Mold (fungus) in the corners formed by the wall and ceiling
There may be several reasons for the violation of the thermal insulation qualities of the ceiling corner.
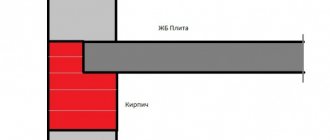
First. Violation of construction technology. The width of support of reinforced concrete floor slabs on the wall should be 100–120 mm. And between the end of the slab and the wall, heat-insulating material is laid (Fig. 187). When installing floor slabs, as a result of a construction defect, the width of the slab support could be increased, for example, the slab extends into the wall not by 120, but by 200–250 mm. The thermal insulation material, which should be laid at the end of the slabs, sagged over time or was not laid at all. As a result, the edge of the floor slab falls into the cold zone of the wall with negative temperatures. Reinforced concrete is a denser material than, say, brickwork, and therefore it conducts heat and cold better. This incorporation of denser materials into less dense ones is called a “cold bridge.” Through this “bridge” the negative heat flow enters the room - the dew point isotherm goes to the inner surface of the wall, located directly under the slab and to the inner surface of the slab itself.
rice. 187. Freezing of the floor due to improper support of the floor slabs
Second. On the top floor of the building, on the floor slabs there is a layer of vapor barrier and insulation (Fig. 188). Freezing of the ceiling corner is possible due to a violation of the vapor barrier and, as a result, wetting of the insulation or due to caking of the insulation. The first sign of the attic floor losing its heat-insulating properties: the formation of icicles on the roof. This is probably a well-known picture when, in the middle of winter, huge icicles grow on one of the houses, but the houses standing nearby are not overgrown with icicles of that size. If there is no upper distribution of the heating system in the attic of such a house, then the attic insulation is most likely to blame for the formation of icicles. It has caked over time or been trampled or wet from a roof leak or as a result of wear and tear of the vapor barrier layer. The insulation, having lost its properties, allows heat to escape from the apartments, the inside of the roof warms up, the snow on it melts and huge icicles grow on the roof. However, the insulation, which transmits heat so well, also transmits cold with the same success; as a result of the isotherm, the dew points reach the inner surface of the floor slabs and walls - fungus appears.
rice. 188. Freezing of the ceiling due to compaction or wetness of the insulation in the attic
Third. External wetting of the wall and, as a result, loss of its thermal resistance. The corner formed by the outer wall and floor slabs, or just the wall above the window opening, becomes moldy. This is a typical case for houses with unglazed balconies and loggias. Melt or rainwater enters the wall at the joint between the balcony slab and the wall of the neighbors above on the floor (Fig. 189). A wet wall loses its heat-shielding properties and displays the dew point isotherm on the inner surface of the wall.
rice. 189. Freezing of the ceiling due to a wet wall
Before solving the issue of wall insulation, it is first necessary to eliminate the causes of freezing.
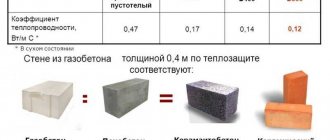
In the attic, the nature of air movement should be studied and additional vents and dormer windows should be installed. The total cross-sectional area of the dormer windows and vents should be 1/300–1/500 of the attic floor area. The width of the vents, if necessary, is made equal to 20–25 mm. It is necessary to measure and adjust the thickness of the insulation to the calculated thickness. Caked insulation is loosened approximately once every five years. For external walls with a width of up to 1000 mm, its thickness can be increased more than the calculated one (up to 50%). The vapor barrier of the ceiling should be checked and, if necessary, restored.
The waterproofing of the joints between the balcony slabs and the wall must be restored or the joint must be sealed with sealant. After restoring the waterproofing of balconies, the walls must be dried.
If eliminating the external causes of wall freezing does not give the desired effect or this is impossible, for example, in the case of an increased support width of the floor slabs, internal insulation of the ceiling corner is performed (Fig. 190). Plastering a corner using a grid is used in the same way as insulating a corner formed by walls, or insulating a corner with heat-conducting sheet materials.
rice. 190. Insulation of the ceiling corner
It is better not to make the internal insulation of the eaves corner an effective insulation. The fact is that insulation blocks the heating of the corner with warm air from the room. This makes the corner freeze even more. If you decide to protect the corner from freezing with insulation, then it is recommended to use as little thickness as possible. Here is a case described in the textbook by Professor K.F. Fokin. In the last century, in one of the houses in Moscow, an experiment was carried out to insulate the cornice corner with polystyrene foam 50 mm thick, the strip width along the wall was 150 mm, and along the ceiling - 250 mm. At first, the result seemed positive - the corner stopped getting damp, but with the onset of frost, mold appeared at the edge of the insulation. Then the insulation was replaced with expanded polystyrene 20 mm thick with the same strip width. The result turned out to be a little better, but also did not satisfy the experimenters. Obviously, expanded polystyrene foam with a thickness of 10 mm and a strip width of 250 mm along the wall and 400 mm along the ceiling can provide a better result, also without giving a full guarantee that mold will not reappear at the boundary of the insulation with the wall or ceiling.
Plastering the corner with a more thermally conductive material, such as expanded clay concrete, gives better results than using insulation and a satisfactory appearance. You can also use fibreboards. Alternatively, the cornice corner can be blocked with a backlit plasterboard box. The lighting should be made from built-in lamps with incandescent lamps, and not with “cold” neon light. Working lamps will heat the air inside the box and dry the cornice corner, moving the dew point isotherm deeper into the wall, thus preventing it from getting wet.
Summing up
Each type of flooring is good for certain structures. During the review, it turned out that wooden floors are the cheapest and least labor-intensive to install. However, this type of flooring can not be used in all types of structures, but only in wooden buildings and traditional private houses. Wooden floors can be used for any of four types of floors - basement, interfloor, attic and attic.
Monolithic reinforced concrete floors can be used in the construction of buildings of almost any design, except for wooden structures. Such floors are more expensive than wooden floors and require certain material and physical costs. However, they are more durable and have more advantages compared to wooden floors. Depending on the type of bulk fillers in the concrete mixture, this floor can be used for all types of floors.
Prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs are the simplest, but most expensive type of flooring, which also has restrictions on installation on certain types of structures (wooden, with a wall thickness of less than 200 mm). They are installed mainly as a floor between the 0th and 1st floors, as well as between the 1st and 2nd floors.
* Subfloor
- a horizontally flat plane that serves as the basis for the finishing coating, and made of boards, chipboard, OSB or thick plywood.
* Finish floor
- finishing coating of a floor, such as tiles, parquet, laminate, linoleum, etc.
When constructing residential buildings, concrete floor slabs are often used. These reinforced concrete products are used both for floor coverings and for the construction of walls. They are made from high-quality concrete using a reinforced frame. The reliability and durability of buildings mainly depends on the quality of the materials used.
Floor slab insulation scheme.
Overlapping with a monolithic slab
They are characterized by increased strength, which allows them to be used in places with an increased risk of sagging. Maximum protection against various deformations, but at the same time poor sound insulation. It is heavy, which is a significant disadvantage of this type during construction.
Hollow-core structures
Drawing of a hollow core slab.
The most popular, due to the lighter weight of the product. Thanks to the voids, these slabs have low thermal conductivity and good sound insulation. Manufacturing costs are significantly lower than in the production of monolithic slabs. They are often made of ribbed or cellular concrete.
Floor slabs are mainly manufactured in fixed sizes. And when designing a building, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of standard manufactured slabs. Depending on the requirements for future construction, the slabs are also classified by weight. Their average weight varies from 500 kg to 4 tons.
The use of concrete hollow slabs in foundation construction has been around for quite some time. But the installation of frost protection for floor slabs is not always thought through.
Damp and freezing walls are one of the most serious factors in the fragility of buildings.
The appearance of mold significantly affects the health of home occupants.
Wall insulation options
For example, using a layer of brickwork you can clad the outside of a wall. This can be done without special skills. For this you will need:
Wall insulation scheme.
- bricks;
- level, tape measure and order, if the wall needs to be built high;
- sand-cement mortar in a ratio of 4:1 or adhesive mortar for masonry;
- drill with mixer;
- trowel and solution container;
- access to electricity.
You can also insulate the walls with plaster insulation on reinforcing mesh. To do this, use dowels to install the reinforcing mesh to the wall. The latter does not have to be metal. Plaster is applied between the wall and the mesh and on top. This can be a cement mortar or a ready-made dry mixture for wet rooms. Moisture-resistant solutions are more expensive, but last much longer than usual, since they have special additives in their composition.
Another of the highest quality methods is the installation of vapor barrier material and insulation on the inside of the concrete wall. Installation is carried out by installing a frame lined with tiled insulation. To make such a frame and fill the distance with insulation between the wall and the finishing material, you can use various fasteners and hardware. These can be mounting brackets, plastic “fungi” dowels, and glue, both in finished form and in the form of a dry mixture that requires preparation. After that, be sure to finish it with plaster or any other finishing material.
Materials for frame and insulation:
- metal profiles or wooden slats;
- screws for metal or wood;
- sealant and polyurethane foam;
- vapor barrier membrane or aluminum foil on isofilm;
- sheet insulation, mineral or fiberglass wool;
- dry mixture for plaster.
Tools for installing the frame and insulation:
- grinder with circles for cutting metal or special scissors;
- drill with mixer attachment;
- screwdrivers or screwdriver;
- tape measure, level and pencil;
- spatulas and graters for grinding;
- solution container.
Scheme for insulating the wall of a frame house.
Between the frame and the wall you need to leave a space of about 50 mm and fill it with expanded clay. This material will perfectly absorb remaining moisture from the wall and stop the appearance of mold. Thus, the wall thickness increases by 150 mm. There are 80 mm foam blocks that successfully replace such frame structures. Installation is carried out using ordinary cement-sand mortar (1:4).
On particularly cold and damp walls, you can install a system called “warm floor”, or run a warm baseboard around the perimeter. This solution is best suited for corner rooms. When choosing a method for heating walls, the most suitable option is electric film or infrared flooring. You should not install it yourself. To heat the seam under the baseboard, you can use a heated floor, where a cable is used as a heating element.
Installing a stationary wall-mounted electric heater will not completely solve the problem of poor-quality insulation between the slabs, but you can install it yourself.
For this you will need:
- drill or hammer drill;
- anchors or dowels;
- hammer;
- socket.
Whatever the reason for freezing of hollow core slabs, it is necessary to significantly reduce the humidity in the premises, be sure to check the efficiency of the ventilation and monitor the quality operation of the heating system. All work to repair the building and eliminate the causes of freezing should be carried out carefully and accurately. If you forget about some detail, you risk encountering this problem again, and very soon.
The need to insulate a concrete ceiling from the inside often arises among owners of the upper floors of buildings with a flat roof. If it is possible to insulate the ceiling from the attic side, then this is the best option to keep the apartment warm.
Multi-storey buildings in cities traditionally have inter-storey floors made of concrete slabs . Some private houses have the same floors, resting on the foundation or its continuation - the ground floor, where utility rooms for various purposes are located.
Floor slab - ceiling and floor at the same time in apartment buildings. The slabs rest on load-bearing walls, the ceiling is covered with several slabs. The sealing of the seams between the slabs and the places where the slabs rest on the walls cracks: either due to shrinkage of the building, or poor work of the builders. Part of the heat leaves apartments precisely through the joints of the slabs: wall or ceiling.
Houses in need of major repairs are usually insulated from the outside using the thermal fur coat method . This method is applicable for insulating the ceiling from the inside. Having some construction skills, you can insulate the ceiling from the inside yourself.
Floor slab structures
Overlapping with a monolithic slab
They are characterized by increased strength, which allows them to be used in places with an increased risk of sagging. Maximum protection against various deformations, but at the same time poor sound insulation. It is heavy, which is a significant disadvantage of this type during construction.
Hollow-core structures
Drawing of a hollow core slab.
The most popular, due to the lighter weight of the product. Thanks to the voids, these slabs have low thermal conductivity and good sound insulation. Manufacturing costs are significantly lower than in the production of monolithic slabs. They are often made of ribbed or cellular concrete.
Floor slabs are mainly manufactured in fixed sizes. And when designing a building, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of standard manufactured slabs. Depending on the requirements for future construction, the slabs are also classified by weight. Their average weight varies from 500 kg to 4 tons.
The use of concrete hollow slabs in foundation construction has been around for quite some time. But the installation of frost protection for floor slabs is not always thought through.
Damp and freezing walls are one of the most serious factors in the fragility of buildings.
The appearance of mold significantly affects the health of home occupants.