Roofing device
The roof for a garage can be different:
There are other options, but usually simple types of roofing are used for a garage - gable, pitched or flat. Their construction requires a lot of material, effort and money. The Mauerlat is placed on the armored belt, and a rafter system is formed on it.
As for the roofing material, it’s up to you to decide. There are many quality products that have their pros and cons. Based on the price, your own preferences and goals. Most often, inexpensive materials are used for the garage, such as corrugated sheets, roofing felt, bitumen shingles or slate.
Garage made of aerated concrete blocks
Aerated concrete is one of the leading building materials. When planning a structure such as an aerated concrete garage, the characteristics of the material used at all stages of construction are taken into account. The correct technology for laying walls, making armored belts and features of the exterior finishing of the building are observed.
Aerated concrete blocks are used in multi-storey and private construction. It differs from known concrete in the absence of crushed stone and consists of sand, cement, lime and aluminum powder.
Preparation of materials and tools
Required building materials:
- plaster mesh for reinforcement;
- furrower;
- brush;
- masonry adhesive;
- mortar of cement, sand, crushed stone;
- wire for tying;
- carriage for adhesive solution;
- Master OK;
- notched spatula;
- formwork;
- shovel;
- level;
- cord plumb line;
- rubber hammer;
- saw on aerated concrete blocks;
- capacity.
Return to contents
Benefits worth noting
Construction from aerated concrete blocks is very popular. And this is explained by the fact that this building material has a number of advantages in comparison with other building materials. It is recommended to use branded aerated concrete, which has been tested for years and remains the most popular. These are the advantages.
The advantage of aerated concrete is its lightness and ease of installation - special glue is used.
- Ideal geometry from a branded manufacturer.
- Light weight (low load on the foundation).
- Fire resistance.
- Resistance to fungi and mold.
- Wide range of types, sizes.
- Ease of processing.
- Relatively low price.
- Savings on finishing. With the correct geometry, the perfect wall is obtained.
- The use of cement is not required (it is laid with special glue).
- Good vapor permeability.
- Ecologically pure.
- Resistant to pests.
- Speed in construction and ease of work.
- Good thermal insulation.
- Frost resistance.
Low thermal conductivity.
What influences the choice?
To choose the right base for aerated concrete, you need to take into account the geological features of the site. For heaving soils, a shallow strip foundation using a monolithic grillage and bored piles is better.
The main rule of choice: the base must be strong and must provide rigidity to the structure.
Pile foundation diagram.
According to some builders, aerated concrete is a very fragile material, despite its high performance characteristics. And with a slight deformation of the foundation, cracks will appear throughout the house.
Fragility is determined by the elastic modulus. The higher this indicator, the more fragile the material. If you look at the regulatory documentation, you can see that this elasticity indicator for aerated concrete is the lowest among all fine-grained, cellular and heavy concrete. Aerated concrete is the more durable material of all types of concrete. Therefore, the heavy type of concrete is more fragile compared to autoclaved aerated concrete.
Most often, the foundation for such a house is made of reinforced concrete. The following types of bases are distinguished:
- monolithic slab;
- bored pile with reinforced concrete grillage;
- shallow belt;
- recessed tape;
- shallow-depth tape bar.
The most expensive is a recessed strip foundation; a shallow strip foundation (block foundation) is very cheap. It is this that is by far the most popular, since it is a cheap and simple way of arranging the foundation. For simple geological conditions, this method ensures the shape stability of the building structure.
Disadvantages: how are they displayed?
Like other building materials, aerated concrete has some disadvantages that are easily eliminated with modern technologies used in construction. The disadvantages are:
Fragility and water absorption are disadvantages of the building material, so it is necessary to apply additional finishing.
- Fragility, especially at low density.
- Poor retention of fasteners. Requires the use of special fasteners.
- Water absorption.
Calculations and projects
Depends on the square footage of the building. The project indicates the length, width and height of the walls. Based on these data, the area is calculated. Aerated concrete has different sizes, based on this the number of pieces or cubic meters is calculated. To make an accurate calculation of building materials, you must not take into account openings for windows, doors and gates. If you plan to build a garage from aerated concrete with your own hands, it is advisable to make a design for the future construction in advance.
When implementing a project for a cottage with a garage, the area, supply of necessary communications - electricity, ventilation, water supply, as well as ease of access and the possibility of additional extensions are taken into account. If you plan to build a turnkey garage or with an attic, then it is better to contact companies involved in planning buildings, where they will make accurate calculations of the necessary materials and offer:
- roof plan;
- opening elements;
- gender explication;
- architectural units in structures.
How to calculate the amount of materials for construction
The price tag for building materials depends on the parameters and number of gas blocks. The required flow rate can be determined in pieces, cubic meters.
The amount of aerated concrete required for the construction of walls can be calculated in several ways:
- Determine the theoretical volume of future walls and reduce by the volume of gates and windows. Divide the result by the volume of 1 piece, increase by 5% and round up. Using a coefficient of 1.05 allows you to have a supply of building materials in case of destruction.
- Carry out a piece by row calculation, taking into account the bandaging of each subsequent row by 20% in relation to the underlying one. Multiply the resulting number by 1.05 and round up.
- Apply the construction formula:
volume of aerated concrete blocks = (sum of wall length x wall height – opening area) x 1.05 x thickness.
Stages of work: what do they include?
Planning the construction of any building begins with determining the location of the structure, excavating the soil and pouring the foundation. The correct choice and installation of the base is a guarantee of the strength and durability of the building. Often, to ensure the stability of the garage, a strip foundation using reinforced concrete slabs is used. The slabs serve as both a base and a floor. The next stage is the construction of walls and roof. The roof of the garage is made of a single-pitch or gable roof. Then the necessary communications are provided, insulation and finishing work are carried out.
House foundation
For the construction of a garage or cottage, there are many types of foundations that should not limit entry. The most used options are monolithic and tape. The size depends on the size of the future structure. When using aerated concrete blocks in the construction of a garage, it is necessary to make a reinforced belt in the foundation. To do this, reinforcing bars or mesh are used when pouring.
Walls and roof
Work order:
- Before laying the first row, make reinforcement.
- Then aerated concrete adhesive is applied to the surface of the blocks and spread with a comb. The thickness of the seam should not exceed 4 mm.
- Laying the walls is done with bandaging. That is, each block is shifted by a distance equal to half the block.
- The evenness of the walls is determined by a building level or a special ruler.
The flat roof of the garage can serve as the basis for an additional building, such as an attic.
The roof for a garage or cottage house can be pitched or flat. The second option is covered with a continuous elastic coating made of polymer-bitumen material; this roof is resistant to temperature changes. The support for it is the walls of the building, the base is screeds or slabs. On such a roof you can make additional buildings, for example, an attic. A pitched roof is formed by bases whose inclination angle ranges from 10 to 60 degrees. The design places emphasis on rafter mechanisms. You can make a pitched roof or a gable roof.
Insulation
One of the advantages of aerated concrete is good thermal insulation. Sometimes additional insulation is done, but it is not always rational. In order not to do unnecessary work, it is enough to choose aerated concrete 375 D-400 for construction. Walls made of this material are durable and do not require insulation. If 250 blocks are selected for construction, then additional work is carried out. Their disadvantage is that when constructing a frame for attaching insulation, the structure of aerated concrete is disrupted. Only basalt insulation is used, polystyrene foam cannot be used.
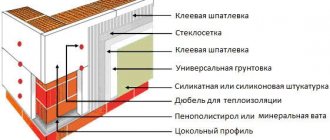
Wall decoration
Without the use of additional insulation, the aerated concrete wall is quite smooth and durable. To protect the outside of the wall from dust and precipitation, it is enough to stuff a thin mesh, apply plaster to the surface of the wall and paint it with film-forming paint. If insulation is used, then the mesh is filled in the same way and plaster is applied. Walls can be covered with siding, clapboard or decorative panels, or treated with special lightweight plaster mixtures for aerated concrete.
Is it possible to use aerated concrete blocks for the foundation?
Since any foundation is a reinforced masonry structure, the main document regulating its construction is the set of rules numbered 15.13330 (last edition of 2012). Clause 9.1 clearly states that cellular concrete blocks cannot be used for foundations, basement walls (sometimes these functions are combined), or even for basement walls.
The second document that should be used to guide the construction of a low-rise building is another set of rules - 31.105 (dated 2002). It specifically stipulates what types of blocks can be used to build basement walls - or rather, the standards by which these blocks are made are given. These are GOSTs:
- 13579. It is used to produce large-format unreinforced FBS wall blocks from heavy concrete and expanded clay concrete.
- 6133. This standard applies to wall stones made of fine-grained, heavy and lightweight concrete with coarse aggregate.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
Attention: Although cellular concrete belongs to the lightweight class, it does not contain coarse filler. They have their own standard (31360) according to which autoclaved wall blocks are made. It says that such blocks can be used for external walls and partitions. There is no mention at all about foundations and basement walls.
So, it is impossible to make a foundation from aerated concrete blocks for a house, and you will not see such a solution in any standard project. Let's see what the manufacturers of this material think about this.
Advantages and disadvantages of aerated concrete foundations: opinion of material manufacturers
In search of an answer to the question of whether it is possible to use aerated concrete for the foundation, we looked at the websites of popular block manufacturers. We have not found a direct statement that it is possible to lay gas blocks in the foundation. If anyone says such things, it is the incompetent market sellers.
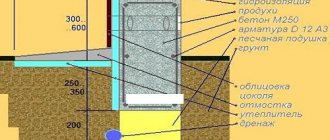
Regarding buried walls, aerated concrete manufacturers have their own opinion. Note that this does not apply to those schemes where the basement walls simultaneously serve as a strip foundation. This refers to the situation when either a monolithic pad or a foundation slab is designed at the base.
To make it clearer, below is an explanatory photo:
If it is possible to use aerated concrete blocks for the foundation, then only this way
With such a design scheme, manufacturers' instructions must provide:
- Installation of a monolithic belt along the top edge of the masonry, reinforced with two rods with a diameter of 12 mm or four with a diameter of 8 mm.
- Carrying out not only horizontal waterproofing (under the base of the reinforced concrete cushion, under the first row of the basement wall and along its upper edge), but also vertical on both sides.
- A blind area around the perimeter of the building with a slope of 0.05% and a width of 1 m.
- Thermal insulation from the outside, using materials with low water absorption. Foam glass is best suited for this purpose, but extruded polystyrene foam can also be used.
- To protect the walls in the basement, water-repellent plasters, bricks, fiber-reinforced concrete tiles, and artificial stone can be used.
At the same time, it is not recommended to raise the aerated concrete plinth above 50 cm above ground level and install it where groundwater is located nearby. True, there is not only ground moisture, but also surface moisture - and water, as you know, will always find its way.
Food for thought
Above are the conditions that, according to the recommendations of the manufacturers, must be met in order to make not even a foundation, but a plinth wall from aerated blocks. The question immediately arises - is this “game” worth the candle? This design cannot be used for a house, and, for example, a foundation for a greenhouse made of aerated concrete will be too expensive and short-lived.
- By and large, any material requires comprehensive waterproofing protection. However, FBS blocks, for example, can simply be coated inside and outside with bitumen mastic - and they will last a hundred years.
- Aerated concrete, so that it does not become covered with cracks, must also be insulated - and not just with anything. By the way, a slab of foam glass recommended for insulation measuring 600*450*60mm costs at least 550 rubles, so all the savings from using a cheap structural material will simply dissolve.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring authorAsk a Question
Advice: The most that can be done is a foundation of aerated concrete blocks for the greenhouse, if they remain, for example, after building a house. There is definitely no need to buy specially porous blocks for this purpose.
- If they are thoroughly treated with penetrating primer on a polymer or cement base, and then plastered, aerated concrete will serve as a foundation for a greenhouse for some time. Such a light construction will not put any special loads on the blocks, so their destruction will not be so fast.
- Due to the light weight of the walls, aerated concrete can be used to make a foundation for a garage built using frame technology. Such a support will not withstand heavy masonry, even if it is also gas-block, and even more so if the ceiling is made of slabs.
These are the features of aerated concrete foundations. This is not a material that in this situation can have any advantages over heavy concrete, or provide any significant savings.
Why aerated concrete?
A do-it-yourself aerated concrete garage is the cheapest way to build a room to protect a car. Another reason for choosing aerated concrete blocks is the lightness of the material, which allows you to build structures with less effort and less powerful foundations, but the strength of the material allows you to provide sufficient protection.
Note!
In addition to the positive characteristics, there are also some negative aspects of foam blocks.
The most important drawback of building a garage from aerated concrete is that it is not a breathable room, and for a garage this characteristic is an important parameter, since a car after traveling in winter and in damp weather brings a fairly large amount of moisture into the room, its condensation and non-weathering negatively affects the walls and the transport itself.
Attention!
In the case of brick garages, moisture comes out much faster and no additional work is required, but aerated concrete blocks cannot remove moisture, and it will be necessary to build an additional ventilation system using an electric cooler, which will increase the cost of time and money. The second equally important negative parameter is intolerance to the effects of fire, and at high temperatures the building can completely burn out, and during combustion the material releases life-threatening substances.
We also read - choose which is better - gas blocks or foam blocks
Factors influencing the choice of foundation
When constructing an individual garage from foam blocks, the key issue is the choice of foundation for it. The building is not a capital object; it has light wall structures. Therefore, it does not require heavy, massive and deep foundations. But choosing a specific type of foundation requires taking into account more serious and important criteria. These include: the type and composition of the soil, the depth of freezing and groundwater, the total weight of the structure, and the placement of the object.
Foam block garage with attic
The load on the foundation for a garage made of foam blocks, as well as the presence of a basement and inspection hole in it, are the starting factors for calculating the foundation of the building. They primarily affect the reliability and stability of the structure and its long-term operation. The total pressure on the foundation is directly proportional to the height of the walls. The large size of the load-bearing part and the multi-story structure of the facility predetermine not only the pouring of a more powerful foundation, but also its additional reinforcement. The presence of a basement and inspection pit significantly complicates the process of soil exploration and also precludes the use of certain types of foundations. Even barely noticeable inaccuracies in the analyzes can lead to errors in the selection of the base and its decommissioning long before the end of the design period. To avoid negative consequences, the study of the earth's structure should be carried out with the participation of qualified specialists.
Under standard conditions, the main work of soil examination does not cause any great difficulties and is carried out by household owners independently. To do this, it is necessary to study reference materials on the area that are freely available, as well as consult with experts who will approve the design documentation of the facility. To specify the information, a well is drilled or a hole approximately 2.5 meters deep is dug at the future construction site. A soil sample is taken from every 15 - 20 cm, which is checked against the initial data in reference books or transferred to experts. For greater accuracy, you can take several samples over the entire area under the garage. The information obtained will answer questions with sufficient accuracy about the type of soil, the depth of groundwater, the freezing point in winter, and the presence of a hard layer.
Determining soil type manually
Garage design and material calculations
The construction of a garage made of aerated concrete begins with a project and the first thing they do is find out the depth of groundwater and other features of the land, which makes it possible to determine the future foundation, then the tasks that the structure will perform are determined:
- Availability of an inspection hole for repairs;
- Gate height and width;
- Availability of shelves for tools;
- Temperature differences for choosing wall thickness.
The project can be implemented in one of two ways:
- Order a project from a company or private designer;
- Independently perform calculations and markup in special programs.
Foundation
Garage foundation
Construction of a garage begins with the foundation. Sibit blocks are light in weight, so the foundation does not need to be made powerful and heavy.
- Place the formwork in the dug trench.
- Install reinforcement in the trench, it will increase the strength of the base.
- Pour the concrete solution. Now you have a fairly reliable foundation for your future garage.
Aerated concrete garage foundation
The most important criterion when building a foundation is the weight of the walls creating pressure, from which they focus on the material and method of laying the foundation depending on the soil.
Aerated concrete foam blocks do not have much weight, for this reason the foundation is made strip with a recess of 40 - 50 centimeters.
- To construct the foundation, a ditch of a certain depth and width is dug, and the previously established markings serve as a guide;
- Sand and crushed stone are poured into the bottom of the trench and compacted;
- Formwork made of wooden blocks and plywood is installed;
- A reinforced frame is laid in the trench.
- The last stage is pouring the garage foundation with your own hands.
Features of choosing a base
Diagram of the construction of a monolithic slab foundation.
Which foundation should you choose? To know what kind of foundation is needed for a 1- or 2-story building made of aerated concrete, you need to calculate the load per 1 linear line in advance. m of foundation. In such houses this load is often 40-120 kN. Since the loads are small, the sensitivity to soil heaving is increased.
Even after taking measures against soil heaving (laying the foundation to the freezing depth), the stability of a light building will not be ensured, because the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete will receive large heaving forces on the sides. It is best to use a shallow foundation.
The principle by which shallow foundations for buildings are designed is as follows. The strip base of all walls must be combined into a single system, which is a horizontal frame that redistributes uneven deformations of the foundation. Some deformations are acceptable, but they must be less than the maximum.
Monolithic foundation
Slab foundation diagram.
Aerated concrete is a fairly lightweight material. This makes installation possible quickly and easily. With a monolithic foundation, resistance to loads during bending deformation increases. A monolithic foundation is considered a unique foundation for a house because it can be used on any type of soil. It withstands harsh climatic conditions and ground movements. The base for aerated concrete blocks should have a slab thickness of 40 cm (30 cm above the ground and 10 cm below the ground).
Since the weight of the walls of a house made of aerated concrete is 7-10 times less than the weight of a brick house of the same area, the total load on the foundation is the same amount less. But several important conditions must be taken into account. Aerated concrete has low resistance to bending loads, so it is necessary to reduce the likelihood of deformation of the foundation under its masonry.
The monolithic base is made of high-strength concrete. For reinforcement, use rods of 12-14 mm. A monolithic foundation on a sand cushion is considered a universal foundation. It withstands any temperature fluctuations and ground movement. Distortions will not appear. The specific type of foundation can be selected after studying the groundwater level and the geological basis of the soil.
Slab foundation
The most reliable option in this situation is considered to be a slab foundation for an aerated concrete house. It will ensure uniformity of shrinkage deformation and reduce it to a minimum. The construction of this foundation will compensate for soil pressure during freezing. It will be an excellent option in places where the soil is heaving.
The monolithic slab base dampens seasonal soil deformation and distributes pressure evenly. A reinforced slab is installed under the entire area of the building, and with any ground vibrations it will move like a monolith, preventing the possibility of uneven deformations in different parts of the house. Longitudinal reinforcement will provide additional protection against cracks in the walls.
Columnar foundation
Another most popular base option is a columnar base with a reinforced concrete grillage. Depending on the size of the house, the diameter of the pillars and their number are calculated. Then they mark their location on the territory and fill them. The next step will be to make the formwork for the reinforced concrete grillage. All pillars must be connected with a reinforced concrete belt into one structure. Based on the size of the future house, calculate the depth of the foundation for aerated concrete construction and its width. If you choose this type of foundation, you don’t even have to think about the basement. However, the low cost and ease of construction today attract quite a lot of supporters, although calculations must be performed no less than in a strip foundation.
Pile-grillage foundation
If we compare the foundations in terms of price-quality ratio, then the most ideal option would be a pile-grillage monolithic foundation. It is quite simple to build, it is economical and quite reliable in operation.
The main parameters of this framework:
- The depth of laying the pile pillars is 2.5 m.
- The gap between the piles is 1.5-2.5 m.
- The cross-section of the binding monolithic beam is 300*400 mm (for the project of a 2-story house with an area of 200 sq.m.)
- Blocks D400-D500
- The width of the blocks is 375 mm.
Pile-slab foundation
A pile-slab foundation can be used as the basis for a house made of aerated concrete. Asbestos-cement pipes can be used as piles. They are installed to a depth of 2-2.5 m and reinforced with pre-tied reinforcement. Then everything is poured with concrete. This creates one whole structure.
We build a garage from aerated concrete: walls
The construction of walls begins from the corners of the structure, and models 20 centimeters wide are most often used as aerated concrete blocks.
Advice!
After placing the first corner blocks, a thread is stretched along them, then, guided by the tensioned element, the walls of the garage are erected. Cement is most often used as a fastening compound, but there is an alternative - an adhesive compound sold in stores.
When building a garage from aerated concrete with your own hands, the second row of blocks is installed offset from the first, so that the higher-laid block in the middle overlaps the vertical joint of the two blocks of the previous row. Thus, work continues until the walls reach the required height.
When the required size is reached, the walls are oriented toward the future roof, and certain areas are made higher and others lower. The most common option for a garage roof is a pitched one, in which case one wall is made higher, and the parallel one is much lower.
Please note - how to heat a garage?
Types of foundations for aerated concrete walls
The point of creating aerated concrete is to make the concrete air-filled and lighter, to ultimately get warm walls and be able to save on heating costs. The strength of the stone decreases in proportion to the degree of porosity; it becomes sensitive to foundation movements caused by natural subsidence of the soil. To avoid the appearance of cracks, it is better to rest the porous masonry on a monolith, even if it is a foundation for a garage made of aerated concrete.
Let's look at what types of foundations will work best in this situation.
Monolithic foundations by slab type
This is the most concrete-intensive, and therefore expensive, type of foundation. It can be considered universal because it is suitable for most types of soil, including deeply frozen, moist, heaving soil. If a house is being built without a basement, the slab may be on the surface of the ground, and even protrude 20-30 cm above its planning level (the so-called floating option). This allows you to do without laying out the plinth, and immediately begin laying walls from aerated concrete blocks.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
Note: Such a foundation is also very convenient for building a garage, when it does not have an inspection hole. The surface of the slab simultaneously functions as a floor, which eliminates the need to fill it. Moreover, the floor will be very durable to easily support the weight of the car. The height of the foundation for a garage made of aerated concrete, poured in the form of a monolithic slab, may not exceed 150 mm.
In addition to the possibility of using the surface of the foundation slab as a floor, its advantages include:
- In organizing a stable foundation on moving soils.
- The most uniform distribution of loads per square meter of building area.
- Possibility of construction in the vicinity of groundwater.
- In high strength and durability.
The slab can go either slightly or quite significantly into the ground. The second option applies only in cases where the house is being built with a basement floor. And this is the same case when manufacturers of aerated concrete blocks offer to use them for laying out basement walls.
Whether to do this or not is, of course, up to you. But it is better to follow the requirements of building regulations and use concrete bricks with fine-grained or expanded clay filling for the construction of buried walls. Although for the basement floor it is best that the basement walls are also cast in a monolith - this is the easiest way to seal them.
The diagram shows the structure of a slab foundation for a house
From a functionality point of view, a slab foundation has no disadvantages, except that such a design is not suitable for construction on difficult terrain. Its only disadvantage is its high cost, which is comparable to half the cost of the entire house box.
Strip foundations
This type of support consists of several reinforced concrete beams closed around the perimeter, which lie under all the load-bearing enclosing structures of the house. On such a foundation, you can build absolutely any walls - from a wooden frame to a monolith. The biggest advantage of the tape is the small volume of excavation work, which significantly reduces the cost of the foundation.
The belt can be constructed using several technologies, depending on the material used. According to the standards, the following can be used for this purpose:
- large rubble stone laid on the mortar;
- rubble concrete (it has no internal reinforcement);
- clay solid brick;
- large-format blocks FBS, UDB (permanent formwork);
- monolithic reinforced concrete.
Depending on the depth of placement in the ground, the tape can be:
- deep;
- shallow.
The choice of option depends on the type of soil, but the total weight of the building also matters. For example, for a house with heavy brick walls, which will be built on loamy soil, a deep foundation is definitely needed. For light outbuildings, a shallow one is sufficient.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
Note: The answer to the question of what kind of foundation to make for a garage from aerated concrete is quite obvious. If a garage is being built without a basement, a shallow-depth tape will be sufficient, since aerated concrete weighs even less than wood. But this type of foundation can be provided only under the condition of insignificant soil freezing in the region and the absence of nearby groundwater.
Garages are often built with a full basement to store vegetables and canned goods. In this case, the foundation, regardless of the construction material, must be laid to the entire height of the basement walls. All of the above also applies to other outbuildings: sheds, temporary buildings, country houses.
Shallow tape structure
If a normal residential building is being built from aerated concrete, then the foundation for it must be built as it should be - with its base laid below the UPG mark. Exactly how much lower depends on the type of soil and is calculated using the formula.
To reduce the pressure of the weight of the building on the ground, the width of the foundation strip is made greater than the thickness of the walls resting on it by at least 10 cm (5 cm on each side). For greater stability, especially on unstable soils, the tape is made with a sole that expands in the form of a trapezoid, or a reinforced concrete pad of rectangular cross-section is added underneath it.
What are the consequences of incorrect placement and incorrect proportions of the tape?
The height of the tape should always be greater than the width, which will avoid transverse deformation of the structure. Basically, it experiences longitudinal loads, which is facilitated by the uneven weight of the building and the forces of frost heaving. The greatest loads can be withstood by the tape, inside of which there is a frame with an alternating cross-section. The reinforcement of the corners requires special attention, since they are the weakest link of the strip foundation.
Columnar foundation
Columnar foundations are designed for the construction of low-rise buildings without basements or ground floors. If there is soil with high density and strength on the site, in order to save money they replace more expensive strip foundations. The pillars are placed in the corner areas of the building, at the intersection points of the walls and the spaces between them, the exact distances are determined by calculation.
At the bottom, the pillars must rest on foundation pads, and at the top they are tied with a reinforced concrete grillage, which works similarly to a strip foundation. The grillage takes the loads from the weight of the building and distributes them to the pillars. For free settlement and better drainage, sand or expanded clay bedding is used under the grillage.
Drawing of a columnar foundation
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
Attention: When deciding which foundation to make for a house, a garage or a greenhouse, you may give preference to the columnar option. For light buildings it is especially good and can even do without a grillage, which is often replaced with wooden or metal beams. However, a grillage is needed for aerated concrete walls. Although such masonry is quite light, it reacts very sensitively to vibrations and movements of the foundation. For such walls it must be rigid.
- Several types of materials can be used to construct pillars under stone walls, including clay and concrete bricks. However, when the pillars are laid deeply, it is inconvenient to work with such material, since it would be necessary to increase the volume of excavation work: dig a foundation pit or trench. And it is inconvenient to carry out mandatory masonry reinforcement in cramped conditions.
- Whatever one may say, it is impossible to come up with anything better than monolithic reinforced concrete or rubble concrete. Although, it will not be possible to save much on excavation work here, since without digging a pit in the ground it is impossible to make a selection for the expanded part of the pillar. The pit must be such that it is possible to install formwork and reinforcement.
- A full-fledged columnar foundation for an aerated concrete house is not the same columns that are laid out of eight bricks or four concrete blocks for light frame buildings. This is a serious design, characterized by high complexity of installation. Therefore, in standard buildings such foundations are not designed at all, and unless there is a real need, it is better not to give preference to pillars.
Pile foundation
Pile foundations, like columnar foundations, are point supports, the tops of which are tied with a grillage. Their use is due to the complex hydrogeological situation on the site, the presence of high groundwater level, weak upper layers of soil, and deep freezing. Piles differ from pillars in that they are installed in the ground by applying the forces of pressing, screwing or driving mechanisms.
The most reliable foundation is made of driven reinforced concrete piles. It is suitable for all types of soil, except rocky, and can be installed on rough terrain. At a lower cost than a deeply laid strip foundation, a columnar foundation can withstand loads of up to 60 tons per support and last almost forever.
In low-rise construction, such piles are used quite rarely, since there are simpler methods of arrangement. One of them is the now popular screw piles. They are hollow metal rods with bladed, pointed tips, which, after being screwed into the ground, are filled with concrete.
How to build a foundation on screw piles
When installing a grillage, their heads are embedded in the concrete body. The result is a fairly rigid structure, the service life of which, however, is no more than 30 years. And all because metal, no matter how you protect it from corrosion, is still susceptible to destruction. This option is suitable for a country house, but for permanent housing built using masonry technologies, it is better not to use it.
TISE
This abbreviation refers to the relatively young technology of environmentally friendly industrial construction of a bored-type foundation with a pile-strip structure. The selection of all materials and tools here is focused on the use of adjustable formwork and a specially designed drill. It consists of a pair of successively connected rods, with a cutting-loosening cup at the bottom, and some kind of plow, which allows you to make a widened support for the pile. Such expansion greatly increases the load-bearing capacity of the pile and prevents heaving forces from squeezing it out of the ground.
TISE drill
On average, the drilling depth with this tool is 2 m, but if deeper installation of piles is necessary, the rods can be extended. The drilling process can be accompanied by the operation of drilling rigs of any type, including a hole drill or a gas drill.
Here are the advantages of the TISE foundation:
- Unlike monolithic pillars, there is no need to dig pits, make drainage so that they do not fill with water, or use heavy equipment.
- It is more profitable and costs 20 percent less than tape, while having no less service life.
- High structural strength.
- Possibility of installation on heaving soil;
- Possibility of construction on difficult terrain;
- Ease of construction, including in cramped conditions.
- Availability for independent execution.
Pile-grillage foundation in section
The process of arranging a bored foundation consists of drilling a well, installing a metal frame into it, and injecting cement-sand mortar or polymerized concrete. In wet soils, pipes are used to casing wells; in dry soils, this is not necessary.
Garage roof
Roofing installation begins with the installation of rafters. There will be a constant load on them, which means that the entire roof will depend on the strength and reliability of the fastening of the rafters.
The rafter system serves as the skeleton of the roofing materials; it must reflect any external influences: strong wind, snow and any other types of precipitation.
The basis of the frame is made up of rafter legs - wooden beams that rest against the frame of the building. The features of the rafter legs are as follows:
- Made from softwood or wood;
- Dry thoroughly;
- Treated with antiseptic agents and fire-retardant impregnation.
The remaining elements of the rafter system are auxiliary and serve to ensure its normal operation:
- To provide additional rigidity, the rafter beams are connected by additional jumpers;
- To install a volumetric roof, it is necessary to install additional supports that will protect the rafters from deflection;
- For better fastening of roofing materials, sheathing is attached perpendicular to the rafters.
Practical recommendations
- The strength of the roof structure depends on the distance between the load-bearing walls. If the distance between them does not exceed 4 meters, then additional supports do not need to be used; it is enough to mount the beams between two posts. If the distance between the load-bearing walls is greater, then additional supports must be used.
- When building the walls of the garage, it is important to remember that its roof will be pitched. Therefore, during construction, one of the walls of the garage must be higher than the other.
- The angle of inclination of a pitched roof should not be less than 25 degrees.
- If the roof angle is 25 degrees, then every meter between the load-bearing walls of the garage adds 300 mm to the height of the second wall. Simply put, the scheme is as follows: if there is a distance of 5 meters between opposite sides, then the increase in the opposite wall will be 1500 mm (5x300), i.e. one wall will be one and a half meters higher than the other.
Pitched roof technology
Preparation for attaching the Mauerlat:
- A wooden beam measuring 200x100 mm, in which every 500 mm. Holes for anchors are drilled.
- Holes are made in the wall for anchor bolts, taking into account that one part of the bolt will be in the beam and the other in the wall.
- Next, holes are drilled from each corner to fasten the beams at all corners.
- For better fastening, glue is poured into the drilled holes for anchors.
- Each beam is fastened with prepared anchors.
Now we do the following:
- Rafters are being prepared that will be located between two load-bearing walls.
- Double teeth are cut into the rafter beams, which will go into the holes cut into the beams.
- Each rafter is installed in turn, it is fastened with a metal clamp with a bolt. The distance between two beams should be 300 mm.
Treating rafters with fireproofing agents
Due to the high probability of fire, the rafter system must be treated with fire-resistant agents.
Only compositions of the 1st and 2nd groups of fire retardant effect according to NPB 251/GOST 16363/ are considered fire retardant. Important structures are impregnated only with products of the highest group.
Article on the topic - installation of roof rafters
Garage floor
The last stage of how to build a garage from aerated concrete is the floors, and due to the load created by the car, the most common is a concrete floor constructed with a loose cushion.
First, the perimeter of the garage is cleared of soil, then the area is covered with a small layer of crushed stone, and sand and gravel are laid on top of it.
Attention!
Each layer is carefully compacted. Concrete is poured on top of the laid cushion, but with such volumes it is better to order special equipment.
Characteristics of foam blocks
Due to their porous structure, these blocks have a low specific gravity and therefore walls made of this material will be lighter than brickwork. The density of foam concrete ranges from 400 to 1200 kg/m 3 and its marking, accordingly, is from D400 to D1200.
For the construction of load-bearing walls, blocks with a specific weight of at least 750 kg/m 3 must be used. Lighter material is used for the construction of internal partitions and as insulation.
The important advantages of foam blocks are:
- low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- good sound insulation performance;
- reduced weight of the building, which allows for the construction of a lightweight foundation.
The negative qualities of this material include increased ability to absorb moisture and reduced mechanical strength.