Wooden houses were very popular at one time, but then with the development of modern building materials they faded into the background. But today, wooden buildings are regaining their former glory. This is due to the fact that only in a wooden house the atmosphere is filled with harmony and tranquility. The decoration in such a house can be made of any material. But this is not very advisable, since walls made of logs look much more attractive and natural than paint or wallpaper.
Scheme of interfloor slabs in a wooden house.
But the question of surface finishing will depend only on personal taste preferences. As for the construction of the wooden floor of the second floor, it is also made from beams. There can be no other option. Reinforced concrete slabs cannot be laid on wooden walls. When finished, the entire structure is made of natural material – wood.
Floors with lightweight concrete and gypsum sheeting
Lightweight concrete rolls can be made of slag concrete, local lime-slag and cement binders, foam concrete and other materials with a strength of at least grade 75. Gypsum rolls are made in the form of solid slabs reinforced with wooden slats, or in the form of hollow gypsum blocks.
In attic floors, only reinforced gypsum rolls are used. Lightweight concrete slabs are laid on tiled beams or on a horizontal flange of a T-joint composite laminated laminated beam. To protect gypsum rolls from water, one layer of roofing felt or bituminized construction paper is laid on their surface and covered with a layer of sand. To improve sound insulation, the seams between the blocks are carefully sealed with gypsum or cement mortar. Ceilings are made of dry or wet plaster. To improve the adhesion of the plaster layer, the underside of the blocks should have a corrugated surface. The disadvantages of such roll-ups include their large dead weight and the high labor intensity of the work.
Floors with sheet materials
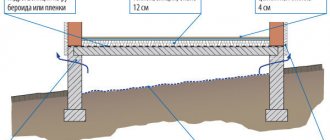
The advantage of hemmed plank floors is significant savings in wood, the absence of wet processes, a more industrial method of ceiling construction and lower weight of structures than in panel-rolled floors. Wood-fiber or insulating asbestos-cement boards and dry plaster boards are used for lining the ceiling.
To improve the soundproofing qualities of the floor, a layer of lime-sand mortar is laid on top of the slabs. If the length of the beams exceeds 3 m, it is necessary to install cross braces and spans, which are made in the form of cross-shaped struts made of bars or sections of boards on nails.
These transverse connections increase the stability of the beams and the overall rigidity of the entire floor under local loads. In the case of a double plank floor, one layer of roofing felt is laid between the layers of the floor to prevent water from entering the ceiling slabs.
In the attic floors, walking boards are laid along the beams. Operating attic floors must have a continuous flooring of boards over beams. In some cases, the ceiling can be lined with boards 2-2.5 cm thick with gaps and have a clean ceiling made of wet or dry plaster. In order to improve the sound insulation of the floor, mineral wool is laid on the roof, covered with one layer of roofing felt and lime-sand mortar
Do-it-yourself wooden floors above the first floor
Wood, unlike other bases (reinforced concrete slabs, monolith) used for floors, is an environmentally friendly material. In addition, a wooden ceiling or floor gives the room a unique look and retains heat well. Previously, wood was used for these purposes quite often. Nowadays, interfloor wooden floors, as a rule, are made only in wooden houses, although there are exceptions.
Wooden floor installation
Wooden floor installation
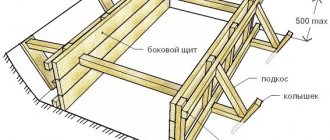
Installation of wooden floors between floors begins with the installation of support beams. The cross-section of beams depends on several reasons, in particular on the length of the span and the load on the floor of the floor above. The type of wood used for them also plays a big role in choosing the cross-section of beams. Pine is most often used, but sometimes oak is used.
The determining factor is the price of wood; naturally, oak is more expensive. In this case, the thickness of the beams can be reduced and the design slightly changed.
Construction and installation of wooden floors
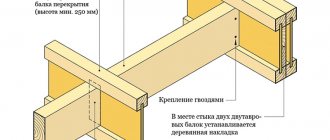
The process of constructing wooden floors involves placing beams into pre-prepared recesses in the wall. The cross-section of the beams is made equal to both height and width. It happens that the height is chosen slightly higher. In any case, the beams are laid on waterproofing, with a gap in both planes of the order of 1-2 cm. This is done in order to eliminate the expansion of the walls when such a floor gets wet or dries out.
Further, to the beams at the level of their lower plane, slats are packed along the entire length, which are used to attach thermal insulation and ceiling lining. An additional layer of waterproofing is laid on top of the thermal insulation, and finally a subfloor is laid.
In the case of oak, in order for the ceiling of the lower floor to look “antique,” the beams are planed before installation. Further overlap is carried out on top of the beams. In any case, the span length for a wooden floor should not exceed 5 m. A span length of 4 m is considered optimal.
Do-it-yourself wooden floors above the first floor
Overlapping with gypsum plaster roll
Gpsorechnye boards reduce the volume of plastering work, allowing you to limit yourself to only sealing the joints and the ceiling surface. They are manufactured in construction workshops or factory conditions using vibration.
The panels can be transverse, which are nailed directly to the beams from below, or longitudinal, in which special ribs are placed between the beams and nailed to them. When the panels are arranged transversely, their number and length are determined by the dimensions of the room and depend little on the spacing of the beams. Shields are manufactured in one width and three lengths. To fill the remaining gaps, a sliding lattice panel is used.
When the panels are arranged longitudinally, their width is related to the location of the beams, so the number of their standard sizes increases. In wooden floors and in houses with stove heating, special attention should be paid to the arrangement of places where parts of the floors adjoin the smoke and ventilation ducts. In addition to installing brick grooves, all gaps between the groove and parts of the wooden floor must be carefully filled with felt impregnated with clay mortar or a layer of asbestos.
Prefabricated flooring made of ceramic beams
Floors made of “Standard” stones are mounted from pre-assembled ceramic beams, laid on supports in the form of a continuous flooring. The preparation of beams from “Standard” stones is carried out first at the factory or construction yard, where the working and installation reinforcement is laid and the upper and lower open channels of the stones are filled with grade 150 concrete.
The seams between the beams when installing the floor are filled with cement mortar. The transmission of compressive forces to the beams is ensured by concrete dowels, which are formed by pouring quarters left at the ends of the stones. The calculation of the floor is carried out according to the methods used in the design of reinforced concrete structures, taking into account the strength of stones and concrete.
Do-it-yourself monolithic ceiling above the first floor
Monolithic reinforced concrete floors are naturally used in cases where the house is not built from wood. Although, covering the basement, if the foundation is made of concrete or brick, is even welcome.
Construction of a monolithic reinforced concrete floor
Such a floor is made, like any reinforced concrete product, using formwork. The difference is that the formwork will rest on “legs” that will rise directly from the floor of the previous floor, or basement. The thickness of the monolithic floor, as a rule, is 20 cm, the minimum is 15 cm, it all depends on the strength of the walls. A thinner ceiling rests on a less durable wall.
If the thickness of the monolithic slab is 20 cm, then the distance between the supports should be at least 1 m. With a thickness of 15 cm, this distance can be increased to one and a half meters.
Installation of monolithic ceiling
It is carried out according to the usual scheme: logs are placed on the supports, transverse beams are placed on them, a step of about half a meter. Shields are placed on top. Once the formwork is ready, they begin to reinforce the monolithic floor.
The reinforcement is made from rods with a diameter of 10-12 mm, which are laid in a grid with cells measuring approximately 20x20 cm. The corners are boiled.
All. You can start pouring concrete. Pouring is carried out in one step; a deep vibrator is used to compact the mixture and remove air bubbles. After pouring, the formwork is not disassembled for at least three weeks (30 days according to Western technologies) until it dries completely. It turns out that we made a monolithic slab on our own. The strength of such a floor is much higher than that of a wooden floor or even a floor made of reinforced concrete slabs.
Installation of monolithic slabs
The use of floor slabs is impossible without the use of heavy construction equipment, in particular, a truck crane. This makes the task more difficult. On the other hand, this is the fastest type of creating an overlap. You just need to take into account that the slab should rest with its ends on the mortar previously applied to the wall.
The width of the support of the monolithic floor on the brick wall at each end of the slab should be at least 10-15 cm.
Do not forget that before installing the slabs, the wall surface must be leveled and leveled. The gaps between the slabs should be sealed with cement mortar.
Prefabricated monolithic ceiling made of hollow ceramic stones
The ceiling consists of hollow ceramic stones, the gaps between which are filled with concrete and reinforcement. The compressed zone of the bending section of the floor is formed by the joint action of the upper part of the concrete filling and the thickened upper wall of the stones. Concreting of the floor is carried out using thin formwork.
This type of flooring is used in the absence of favorable conditions for preparing prefabricated deck beams outside of construction. If it is necessary to increase the rigidity and load-bearing capacity of the floor, it can be made with a concrete slab on top. In this case, the ceiling turns into reinforced concrete often ribbed with ceramic liners.
The overlap is calculated as iron-stone, similar to reinforced concrete. In order to improve industrial construction methods, it is advisable, in the presence of installation and transport means, to assemble floors from prefabricated decks made up of several rows of stones, the spaces between which are reinforced and filled with concrete.
Types of floors
Depending on the location, attics are distinguished, which separate the living space and the roof.
Creating thermal protection is their main task. Another type of ceiling - interfloor - serves to separate residential floors from one another and provides sound insulation. And the basement, the third type, is an intermediate link between the floors and the basement. In addition, another classification is known, presented in the table. Types of floors
| Titles | Application | Appearance |
| Ribbed | Cellars | Vertical ribs in 1-2 directions |
| Attic spaces | ||
| Hollow | Interfloor ceiling | Round and oval voids |
| Monolithic | High-rise buildings and buildings | Reinforced concrete complete covering |
Fireproof and prefabricated monolithic floors, floors made of small elements
Fireproof floors made of small elements can be prefabricated monolithic, made of lightweight concrete stones, gypsum concrete and lightweight concrete slabs laid on the edges of prefabricated reinforced concrete beams, or prefabricated, made of slag concrete and other stones, pre-connected with each other using reinforcement and concrete or cement mortar
The advantages of fireproof floors are: industrial, durability, fireproof, no need to waste wood, the ability to use local raw materials. The disadvantages include significant labor costs during construction, the inevitability of wet processes under construction conditions, as well as their significant weight.
When should formwork be removed?
Scheme of small-panel collapsible formwork on frames for monolithic floors.
After meeting certain requirements, the formwork is removed from concrete monolithic structures. The side elements of the formwork, which are least exposed to the load from the weight of the monolithic structure, are allowed if the concrete coating has reached its maximum strength. It is worth being more careful when removing the load-bearing formwork of monolithic concrete structures.
This action must be carried out when all standards for achieving concrete pouring, the so-called design strength, are met: load-bearing elements of a monolithic structure with a span of up to 2 m - 50%; load-bearing structures of beams, purlins, vaults, crossbars and slabs with a span of 2 to 6 m - not less than 70%; load-bearing structures with a span of 6 m - no less than 80%; load-bearing structures reinforced with load-bearing frames - no less than 25%.
Return to contents