Driven reinforced concrete piles (S, SK, SP, SO, SD, STs)
What are the types of driven piles?
What determines the grade of concrete for the production of driven piles in terms of water resistance and water resistance?
How are driven piles marked? How are the symbols for marking driven piles deciphered?
What reinforcement is used for the production of driven piles?
Rules for applying markings to reinforced concrete driven piles. What indicators should be contained in the title blocks?
How to properly store and transport driven reinforced concrete piles?
What are the types of driven piles?
Answer: According to GOST 19804-91, driven piles are divided into the following types:
C – reinforced concrete driven piles of square continuous cross-section, solid and composite, with transverse reinforcement;
SK – reinforced concrete driven piles of round section 400 - 800 mm, solid and composite;
SP – reinforced concrete driven piles of square section with a round cavity, solid;
SO - reinforced concrete shell piles with diameters of 1000 - 3000 mm, solid and composite;
1SD - reinforced concrete column piles of square solid section, double-cantilever, located along the extreme axes of the building;
2SD – reinforced concrete column piles located along the middle axes of the building;
SC – driven reinforced concrete piles of square solid cross-section, solid, without transverse reinforcement of the shaft, with prestressed reinforcement in the center of the pile.
What determines the grade of concrete for the production of driven piles in terms of water resistance and water resistance?
Answer: The grade of concrete from which driven piles are made, according to the requirements
GOST 19804-91 depends on the construction area, the values of the design temperatures of the outside air and the operating mode. At the same time, driven piles are made from heavy concrete with a compressive strength class of at least B15 and a frost resistance grade of at least F150. The grade of concrete for water resistance is W2 to W6, depending on operating conditions.
How are driven piles marked? How are the symbols for marking driven piles deciphered?
Answer: Driven reinforced concrete piles are marked in accordance with GOST 23009. The brand of a driven pile consists of several alphanumeric groups separated by hyphens:
The first group - indicates the type of pile and geometric dimensions in decimeters; for double-cantilever type piles, the size of the pile from top to console is additionally indicated;
The second group is the serial number of the reinforcement option for a pile with non-prestressing reinforcement and the class of prestressing reinforcing steel for a prestressed pile;
The third group is additional characteristics of driven piles, for example, for composite piles - the type of joint (b - bolted joint, c - glass joint, welded joint), for CO type piles - the presence of a tip (denoted by the letter “n”).
Example of a symbol:
С60.30-AV – solid square pile of type C, length 600 mm, cross-sectional size 300 mm with prestressed reinforcing steel class AV:
| Name | Length, mm | Cross section | Sketch |
| С60.30-AV | 6000 | 300 |
What reinforcement is used for the production of driven piles?
Answer: For reinforcement of driven piles the following is used:
as prestressed longitudinal reinforcement - thermally and mechanically strengthened rods of classes At-V, At-VSK, At-IV, At-IVS and AT-IVK, hot-rolled rods of classes A-V and A-IV, reinforcing ropes of class K-7, high-strength wire of periodic profile of class BP-II;
as non-prestressed longitudinal reinforcement - hot-rolled rod of periodic profile of classes A-III A-II and Ac-II; thermomechanically strengthened classes At-IIIC and At-IVC;
as structural reinforcement - hot-rolled smooth wire of class A-I; ordinary wire of periodic profile of class BP-I.
Rules for applying markings to reinforced concrete driven piles. What indicators should be contained in the title blocks?
Answer: Markings must comply with the requirements of GOST 13015.2. Markings are applied to the side surface of reinforced concrete products. Markings are divided into basic, informational and installation.
According to GOST, main inscriptions must contain:
- brand of reinforced concrete structure;
- name of the manufacturer or registered trademark of the manufacturer;
- technical control stamp.
Information inscriptions on driven piles must contain:
- date of manufacture of the product;
- weight of the structure.
Installation signs consist of images indicating:
- place for slinging a reinforced concrete structure;
- top of the structure;
- place of support of the structure;
- installation risks on the structure
How to properly store and transport driven reinforced concrete piles?
Answer: Storage and transportation of driven reinforced concrete piles must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 13015.4. piles should be laid in horizontal rows with the same end orientation. Between horizontal rows in stacks, wooden spacers should be placed at the gripping points or nearby near the mounting loops. When storing round piles, special bars must be used to prevent rolling.
The height of the stack should not exceed its width by more than twice.
Loading and unloading of piles should be carried out using lifting loops or using special gripping mechanisms in places marked with installation signs.
sv777.ru
TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
1.1. Piles should be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard, technological documentation approved by the manufacturer, according to working drawings of the series 1.011.1-9, 1.011.1-10, UD-40-88, 3.500.1-1, 3.501.1 and GOST 19804.2 -GOST 19804.7.
It is allowed to manufacture piles that differ in types and sizes from those given in this standard, according to technical specifications and working drawings agreed upon with the Fundamentproekt Institute and approved in the prescribed manner.
1.2.
Main parameters and dimensions
1.2.1. Piles are divided into the following types:
C - square solid section, solid and composite, with transverse reinforcement of the trunk;
SP - square section with a round cavity, solid;
SK - hollow round section with diameters 400 - 800 mm, solid and composite;
SO - shell piles with diameters of 1000 - 3000 mm, solid and composite;
1SD - column piles of square solid section, double-cantilever, located along the extreme axes of the building;
2SD - the same, located along the middle axes of the building;
SC - square solid section; solid, without transverse reinforcement of the shaft, with prestressed reinforcement in the center of the pile.
1.2.2. The shape and main dimensions of the piles must correspond to those indicated in the table. 1.
Table 1
| Pile type and characteristics | Pile sketch | Main dimensions of the pile, mm | Designation of a standard or series of working drawings | |
| b or | l | |||
| Type C Solid with tension-free reinforcement | 200 | 3000 — 6000 | Series 1.011.1-10, issue. 1; UD-40-88; 3.500.1-1 | |
| 250 | 4500 — 6000 | |||
| 300 | 3000 — 12000 | |||
| 350 | 4000 — 16000 | |||
| 400 | 4000 — 18000 | |||
| Type C Solid with prestressed reinforcement | 200 | 3000 — 6000 | GOST 19804.2 Series 3.500.1-1 | |
| 250 | 4500 — 6000 | |||
| 300 | 3000 — 15000 | |||
| 350 | 8000 — 20000 | |||
| 400 | 13000 — 20000 | |||
| Type C Composite with non-prestressing reinforcement | 300 | 14000 — 24000 | Series 1.011.1-10, issue. 8 | |
| 350 | 14000 — 28000 | |||
| 400 | ||||
| Type C Composite with prestressed reinforcement | 300 | 14000 — 20000 | Series 1.011.1-9 | |
| 350 | 14000 — 24000 | |||
| 400 | 14000 — 28000 | |||
| SP type Solid with non-tensioned and prestressed reinforcement | 300 | 3000 — 12000 | GOST 19804.3 | |
| 400 | ||||
| Type SK Solid with tension-free reinforcement | 400 500 | 4000 — 18000 | GOST 19804.5 Series 3.501.1 | |
| 600 | ||||
| 800 | 4000 — 12000 | |||
| CO type Solid with tension-free reinforcement | 1000 | 6000 — 12000 | ||
| 1200 | ||||
| 1500 | ||||
| 1600 | ||||
| 3000 | ||||
| Type SK Composite with non-prestressing reinforcement | 400 | 14000 — 26000 | GOST 19804.6 Series 3.501.1 | |
| 500 | 14000 — 30000 | |||
| 600 | 14000 — 40000 | |||
| 800 | 14000 — 48000 | |||
| CO type Composite with non-prestressing reinforcement | 1000 | 14000 — 48000 | ||
| 1200 | ||||
| 1500 | ||||
| 1600 | ||||
| 3000 | ||||
| Type 1SD | 200 | 5000 — 6000 | GOST 19804.7 | |
| 300 | 5000 — 7500 | |||
| Type 2SD | 300 | 5000 — 7500 | ||
| SC type | 250 | 5000 — 6000 | GOST 19804.4 | |
| 300 | 3000 — 9000 | |||
Notes:
1. Piles of types SK and SO are made with and without a tip.
2. It is allowed to produce solid piles of type C without a tip. In this case, the area of application of piles according to soil conditions must correspond to the area of application of SP type piles.
3. Piles of square solid cross-section may be manufactured with a technological slope of two opposite faces of no more than 1:15 without changing the cross-sectional area. In this case, piles with a length of more than 12,000 mm should be made only in split forms.
1.2.3. The consumption rates of concrete and steel for piles must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings for these piles.
1.2.4. Concrete grades for frost resistance and water resistance of piles, depending on the mode of their operation and the values of the design temperatures of the outside air in the construction area, should be assigned in the working drawings of a particular building or structure in accordance with the instructions of the application.
1.2.5. Piles are designated by marks in accordance with the requirements of GOST 23009. The mark of a pile consists of alphanumeric groups separated by hyphens.
In the first group, indicate the designation of the type of pile, its length in decimeters and the size of the side (diameter) of the cross section in centimeters; for a pile of type SD, after the length, additionally indicate the size from the top of the pile to its console in decimeters.
In the second group they indicate: for a prestressed pile - the class of prestressing reinforcing steel; for a pile with non-prestressing reinforcement - the serial number of the reinforcement option in accordance with the working drawings.
The third group indicates:
- for piles of type SK or SO - the presence of a tip, indicated by the lowercase letter “n”;
- for a composite pile - the type of joint, denoted in lowercase letters: b - bolted joint, sv - welded joint, c - glass joint;
— for piles of all types (if necessary) — additional characteristics reflecting special application conditions or design features.
An example of a symbol (brand) of a type C pile with a length of 6000 mm, a cross-sectional size of 350 mm, with prestressed reinforcing steel of class AV:
C60
.
35
-
AV
Same, type CO, length 14000 mm, diameter 1000 mm, third reinforcement option, with bolted joints:
CO140
.
100
-
3
-
b
The same, type 1SD, length 7500 mm, size from the top of the pile to its console 3500 mm, cross-sectional size 300 mm, fourth reinforcement option:
1SD75
.
35
.
30
—
4
Note. It is allowed to accept the designations of pile brands in accordance with the working drawings for these piles until they are revised.
1.3. Characteristics
1.3.1. Piles must meet the requirements of GOST 13015.0:
- according to the actual strength of concrete: at design age, transfer and tempering (clauses 7.2, 7.4 - 7.7);
— on frost resistance and water resistance of concrete (clause 7.8);
— to steel grades for reinforcing and embedded products, including for mounting loops (clauses 8.5, 8.6);
— on corrosion protection (clauses 7.15, 8.7).
The piles must meet the crack resistance requirements established during the design and withstand the control tests specified in the working drawings for these piles.
1.3.2. Piles should be made of heavy concrete in accordance with GOST 26633 classes of compressive strength specified in the working drawings for these piles.
When supporting piles on rocky and coarse soils, the concrete class for compressive strength should be taken at least B25, regardless of the length of the pile.
1.3.3. Fractionated crushed stone from natural stone or gravel should be used as a coarse aggregate for concrete piles, and the fraction size should not be more than 40 mm.
1.3.4. The transfer of compression forces to concrete (releasing reinforcement tension) in piles with prestressing reinforcement should be carried out after the concrete reaches the required transfer strength.
The normalized transfer strength of concrete must be at least 70% of the strength corresponding to the class of concrete in terms of compressive strength.
1.3.5. The normalized tempering strength of concrete piles must be equal to 100% of the concrete compressive strength class.
1.3.6. To reinforce piles, the following types and classes of reinforcing steel should be used:
- as prestressed longitudinal reinforcement - thermomechanically strengthened rod of classes At-V, At-VCK, At-IV, At-IVC and AT-IVK in accordance with GOST 10884, hot-rolled rod of classes AV and A-IV in accordance with GOST 5781;
— reinforcing ropes of class K-7 according to GOST 13840;
— high-strength periodic wire of class BP-II according to GOST 7348;
- as non-prestressed longitudinal reinforcement - hot-rolled bar of periodic profile of classes A-III, A-II and Ac-II according to GOST 5781, thermomechanically strengthened classes At-IIIC and At-IVC according to GOST 10884;
- as structural reinforcement (spirals, mesh, clamps) - ordinary periodic profile wire of class BP-I according to GOST 6727, hot-rolled smooth rod of class AI according to GOST 5781.
It is allowed to use reinforcing steel of class AI in accordance with GOST 5781 as non-prestressed longitudinal reinforcement.
1.3.7. The values of actual stress deviations in the prestressing reinforcement should not exceed the limits specified in the working drawings for these piles.
1.3.8. The shape and dimensions of reinforcement and embedded products and their position in piles must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings for these piles.
1.3.9. Welded reinforcement and embedded products must meet the requirements of GOST 10922 (with the accuracy class of piles and this standard.
Welded reinforcement and embedded products must meet the requirements of GOST 10922 (with the accuracy class of piles and this standard.
1.3.10. The values of actual deviations from the linear dimensions of reinforcing products and from the dimensions that determine the position of these products in piles should not exceed the limits specified in Table. .
table 2
In millimeters
| Name of geometric parameter | Maximum deviation |
| Piles with non-prestressing reinforcement | |
| Distance from the outermost transverse rod (spiral, mesh, clamp) to the end of the frame | ±10 |
| The pitch of the spiral, mesh, clamps at the pitch value: | |
| - up to 50 incl. | ±10 |
| - St. 50 to 100 incl. | ±15 |
| » 100 | ±25 |
| Piles with prestressed reinforcement | |
| Distance from the outer mesh (clamp, spiral turn) to the end of the pile | ±10 |
| The pitch of the spiral, grid clamps at the pitch value: | |
| - up to 50 incl. | ±10 |
| - St. 50 to 100 incl. | ±25 |
| » 100 | ±50 |
1.3.11. The values of actual deviations of the geometric parameters of piles should not exceed the limits specified in the table. .
Table 3
In millimeters
| Name of deviation of the geometric parameter of the pile | Name of the geometric parameter of the pile | Maximum deviation |
| Deviation from linear size | The length of the prismatic (cylindrical) part of the pile with non-prestressing reinforcement at the length of the pile: | |
| — up to 8000 incl. | ±25 | |
| - St. 8000 to 16000 incl. | ±30 | |
| » 16000 | ±40 | |
| The same, piles with prestressed reinforcement | ±50 | |
| Size (outer diameter) of the cross section of the pile: | ||
| - up to 250 incl. | +15; -6 | |
| - St. 250 to 500 incl. | +20; -8 | |
| » 500 » 1000 » | +25; -10 | |
| » 1000 » 1600 » | +30; -12 | |
| » 1600 » 2500 » | +40; -15 | |
| » 2500 | +50; -16 | |
| Pile wall thickness of types SP, SK and SO: | ||
| - up to 120 incl. | +10; -5 | |
| - St. 120 to 250 incl. | +25; -6 | |
| Point or tip length | ±30 | |
| The distance from the center of the point or tip to the side surface of the pile. | 15 | |
| The distance from the center of the lifting eye, pin, bushing and sling mark to the ends of the pile. | 50 | |
| Deviation from straightness of the profile of the side faces of the prismatic part of the shaft (guides of the cylindrical surface) of the pile along the entire length: | — | |
| — up to 8000 incl. | ±25 | |
| - St. 8000 to 16000 incl. | ±30 | |
| » 16000 | ±40 | |
| Deviation from perpendicularity of the end plane: | — | |
| - in the head there are piles and piles-shells | 0.015 pile cross-sectional size | |
| — in the junction area of a composite pile of solid square section | 0.01 cross-sectional dimensions of the pile | |
| — in the area of the junction of the composite pile-shell | 0.005 pile cross-sectional size |
1.3.12. Exposure of working and structural reinforcement is not allowed on the surface of the piles. The ends of the prestressing reinforcement after tension release must be cut flush with the end surface of the pile.
The values of actual deviations in the thickness of the protective layer of concrete up to the longitudinal reinforcement should not exceed the maximum, mm:
+15; -5 - in piles of solid square section with non-prestressing reinforcement;
+10; -5 - the same, in piles with prestressed reinforcement at the end sections;
+15, -5 - the same, in piles with prestressed reinforcement in the middle part;
±5 - in square piles with a round cavity and in shell piles at the end sections;
+10, -5 - the same, in the middle part.
1.3.13. Requirements for the quality of concrete surfaces and the appearance of piles (including the width of the opening of surface technological cracks) are in accordance with GOST 13015.0. In this case, the dimensions of cavities, local depressions on the concrete surface and concrete edges of pile ribs should not exceed, mm:
- diameter or largest size of the shell……………………………………… 20
— depth of the depression………………………………………………………………………………… 10
— depth of concrete ribs……………………………………………………………… 20
- the total length of the concrete edges per 1 m of the rib, with the exception of the open surface (leveled during the vibration process) of trapezoidal piles………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………. 100
- the total length of the concrete edges per 1 m of the edge of the open surface of trapezoidal piles is not regulated
The height of the beads on the end surface of the piles should not be more than 5 mm.
1.4.
Completeness
Composite piles are supplied to the consumer complete with connecting products specified in the standards or working drawings for the piles.
1.5.
Marking
Marking of piles is in accordance with GOST 13015.2. Markings and signs should be applied to the side surfaces of piles at a distance of 500 mm from the end or at the end of the piles.
characteristics, markings and weight, immersion, price
In modern construction, many types of reinforced concrete products are used. Slabs and beams, floors and columns, finished blocks and the columns themselves - this list can be stretched to a whole page.
But in this article we would like to talk about a specific type of reinforced concrete products - reinforced concrete supports. After all, the walls of most modern, multi-story buildings are supported by driven composite reinforced concrete piles. And other types of reinforced concrete piles do not go unnoticed by both developers and construction customers.
Therefore, in this article we will consider the range of such products, simultaneously touching on the topic of arranging the foundation using some types of reinforced concrete products.
Reinforced concrete pile: varieties of assortment
The following types of supports can be made from reinforced concrete:
- A monolithic driven pile without internal voids, driven without excavation. Moreover, monolithic reinforced concrete rods can be driven into the ground with a hammer, pressed with a press or a vibrating attachment.
- A shell-type hollow pile, immersed with soil excavation (into a pre-equipped well).
- A cast-in-place pile poured into formwork, immersed in a pre-drilled shaft.
Belonging to each type is reflected by the marking of reinforced concrete piles, but these types of supports, in turn, are divided into many varieties of standard assortments, which are worth talking about separately.
Monolithic driven-type piles are divided into the following types of assortment:
- Round, square, T-shaped, trapezoidal supports (according to the cross-sectional shape).
- Composite or entire piles (depending on the design features of the support)
- Pear-shaped, camouflage, pointed or blunt supports (according to the shape of the lower end).
Shell piles are divided into the following types of assortment:
- Supports with and without transverse reinforcement (according to reinforcement methods).
- Square with a round cavity and round with a similar support cavity (according to the cross-sectional shape).
- Whole or composite piles (according to design).
- Prismatic - expanding or tapering towards the bottom - or cylindrical - with smooth walls - supports (according to the shape of the longitudinal section).
Driven piles are divided into the following types of assortment:
- Printed solid type, without thickening of the support body.
- Stuffed with thickenings in the bottom part of the supports.
In short, the cross-sectional shapes, types of construction, dimensions and price of reinforced concrete piles can be different, as well as the scope of application of such supports. However, all piles are made from the same set of structural materials: steel type A1-A111 and concrete grades B7.5 - B22. Therefore, the characteristics of various units in the range of such products are almost identical. And then we will talk specifically about the general qualities of reinforced concrete supports.
Technical characteristics of reinforced concrete piles
Most of the characteristics of piles, as well as any other reinforced concrete structures, are determined by the grade of concrete used in the manufacture of the support.
That is, the higher the grade of concrete, the stronger the product. After all, the numbers in the marking of the mixture grade indicate the compressive strength (in MPa). Moreover, in the production of piles, concrete of class B7.5 (aka M100) and higher is used. Thus, the minimum compressive strength is determined by this type of mortar.
Frost resistance and moisture resistance of piles are determined according to the same principle. That is, these characteristics depend on the grade of concrete and are determined according to the relevant GOSTs. Moreover, the characteristics of frost resistance and moisture resistance are indicated in the product labeling, after the letters “F” and “W”, respectively. For example, for brand B7.5 these indicators are equal to at least 50 freeze-thaw cycles (F50) and a pressure of 2 MPa from the water column (W2).
Well, the weight of reinforced concrete piles is determined, first of all, by the dimensions of the support. And the larger the dimensions, the greater the mass of reinforced concrete products. In addition, the type of concrete also affects the weight of the product: after all, the density of heavy grades (2.5 tons/m3) is higher than that of ordinary concrete (1.8 tons/m3).
Advantages and disadvantages of reinforced concrete piles
The undeniable advantages of concrete and reinforced concrete piles of any type of assortment include the following characteristics of such products:
- Long period of operation. If the installation of the product took place without violations of technology, then the support will live for almost 100 years. Moreover, repairs of reinforced concrete piles (both major and planned) are not carried out at this time.
- High strength characteristics. A reinforced concrete support, pierced with threads of stressed or unstressed reinforcement, can withstand the weight of even multi-story buildings built from heavy panels.
- Stability of the structure. The concrete pile is immersed into the ground to a considerable depth, which allows it to rest on layers of soil with maximum bearing capacity. From this same feature, one more advantage can be derived - applicability to all types of soil.
- Possibility of mounting supports on difficult terrain. The foundation, or rather its piled part, can be assembled from supports of different lengths. Therefore, the steep slope of the site for such foundations is not a hindrance.
The disadvantages of piles made of reinforced concrete products include only a significant mass of such products. This characteristic complicates the process of installing and transporting piles.
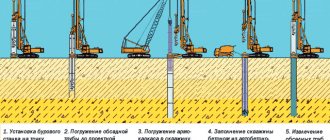
Technology for driving reinforced concrete piles
To immerse the support into the ground, a static or dynamic force must be applied to its head. Moreover, the static pressure coming from presses, vibrating hammers and other tools will be preferable to the dynamic impact load coming from a piledriver or other mechanical hammer.
Well, the specific technology that ensures the support is immersed in the ground is determined by whether the pile belongs to a specific type of assortment.
Driving of driven and shell piles
For example, driven and shell supports are driven into the ground under the action of a hammer, pressing or vibrating device. The force from the tool or apparatus is projected onto the head of the support, and the vertical position is controlled using guides or a hydraulic level.
This technology ensures maximum installation speed. However, an impact load can destroy the pile itself or part of it. In addition, impact technologies are also characterized by a high level of noise pollution. Therefore, driven piles are driven only in areas remote from residential areas and high-rise buildings.
Driving of cast-in-place and bored piles
Driven piles are installed in a pre-arranged hole. That is, at the very beginning you need to drill a shaft, and then a ready-made support or formwork is inserted into this shaft, which is filled with a reinforcing frame and concrete mortar.
This technology is used literally everywhere. It is not associated with the risk of high noise pollution and does not require the presence of heavy construction equipment (cranes, piledrivers, etc.) on the construction site. Therefore, cast-in-place and bored reinforced concrete piles can be installed even within the city.
An alternative option is to stuff it into an inventory tube with a pointed tip that is immersed (under the blows of a hammer or vibratory hammer). Or stuffing it into a hole dug in the ground by a special machine. This method of immersing driven supports is comparable in speed to the installation of driven structures.
However, this method of immersion has not only advantages, but also disadvantages of driving technologies (primarily a high level of noise pollution). Therefore, in the case of immersion of packed supports, a long, but still quiet, packing into the well is chosen.
www.bobrovka.ru
types, main characteristics, pros and cons of products
Reinforced concrete piles are special structures that are buried in the soil at the base of buildings or structures to increase the strength of the foundation. Reinforced concrete piles are the basis of any construction, so no structure can do without them. Their use can increase the strength and durability of a building under construction, regardless of climatic conditions and soil type.
Types of reinforced concrete piles
Reinforced concrete products are qualified according to various criteria. Designs can be completely different in shape, volume, type of design and scope of application.
Depending on the composition and labeling, the following are distinguished:
- Monolithic. They do not have a void inside and are installed using a sledgehammer. Such structures are divided into round, square, rectangular, cone-shaped, blunt-pointed, and they can also be composite or welded.
- Printed. The production of products takes place on the site of buildings under construction. They are immersed in a pre-prepared hole. Such reinforced concrete piles are divided into thickened and solid. The former do not have external seams and joints, the latter are a type of homogeneous product with a thickening of the lower part of the supports.
- Hollow.
Any type of product is used during construction. But when choosing structures, it is necessary to take into account the number of storeys of the building, as well as the type of soil and soil.
Particular preference, as a rule, is given to driven reinforced concrete piles, because they allow the construction of any buildings, regardless of the climatic location of the settlement.
Features of designs
The characteristics of a structure are directly related to the grade of concrete from which it is made. The higher the quality of the concrete, the stronger the products will be. This characteristic of the concrete used can be learned from the markings indicated in GOST.
When choosing structures, customers focus on the load they can withstand. As a rule, the average support for a typical support does not exceed sixty tons, so more products are needed to support heavier structures.
The materials used in the manufacture of the supports make them quite resistant to corrosion and can prevent deformation during operation. Reinforced concrete structures have a service life of 100 to 120 years.
Advantages and disadvantages of products
The scope of application of the foundation is quite wide. They are used in the construction of both residential and industrial premises. Due to the fact that the supports are quite strong, buildings of any complexity can be erected on them. But before using reinforced concrete products, you need to know their main advantages and disadvantages.
The main advantages of the designs include:
- Sustainability. When installed in the soil, a concrete foundation rests on it, using all its load-bearing capacity, thus the structure is able to withstand natural disasters.
- The shortest possible time for construction of objects.
- Availability. Purchasing supports is not difficult, regardless of your region of residence.
- Long period of use. If all requirements are met when installing a reinforced concrete pile, then such a support can last ninety years or more.
- Installation in difficult conditions. The structures are easily installed in frozen or very wet soil.
- Affordable price. Compared to the cost of other foundations, reinforced concrete piles are quite cheap and easy to use.
- High strength. Reinforced concrete structures can support multi-story and massive buildings.
In addition to advantages, like any product, reinforced concrete piles also have disadvantages.
But in the case of reinforced concrete piles, there are only two of them: massiveness and weight of the product. It is these disadvantages that complicate installation, because multi-ton structures can only be installed using a crane and a jackhammer, which leads to additional costs.
Additional equipment for installation
All equipment for installing piles can be divided into mounted and basic pile driving machines, equipped with attachments.
Technical means for diving include:
- Impact hammer. There are hydraulic and diesel. All impact hammers are classified as light (have an impact weight of up to two tons and immerse a concrete product weighing up to three tons), medium-heavy, which has a maximum impact weight of up to three tons, and heavy - more than three tons.
- Pillar masts. They fix and direct the movement of the concrete product during loading into the ground.
- Pile driving machines. Capable of loading concrete products independently.
When installing structures into the soil, you need various specialized equipment, from an impact hammer to a construction hammer. This technique is capable of installing reinforced concrete products in the shortest possible time.
twoidvor.com
Load-bearing capacity of a bored pile - table of soil characteristics
As can be seen from these formulas, much depends on soil resistance. Bored foundations are built on sedimentary rocks - sand, clay, etc. We present the resistance values for different breeds.
Base resistance:
- clays - from 24 tons per square meter (soft-plastic, highly porous) to 90 (hard, low-porous);
- loams – from 21 to 47;
- sandy loam – from 33 to 47;
- silty sands of medium density – from 20 (wet) to 30 (low moisture);
- dusty dense – 30-40;
- fine-grained - 25-30 and 37-45, respectively;
- average – 40 and 55;
- coarse-grained - 50 and 70;
- gravel – 45-75 (depending on the mineral composition);
- crushed stone with sand – 90.
Lateral resistance depends on the depth of the layer. For example, for clays at a depth of half a meter it varies from 2.8 (hard clays) to 3 (soft), and at a depth of 3 meters - 0.8-4.8.
Types of reinforced concrete piles and methods of marking them
In accordance with current GOSTs, each reinforced concrete pile is marked on the side, which must contain the following information:
- about the brand of reinforced concrete piles;
- about where the reinforced concrete structure was made;
- about the fact of passing technical control.
In addition, the driven piles indicate their weight and production date. Images on the pile should indicate where the structure is supported and slinged, where its top is located, as well as the main installation risks.
Main types of reinforced concrete piles
Determined in accordance with the letter designations on the design markings:
- Type C - driven reinforced concrete piles, which can be composite or solid, have a standard square cross-section, and are transversely reinforced.
- Type SK - driven reinforced concrete piles, which can be composite or solid, have a circular cross-section, the diameter of which ranges from 40 to 80 cm.
- Type SP - driven reinforced concrete piles, which can only be solid, are characterized by a square cross-section, inside of which there is a round cavity.
- Type SO - special reinforced concrete piles, which can be composite or solid, have a diameter ranging from 100 to 300 cm.
- Type 1 SD - special column-type reinforced concrete piles that have a solid square cross-section. They refer to double-cantilever structures, which are located along the extreme axes of the construction site.
- Type 2 SD - special column-type reinforced concrete piles placed along the middle axes of the construction site.
- Type SC - one-piece driven reinforced concrete piles that have a solid square cross-section. They do not assume the presence of a reinforced barrel.
Material for the production of driven reinforced concrete piles
In accordance with the requirements of GOST 19804-91, reinforced concrete piles must be selected for construction whose material characteristics correspond to the climatic conditions of the construction area. Most structures are made from heavy grades of concrete, which are characterized by:
- compressive strength from B15;
- high level of frost resistance - from F150 and above;
- sufficient water resistance indicators - at least W2 to W6.
The water resistance indicator depends on the conditions in which the driven structures are used.
Specifics of marking reinforced concrete piles
Design markings include letters, numbers, and icons. It is written with a hyphen.
The first group of markings indicates the geometric dimensions of the structure, as well as its type. The second contains data on the reinforcement of the structure, as well as the class of reinforcement used in production. The third contains information about additional design characteristics, types of joints, the presence or absence of a tip, etc.
Reinforcement in driven reinforced concrete piles
For durable driven structures, the following can be used:
- longitudinal prestressing reinforcement, which has additional heat treatment, additionally strengthened mechanically through the use of hot-rolled steel rods;
- longitudinal non-tensioned reinforcement;
- structural reinforcement.
December 04, 2017
asm-svai.ru
GOST 19804-2012 Prefabricated reinforced concrete piles….
Active
INTERSTATE STANDARD
FACTORY MANUFACTURED REINFORCED CONCRETE PILES
General technical conditions
Prefabricated reinforced concrete piles. Specifications
Date of introduction 2014-01-01
The goals, basic principles and basic procedure for carrying out work on interstate standardization are established by GOST 1.0-92 “Interstate standardization system. Basic provisions" and GOST 1.2-2009 "Interstate standardization system. Interstate standards, rules and recommendations for interstate standardization. Rules for the development, adoption, application, updating and oFundamentproject" (OJSC "Fundamentproject"), NIIOSP named after Gersevanov - OJSC "National Research Center Construction"
2 INTRODUCED by the Technical Committee for Standardization TC 465 “Construction”
3 ADOPTED by the Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission on Standardization, Technical Regulation and Conformity Assessment in Construction (Minutes dated December 18, 2012 N 41)
The following voted for adoption:
| Short name of the country according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 | PoMK country code (ISO 3166) 004-97 | Abbreviated name of the state construction management body |
| Armenia | A.M. | Ministry of Urban Development |
| Kyrgyzstan | KG | Gosstroy |
| Moldova | M.D. | Ministry of Construction and Regional Development |
| Russia | RU | Ministry of Regional Development |
| Tajikistan | T.J. | Construction agency |
| Uzbekistan | UZ | Gosarchitectstroy |
4 By Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated December 27, 2012 N 2014-st, the interstate standard GOST 19804-2012 was put into effect as a national standard of the Russian Federation on January 1, 2014.
5 INSTEAD GOST 19804-91, GOST 19804.2-79, GOST 19804.4-78, GOST 19804.5-83
1 area of use
1.1 This standard establishes general requirements for prefabricated reinforced concrete piles.
1.2 This standard is intended for the development of regulatory documents and technical documentation for specific types of products.
1.3 The scope of application of piles depending on the type of structure and soil conditions is given in Appendix A.
Weight, mass and dimensions of screw piles
The article will talk about the weight, mass and dimensions of screw piles with the most popular shaft diameters.
The content of the article:
1. Barrel diameter 57 mm
2. Barrel diameter 76 mm
3. Barrel diameter 89 mm
4. Barrel diameter 108 mm
5. Barrel diameter 133 mm
It is often necessary to determine how much a screw pile of a particular length and design weighs. For example, this may be required to choose the method of transporting them from the warehouse to the site.
The tables below take into account only the most popular diameters, lengths and metal thicknesses for screw piles. It is also necessary to understand that weight may vary depending on a number of additional parameters:
- open/closed (with rolled cone) type barrel;
- cast/welded tip;
- diameter, configuration and thickness of blades, etc.
More detailed information about all parameters of screw piles produced according to TU 25.11.23-004-20882284-2017, as well as the reasons for assigning each of them, can be found in the “Types of screw piles” section. The article “Classification of screw piles” will tell you what role each parameter plays, including in determining the scope of application of each structure.
Barrel diameter 57 mm
| Length, mm | Weight, kg | |||
| Broad-blade single-blade | Broad-bladed bilobed | |||
| Wall thickness, mm | ||||
| 3 | 3,5 | 3 | 3,5 | |
| 2 100 | 8,7 | 9,9 | 9,1 | 10,4 |
| 2 600 | 10,7 | 12,7 | 11,1 | 13,2 |
| 3 100 | 12,7 | 15 | 13,1 | 15,5 |
| 3 600 | 14,7 | 17,3 | 15,1 | 17,8 |
| 4 100 | 16,7 | 19,6 | 17,1 | 20,1 |
| 4 600 | 18,7 | 21,9 | 19,1 | 22,4 |
Barrel diameter 76 mm
| Length, mm | Weight, kg | |||||
| Broad-blade single-blade | Broad-bladed bilobed | Narrow-bladed with a cone-shaped tip | ||||
| Wall thickness, mm | ||||||
| 3 | 3,5 | 3 | 3,5 | 3 | 3,5 | |
| 2 100 | 12,1 | 13,8 | 16,2 | 18,0 | 11,2 | 13,0 |
| 2 600 | 14,8 | 17,6 | 18,9 | 21,7 | 13,9 | 16,7 |
| 3 100 | 17,5 | 20,7 | 21,6 | 24,9 | 16,6 | 19,8 |
| 3 600 | 20,2 | 23,8 | 24,3 | 28,0 | 19,3 | 23,0 |
| 4 100 | 22,9 | 27,0 | 27,0 | 31,1 | 22,0 | 26,1 |
| 4 600 | 25,6 | 30,1 | 29,7 | 34,2 | 24,7 | 29,2 |
| 5 100 | 28,3 | 33,2 | 32,4 | 37,4 | 27,4 | 32,4 |
Barrel diameter 89 mm
| Length, mm | Weight, kg | |||||
| Broad-blade single-blade | Broad-bladed bilobed | Narrow-bladed with a cone-shaped tip | ||||
| Wall thickness, mm | ||||||
| 3 | 3,5 | 3 | 3,5 | 3 | 3,5 | |
| 2 600 | 19,0 | 22,2 | 21,2 | 24,5 | 16,4 | 19,7 |
| 3 100 | 22,1 | 25,9 | 24,4 | 28,2 | 19,6 | 23,4 |
| 3 600 | 25,3 | 29,6 | 27,6 | 31,9 | 22,8 | 27,1 |
| 4 100 | 28,5 | 33,3 | 30,8 | 35,6 | 26,0 | 30,8 |
| 4 600 | 31,7 | 37,0 | 33,9 | 39,3 | 29,1 | 34,5 |
| 5 100 | 34,9 | 40,7 | 37,1 | 43,0 | 32,3 | 38,2 |
| 5 600 | 38,0 | 44,4 | 40,3 | 46,6 | 35,5 | 41,8 |
Barrel diameter 108 mm
| Length, mm | Weight, kg | |||||
| Broad-blade single-blade | Broad-bladed bilobed | Narrow-bladed with a cone-shaped tip | ||||
| Wall thickness, mm | ||||||
| 3,5 | 4,0 | 3,5 | 4,0 | 3,5 | 4,0 | |
| 2 600 | 26,8 | 30,9 | 33,1 | 37,2 | 23,9 | 28,0 |
| 3 100 | 31,3 | 36,1 | 37,6 | 42,4 | 28,4 | 33,1 |
| 3 600 | 35,8 | 41,2 | 42,1 | 47,5 | 32,9 | 38,2 |
| 4 100 | 40,3 | 46,3 | 46,6 | 52,6 | 37,4 | 43,4 |
| 4 600 | 44,8 | 51,5 | 51,2 | 57,8 | 41,9 | 48,5 |
| 5 100 | 49,4 | 56,6 | 55,7 | 62,9 | 46,4 | 53,6 |
| 5 600 | 53,9 | 61,7 | 60,2 | 68,0 | 50,9 | 58,8 |
| 6 100 | 58,4 | 66,8 | 64,7 | 73,1 | 55,4 | 63,9 |
Barrel diameter 133 mm
| Length, mm | Weight, kg | |||||
| Broad-blade single-blade | Broad-bladed bilobed | Narrow-bladed with a cone-shaped tip | ||||
| Wall thickness, mm | ||||||
| 4,0 | 4,5 | 4,0 | 4,5 | 4,0 | 4,5 | |
| 3 100 | 44,4 | 53,1 | 55,6 | 64,2 | 32,9 | 41,5 |
| 3 600 | 49,6 | 59,4 | 60,7 | 70,6 | 38,0 | 47,9 |
| 4 100 | 54,7 | 65,8 | 65,8 | 77,0 | 43,1 | 54,2 |
| 4 600 | 59,8 | 72,2 | 71,0 | 83,3 | 48,3 | 60,6 |
| 5 100 | 65,0 | 78,5 | 76,1 | 89,7 | 53,4 | 67,0 |
| 5 600 | 70,1 | 84,9 | 81,2 | 96,0 | 58,5 | 73,3 |
| 6 100 | 75,2 | 91,2 | 86,4 | 102,4 | 63,6 | 79,7 |
| 6 600 | 80,3 | 97,6 | 91,5 | 108,8 | 68,8 | 86,0 |
| 7 100 | 85,5 | 104,0 | 96,6 | 115,1 | 73,9 | 92,4 |
Information on the weight of screw piles with shaft diameters of 159, 168, 219, 273 and 325 mm is available on request.