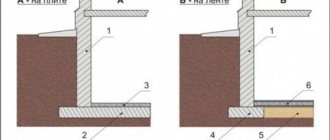
When we are planning the laying of a furnace, one of the main points at the project preparation stage is the question of how to properly arrange the foundation for the furnace.
Since its proper design ensures full activity of the furnace itself throughout its entire service life, and, on the contrary, if we make a mistake with its design, then the well-being of the furnace is at risk. When laying a foundation for a stove, the main task is to ensure that its movements (settlement or heaving deformations) do not differ greatly from the permissible deformations of the house foundation.
In this case, you need to take into account:
— the design of the foundation of the house itself: columnar, strip, slab; — foundation materials: rubble, brick, small concrete blocks, prefabricated foundation blocks and pillows, monolithic reinforced concrete; — soil heaving: non-heaving, weakly, moderately and strongly heaving; — thermal regime of the house: seasonal heating or permanent residence; - when the foundation of the furnace is being built - simultaneously with the foundations of the house or after its construction, in summer or winter.
Requirements for furnace foundations.
First of all, the foundation for the furnace must withstand the design load, which consists of several components:
- own weight of the stove;
- weight of the heater being installed;
- water tank volume.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the weight of the brick lining or other external decoration, if any. The operation of a bathhouse inevitably involves high water consumption. Therefore, when designing a stove base, you should consider its design in such a way as to minimize the ingress of moisture directly under the stove. This will relieve the soil from waterlogging, which is fraught with both rapid destruction of the foundation and the appearance of the effect of soil heaving. The dimensions of the base are selected so that its length and width are at least 100 mm greater than the dimensions of the stove. Such a reserve will allow you to unload and preserve intact the most fragile places in the foundation structure - the upper edges. The location for the furnace foundation is chosen depending on the design features of the furnace itself. The main requirement is to ensure free installation of the chimney at a minimum distance from the roof ridge. In this case, it is necessary to calculate the likelihood that the chimney may rest against any supporting structures.
IMPORTANT: If the dimensions of the building are small, then the stove foundation may be in close proximity to the main foundation. In this case, it is necessary to check the possibility of creating a gap of at least 50 mm wide. It is unacceptable to combine foundations into a single structure.
Foundation for a brick oven
The weight of such a stove is usually very large (up to 8 tons when wet and up to 4 tons when dry), so the base must be solid. To roughly calculate the weight, you can multiply the weight of one brick by its quantity and add 40% to the weight of the mortar (clay mortar has a very large weight). There is one more feature: the foundation for a brick kiln cannot be placed near the walls; it must be at least 0.5 meters away from the main structures.
Dimensions
The dimensions of the foundation for a brick kiln should be no less than 10-15 cm larger than its dimensions. But this is when the groundwater is low. Then, for greater stability, the base can be deepened as much as the weight or degree of heaving of the soil requires. For example, on sandy loam soils for a medium-sized brick kiln, it is enough to deepen the foundation by 80 cm.
If groundwater is close, you will have to deepen it to a minimum. In order to achieve normal stability in this case, the foundation is made much larger in length and width.
Foundation on stilts
A heavy brick oven on non-heaving soils can be placed on a reinforced concrete slab 15 cm thick (the slab must be monolithic, i.e. without voids).
To increase the stability of such a foundation, it is advisable to make piles. They can be made from asbestos-cement pipes, reinforced with reinforcement and filled with concrete. Sheets of roofing felt, roofing felt, etc. can be used as formwork (instead of pipes). which are rolled into a tube. They are also reinforced, then filled with concrete and backfilled. The production of piles one to one repeats the technology of constructing a pile foundation.
Foundation diagram for a furnace made of reinforced concrete furnace on piles
One option is to use metal screw piles. Due to the presence of special blades, they are screwed into the ground, which speeds up the process. Their disadvantage is the price and a large number of low-quality products. Advantages: quick installation and soil compaction that occurs when such piles are screwed in. If the soil allows, you can screw them in yourself, otherwise (on hard and rocky soils) the work of a special machine is required.
One of the types of piles
The depth of the piles is 30-50 cm below the freezing depth of the soil (crushed stone is poured onto the bottom of the hole dug under the pile, it is compacted, and then they begin to make the pile). 10 days after production, a monolithic reinforced concrete slab is laid on the piles. A waterproofing layer is laid on top of it (roofing felt in two layers, hot impregnation with a bitumen composition, etc.)
You can make a foundation for a brick kiln from rubble and concrete. It requires a minimum of costs (if you find a bottle nearby). To do this you need:
- Dig a pit (larger in size than the required foundation);
- Place a layer of crushed stone on the bottom and compact it. The thickness of this bedding in a compacted state is at least 15 cm. On highly heaving soils, another layer is made of sand, which is double-filled with water to compact it. Only after the water has receded again and the sand has dried, crushed stone is poured. Next, we continue the process of pouring the foundation using generally accepted technology.
Foundation diagram for a furnace made of concrete and rubble stone
- The next step will be to install and waterproof the formwork according to the dimensions of the future foundation. Waterproofing of the inner surface of the formwork is carried out with bitumen impregnation or a layer of roofing felt. Then you need to lay large stones on the bottom, and fill the space between them with small crushed stone.
- The laid stones are poured with cement mortar (for 1 part 400 cement, take 3 parts sand and part (slightly less) water).
- The layers are repeated until 6 cm remains to the floor level. The surface of this layer is carefully leveled.
- The foundation is covered with polyethylene or roofing felt and left to dry for 10-14 days.
The foundation is covered with polyethylene or roofing felt and left to dry for 10-14 days.
In order for the shrinkage of the brick kiln to be uniform, it is advisable to lay the brick pipe (it is the one that gives the main part of the load) as close to the center of the kiln foundation as possible.
Brick stove foundation
According to building codes, pouring a foundation for a brick stove is required if the load on the floor exceeds the permissible values. The need for additional strengthening of the foundation can be determined after relatively simple calculations.
The preparation of the foundation is envisaged in the early stages of designing a residential building or bathhouse, even before the construction of walls. During preparation, the burial depth is calculated, and the type and material of the base is selected.
Calculations are based on the actual load experienced by the foundation under the weight of the brickwork. The mass of one cubic meter of laid brick, including the mortar required for laying, is 1350 kg.
According to SNiP, the maximum possible load on the floor, which does not require additional strengthening of the foundation base, is 750 kg. Greater weight leads to the need for additional measures aimed at strengthening the load-bearing surface.
A light brick stove without a foundation requires no more than 200 pcs. stone The total weight of the structure varies from 600 to 750 kg. If you install a stove of more than 200 pcs. brick, you will need to make the right, suitable foundation, taking into account:
- Weight and load on the base.
- Financial expenses.
- Depth of soil freezing, atmospheric and weather conditions.
The thickness of the foundation is proportional to the load on the foundation. For a light stove, it is enough to pour a concrete pad 10-15 cm thick. Complex brick structures require the manufacture of a foundation base.
If it becomes obvious that the construction of a foundation for a brick kiln is required, it is necessary to wisely select an option for strengthening the foundation. The following solutions to the issue are widespread:
- Bored and screw piles.
- Brick pillars.
- Reinforced concrete slabs and strip foundation.
- Strengthening wooden floors and supporting structures.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with a stove with a water heating boiler with your own hands: a stove boiler in a brick oven for heating a house
When choosing a suitable option, take into account the design features of the furnace, the period of work, and financial costs.
Pile foundations
One of the economical options for making a foundation is the use of bored or screw piles. The device allows you to do without extensive excavation and concrete work, and at the same time ensures the strength of the base for installing the furnace.
Pile or needle foundations are made quickly, which reduces the work time by half compared to concreting:
- Bored piles - for installation, a hole is drilled in the ground using a drill in order to reach solid soil. If this is not possible due to the characteristics of the soil, they go deeper below the freezing level. After drilling a hole, at the very bottom, a special drill is used to expand the hole, making a “skirt”. A metal frame is installed to prevent soil shedding. Fill the dug hole with concrete with mandatory reinforcement of a bored pile. The columns are tied together with reinforcement. A concrete pad or tape is poured on top.
- Screw piles - the structure of a pile-screw foundation is the same as its bored counterpart, only special metal rods are used as supports. In shape, the drills resemble a threaded screw with a large pitch. For installation, the piles are screwed into the ground. Twisted piles are cut to one level. The metal elements are left in the ground, the internal cavity is filled with concrete. A concrete pad is poured on top with the obligatory tying of screw piles together.
Screw and bored piles have approximately the same load resistance. Existing SNiP allow the use of a needle foundation in the construction of a residential building. Therefore, pile screw and bored foundations are successfully used for brick kilns.
The peculiarity of the foundation on screw piles is that metal screws screwed into the ground remain in the ground. The service life of the product is limited to 50-60 years. During this time, the steel supports rot and become unusable.
A columnar type foundation is made in the same way as a bored foundation, with the difference that the pillars are made of brick. Almost any rubble karmic stone is suitable for the work.
During the work, some nuances are taken into account:
- Brick used for the foundation - the base is laid out of a material that is moisture-resistant, durable and able to withstand frost without loss of strength characteristics.
- Criteria for choosing a material - it is better to lay the base from solid ceramic bricks. Material that has defects is suitable: chips, inclusions, etc. It is impossible to make a foundation from sand-lime brick. Sand-lime brick quickly absorbs moisture, cracks, and becomes covered with mold and mildew. Over time, the columns begin to sag and become unable to withstand further load.
- The distance between the columns - as a rule, the supports are placed in the corners of the future furnace structure and in steps every meter from each other.
It is better to use ceramic bricks for the foundation. A used brick will do. During masonry, a sand-cement mortar with the addition of fine and medium crushed stone is used.
Concrete base for a brick oven can withstand maximum load. Most often, a strip foundation is made. In some cases, a ready-made reinforced concrete slab is laid as a base.
Each option has its own characteristics:
- The foundation is made of concrete blocks - it is characterized by speed of installation and the ability to withstand high loads. In buildings where reinforced concrete slabs are installed as interfloor partitions, the stove can be installed on the second floor, of course, if the other technical characteristics of the house allow this. Lack of reinforced concrete products, the need to use special loading equipment and the inability to carry out the work independently.
- Strip foundation - brand of concrete mixture used M 400. Before pouring, trenches are dug and formwork is installed. The lowest point of the strip foundation should be below the freezing level. A gravel backfill is made at the bottom of the dug trench. At the lowest point of the future foundation, a “tooth” or “skirt” is made, expanding the base of the pit at an angle of 45°. A knitted reinforcement frame is laid in the ditch. The thickness and pitch of the reinforcement are 1/10-15 cm, respectively. After manufacturing the metal reinforced frame, the base is filled with concrete mixture.
Materials and tools.
Most often, concrete and rubble concrete foundations are laid under the furnaces. To install them you will need the following list of tools:
- trough or mechanical concrete mixer;
- shovels and bayonet shovels;
- boards, sheets of chipboard or other sheet material of sufficient strength;
- nails and hammer;
- building level.
Materials you will need:
- sulfate-resistant cement SSCP. You can also use cheaper PC, but in this case there is a risk of reducing the strength of concrete under the influence of sulfates, the content of which in groundwater is very high;
- coarse sea, river sand or pre-screened mountain sand;
- crushed stone;
- dense sheet waterproofing (polyethylene or roofing felt).
A rubble concrete foundation for a furnace will also require the presence of rubble stone in an amount sufficient to densely lay the entire volume of the pit.
Types of bases
When talking about what kind of foundation is needed for a furnace, three main options are considered:
- rubble concrete;
- solid poured concrete;
- support-pile foundation.
The classic foundation for a furnace is built from cement-based rubble or concrete. The base itself should be 50-100mm larger than the area of the oven itself around the entire perimeter. The height of the foundation should be the same as the foundation of the bathhouse or wooden house itself.
Roofing felt or 2 layers of roofing felt for waterproofing are laid on the finished base, bricks are laid on the insulation and outlets are prepared from metal corners, from which fireproof cuts are made.
Nuances of construction
The first nuance is that the foundation for the furnace is not connected to the main foundation of the building. In addition, if they are located close enough, then a sand cushion about half a meter wide must be laid between them.
The second nuance: under no circumstances should you add concrete to the old foundation, since further installation of the entire furnace structure will cause shrinkage, cracks and many other problems will arise.
The most classic foundation for a furnace is built with a solid slab. The depth of the base depends on the following factors:
- ground water level;
- soil type;
- depth of soil freezing.
To avoid surprises in the future, before starting construction of the foundation, it is worth conducting a geological exploration of the entire site; its cost fluctuates around $50. Thus, you will be able to obtain accurate data on the groundwater level, soil type, and soil freezing depth. This data will help determine exactly what foundation depth should be selected.
Example of depth calculation:
- sandy and dry soils – 80 cm;
- heaving - below the freezing zone, at least 1 meter;
- The weight of a brick kiln is calculated using the formula: 1350xV=P, V is the volume of the masonry.
If mistakes were made in the design and construction, then the following problems may arise in the future:
- through cracks on the stove and its foundation;
- destruction and collapse of masonry (brick kiln);
- violation of the integrity of the chimney;
- subsidence of the base, the stove will be lopsided.
The biggest problem is that such mistakes cannot be repaired normally. The situation will worsen and the oven will collapse.
After the depth of the future foundation for the stove and its dimensions have been determined, it is necessary to correctly select the place where the stove will stand. This directly affects the location and outlet of the chimney. An unsuccessfully chosen location will create a lot of problems in the future with bypassing the load-bearing structures and extending the chimney pipe, and its outlet to the street.
Concrete foundation.
Preparing the pit.
There are two options for pouring a concrete base:
- shallow;
- recessed
The first option is convenient due to the low labor intensity of its arrangement and low material costs. It will be enough for him to only remove 10-15 cm of the top fertile layer. However, it is not recommended to use it on unstable soils, since in winter it can simply warp due to movements of freezing and thawing soil. Therefore, most often they opt for buried foundations. They got their name because of the relatively large depth of the foundation pit for filling (50 cm or more). The dimensions of the pit must allow the formwork of the required dimensions to be placed in it. If the soil is very dense and hardly crumbles, then you can abandon the formwork and pour it directly into the pit.
Formwork, cushion and waterproofing.
Strictly according to the specified dimensions of the future foundation, formwork made of boards or other similar materials is installed in the pit. The design of the formwork can be arbitrary, the most important thing is that it must be able to withstand the mass of poured concrete without losing its geometry. A cushion of crushed stone about 10 cm thick is poured into the bottom of the pit and compacted. The surface of the cushion must be strictly horizontal; a building level is used for control. Next, the inner surface of the pit is covered with sheet waterproofing. The sheets are laid overlapping, the excess from above is not cut off, but is laid through the upper cut of the formwork. To fix them, it is convenient to use a construction stapler.
Pouring concrete.
The concrete solution is mixed at the rate of 1 part cement to 2 parts sand and 4 parts crushed stone. In this case, approximately 125 liters of water are consumed per 1 cubic meter. Water must be added until the solution is in such a state that its liquid component acquires the consistency of sour cream. It is advisable to carry out the filling process in one step. Layers poured at different times may dry out on top, which will not provide the required level of strength. During pouring, it is highly advisable to perform vibration shrinkage. This will remove air bubbles that inevitably enter with the solution, reducing the strength of concrete.
Do I need a foundation for the stove and what dimensions?
The dimensions of the stove base depend more on the characteristics of the soil and the weight of the unit itself: for example, a fresh stove will weigh about 8 tons, and in a dried state it will weigh half as much. Sometimes an independent foundation is created for the main chimney, thanks to which uneven shrinkage of the furnace does not occur.
Pouring the foundation for the future stove - the first stages of work
But how deep the foundation for the stove should be laid depends on many factors: the heaving and strength of the soil, the depth of its freezing, the depth of the foundation of the steam room, the level of groundwater and whether the bath itself is finished at the time of its construction. For example, on sandy and dry soils, the foundation for a stove in a bathhouse must be made at a depth of 80 cm, and on heaving soils, it must be below the freezing depth, i.e. by 1 m 50 cm, and no less.
And you can calculate the exact weight of the brickwork using the following formula: P = 1350xV, where the V value is the total volume of the masonry in meters.
Rubble concrete foundation.
When the foundation for a furnace is laid using rubble stone, this allows several advantages to be achieved: - cement consumption is reduced; — the cost of the project is reduced (if it is possible to extract rubble stone yourself); — the strength and durability of the structure increases. The list of necessary tools and materials for a rubble concrete foundation is completely identical to that described above, with the exception of the rubble stone itself. A pit is prepared, a cushion of crushed stone is filled and compacted, formwork is installed and waterproofing is laid. The differences are as follows: each layer of rubble stone placed in a pit is filled with a cement mortar consisting of 1 part cement and 3 parts sand. Crushed stone is not added to the solution.
IMPORTANT. It is unacceptable to pour two or more layers of rubble stone at once. This will lead to the formation of air cavities between the stones, reducing the strength of the foundation.
Foundation calculation with example
The choice of base for the furnace directly depends on the total weight of the structure; to do this, you first need to calculate it by counting the amount of brick and cement mortar used. Typically, 1 cubic meter of brickwork weighs 1350 kilograms - keep this in mind.
If the total weight of the heating system exceeds 750 kilograms, then a high-quality foundation will require a strong and durable foundation, with a deep foundation made of rubble or concrete stone. With a lighter structure, a base made of roofing iron, asbestos sheets, or even ordinary wood may be suitable.
When making calculations for the foundation of a brick stove, take into account the type of soil on the site. On soft, swampy and easily sinking wet soil, the foundation should have a height of at least 150 centimeters, while on dry soil the foundation can have a depth of only 70 centimeters.
1350*0.8=1080kg
We add 70 kg and we get the total weight of the heating system - 1150 kilograms. Since our soil is quite hard, but the furnace has a large mass, we will install a foundation with a depth of 1 meter - this will be enough for long-term stability.
If the foundation for a brick stove is laid before the walls are erected, then before installing it you need to determine where the heating system will be installed - it will be impossible to change the decision, so before you start building the foundation, think about where exactly your stove will be located.
Drying.
The process of drying the poured foundation for a furnace is divided into several stages: • for the first ten days, the foundation is dried with periodic wetting of its surface with water. A damp surface will prevent cracks from appearing. If wetting several times a day is impossible for one reason or another, then there is an option to cover the wet filling with film and leave it in that state; •on the eleventh day the film is removed; •then the filling gains strength over another 5-6 days. Then you can begin laying or installing the stove.
What to pay attention to.
In order for the stove base to be strong and not require periodic repairs, the following points should be taken into account when pouring it: the cement for the mortar must be of high quality, the presence of lumps in the powder is unacceptable; Only tap water should be used. Water from open sources will contain many impurities, incl. and organic origin. If they get into concrete, the quality of the material will noticeably suffer; if the soil is mobile and requires the installation of durable formwork, then only new high-quality boards and chipboard sheets can be used to create it. The presence of knots, cracks or places of rot will not allow the concrete solution to be retained in the volume specified for it.
If you follow these recommendations, the foundation will easily support even a massive furnace for many years. At the same time, you will not have to use the services of expensive construction companies to fill it. Simple technology will allow you to do all the work yourself.