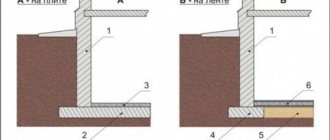
Advantages of a foundation without formwork
When arranging a strip foundation in the ground, there is no need to build a channel of boards to enclose the trench. Such a foundation is built at ground level, so when demolishing a building there is no need to destroy the above-ground part. The foundation in a trench without formwork is made up to the level of the top layer of soil. This is the most economical type of construction. Costs go only to the building material that will be poured into the ground. Do you need formwork in the ground?
But do not forget that this method of filling is only available if the site has non-friable or moderately friable soils that allow the formation of vertical walls without supports.
Shape and dimensions of the foundation pit
With the forms, everything is simple: a rectangular pit is dug under a slab-type foundation, a pit-trench is dug under a strip foundation, and many pits or wells are installed at the construction site under a columnar foundation.
But the dimensions (dimensions) of the pit are determined according to more complex rules. And further in the text we will outline the canons for determining these dimensions. So.
Required depth
The depth (height) of the pit depends on two parameters - the level of soil freezing and the height of groundwater. Moreover, the first parameter - the level of soil freezing - forces you to build a fairly deep pit: after all, the base of the foundation should be immersed in the soil 30-40 centimeters lower than the depth of soil freezing.
The second parameter - the groundwater level - limits the depth of the base: after all, when buried in watery soil, reliable waterproofing will have to be built around the foundation, which will increase the construction cost.
Simply put: the sole should not be closer than half a meter to the groundwater level.
As a result, when determining the depth, you have to balance between two parameters, which makes it somewhat difficult to find an economically viable construction site.
Width and length
The width and length of the pit depend on the dimensions of the structure itself and the depth of the foundation base.
Everything is clear with the size of the house - the dimensions of the foundations should exceed the length and width of the facade by 30-40 centimeters (15-20 centimeters on each side): after all, the layer of facade finishing should not hang over the void.
The dependence of the dimensions on the depth is manifested in the following: the transverse profile of the pit has the shape of a trapezoid, since, according to safety rules, the walls of excavations in the ground must be built with slopes.
That is, the dimensions of the house, increased by 30-40 centimeters, are projected only onto the bottom of the pit, and the upper part (cut at zero ground level) must exceed these dimensions by an amount equal to the depth of the base base.
It is these proportions that ensure the 45-degree slope of the pit walls, protecting the work of builders from soil shedding.
As a result, at the zero level the length and width of the pit are equal to the length and width of the house increased by the depth of the pit. At the level of the base of the foundation, the dimensions of the pit should coincide with the dimensions of the facade of the house (of course, increased by 30-40 centimeters). However, when the base is deepened to a level of up to 0.5 meters, this rule can be neglected by constructing a foundation pit with vertical walls.
Strip foundation in formwork or ground? What to choose
When constructing residential buildings, as a rule, formwork is installed to fill the foundation. It is necessary to ensure that the concrete solution does not spread throughout the entire trench and is not absorbed into the soil. Formwork helps prevent the soil from crumbling, as well as the solution drying out too quickly. The moisture does not evaporate as intensely, which allows the concrete to mature and obtain a strong foundation for the walls. Formwork over the trench is necessary for permanent buildings and houses in which the construction of a basement or underground room is planned. The work is carried out in stages: trench - formwork - foundation.
Is it possible to build a house without formwork?
Formwork for a strip foundation in the ground is not needed for small outbuildings and temporary buildings. This option of pouring the base is appropriate only for stable soil that does not crumble. The foundation is made directly in the ground. In what situations is it rational to pour concrete into the ground or formwork?
In areas with high humidity and unstable soils, formwork is necessary to ensure strength. Without it, it is impossible to make a high-quality foundation.
After dismantling the formwork, there remains a space where waterproofing can be easily installed. How to pour a foundation without formwork? It is rational to install formwork on dense and clayey soils, but only for small and light buildings.
When pouring a foundation in the ground, the soil is used as formwork. To make the mortar, it is necessary to use cement of at least M 300. The work is carried out in warm weather, in the absence of frost. Pouring concrete into the ground without formwork includes the following steps:
- digging a trench for the foundation;
- laying a sand cushion;
- pouring solution into the trench.
Pouring the floor slab
- Channels are laid on concrete walls in increments of 300-350 mm;
- In the center of the structure, a hatch structure is installed directly on the channel. In general, a reliable hatch design is a square frame with dimensions of 700x700, welded from four channels No. 20-No. 25 with the shelves facing outward. Hinges and a hatch panel with a handle are welded on top of the frame. There should be a hole with a diameter of 20-25 mm in the hatch panel for air to escape. Accordingly, the channels should not overlap the “mirror” of the hatch. To do this, they are cut “to size”, and the free end of the resulting piece of channel is attached to the channel shelf of the hatch frame with wire or screws;
- From the bottom of the planned ceiling, stepping back downwards (from the upper cut of the wall) 50 mm, over the entire area of the ceiling, with the help of logs or wooden beams, panels of “supporting” formwork are placed. In this case, a hole is cut in the formwork at the location of the hatch to allow exit from the pit. The horizontality of the shields is controlled by the building level;
- For the strength of the slab, the channels are tied together with steel binding wire;
- Having retreated from the outer perimeter of the pit walls to a distance of 50-100, formwork with a height of 100 mm is installed from wooden boards along the perimeter of the pit;
- Pouring the floor slab. The result is a monolithic slab 150 mm thick, in the center of which channels No. 10 are located;
- After soaking the poured slab for 72 hours, retreating about the hatch structure by 250-300, the formwork is installed (height depending on the height of the channel of the hatch frame) and is also filled with concrete.
After the concrete has completely dried, the inner surface of the walls and ceiling are treated with waterproofing mastic. The upper part of the slab is covered with soil up to the upper edge of the hatch.
A filter made of crushed stone of different fractions is poured into the bottom of the pit. The gaps of the drainage pipes are cleared of pieces of concrete. The cesspool is ready to receive waste!
Strip foundation in the ground without formwork: work order
Before pouring a foundation into the ground without formwork, it is recommended to carefully examine the quality of the soil. Fertile layers of earth and heaving soil are not suitable for a foundation in a trench without formwork. Such soil can present unexpected unpleasant surprises after the construction of a house. It is quite difficult to determine the quality of the soil, so this type of construction is not always technically justified.
Preparing the trench
Preparing the trench
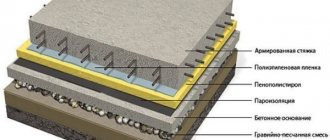
The foundation without formwork in the ground should be approximately 20-30 cm wider than the thickness of the walls being erected. The trench is dug to a depth of 80-100 cm. A shock-absorbing cushion must be formed at the bottom. To do this, a layer of sand 10-20 cm thick is poured along the entire length of the dug hole. It is recommended, but not necessary, to lay a layer of fine gravel on top of the sand, while the sand cushion can be left 7-10 cm thick. The cushion is thoroughly compacted with a vibrating plate or manually.
Laying with geotextile film
Laying geotextiles
Can formwork be replaced with geotextile film? Such a replacement can be made, but a concrete-filled foundation will be regarded as a strip foundation without formwork. The film is used with a thickness of at least 200 microns. It is laid on the walls of the trench, gluing the joints on both sides with construction tape. The film serves as a barrier, preventing the concrete milk from evaporating before the concrete hardens. It is recommended to lay roofing felt overlapping on top.
Types of formwork
Formwork is the form for pouring the concrete mixture used to create the foundation. The use of formwork is considered a universal method, since it is suitable both for the manufacture of foundations and for the construction of columns, ceilings, construction of walls and other structures.
The following types of formwork are distinguished:
- Removable or collapsible. After pouring and hardening of the mixture (i.e. after a few days), it must be dismantled. It can be used repeatedly to form the foundation, therefore it is often referred to as reusable formwork.
- Fixed. It remains as insulation along the edges of the foundation and is not removed after the mixture hardens. Typically made from polystyrene foam blocks.
- Combined. Instead of sheets of plywood or iron, polystyrene foam blocks are inserted inside the removable formwork. When dismantled, they are left as insulation and as additional protection from all sorts of external influences on the foundation.
Each of the listed types has its own advantages and disadvantages. Thus, removable formwork consists of many parts, it is quite difficult to install, but it is cheaper due to the use of boards, plywood and metal sheets.
Permanent formwork is made from solid panels using a production method and is used mainly for pile and columnar foundations, being an additional strength factor. Combined formwork combines the advantages and disadvantages of both previous types.
Preparing the area
Before the prefabricated formwork is installed, it is necessary to clear the site of construction debris. The next stage will be marking the area for the future foundation. It is most convenient to carry it out using pegs and wire or rope stretched between them.
In this way, guides will be set for further digging of a trench or foundation pit for laying the foundation. The horizontal tension of the rope or wire is adjusted with a special building level or level.
It must be taken into account that the foundation under the structure should be 3-5 cm larger than the base. A trench or pit can be dug either manually or using special equipment. The depth of the excavated area must be at least 50 cm. The base should be leveled horizontally.
Application of formwork for slab foundations
A sand cushion must be laid at the bottom of the trench or pit. It reduces the impact of soil on the foundation and serves to evenly distribute the load. The thickness of the sand cushion depends on the nature of the building. Sand is poured in layers of 10 cm, poured and compacted.
The final step will be to reinforce the sand cushion with gravel or fine crushed stone. To prevent crushed stone from falling into the sand, the bottom of the trench or pit is lined with geotextile fabric or polyethylene. A 10 cm layer of crushed stone should be leveled horizontally.
Formation of formwork panels
Installation of prefabricated formwork begins with the formation of panels from boards or plywood. To do this, take an edged board 30-40 mm thick and 100-150 mm wide.
Shields are formed from longitudinal boards and bars located across them. The distance between the longitudinal boards should not exceed 2 mm so that the future foundation does not foam or leak.
At the joints, the wooden parts are fastened with self-tapping screws or nails. In this case, the caps should be located inside, on the side of the future concrete mixture.
After the plywood panels are ready, they need to be laid. The panels are laid on a frame made of bonded bars. The sheet of plywood used should be 5-15 mm thick (so that the pressure of the mixture does not simply break the formwork). Instead of plywood, iron sheets are sometimes used.
In addition to shields, you will need:
- Cross bars.
- Stops and braces.
- Pegs for support.
- Thrust bars.
- Connecting strip.
- Overlay bars for emphasis.
- Waterproofing material.
When constructing shields, it is necessary to take into account the strength of the soil in which the future foundation will be located. If it is strong enough, then the role of the underground part of the formwork will be played by the walls of the trench.
Otherwise, it is necessary to dig a pit or trench 15-25 cm wider, taking into account the spacers for the formwork, and make the panels themselves larger. The height of the formwork panels should be 5-8 cm higher than the expected level of the future foundation.
Formwork materials
Formwork is a pre-prepared frame for pouring the foundation. The main task of the formwork is to hold the foundation in the desired place of the stated shape until it hardens. Installation of formwork is a mandatory step in installing the foundation of a house or any other building that requires a foundation. Before we begin to study the technology of installing formwork, we will consider the types of materials used to construct the frame. The most common formwork materials are:
- Metal formwork.
Metal formwork is mounted from steel sheets up to 2 mm thick. The advantage of metal formwork is the ease of working with it, as well as flexibility and ductility. The steel sheet bends easily, which allows you to get the formwork (and, consequently, the foundation) of the desired shape. This feature is especially important if you want to round the corners of the foundation. The disadvantage of metal formwork is price; while saving on the overall construction budget, metal formwork will not suit you.
- Reinforced concrete formwork.
Reinforced concrete formwork is convenient, practical and popular. But, in addition to the high price, it has one significant drawback: the large weight of the slabs obliges the owner of the building to hire a team of workers with special lifting equipment. However, using reinforced concrete as formwork saves the amount of concrete that will be required at the foundation pouring stage. It turns out that at one stage the financial losses are greater, at another - less. - Polystyrene foam formwork.
Expanded polystyrene blocks for formwork are produced industrially, and this is their main difference and advantage. Assembling formwork from expanded polystyrene is simple and quick; the blocks are attached to each other using a special locking groove. The only disadvantage of block formwork is the high cost of materials.
- Wood formwork.
Wooden formwork is possible from various types of wood: sheets of wooden plywood, OSB boards, and even ordinary boards are used. The advantage of wood formwork is its low cost when comparing this type of materials with those listed above. In addition, the installation of wooden formwork is not complicated and intuitive; any man with experience in carpentry can handle it. However, wooden formwork also has a drawback: it must be properly strengthened, especially in places where the thickness of the concrete being poured increases.
Installation of panel formwork for strip foundations
For the most popular strip foundation, formwork panels are knocked together from unedged boards with a thickness of 30 mm and a length of 1.5–2 m. The inner side of the boards is made smooth, so the stiffening ribs are attached to the front side of the formwork, and the nails are driven in from the inside and bent on the outside.
On both sides of the trench, support posts are driven strictly vertically in increments equal to the length of the formwork panel. For racks, timber with a cross section of 50x50 mm and larger is used. The posts are deepened into the ground by 50–70 cm. The first beacon shields are placed and attached along the support posts. The vertical middle of the support posts is the point where the following shields join together.
During installation, for the reliability of the structure, clamps are used - longitudinal boards, staples, tension hooks and tie rods. Every 3–4 m, a transverse tie beam is attached to the upper edge of the shields. On the outside of the boards, inclined struts are installed in increments of 0.5–0.7 m. When pouring a concrete foundation, struts prevent the structure from expanding.
1. Sand cushion. 2. Concrete preparation. 3. Formwork panels. 4. Spacers. 5. Pipe-sleeve. 6. Support pillars. 7. Cross tie