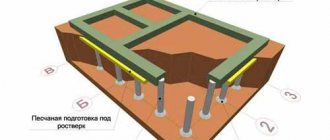
The construction of any building begins with the creation of a project and calculation of the foundation. The first stage of construction is laying the foundation. The latter is considered the load-bearing structure of the building; it can be:
- pile;
- tape;
- columnar;
- slab.
The most common type of foundation is considered to be a strip foundation, which implies the same section thickness under the entire perimeter of the building. Strip foundations are also divided according to materials:
- rubble;
- concrete;
- rubble concrete;
- brick.
Pouring a concrete foundation
You must always start with the calculation part; you should understand that the integrity and practicality of the entire building as a whole depends on the foundation, and it does not matter at all what you plan to build, the foundation for a residential building or for a bathhouse.
Initially, a trench is prepared, the size of which corresponds to the depth of the foundation strip. Formwork is installed along the perimeter of the ditch, and fixation is carried out using spacers. Install the reinforcing part, which consists of steel rods. It is recommended to pay close attention to the corners of the structure, since these are quite vulnerable parts of the building’s base structures. When the installation of the formwork is completed and the reinforcement has been laid, you can begin pouring concrete. In some cases, it is not possible to continuously pour concrete, and this action is performed in several stages, especially when mixing the solution yourself.
In modern construction, two methods of pouring concrete mixture in parts are used.
Is it possible to pour a foundation without reinforcement?
Is there groundwater in your area, what properties does the soil have, is there a possibility of flooding during spring floods, how deep does the soil freeze, is there a risk of earthquakes - all this needs to be taken into account.
Concrete has high compressive strength and extremely low tensile strength - even slight movements of the earth cause cracks and tears to appear in the foundation of the house.
Engineering-geological diagnostics of the soil should be done at the initial stages of design, and the results of laboratory studies will show whether reinforcement is needed.
In most cases, reinforcement is necessary; in our country, soils with a high degree of mobility predominate. Reinforcing rods increase the tensile strength of concrete several times, give it elasticity, and extend the service life of the foundation.
If you are sure that there is no need to reinforce the foundation: the soil in your area is motionless and extremely strong, there is no groundwater and there is no seismic danger, then no one has the right to dissuade you.
You make a decision at your own peril and risk. By saving money, you take responsibility for all possible risks.
If you refuse to reinforce the foundation of the house, sign an addendum to the contract with the construction team, which states that you will not make claims against them if the foundation cracks or subsides.
Methods of pouring concrete in parts
Choose the filling method in accordance with the time period for the break, and this is:
- less than twelve hours break. In this case, concrete is poured in layers, between which a cushioning layer is placed, such as roofing felt or film. This will help prevent the concrete layer from hardening in 12 hours, which will allow you to continue pouring the next layer. This method of joining seams is called a “hot seam”;
- more than twelve hours break. In this case, you should wait until the filled layer has completely hardened. If the concrete does not harden completely, a crust will form that will hide the uncured portion of the concrete. By pouring a second layer, the crust may burst, which will lead to an irreversible process of destruction. This joining method is called a “cold seam”.
Pouring concrete in parts: hot or cold seam
» Pouring concrete in parts
Pouring concrete in parts. The process of pouring concrete should ideally take place in one step to create a solid or monolithic reinforced concrete structure. The fastest and most convenient way to pour concrete is to pour it from a mixer machine. Concrete is delivered to the work site using a mixer that holds up to 8 cubic meters of concrete mixture. But there are times when, for some reason, it is not possible to pour concrete at one time. For example, you don’t meet the daylight hours, the supplier let you down, the truck with concrete didn’t arrive in time. Also, if you prepare the concrete mixture yourself using a household concrete mixer, pouring concrete in one step is very problematic, especially if you need to pour several cubes. In this case, pouring concrete should be carried out in parts.
There are two ways to pour concrete in parts, which depend on the period over which it is planned to pour concrete. The first method is possible provided that work is interrupted for less than 12 hours. Concrete should be poured in layers and be sure to cover the poured layer of concrete with film or roofing felt after finishing the concrete work. In a time period of less than 12 hours, the surface of the concrete covered with film will not have time to dry. Before resuming pouring, it is necessary to remove the concrete “milk” from the surface of the poured concrete layer. This connection of uncured layers of concrete is called a “hot joint”.
The second method is used when the interval between pouring is more than 12 hours. In such a situation, it is necessary to wait until the first layer of concrete has completely hardened. If hardening is not complete, the outer surface of the poured concrete will be covered with a crust, and underneath it the mixture has not yet had time to harden. If a new pour is started on such an unhardened layer of concrete mixture, the crust will not withstand the pressure and will crack, which can subsequently lead to negative results during the operation of the foundation. This method is called “cold seam”.
As already mentioned, when pouring concrete in parts, it should be poured in layers. Layers of poured concrete can be either horizontal or vertical. A horizontal layer is poured to half the height of the formwork and does not require delimitation. It is not recommended to make the layer too thin.
Important! The seam of the poured concrete should not pass in the place where the reinforcement threads are located. It is desirable that the layer height be higher or lower than the reinforcement.
To fill in vertical layers, the formwork should be divided into separate sections using partitions. Such pouring is carried out if concreting occurs in stages, in small parts.
Recommendations for pouring concrete in parts:
- Think through the stages of pouring concrete in advance.
- Divide the entire pouring area into sectors.
- Optimally distribute the volume of concrete mixture delivered to the site according to the pouring plan.
- Concrete should be poured evenly over the area to be poured.
- When pouring on a “cold joint”, the surface of the previously poured concrete should be cleaned and, if necessary, the cement film (milk) should be removed from it. The cement film prevents the concrete from adhesion to each other. Cement laitance can be removed either mechanically, using a hammer and a brush, or with chemical compounds (Gambit FREZ N-1, etc.).
- When pouring concrete using a “hot seam”, it is necessary to cover the concrete layer with film or roofing felt in the intervals between concreting.
Important! When pouring concrete at subzero temperatures, the surface of the concrete should be cleared of snow and ice.
You can find out the cost of building your foundation by phone or send us a request for calculation
We offer services for the construction of monolithic foundations for a country house in St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region with high quality work and at reasonable prices.
Fill layers
Fill layers are divided into horizontal and vertical. Horizontally located layers can be poured to half the height of the formwork immediately, without delimitation. The layer should not be very thin; various seams should not be arranged in those places where the reinforcement fibers are laid. The layer can end either above or below the reinforcing threads.
To organize vertical layers, it is necessary to install additional partitions. This type of pouring has become widespread during the gradual concreting of the foundation, in small parts. The resulting sections of the partitions are filled with concrete mixture gradually one after another.
What you need to know about concrete maturation
Before becoming more familiar with each of the technologies, it is necessary to have an accurate understanding of the time and intervals of concrete hardening, which significantly affect the final result of the quality of the foundation. The setting and hardening parameters of the material vary depending on the brand of the mixture and the humidity and temperature conditions of the environment.
Grasping
This term denotes a short stage, which is characterized by the gradual binding of the constituent components of the solution to each other: cement and water. At a design temperature of 20 degrees, the minimum setting period is about 3 hours, while the structure of the mixture at the initial stage remains in a viscous-liquid state.
Hardening
This process, which occurs immediately after the mixture sets, lasts for years. However, after 28 days the material acquires the strength indicator regulated by the brand. Moreover, hardening and a set of strength characteristics occur more dynamically in the first days, and then slow down more and more. The most common grade of concrete for foundation construction is M300. For buildings with lightweight structures, it is allowed to use the M200 mixture.
If you take into account all the features of the maturation of the concrete mass and follow simple but important rules, then pouring the foundation in parts is justified and possible. The next layer after the first is poured without exceeding the time interval:
- 2, maximum 3 hours in warm summer;
- 4 hours if work is carried out in the cool off-season;
- 8 hours when concreting is done in winter.
By pouring in parts at the liquid setting stage, the developer does not break the cement bonds, and after hardening, the concrete is transformed into a monolithic stone structure.
Basic rules for pouring in parts
When starting construction work on building a foundation, you need to think through a clear pouring plan. The entire area should be divided into areas of approximately equal size. Based on the pouring plan, it is necessary to correctly distribute the ready-made concrete mixture available at the site. Concrete is distributed evenly over the area of a certain area that is poured.
If a cold seam was used, then it is worth clearing the previously made surface of the cement film so that it does not interfere with the full adhesion of the layers.
Scrap metal and stones instead of fittings
When you decide to reinforce the foundation, but still want to save money, use stones and scrap metal instead of reinforcement. The strengthening method is suitable only for outbuildings (barn, barn, garage) and on very inactive soil.
It is absolutely impossible to build a residential building on such a foundation. The main task when using such “reinforcement” is its competent, uniform distribution throughout the volume of the concrete mixture.
To improve adhesion to concrete, the reinforcement has a special ribbed surface, longitudinal and transverse protrusions; it is extremely strong and provides the foundation with resistance to tension and compression. Boulders, scrap metal and substandard bricks do not have such properties, so they cannot be considered a full replacement for reinforcing bars.
If you decide to make a foundation for a small-sized structure, you should not run to the store and buy expensive fittings. Metal products are suitable instead:
- Used corners;
- Used channels;
- Thick wire, various metal objects.
Of course, not any metal will replace fittings, but only high-quality metal, without visible signs of corrosion and rust.
Possible consequences
The foundation is constantly experiencing strong loads: the upper part is subjected to compression, the lower part is subject to tension. By depriving the foundation of reinforcement, you deliberately reduce the ability to withstand tensile loads by more than 10 times.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the rest room in the bathhouse interior design
The walls of a house whose foundation is poured without reinforcement do not have a strong connection with each other, which is fraught with the appearance of a large number of large cracks between them. Over time, a building can very quickly become unusable.
During the process of mandatory shrinkage of the house, which lasts at least 5 years, the foundation without reinforcement may crack, unable to withstand the loads. A slight deformation of the soil, frost heaving of the soil and its expansion when wet can lead to disastrous consequences that cannot be prevented.
Typically, a house that does not have fittings has an extremely short service life.
Often, following the foundation, the communications of the house are deformed and destroyed, in particular the sewerage system. The basement of the house is subject to flooding at the slightest precipitation.
Fill options
The height of the level of concrete poured into the formwork should not exceed half a meter.
After installing the formwork and calculating the required amount of concrete, you can determine the method of pouring the foundation, as well as the amount of time this work is expected to take. It is more rational to order concrete from a factory and pour the foundation from a machine and not alone. But is there room on the site for machines to operate? Is it possible to order all the necessary equipment within the time frame required to continue the work?
Concrete can be poured into the foundation formwork in layers of about 20 cm. In any case, the height of the level should not exceed half a meter. Each layer is distributed evenly along the entire perimeter of the formwork and along its entire length. To prevent voids from forming, the poured layer is compacted. Tamping is completed when a white liquid appears on the surface of the layer. The walls of the formwork are tapped. These actions are designed to remove air from the concrete and prevent the formation of voids in the monolith. The procedure is carried out until the layer reaches the level of the fixed rope, which indicates the height of the “sole”. After this, the surface is leveled with a trowel. The fittings also make several punctures to release air. The formwork is tapped again.