reduce the impact of tangential forces on the foundation, it is recommended to replace heaving soil in contact with vertical surfaces of the foundation or with basement walls with non-heaving soil.
Backfilling, which is carried out along the entire perimeter of the building, must (as in the previous case) be protected with a layer of filter material (Fig. 1). Significant moistening of heaving soils leads to the fact that when they freeze, they increase in volume much more than soils with less moisture. This entails an increase in the level of deformation, and, as a consequence, the need for more serious protection of foundations from the effects of frost heaving forces. One of the ways to reduce the activity of heaving soils is to install drainage, which makes it possible to reduce soil moisture by lowering the groundwater level.
The traditional design is a system of drainage pipes placed in a layer of washed gravel that retains soil particles. The pipes are laid with a slight slope to ensure water flows into a special well or sewer. Despite the presence of a gravel filter, during the operation of the drainage system, the drainage holes gradually become clogged with soil particles. Cleaning drainage is a rather labor-intensive process that requires the construction of special wells. Clogging of the system can be prevented by laying filter material (Taipar or fiberglass) around the drainage pipes, which does not allow the smallest particles to pass through and ensures efficient operation of the drainage system for a long time (Fig. 2).
| Rice. 2 |
| 1 - existing foundation; 2 — drainage tubes; 3 - filtering material; 4 - washed gravel |
If there is filter material, it is not necessary to lay a layer of gravel around the drainage pipes.
Protection of structures from frost heaving deformations by insulating soils
Insulation of foundation bases
The measures considered make it possible to reduce the impact of frost heaving forces, but not to eliminate their cause. Thermal insulation around the building can prevent frost heaving of the soil. The essence of this method is that the soil located near the building is protected from freezing by thermal insulation materials, thereby eliminating the cause of frost heaving.
To insulate the material, insulation materials are used that are capable of maintaining the necessary heat-protective qualities in a humid environment and absorbing loads from structures located above them. These requirements are best met by extruded polystyrene foam of various brands.
| Rice. 3 |
| 1 - basement wall; 2 - sand bedding 200 mm thick; 3 - extruded polystyrene foam; 4 - sand and gravel backfill 300 mm thick |
Of no small importance is the fact that the proposed technology can be implemented both during the construction of new houses and during the operation of existing buildings, and the placement of thermal insulation material around the perimeter of the building allows not only to protect the soil from freezing, but also to insulate basements (Fig. 3 ).
The soil around the house is dug to a depth of 0.5-0.6 m. The dimensions of the excavation should ensure the laying of insulation with a width of at least 1.2 m. After this, a layer of washed sand with a thickness of at least 200 mm is poured onto the bottom of the trench, and a slight slope of the sand cushion is arranged in side away from the foundation and compacted thoroughly. Thermal insulation boards made of extruded polystyrene foam are laid on the sand. The thickness of the slabs is taken depending on the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation (Table 2).
| Table 2. | |||||
| Thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation, W/m °C | 0,03 | 0,035 | 0,04 | 0,045 | 0,05 |
| Insulation thickness not less than, mm | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
| Rice. 4 |
| 1 - external walls of the house; 2 - insulation made of extruded polystyrene foam around the perimeter of the house; 3 - additional insulation with extruded polystyrene foam in the area of external corners. |
We should not forget that heat losses through the outer corners of the building significantly exceed losses through the surface of the wall, therefore additional insulation must be provided in the corner area.
To do this, at a distance of 1.5-2 m from the corner, insulation is laid with a thickness 1.4-1.5 times greater than that shown in the table (Fig. 4). Then the insulation is covered with a layer of sand or gravel at least 300 mm thick to the ground surface. Such insulation will prevent soil freezing and the appearance of frost heaving forces.
Insulation of the foundation from the inside
Most often, developers have a question: is there a need to insulate the foundation from the inside, is it already insulated from the outside? There is no specific answer to this question, it all depends on desire, however, for greater heat conservation in the house, it is recommended to perform double-sided insulation.
In addition, the question may arise: is it possible to get by with only internal insulation? Of course, you can get by, but you should remember that internal insulation does not protect the foundation itself from negative weather conditions, and after some time the foundation may begin to crack and collapse.
Foam plastic or polystyrene foam can be used as internal insulation, but the best option is polyurethane foam, which is sprayed onto the foundation walls. Polyurethane foam forms a uniform, monolithic layer of insulation and lasts a very long time. Its cost is high, so most often developers give preference to ordinary polystyrene foam. Do not forget that before any type of thermal insulation, it is necessary to perform waterproofing with any material (mastic, rolled materials, etc.).
In conclusion, it must be said that insulating the foundation of a house is an important point, especially if the built house will be lived in all year round. This will significantly save money on space heating and protect the foundation from the effects of external negative factors.
How to protect concrete from cracks?
In general, concrete protection occupies one of the important places in the construction of various types of structures. To consolidate concrete, it is important to choose the right and high-quality means and materials, because without them, the concrete layer will begin to crumble within a year or two.
In practice, there are many options for protecting concrete from cracks. But the most commonly used are 2:
- Special strengthening impregnation, which can be purchased at any construction market. When such a product is applied to the outer layer of concrete, a certain protective film is formed that will prevent natural phenomena from affecting the concrete. In most cases, a primer is used for these purposes due to the high quality and durability of the composition.
- The waterproof layer is a temporary solution; after a short amount of time it has to be reused. It is worth noting that if applied correctly, concrete will last a long time. How it works: the waterproof layer penetrates many holes in the concrete, thereby filling them and preventing water from destroying the foundation.