Preface
The goals, basic principles and basic procedure for carrying out work on interstate standardization are established in GOST 1.0-2015 “Interstate standardization system.
Basic provisions” and GOST 1.2-2015 “Interstate standardization system. Interstate standards, rules and recommendations for interstate standardization. Rules for development, adoption, updating and cancellation"Information about the standard 1 DEVELOPED by the Joint Stock Company "TSNIIEP Dwellings - Institute of Integrated Design of Residential and Public Buildings" (JSC "TSNIIEP Dwellings")
2 INTRODUCED by the Technical Committee for Standardization TC 465 “Construction”
| Short name of the country according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 | Country code according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 | Abbreviated name of the national standardization body |
| Armenia | A.M. | Ministry of Economy of the Republic of Armenia |
| Kyrgyzstan | KG | Kyrgyzstandard |
| Russia | RU | Rosstandart |
4 By Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated November 11, 2020 N 1681-st, the interstate standard GOST 8717-2016 was put into effect as a national standard of the Russian Federation on May 1, 2020.
5 INSTEAD GOST 8717.0-84, GOST 8717.1-84
General concept of design
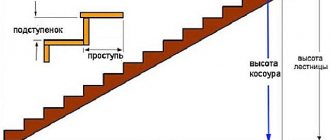
Arrangement of stairs on a stringer.
- width - 110, 120 and 140 cm;
- net tread depth - 280, 290, 300 and 310 mm;
- step height - 14, 15, 16 and 17 cm.
Elements can be cast from concrete in the form of solid blocks, but such products are too heavy. More often, reinforced concrete steps with a void inside (hollow) are used; their weight does not exceed 80 kg, making manual installation of this part of the structure possible. There are 2 types of product shape:
- Regular. From the end they look like a rectangle with slightly inclined sides.
- Frieze. They have a cutout in the lower part for docking with the support platform. On 1 flight there are 2 such steps - at the top and at the bottom.
When constructing a staircase on metal stringers with frieze steps, it is possible to reduce the thickness of the monolithic platform slab to 10 cm, thereby reducing its weight and cost. In such a march, the upper and lower steps partially extend onto the landings due to special cutouts. If the entire flight of stairs is made from ordinary steps, then the thickness of the landing should be equal to their height, at least 14 cm. Otherwise, thresholds will form above and below, which is unacceptable.
Dimensions of a flight of stairs.
The beams for stairs on metal stringers are steel channels or I-beams. They are selected by cross-section and size depending on the length of the flight, as well as the magnitude of the static and dynamic load. The static load is the total weight of the structure, including the beams themselves, and the dynamic load is the deflection from the impact of passing people and carrying things and furniture.
The strength and reliability of stairs are calculated with a large margin.
The installation of reinforced concrete stairs on metal stringers consists of 3 stages:
- installation of metal structures;
- installation of monolithic platforms;
- laying steps with fastening by welding.
Prefabricated concrete staircase on channel stringers
The design of prefabricated reinforced concrete stairs mainly consists of stacked reinforced concrete steps laid on metal stringers made of channels or I-beams.
This type of construction is the most reliable and durable compared to wood. Prefabricated concrete stairs can be installed both indoors and outdoors. A concrete staircase using beautiful high-quality finishing materials can decorate the interior of both private and public buildings. Prefabricated concrete staircases on metal stringers are made on site at the construction site. Stringers are welded to the platform beams or connected using bolts. The landings on this type of stairs are made of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs or a monolithic slab resting on a landing beam is poured.
The steps are mounted on stringers, the seams are filled with cement-sand mortar. In public buildings, metal stringers are painted or treated with some kind of fire-retardant material and then finished with plasterboard. Prefabricated concrete stairs are assembled from reinforced concrete steps, which can be triangular, rectangular or in the shape of a right angle, the stairs are finished with natural stone or ceramic tiles.
When lining stairs used outdoors in winter, it is worth providing treads with corrugated tiles to prevent people from falling. There is a fairly wide selection of this type of tile on sale. Also nowadays, treads with electric heating are produced for external stairs, preventing the formation of ice.
Prices for installation of prefabricated concrete steps on steel stringers
TERM-38-01-002-01Manufacture of beams and stringers. MONORAILS, BEAMS AND OTHER SIMILAR STRUCTURES OF INDUSTRIAL BUILDINGS, ASSEMBLY USING A CRANE ON A VEHICLE WALKER = 66% (HP = 228 rub.) SP = 65% (SP = 225 rub.)
TER- 09- 03- 002- 12UK TER IZD.3 TB7 P7 Kozp=1.15 Cam=1.15 OP P1.9.16; APPENDIX 9.3 P2 Kozp = 1.1 INSTALLATION OF BEAMS, COVERING BEAMS, COVERINGS AND FOR INSTALLATION OF EQUIPMENT OF MULTISTORY BUILDINGS WITH BUILDING HEIGHTS UP TO 25 M (ON THE TERRITORIES OF OPERATING ENTERPRISES WITH AN EXTENSIVE NETWORK OF TRANSPORT AND ENGINEERING COMMERCIALS MUNICATIONS AND CRIMEST CONDITIONS FOR STORAGE OF MATERIALS) - ON REINFORCED CONCRETE AND STONE SUPPORTKem = 1.3 Kzpm = 1.3 (Adjustment for market value) HP = 90% (NR = 383 rub.) SP = 85% (SP = 362 rub.)
TER- 13- 03- 002- 04OP P1.13.7 Kozp = 1.1 PRIMER OF METAL SURFACES AT ONE TIME WITH GF-021 PRIMER (MANUALLY) NR = 90% (NR = 32 rub.) SP = 70% (SP = 25 rub. .)
TER- 07- 05- 015- 01UK TER IZD.3 TB7 P7 Kozp = 1.15 Kam = 1.15 CONSTRUCTION OF STAIRS ON A READY BASE FROM INDIVIDUAL SMOOTH STEPS (ON THE TERRITORIES OF OPERATING ENTERPRISES WITH AN EXTENSIVE NETWORK OF TRANS SPORTS AND ENGINEERING COMMUNICATIONS AND CONSTRAINT CONDITIONS FOR STORAGE OF MATERIALS) Kem = 1.3 Kzpm = 1.3 (Adjustment for market value) HP = 155% (NR = 3351 rub.) SP = 100% (SP = 2162 rub.) 1.53
100M STEPS 01- 403- 1261 ConstructionPrice, May 2014 STAIR STEPS LS 15- 1 / CONCRETE B15 (M200), VOLUME 0.066 M3, ARRA CONSUMPTION 1.59 KG/ (SERIES 1.050.9- 4.93)102
I. SCOPE OF APPLICATION
This standard establishes the types, main parameters and dimensions of reinforced concrete steps, general technical requirements for them, step designs, reinforcement and embedded products for them. This standard applies to reinforced concrete, concrete steps made of heavy and dense silicate concrete and intended for the installation of internal and external stairs of buildings and structures.
Concrete steps are designed for constructing stairs on a solid base. The steps are used: - for heated buildings and structures; - for unheated buildings and structures and in the open air at the design temperature of the outside air (the average temperature of the coldest five-day period of the construction area according to regulatory documents * and technical documentation) up to minus 40 ° C inclusive;
_______________* In the Russian Federation, SP 131.13330.2012 “SNiP 23-01-99* Construction Climatology” (with amendment N 2) is in force. - with a non-aggressive degree of environmental influence on reinforced concrete structures. It is allowed to use steps in buildings and structures with a calculated seismicity of up to 9 points inclusive, in unheated buildings and structures and in the open air at a design outdoor temperature below minus 40°C, as well as under conditions of exposure to an aggressive environment, subject to additional requirements established by regulatory documents** and technical documentation and specified in the order for the manufacture of steps .
_______________** In the Russian Federation, SP 14.13330.2014 “SNiP II-7-81* Construction in seismic areas” (with amendment N 1), SP 63.13330.2012 “SNiP 52-01-2003 Concrete and reinforced concrete structures” are in force. Basic provisions” (as amended No. 2), SP 28.13330.2012 “SNiP 2.03.11-85 Protection of building structures from corrosion” (as amended No. 1), SP 95.13330.2011 “SNiP 2.03.
1.1. A standard technological map (hereinafter referred to as TTK) is a complex organizational and technological document developed on the basis of methods of scientific organization of labor for performing a technological process and defining the composition of production operations using the most modern means of mechanization and methods of performing work using a specific technology.
TTK is intended for use in the development of Work Performance Projects (WPP) and other organizational and technological documentation by construction departments. The TTK is an integral part of the Work Performance Projects (hereinafter referred to as the WPR) and is used as part of the WPR in accordance with MDS 12-81.2007.1.2.
This TTK provides instructions on the organization and technology of production of work on the installation of stairs from prefabricated reinforced concrete steps laid on steel stringers. The composition of production operations, requirements for quality control and acceptance of work, planned labor intensity of work, labor, production and material resources, measures for industrial safety and labor protection.1.3.
The regulatory basis for the development of a technological map is: - working drawings; - construction codes and regulations (SNiP, SN, SP); - factory instructions and technical conditions (TU); - standards and prices for construction and installation work (GESN-2001, ENiR , VNiR, TniR); - production standards for material consumption (NPRM);
– cost reduction; – reduction of construction duration; – ensuring the safety of work performed; – organizing rhythmic work; – rational use of labor resources and machines; – unification of technological solutions. 1.5. On the basis of the TTK, as part of the PPR (as mandatory components of the Work Project), Working Technological Maps (RTC) are being developed for the implementation of certain types of construction and installation work for the installation of stairs from prefabricated reinforced concrete steps laid on steel stringers.
The RTK regulates the means of technological support and the rules for performing technological processes during the execution of work. The design features of their implementation are decided in each specific case by the Working Design. The composition and degree of detail of materials developed in the RTK are established by the relevant contracting construction organization, based on the specifics and volume of work performed.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the cladding of semicircular steps
The RTCs are reviewed and approved as part of the PPR by the head of the General Contracting Construction Organization.1.6. The TTK can be tied to a specific facility and construction conditions. This process consists of clarifying the scope of work, means of mechanization, and the need for labor, material and technical resources.
The procedure for linking the TTK to local conditions: - consideration of map materials and selection of the desired option; - verification of the compliance of the initial data (amount of work, time standards, brands and types of mechanisms, building materials used, composition of workers) with the accepted option; - adjustment of the volume of work in accordance with the selected option for carrying out work and a specific design solution;
- recalculation of calculations, technical and economic indicators, the need for machines, mechanisms, tools and material and technical resources in relation to the chosen option; - design of the graphic part with a specific link to mechanisms, equipment and devices in accordance with their actual dimensions. 1.7.
A standard flow chart has been developed for engineering and technical workers (work managers, foremen, foremen) and workers performing work in the third temperature zone, in order to familiarize (train) them with the rules for carrying out construction and installation work on the installation of stairs from prefabricated reinforced concrete steps , laid on steel stringers, using the most modern means of mechanization, progressive designs and methods of performing work. The technological map has been developed for the following volumes of work: - total horizontal projection area within one floor - S = 20.0 m.
II. GENERAL PROVISIONS
2.3. The sequentially performed construction and installation work on the installation of stairs from prefabricated reinforced concrete steps laid on steel stringers includes the following technological operations: - preparatory work (marking nests, installing scaffolding, a garbage container, a mast lift);
- punching nests and grooves in brick walls with marking and cleaning; - installation of metal stringers with fastening the stringer to the platform beams; - laying reinforced concrete steps of the first flight; - laying flat reinforced concrete slabs of the first platform on metal beams; - installation of metal stringers with fastening the stringer to platform beams;
We suggest you read: How to clean a pan from burnt porridge -
- laying reinforced concrete steps of the second flight; - laying flat reinforced concrete slabs of the second platform on metal beams; - installing metal railings; - installing handrails. 2.4. The technological map provides for the work to be carried out by a complex mechanized unit consisting of: Liebherr 63 LC tower crane (maximum boom radius = 45 m, lifting capacity Q = 5.0 t, lifting height = 39.1 m, load lifting/lowering speed = 54 m/min );
concrete mixer Al-Ko TOP 1402 GT (m=48 kg, loading volume V=90 l); mobile gasoline power station Honda ET12000 (3-phase 380/220 V, N=11 kW, m=150 kg); construction mast lift PMG-1B-76115 (lifting capacity Q=0.5 t, lifting height H=76 m, lifting speed V=0.31 m/sec); mobile compressor from Atlas Copco XAS 97 Dd (P=5.3 m/hour, =0.7 MPa, m=940 kg);
Fig.1. Tower crane Liebherr 63 LC
| Fig.2. Mast lift PMG-1B-76115 | Fig.3. Welding generator EP-200X2 |
| Fig.4. Atlas Copco compressor | Fig.5. Jackhammer MO-2K |
| Fig.6. Concrete mixer Al-Ko TOP 1402 GT | Fig.7. Honda ET12000 power station |
2.5. For the installation of stairs from prefabricated reinforced concrete elements, the following building materials are used: electrodes 4.0 mm E-42A, meeting the requirements of GOST 9466-75; cement-sand mortar that meets the requirements of GOST 28013-98; rolled I-beam steel that meets the requirements of GOST 8239-89;
Fig.8. Stair steps
2.6. Construction and installation work on the installation of stairs from prefabricated reinforced concrete steps laid on steel stringers should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of the following regulatory documents: - SP 48.13330.2011. "Organization of construction. Updated version of SNiP 12-01-2004”; - SNiP 3.03.01-87*.
“Load-bearing and enclosing structures”; - P2-2000 to SNiP 3.03.01-87. Concrete work on a construction site; - Manual for SNiP III-18-75. “Methods for monitoring welded joints of metal structures and pipelines performed in construction”; - SP 52-101-2003 “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures without prestressing reinforcement”; - SP 63.13330.
2012 “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures. Basic provisions. Updated version of SNiP 52-01-2003”; - STO NOSTROY 2.33.120-2013. “Organization of construction production. Major repairs of apartment buildings without evicting residents. Work rules. Acceptance rules and control methods”;
– STO NOSTROY 2.10.64-2012. “Welding work. Rules and control of installation, requirements for work results”; - GOST 8717.0-84. “The steps are reinforced concrete and concrete. Technical conditions”; - GOST 23120-78. “Steel staircases, landings and fencing. Technical conditions”; - GOST 28013-98. “Construction solutions.
General technical conditions”; - GOST 9467-75*. “Electrodes coated with metal for manual arc welding of structural and heat-resistant steels”; - GOST 24258-88. “Means of scaffolding. General technical conditions”; - SNiP 12-03-2001. “Labor safety in construction. Part 1. General requirements”;
– SNiP 12-04-2002. “Labor safety in construction. Part 2. Construction production”; - GOST 12.3.009-76*. SSBT. “Loading and unloading work. General safety requirements”; - GOST 12.3.020-80*. SSBT. “Processes of cargo movement at enterprises. General safety requirements”; - POT RM-007-98.
“Inter-industry rules for labor protection during loading and unloading operations and placement of goods”; - RD 11-02-2006. “Requirements for the composition and procedure for maintaining as-built documentation during construction, reconstruction, major repairs of capital construction projects and requirements for inspection reports of work, structures, sections of engineering support networks”;
– RD 11-05-2007. “The procedure for maintaining a general and (or) special log of work performed during construction, reconstruction, major repairs of capital construction projects”; - Collection of forms of executive production and technical documentation, approved by the order of Rosavtodor dated May 23, 2002 N IS-478-r; - MDS 12.-29.2006. “Methodological recommendations for the development and execution of a technological map.”
Steel beam installation work
Staircase without frieze steps.
- Rolled metal is cut to length and marked.
- In the designated places, corners with holes are welded to the beams, where bolts will be inserted when installing the stringers.
- The beam is installed horizontally, aligned and attached to the wall. The method of fastening is embedding into the wall, or more precisely, into a special opening made on each side.
To install each element in the design position, lifting mechanisms are used, since manual installation of heavy metal is not allowed. The next step is making stringers with 1 or 2 bends. These bends are made at the ends of the elements in order to mount the junction unit to the supporting platform beam. Since the stringer is placed with a slope, its ends must be turned and be in a horizontal plane.
Bending an I-beam is done by cutting it and adding a corresponding gusset insert. To increase the reliability of the connection, thick metal plates are welded on the sides to the joining point. There are holes at the ends of the stringers that allow you to insert a mounting bolt and then adjust the position of the structure.
3.1. In accordance with SP 48.13330.2001 “Construction organization. Updated version of SNiP 12-01-2004” before the start of construction and installation work at the site, the Contractor is obliged, in the prescribed manner, to obtain from the Customer design documentation and a permit (order) to perform construction and installation work.
Carrying out work without permission (warrant) is prohibited. 3.2. General requirements3.2.1. Carrying out work on the repair of stairs, as well as installing stairs again during the renovation of buildings, is allowed only according to an approved project, including recalculation of the strength characteristics of load-bearing elements and linked to the design of the building being overhauled or reconstructed. 3.2.2.
The project must contain the necessary instructions and working drawings for the work. Both the design and the execution of work must provide for measures against the occurrence of deformations and damage to foundations and walls that cannot be repaired. 3.2.3. The main reasons for replacing various structural elements in a building are the different conditions of their operation, as well as the different durability of the materials from which they are made.
For example, in buildings of traditional construction, floors made of wood were periodically replaced. Currently, wooden floors are replaced with structures made of reinforced concrete, which have a service life corresponding to the lifespan of walls, foundations and stairs. Structures are replaced in all types of buildings, but to varying degrees .
In any building, roofs, fillings of window and door openings, floors, some types of exterior and interior decoration, as well as engineering equipment are replaced. In buildings of traditional construction, floors, roofs, partitions, and often stairs are added to the replaceable elements.3.2.4. When replacing stairs, the main direction of solutions is to use prefabricated elements wherever possible, preferably of larger sizes.
Due to the large variety of entire stairs, flights and steps in width, height and number of steps in a flight, it is often necessary to use staircase designs from individual steps along stringers and landing beams. 3.2.5. For the complete replacement of internal structures and the construction of new stairs, an assortment of prefabricated industrial structures of conventional and folded LM flights and LP platforms with different dimensions in horizontal projection and height has been developed. This makes it possible to create almost all the necessary combinations of products required for stairs in reconstructed buildings.
The initial data for the development of such an assortment are the following: - floor height - from 2.70 to 3.90 m; - staircase width - from 2.40 to 3.00 m;
c – a staircase of folded steps with walking on top; d – the same, with walking below
Prefabricated steps use conventional, solid sections, but folded ones have also been developed. The latter are convenient in reconstruction conditions in that with some shift the slope of the march can be changed in the direction of increasing it from 1:2 to 1:1.5. Folded steps are used both for walking along the upper part of the fold and along the lower part (see Fig. 9, c, d).
Due to the need to replace or remake not the entire staircase, but its individual links, in practice flights of stairs are often used from individual steps along stringers and platforms from various slabs (in particular, the PRT type) along beams. Stringers and landing beams were offered from special precast reinforced concrete products, but due to their limited circulation and a wide variety of sizes, they were not widespread.
Now they are made from reinforced concrete beams, beams and even rolled metal of suitable size.3.2.6. The selected method of repair and installation of stairs should be determined based on the requirements of the most economical execution of work within the established time frame and ensure minimal labor costs, cost, as well as the possibility of performing related work on a combined schedule.
During complex overhauls, the installation of stairs should be carried out in parallel with the installation of prefabricated floors.3.2.7. In order to reduce the cost of manual labor when performing labor-intensive processes, small-scale mechanization tools and rational devices should be widely used: light “window” cranes, winches for installing formwork and reinforcement, devices for stripping, templates and conductors for installing reinforcement, anchor bolts and mortgages parts, pneumatic and electrified tools, portable power supply cabinets, etc. 3.2.8.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what shovel cuttings are made of
Fig. 10. An example of a design solution for the installation of a new staircase during a comprehensive overhaul of a residential building
1 – I-beams, 2 – metal stringers, 3 – new masonry walls
3.3. Preparatory period3.3.1. Before the start of the main period of work, it is necessary to develop a set of organizational and technical measures and carry out preparatory work. 3.3.2. Organizational and technical measures related to the preparatory period: - no later than two weeks before the start of the main work, move from all apartments of the house all residents to flexible living space;
– to inspect the building again with representatives of the Customer’s technical supervision in order to identify the degree of its destruction and compliance with the working drawings, clarify the degree of wear and destruction, establish methods of fastening walls, staircase ceilings and other structures during dismantling and installation, as well as identify additional work missed or unaccounted for by projects and estimates;
- provide the site with working documentation approved for the execution of work and organize a thorough study of the design and estimate documentation by craftsmen and work producers; - develop a work plan for the dismantling, installation and erection of building structures of the building being overhauled, coordinate it with all subcontractors and suppliers;
– place orders for the production of elements of prefabricated structures, building parts and other products required for building repairs; - deliver to the site lumber, necessary reinforcement elements (frames, meshes, rods, etc.) semi-finished products, building parts and structures in the quantity established by the PPR , and place them in accordance with the construction plan;
- appoint persons responsible for the safe performance of work, as well as their control and quality of execution; - staff the team (link) with workers - installers, masons, concrete workers, electric welders and construction machine operators of appropriate qualifications; - familiarize foremen and team members with the Work Project, Technological maps and technical documentation, as well as issue work orders, calculations and Limit cards for materials to teams and units for the entire scope of assigned work; - instruct team members on safety precautions and provide workers with personal protective equipment;
- install temporary inventory household premises for storing building materials, tools, equipment, heating workers, eating, drying and storing work clothes, bathrooms, etc.; - develop schemes and arrange temporary access roads for traffic to the place of work;
- arrange temporary storage areas for receiving structures, building parts and materials; - prepare machines, mechanisms and equipment for work, deliver them to the site, install and test them; - deliver to the work area the necessary equipment, devices for safe work, electrified, mechanized and hand tools;
- supply electricity, water and compressed air for production purposes to sources of consumption; - install fences around the building being repaired in the form of temporary fences with canopies at least 1 m wide or continuous covered galleries and put up warning signs illuminated at night;
- establish certain places for workers to enter the building where structures are being repaired; - at the passage to the place of repair of the building, post a notice about the categorical prohibition of access to the work area for persons not related to the work; - disconnect all connections from the main electrical, gas, and water supply lines , heating, sewer and other networks and measures have been taken against damage to the remaining main networks;
Construction of staircases
Width of the stairs according to GOST.
To move along the stairs, you need to make platforms using previously installed beams. Work is carried out in 2 ways:
- ready-made reinforced concrete slabs are laid on top of the site metal structures by crane;
- a durable monolithic floor is installed.
The first method is simple, but requires the use of lifting equipment. The finished slabs are placed on the beams, their embedded parts are welded to the I-beam. Finally, a leveling screed and a suitable floor covering are laid on the slab.
Pouring a concrete platform involves assembling panel formwork, knitting a frame from periodic profile reinforcement and laying a concrete mixture. The disadvantage is that you have to wait at least 28 days for the concrete to harden.
When all metal structures are installed in the design position and welded, the steps can be laid on steel stringers. The sequence of work is as follows:
- The first step is placed, starting from the bottom. It is aligned horizontally and relative to the walls, and then welded to the beam from below. For this purpose, the step is provided with steel embedded parts connected to its reinforcement frame.
- A narrow strip of cement-sand mortar is placed on the rear edge of the tread. It does not increase the strength of the structure, but simply closes the gap between the staircase blocks.
- The second and subsequent stages are installed, repeating the steps of fastening and sealing the seam.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the difference between an expensive Euro picket fence and a cheap one
This video talks about the nuances of making a staircase.
After completing the installation work, reinforced concrete treads can be lined with any suitable material - porcelain stoneware, marble - or even self-leveling floors can be made.
Welding reinforced concrete steps to metal stringers
Prefabricated steps made of reinforced concrete are laid not only on a solid base, but also on metal stringers. Thin and durable metal stringers visually lighten the structure. The configuration of the stringers can follow the shape of flights of stairs and have a broken, curved profile. In this case, the stringers are welded from short rectangular sections of metal pipe. For their manufacture, channels, I-beams and rectangular pipes are used.
Reinforced concrete staircase elements are attached to the metal stringers installed and attached to the wall: lower frieze, upper frieze and main steps. The embedded parts of the steps are welded to metal stringers. The structure is quite strong and does not require a solid foundation.
When manufacturing reinforced concrete steps, it is necessary to take into account all the requirements of GOST, otherwise there is a possibility of deformation of the staircase or even its destruction. They must withstand all types of loads that are applied to the products. The height and width of treads and risers must necessarily comply with the standard specified in GOST. Failure to comply with the stipulated standards is punishable by law.
In the video selected for this article you will see the most beautiful reinforced concrete staircase structures on a solid base and on metal stringers. Enjoy the gorgeous staircases! Can you believe that they are made of concrete, the price of which is quite affordable? What do you think about it?
Read more here
- Author: AlikaAl
Share with your friends!