Preparation and standards of SNiP
SNiP - building codes and regulations - spell out the basic requirements that should be adhered to when carrying out construction work (technology, size and thickness of materials).
Stages of foundation preparation:
- calculation and measurement of the area of the future building;
- digging a trench;
- preparing the base (removing debris, weeds, stones, digging up bushes).
Calculation before carrying out work is very important, since an imperfect terrain may be chosen for the object being built (hill, near water bodies, on muddy or clay soil, peat bogs), the size and height of the structure are taken into account.
When constructing structures, it is necessary to adhere to certain standards, which are stated in the documents: SNiP 52−01 2003 (rules that apply to structures made of concrete and reinforced concrete); SP 50−101 2004 (on the construction of foundations); SP 25−101 2003 (foundation without the use of reinforcement), etc. The standards take into account soil characteristics, ecology, type of building being constructed and many other features. All construction organizations must comply with these requirements. Deviations according to SNiP should not exceed 20 mm.
Legislative framework of the Russian Federation
valid Editorial from 20.08.1985
detailed information
| Name of document | "CAR ROADS. SNiP 3.06.03-85" (approved by Decree of the USSR State Construction Committee dated 20.08.85 N 133) |
| Document type | decree, norms, rules |
| Receiving authority | gosstroy ussr |
| Document Number | SNIP 3.06.03-85 |
| Acceptance date | 01.01.1970 |
| Revision date | 20.08.1985 |
| Date of registration with the Ministry of Justice | 01.01.1970 |
| Status | valid |
| Publication |
|
| Navigator | Notes |
"CAR ROADS. SNiP 3.06.03-85" (approved by Decree of the USSR State Construction Committee dated 20.08.85 N 133)
CONSTRUCTION OF CRUCCHED STONE BASES AND COATINGS USING THE CAM METHOD
7.4. Work on the installation of crushed stone bases and coatings using the wedging method should be carried out in two stages:
distribution of the main fraction of crushed stone and its preliminary compaction (compression and inter-jamming);
distribution of propping crushed stone (splitting two or three times) with compaction of each fraction. For bases, one-time decluttering is allowed. When using crushed stone of sedimentary rocks with a strength grade of less than 600 when constructing foundations, the work can be performed in one stage.
Additional compaction, if necessary, should be carried out by regulating the movement of construction vehicles along the width of the base (covering).
7.5. At the first and second stages, the base is compacted with rollers on pneumatic tires weighing at least 16 tons with an air pressure in tires of 0.6 - 0.8 MPa, trailed vibrating rollers weighing at least 6 tons, lattice rollers weighing at least 15 tons, self-propelled smooth drum rollers weighing no less than less than 10 tons and combined ones weighing more than 16 tons. The total number of passes of static type rollers must be at least 30 (10 at the first stage and 20 at the second), combined types - at least 18 (6 and 12) and vibration type - at least 12 (4 and 8).
Foundations made of crushed stone of less than 600 strength grades and Pl2, Pl3 plasticity grades are compacted with rollers on pneumatic tires weighing no more than 16 tons in no less than 20 passes or with vibrating plates.
7.6. To reduce friction between the crushed stones and accelerate mutual jamming, rolling should be done by pouring water over the crushed stone (approximately 15 - 25 l/m2 when compacting slag crushed stone - 25 - 35 l/m2 at the first stage and 10 - 12 l/m2 for the proppant fraction).
7.7. At the second stage, the crushed stone layer should be separated by fractions of fine crushed stone with successively decreasing sizes.
When using hard-to-compact crushed stone, the crushed stone layer before distributing the proppant material should be treated with organic binding material at the rate of 2 - 3 l/m2.
The consumption of crushed stone proppant fractions should be taken according to the table. 6.
7.8. After compaction of the coating is completed, fine stones from igneous rocks of a strength grade of at least 800 (from sedimentary rocks - at least 600) should be distributed over its surface in an amount of 1 m3 per 100 m2 and compacted in approximately 4 - 6 passes of the roller.
After compaction of the slag layer from active and highly active slag is completed, and if the overlying layer is not immediately formed, it should be watered for 10 - 12 days at the rate of 2 - 2.5 l/m2.
Table 6
| Size of the main fraction of crushed stone, mm | Consumption of proppant fractions, m3, per 1000 m2 with their sizes, mm | ||
| 20 — 40 | 10 — 20 | 5 — 10 | |
| 40 — 70 | — | 15 | 10 |
| 70 — 120 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
Note. When constructing foundations from crushed stone of a fraction of 40 - 70 mm using the wedging method, it is allowed to use a disposable wedge with a mixture of crushed stone and sand-crushed stone fractions of 5 - 20, 0 - 20, 0 - 10 mm, and when using crushed stone of 70 - 120 mm, use fractions of 5 - 40 mm . The consumption of mixtures must comply with the total requirements of table. 6.
Installation and pouring of concrete footings
Under heavy loads, the soil can sag and collapse. To prevent compression and deformation of the soil and structure, prepare a base (sand, gravel or crushed stone, membrane, concrete). The installation of concrete footings for the foundation is selected responsibly , after carefully studying the area. On weak ground or in seismically hazardous regions, the foundation is strengthened with concrete.
Concrete base
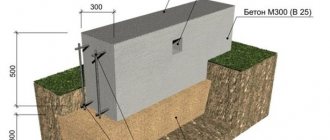
The concrete pad is the most reliable and expensive. Initially, a trench is dug according to the size of the future structure, rubbish and stones are leveled and removed. Soft soil should be compacted and sprinkled with crushed stone and sand. Cover the top with film. The concrete base should protrude 15 centimeters.
Then a thin solution of cement is mixed with gravel and sand, which are added gradually. After pouring, the mixture is leveled and covered with polyethylene so that the mixture dries gradually. You can use inexpensive concrete M 100 class B 3.5 - B 7.5.
For reliability and strength, the base is knitted with reinforcement before pouring the mortar. Its cross-section should be at least 8 mm, and the rods should protrude by 20 cm.
The thickness of the pillow is approximately 10 cm. After the solution has dried, it is treated with bitumen (roofing felt or film).
Advantages of footing:
- prevents moisture from rising to the foundation through the ground;
- levels the area;
- increases service life;
- concrete milk is not absorbed into the soil;
- protects reinforcement from corrosion and distortion;
- protects from excess moisture.
The concrete base promotes uniform distribution of loads and prevents soil shrinkage. Thanks to alignment, further work will be faster and more comfortable.
Crushed stone pillow
Pour crushed stone into the prepared pit, level it and be sure to compact it. You can use special vibrating ramming equipment. The layer should be at least 20 cm. It is better to choose gravel. It is durable and much cheaper than, for example, granite, which is better used when constructing buildings higher than one floor. This material is resistant to temperature changes and durable.
For waterproofing, you need to apply bitumen, which can be replaced with polyethylene. This base is suitable for outbuildings, bathhouses, and garages.
Economical sand preparation
It is best to lay a sand cushion in spring and autumn. It will protect from excess moisture. Pour 2 cm of sand into a small pit dug and compact it. Before use it is better to moisten the material to increase density. You can water the sand after laying it. The load on the foundation with such a base will be distributed evenly.
When choosing a sand-gravel mixture, you must give preference to one in which there is more crushed stone than sand. Such bedding will be fragile, but very economical and less labor-intensive. It is not suitable for serious, long-term objects (for example, high-rise buildings).
When using any material, it is important to first determine the highest point that groundwater reaches. To simplify further work, it is necessary to make holes for communications in advance before the concrete has cooled. It is not necessary to have a construction education to build an object yourself. It is important to have a competent mentor and assistant.
A properly made foundation will ensure a long service life of the facility and protect it from cracks under excessive loads of the structure. If the soil is hard, level, there are no slopes, and the future structure will be small, then it is not necessary to use concrete footing.
Why do you need a pillow under the foundation?
A crushed stone pillow performs several tasks:
- evenly redistributes the load from the foundation;
- significantly reduces point pressure on the ground;
- helps to level the bottom of the pit;
- significantly reduces the likelihood of soil shrinkage;
- protects the foundation from groundwater.
Crushed stone is a product of crushing natural materials. Depending on the original breed, it comes in several types:
- Limestone. It has the lowest strength, but is also relatively inexpensive and shows good frost resistance.
- Crushed gravel. It has high strength and is most often used in construction.
- Granite crushed stone. It is used in the construction of massive buildings, the production of reinforced concrete blocks, and is characterized by increased strength characteristics.
Also pay attention to the crushed stone fraction; most often, grain sizes of 20–40 mm are used.
Preparation device (work stages)
First you need to clear the soil surface and make a pit. Proper preparation of the depression involves a number of works aimed at bringing the soil to the desired state. In other words, the soil must withstand the heavy loads specified in the project. It is necessary that after the foundation is laid, the soil tightly grips the foundation from below. First, you should form a pit, clean its bottom with a bulldozer, and then thoroughly compact the base. In addition, during compaction of the pit, the soil should be moistened or dried. Most often, trenches are dug by hand. In addition, builders visualize the surface of the base itself and set the corners of the walls using pegs. After the pit is dug, specialists begin the following stages of construction:
- marking the construction site for the foundation;
- leveling the area;
- preparing the required amount of crushed stone (layer - ten centimeters);
- compacting the pillow using a vibration device;
- installation of formwork (its height depends on the layer of concrete mixture layer;
- pouring mortar to the top of the formwork;
- reinforcement of the pillow (cross-section of the rods - at least eight millimeters);
- compacting the cement mixture with a vibrating plate;
- installation of a reinforcement cage that allows you to fasten the crushed stone cushion to the base (they should protrude above the poured concrete by about twenty to thirty centimeters).
You can install a reinforced frame in concrete, but you can do without this material. In practice, the two options have almost no differences. The only difference is that a pillow created without reinforcement is limited in size.
MEMBRANE INSTEAD OF CONCRETE
The most modern and economical way to prepare the base for a foundation is to use profiled geomembranes. This is a rolled polymer material used in construction for waterproofing, drainage, and also for preparing foundation bases. The membrane is laid on a leveled and compacted base. The reinforcement is placed on top of the membrane. Pouring the slab can begin immediately after laying out the membrane and the reinforcing frame on top of it.
Read: Screw piles
The use of membranes instead of concrete preparation can significantly speed up the production of the foundation due to the time required for hardening of lean concrete. The membrane provides additional protection for the foundation slab from rising ground moisture, and also effectively prevents the loss of cement laitance when laying the concrete mixture.
Haha
Like
Wow
Satisfied
Sadness
I'm angry
What is a footing for a foundation slab?
Footing: simplest and capital. Purpose and methods of the device
In fact, it is very simple to understand what a footing is. Here even the name speaks for itself - this is a layer of thin concrete, which is prepared for comfortable and economical pouring of the main volume of the mixture. In fact, this layer is placed under the main layer of concrete when constructing slab foundations, for example.
But why exactly this needs to be done (and whether it is necessary at all) is worth understanding in detail. In addition, it will be useful to consider what the installation instructions for such a base are.
Photo of the simplest concrete substrate
Let's start with the most important thing.
Purpose of the footing
Pouring the solution onto a pre-prepared base
It is worth noting that the preparatory layer can be made in different ways and different materials can be used. However, the meaning and purpose of this work remains the same (