September 25, 2020 Stroyexpert Home page » Foundation » Installation
The construction of a foundation without prior protection from precipitation and groundwater is fraught with the penetration of moisture through the structure of concrete, which has pores in the surface of walls and basement floors. The appearance of dampness in basement-type rooms is a prerequisite for an increased level of humidity in it, the appearance of fungus and an unpleasant odor. In addition, the presence of any surfaces without insulation is a potential place for loss of a limited amount of heat in the room. Finally, cracks that form when exposed to moisture can reduce the strength of the structure and reduce the service life of the structure.
Where does dampness come from in basements?
The appearance of dampness on the walls of basement-type premises, which contributes to the appearance of fungal formations, which in turn are a source of unpleasant odor, is associated with poor-quality waterproofing or its absence.
Results of poor foundation waterproofing
Other consequences that arise from non-compliance with SNiP standards are leakage in the area of the seams or at the junction of foundation elements. Among the factors influencing the appearance of dampness are the following:
- Lack of tightness at the joints of the material used for waterproofing. The defect appears as a result of improper installation or changes in the internal properties of the material under the influence of groundwater or precipitation.
- Performing a blind area in violation of technology, causing damage or destruction. In case of precipitation penetration from the outside of the building, waterproofing should be done in these places. Carrying out this operation involves eliminating the poor-quality blind area and building a new one.
- Systematic formation of condensate associated with temperature changes in the external environment. This occurs when the basement structure is improperly designed, in which warm air tending to rise upward interacts with the cold surface of the walls.
Measures to prevent dampness
Preventive measures to prevent high humidity in basements include:
- elimination of damaged foundation layers;
- processing of cleaned surfaces with a metal brush or using fixed brushes or abrasive on the surface of the hammer drill;
- digging canals;
- drainage for the purpose of draining water;
- laying horizontal and vertical waterproofing;
- construction of a blind area.
Waterproofing and foundation drainage
Requirements for waterproofing and blind area
To eliminate the destructive influence of water on the surface of the foundation and walls, a number of conditions must be met to ensure protection against the penetration of any types of moisture. Among the main requirements for waterproofing:
- ensuring the presence of a protective coating around the perimeter of the entire fenced area;
- applying a protective layer against the threat of groundwater penetration during the spring flood and the action of hydrostatic pressure;
- correct selection of a waterproofing scheme, taking into account seasonal fluctuations in groundwater levels, the type of existing groundwater, and the coefficient of water permeability;
- selection of protective material in accordance with individual conditions at the site of foundation construction;
- applying a protective layer to the level of the base in order to prevent the impact of snow on the foundation and walls during large amounts of precipitation;
- When the groundwater level is close to the surface of the earth, there is a high risk of creating an overly moistened area; to avoid this, a drainage system for water removal is installed.
Groundwater impact results
Why is insulation needed?
The concrete surface of the foundation must be protected from exposure to liquid. This is necessary to achieve the following results:
- preventing water from entering the basement or ground floor of the house;
- protection of concrete from washing out particles and aggressive environments;
- preventing the harmful effects of cold.
The simultaneous action of water and negative temperatures is dangerous for the material. Capillary moisture penetrates into the thickness of the foundation and freezes there. Water is a unique substance, only it expands when it freezes. Thus, the pressure inside the underground wall increases, which leads to its destruction.
Performing a blind area
The construction of any type of foundation must include several types of protection from the effects of groundwater and precipitation. To protect the foundation and walls of the structure from the effects of rain, melted snow and other types of precipitation, a blind area is made along the entire perimeter of the building. The blind area is a strip of asphalt, stone, tiles or concrete of varying widths and thicknesses, at an angle of up to 10°. The width of the blind area, as a rule, is in the range of 60-120 cm, the thickness is selected based on the conditions of the site and the material used. It is performed in the direction from the foundation and walls of the building in order to drain precipitation. The requirements for the material for the blind area are the absence of mechanical damage and moisture transmission. This type of coating is used for any type of construction and, when done correctly, does an excellent job of protecting the building from moisture penetration.
Types of blind areas
Waterproofing using spray material
Waterproofing with sprayed materials is considered the most modern technology. Its main advantage is that it meets all the necessary requirements and clearly performs all tasks. In addition, such material can be used not only to provide foundation protection for the first time, but also to repair old insulation. Today, builders also use sprayed waterproofing materials for roofing work.
The main advantages of spraying include:
- Long service life.
- Ease of application of the material.
- Absence of any seams or joints.
- Fast drying and hardening.
- It has no toxic properties and does not cause any harm to health.
- Resistant to ultraviolet rays.
- Elastic.
The only disadvantages of sprayed materials include the relatively high cost of the work, as well as the need to use special equipment to carry out the coating.
The technology for applying the material involves preparatory work, and then spraying the substance using a special device. Geotexy is also applied for fixation. A video of how the spraying procedure is performed can also be seen online.
Waterproofing against groundwater
The situation is more complicated with waterproofing equipment to prevent exposure to groundwater. One of the main factors, depending on which a certain type of waterproofing device is chosen, is the groundwater level at the construction site. Even with deep groundwater, during a seasonal rise in its level, there is a danger that it will reach the level of the foundation and walls of the structure. In some cases, for example, when building a house on water-resistant soils, water moves in the direction of least soil resistance, that is, in the direction of the foundation. Water-resistant soils include sandy loam, loamy and clayey types.
Types of groundwater
When choosing the type of waterproofing, it is important to take into account the specifics of the foundation and the pressure characteristics of groundwater. In general, according to the last feature, 4 types of groundwater are distinguished:
- groundwater in a free-flowing state;
- sources of moisture with low pressure;
- pressure type of groundwater is characterized by the possibility of independent release to the surface;
- sources of moisture in a closed volume, also classified as suspended.
Classification of groundwater
Which foundation needs to be protected from moisture?
Waterproofing materials are laid and a deep foundation is created if a house with a residential basement is being built, in which an optimal microclimate for people must be provided. Here, the degree and quality of waterproofing directly depends on how wet the soil is in the area. But, even if the soil is dry and underground water runs deep, hydro- and thermal insulation, even the most minimal, is necessary. These measures are dictated by the fact that it is impossible to predict how the map of underwater currents and groundwater may change over time.
Waterproofing scheme for strip base
Important: If the soil under the house is minimally moistened, but is in contact with the surfaces of the walls in the basement without waterproofing, then such contact will provide the most optimal conditions for the development of microorganisms, bacteria and mold.
Waterproofing the foundation and basement: types and technology
Types of waterproofing of foundations and basements
To fully protect against moisture, it is necessary to perform waterproofing in two planes:
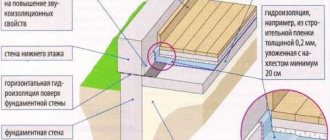
- Vertical insulation is performed to protect against the influence of groundwater from the basement walls. This can happen when the groundwater level rises or when a structure is built on water-resistant soils. There are two options for protection against moisture: using bitumen in rolls, glued to the surface of the wall, or by applying several layers of bitumen in a liquid state to them.
- The horizontal type of moisture insulation is used if the base of the basement coincides with the location of groundwater in height or if there is high-density clay soil. The horizontal type of moisture insulation is carried out in the form of a protective layer applied along the perimeter of the plane according to one of three options, depending on the location and pressure characteristics of groundwater.
In the first case of groundwater location below the level of the base of a structure without a basement, for protection it is enough to apply a 2-3cm layer of cement-sand mixture at a height of 15-30cm from the base over the entire area of the foundation.
Horizontal and vertical waterproofing of the foundation
In the case of low groundwater levels and the presence of a basement in the house, a protective coating is provided on the outside and during the construction of the foundation. Possible combinations include combining protection along the edge of the foundation structure, covering the walls with molten bitumen and performing protection at floor level.
When groundwater occurs close to the surface of the soil for foundations and walls of a room, waterproofing involves performing several types of protection. Among them: uniform application of a 20-30cm layer of cement-sand mixture, laying of protective material in several layers, vertical type protection carried out by applying several layers of bitumen placed on mastic.
Waterproofing of foundations and walls for different levels of groundwater provides for protection according to one of the following schemes:
- When installing waterproofing in an area with groundwater located at a depth of up to a meter from the foundation level, taking into account the rise of capillary-type water, it is recommended to carry out coating protection.
- When groundwater is located at a greater depth, some experts recommend abandoning waterproofing, however, taking into account the possible impact of site development on groundwater, it is better to carry out protection using coating-type insulation.
- In the case of a high location of groundwater, reaching the level of the lower part of the base of the building, it is recommended to jointly perform waterproofing with the installation of a drainage system.
Waterproofing technology
For strip foundation
Before waterproofing, it is necessary to ensure that the surface of the foundation is as flat as possible. It is necessary to apply molten mastic with bitumen to the surface of the base, placing them in an even layer. On top there is a roofing material covering with an overlap of up to 20 cm. It is possible, after leveling and drying the surface, to apply protection in the form of a spray coating on which a reinforced coating is applied. Another option for a protective coating is to apply a cement-sand mortar.
For pile foundation
For the manufacture of structural elements, it is assumed that moisture-resistant grades of concrete will be used. Considering the difficulty of performing waterproofing at the location of the pile foundation support structures, it is carried out at the level of the grillage.
Waterproofing of pile foundation
Insulation of walls and floor surfaces from the inside of the room is carried out to protect the joints of elements. If there are large gaps left at the joints, they are sealed by packing them with a layer of clay. The thickness of the places where the base elements are connected must be at least 2 cm. After sealing the seams, mastic is applied to the surface of the walls, followed by fastening the reinforcement and sealing the area with a layer of plaster.
Typical foundation waterproofing schemes
Application of coating protection
Coating protection is represented by liquid compositions based on bitumen mastic using various additives. When painting the foundation and basement walls from moisture, a layer of a special mixture is applied to the prepared surfaces, which has hydrophobic characteristics after drying. The most common practice is to make several thin layers of a protective composition, on which a layer of clay is applied. The thickness of the clay coating is up to 5cm. The areas between the blocks or bricks are filled with mastic, after which the wall is treated with a spatula until flatness is achieved.
Coating waterproofing of the foundation
Application of penetrating waterproofing
This type of protective coating is characterized by penetration into the structure of the material, due to which a monolithic composition without gaps is formed, which has hydrophobic characteristics. An additional advantage of this type of protective coating is that the resulting structure is resistant to temperature fluctuations. In this case, there is no possibility of condensation forming, since this type of protection has the ability to allow steam to pass through. Molten glass is used as a material for penetrating waterproofing. After cleaning the wall surface from the previous coating and brushing it with a metal brush, the composition is prepared. It is done by adding powder to water while stirring the mixture. The mixture is applied starting from the corners, after preliminary moistening the surface. Several more can be applied to the first layer with a break between approaches of up to 3 hours necessary for the previous layer of the mixture to dry.
Penetrating waterproofing
Waterproofing using cement-sand mortar
It is common practice to use a hydrophobic type of cement or Portland cement to perform a protective coating. This type of coating is highly reliable and has the best characteristics, while at the same time having the greatest labor costs. After cleaning the surface of the walls and wetting them with water, the solution is prepared. The mixture should have a thick and at the same time plastic consistency and should not contain large fractions. The consistency will depend on the planned thickness of the applied coating. The composition is evenly distributed over the plane of the foundation and walls.
Waterproofing the foundation with building mixtures
Waterproofing using lubricants
Do-it-yourself waterproofing of a strip foundation using coating is one of the easiest ways to protect the foundation from moisture. The method of this type of waterproofing works on the principle of applying paint. You just need to purchase the material, and then use a brush to cover the entire surface of the foundation with coating. To ensure waterproofing in this case, liquid glass, various bitumen mastics and much more can be used.
Using coating for waterproofing strip foundations has its advantages:
- Low cost of substances, and of the work itself to ensure protection.
- Good elasticity of the substance, which is ensured due to its consistency.
- Absence of any joints or seams.
- High degree of hydrophobicity after concrete coating.
- Ease of waterproofing work. Coating concrete with coating does not require the use of any complex tools or equipment, nor does it require any special skills.
- High degree of bonding to the foundation surface.
In addition to the listed qualities, the coating also has some disadvantages. Firstly, it is fragility. The shelf life of such a substance is on average about six years. After this time, the mastic or other substance becomes inelastic and brittle, and, accordingly, unable to provide adequate protection. As a result, the homeowner will have to carry out repairs and re-waterproofing work. You should pay attention to this when choosing a waterproofing method. If cracks appear on the mastic or liquid glass after a period of time, it is necessary to take measures to carry out repeated work as quickly as possible, since moisture can penetrate through the cracks to the concrete and provoke the process of its destruction.
If we take into account the fact that coating options are characterized by their low cost, waterproofing can be done every 7-8 years without spending a lot of money. However, if this option does not suit you, you can choose substances with the addition of polymers, rubber or latex. Such connections last much longer and are more resistant to external influences.