Definition of the term “pile foundation”
In general, a pile foundation consists of piles immersed in the ground, united on top by reinforced concrete (concrete) beams or a slab (grillages).
When is it advisable to use a pile foundation?
Let's consider the prerequisites for using pile foundations in private construction.
The need to construct a pile foundation under special conditions
Reason 1
. In some cases, during the construction of a country house or cottage, there may be a relatively weak layer of soil in the upper part of the base of the building being constructed.
Weak soils include:
- Loams and clays in a fluid-plastic state;
- Loess-like soils contain more than 50% dust particles with a small presence of clay and lime particles. In the presence of water, loess-like soils become wet and lose stability;
- Quicksand - sandy-clayey soils, highly saturated with water;
- Plant soils - various soils with an admixture of 1...20% humus, peat and peaty soils, silts, sapropels, clay soils, yoldium clays, soils of wet saline soils.
In this case, there is a need to transfer pressure from the building to denser soil lying at a certain depth depending on geological conditions.
Then it is recommended to build foundations from piles, which are capable of supporting greater loads compared to shallow foundations. Foundations are especially effective in heaving soils with deep freezing of more than 1.5 meters. In this case, a pile foundation is more reliable than a columnar and even more so a strip foundation
Reason 2.
It is possible to use pile foundations in dense soils in order to reduce the volume of excavation work, concrete consumption, and reduce labor intensity and construction costs. When installing a pile foundation, there is no need to dig a pit, store excavated soil, remove soil, backfill, etc. If you have a need to build a foundation in a short time, with little effort and at minimal cost, then a pile foundation is your option. For example, to build one pile 3 meters long and 300 mm in diameter, you will need to carry out excavation work with a volume of 0.2 m3 of earth (using a drill), and in the case of installing a strip foundation, the volume of excavation work will be much larger (depending on the width of the base foundation). This option is acceptable if the house design does not include a basement.
Reason 3.
If, when calculating a strip foundation, the width of the foundation turns out to be too large (more than 1.5 m), it makes sense to use a pile foundation, which will reduce material consumption.
Reason 4.
If the choice of foundation type is dictated by the type of supporting frame, for example, if you decide to use a frame supporting frame on a foundation composed of weak soils, then it would be rational to use pile bushes for each column rather than making a strip foundation.
The designs of pile foundations are very diverse and depend on:
- from the choice of pile type,
- the method of their manufacture and immersion in the ground,
- their location under a building under construction,
- on the nature of the work of the pile in the ground,
- from the grillage design.
For the manufacture of pile foundations, a large amount of special construction equipment is used, which, of course, is not acceptable for country house construction. Therefore, we will focus on those designs of pile foundations that are within the power of an individual developer.
Design advantages
The speed of construction is the first and one of the important advantages that allows you to build a pile foundation with your own hands. Calculation of the required number of elements and dimensions will depend primarily on the size of the house. It must be said that the construction of such a foundation is considered the fastest way to build a zero cycle. For example, you can build a pile-screw foundation with your own hands in 2-3 days. And if the building is small, then the installation can be completed in a day. Another advantage of the design is the ability to operate year-round. The most affordable way to organize a foundation for buildings, even in regions with harsh climatic conditions, is considered to be a pile foundation. Another advantage of the structure is almost always the absence of the need to wait for the concrete to set, as is necessary when constructing traditional structures. You will have to wait for the mixture to harden when building a pile-rammed foundation with your own hands.
Types of piles for country construction
Piles are relatively long pointed or heeled concrete, wood or metal rods of square or round cross-section, immersed in the ground in finished form or manufactured directly into the ground. It is used in country house construction to strengthen the soil as the foundation of a building.
Piles can be used on any type of soil except rock. This type of foundation is technologically and economically feasible to use in private construction:
- For the construction of buildings in areas with high groundwater levels;
- If dense soils are located deep and when the upper layers of the natural foundation are characterized by weak bearing capacity (peat bogs, floating rocks);
- With a large freezing depth of 2 m;
- On steep slopes;
- If the mass of a private house is too large (more than 350 tons).
The finished pile has a sharp end on one side, with which the pile is driven into the ground using special equipment (hammers) through moving layers of soil until it reaches a solid layer.
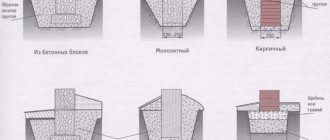
To make piles directly in the ground, wells are drilled into it, followed by reinforcement and pouring with concrete.
Piles are distinguished by their manufacturing method, material, shape of the transverse and longitudinal sections, and the method of their immersion in the ground.
The required length of piles is calculated in advance by the designer.
As a rule, in individual housing construction, the length of the pile is from 1.5 to 6 m, the distance between the piles does not exceed 2 m.
Depending on the method of their deepening into the ground, the following types of piles can be considered:
- Forgettable - loaded into the ground without excavation. For this purpose, special mechanisms are used, such as vibrating hammers, vibrating and pressing devices;
- Pressed concrete and reinforced concrete, installed in the ground by placing concrete mixture into drilled wells;
- Reinforced concrete drills, installed in the ground by installing reinforced concrete elements in drilled holes;
- Screw - have the shape of a drill and are screwed into the ground using special machines.
1 - wooden, 2 - reinforced concrete solid section, 3 - reinforced concrete hollow, 4 - steel screw, 5 - pressed concrete in the manufacturing process.
In private construction, piles of options 1, 2, 4, 5 are mainly used.
According to the nature of their work, piles are divided into:
- Rack piles that transfer pressure from buildings and structures to strong soil located under a layer of soft soil. Rack piles have a small smooth surface to which soil does not cling. Rack piles, cutting through layers of soft soil, transfer the load with their tip to deep, strong soil. In this type of piles, the most important thing is that the base is wide enough, since it takes on more than 80% of the load. These include TISE piles - these are piles with widening in the lower part and piles concreted in a casing or sometimes without it, concreted directly in the well, but 15-20% of strength is lost. They are used when there is weak soil directly under the base and such piles practically do not produce settlement.
- Friction piles that transfer the load to the surrounding soil through friction against the side walls. These piles have a developed lateral surface and along their entire length they cling to the ground. For them, the area of the tip is less important; the main thing is that their surface is uneven, with many protrusions. For example, bored piles, when concrete is simply poured into a well (sometimes under pressure). In this case, the side surfaces of the pile provide 60-70% of the load-bearing capacity. They are used when carrying out serious excavation work turns out to be very expensive. They are more often used when there is a high groundwater level or a relatively thick layer of weak soil, under which there is stronger soil, but not enough to hold the stand pile).
Construction of pile racks.
Installation features
M400 solution is used for concreting piles. If the construction of the structure is carried out in winter, then special frost-resistant plasticizers must be added to the mixture. In summer, the solution must be used up as quickly as possible to avoid subsequent cracking. To enhance rigidity and give additional strength, the foundation piles are combined using reinforced concrete tape. The width of the formwork and monolithic structure will depend on the weight of the structure. For reinforced concrete tape, the optimal height and width is 400 mm. For a monolithic structure, it is necessary to make formwork. The grillage is reinforced by tying it to pre-released reinforcement from the piles. Then layer-by-layer concreting is carried out. Under natural hardening conditions, the solution will gain 50% strength within a week. After this, it will be possible to begin construction of the building.
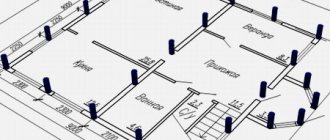
Placing piles in the foundation
It can be in the form:
- Single piles - for free-standing supports;
- Pile belts - under the walls of buildings and structures when transferring loads distributed along the length to the foundation with piles arranged in one, two rows or more;
- Pile bushes - under each column in the case of a frame load-bearing skeleton of a building.
The placement, type, size, depth and methods of immersion of piles are indicated in the projects (parameter b - pile pitch). Piles are generally installed vertically in the ground, but there are options for placing them obliquely. This option is used when significant horizontal forces act on the foundation. For example, if the site for the foundation has a slope and soil movement is possible during the spring melting of snow or heavy long-term precipitation. Basically, in the construction of country houses, both single piles and pile strips are used. Reinforcement with pile bushes in private construction occurs if the building site partially has a weak foundation (quicksand is found at the site of drilling a single well) or the soil is unevenly saturated with water, as well as when strengthening, for example, a large doorway (garage door).
First stage. Soil preparation and development
During this stage, three main actions must be performed:
- Carry out the alignment of the axes;
- Carry out soil excavation with an excavator in one work shift;
- Modify the soil manually to ensure placement of piles and grillage;
Material for making piles
- Reinforced concrete (concrete) - its use is preferable from the point of view of durability (100 years or more). The advantage of concrete piles is that, if you have the appropriate equipment, they can be manufactured right on site. For the manufacture of piles, concrete of at least M200 is used;
- Steel - piles are made in the form of various rolled steel profiles or pipes. However, the use of metal is not recommended for three reasons:
- Crane equipment is required for installation of piles with a diameter of more than 100 mm and a length of more than 3 m;
- High metal consumption;
- Anti-corrosion coating of piles is required.
- Wood - wooden piles are a straight log, cleared of bark (sanded), growths and branches with a diameter of 22-34 cm and a length of up to 8.5 meters from hard coniferous species (pine, spruce, larch, fir). The natural conicity (run) of the logs is preserved. Despite their cheapness in our latitudes, they are practically not used for pile foundations when building a country house, as they are subject to rapid rotting. Although this option cannot be excluded when using modern chemical preparations for treating wood against rotting.
So, for private construction, reinforced concrete piles of solid section, steel screw piles, and bored concrete piles are most suitable. In terms of the method of deepening, preference should, of course, be given to the bored version. For light buildings, such as country houses, an acceptable option is a strip arrangement of piles. As discussed above, the use of post or friction piles depends on the geological conditions, but generally it is a combination of the operating conditions of the pile.
Grillages for pile foundations
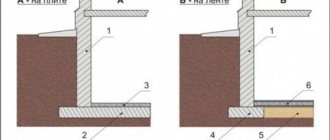
A pile foundation with a grillage (pile grillage foundation) is a building structure that combines piles and serves to uniformly transfer the load of the structure onto them and onto the soil foundation. There are prefabricated, precast-monolithic and monolithic grillages.
Grillages are high and low. A low grillage is usually located below the ground surface and it transfers part of the vertical pressure to the foundation soil, while a high grillage transfers these loads to the piles. The installation of prefabricated reinforced concrete and monolithic grillages represent the most acceptable options for country house construction.
Metal grillages are usually welded on site and “tied” to the piles with reinforcing bars. When arranging a large foundation, installing individual elements of a channel or I-beam requires the use of crane equipment, which is not always convenient in individual construction, because requires the organization of access roads and a site for the crane.
The most suitable for private construction is a reinforced concrete grillage. To make a cast reinforced concrete grillage, formwork is assembled between the piles, into which reinforcement from steel rods is placed. Some of the vertical rods are welded to the piles and “connected” them together with long reinforcing rods located inside the formwork.
For an overview of the types of foundations for a house, read the article Foundation of a house. Choosing the type of foundation for a house.
How to tie piles with iron corners
Metal strapping on screw piles increases the overall strength of the foundation. Metal can be used to connect supports both for frame houses and for heavier ones - foam concrete ones. If the structure is light, a corner will do; if not, choose an I-beam or channel.
- Features of metal strapping:
- steel beams are welded to the pipes themselves;
- The material can be welded with a bevel, giving additional rigidity to the structure;
- beams are treated with anti-corrosion primer.