When building a house, every person thinks: how to build it so that the house will last for centuries, what to rely on when choosing materials? Thanks to this article, you will always know which brick to choose. She will explain in detail the main differences that need to be taken into account when choosing a brick for a plinth.
The base is a foundation that is located above ground level. The brick that is used when laying the foundation should not deform under different weather conditions under the influence of heavy loads. It should also look appropriate and match the architectural style of the house. Manufacturers offer a huge number of different types of material, but you need to find out which one should be chosen for the construction of the base.
Foundation characteristics
Scheme of a retaining brick foundation: 1 – Crushed stone, 2 – Brickwork, 3 – Drainage hole in the masonry, 4 – Concrete foundation.
The base of a brick building is masonry on one of the types of mortar: cement-lime, cement-sand or simply cement. The foundation has a pre-planned specific geometric shape, is installed in the ground, being the basis for the entire building. Its task is load perception, transmission and distribution.
The operational characteristics of the foundation include such parameters as rigidity, flexibility, average strength, resistance to chemically aggressive environments, biogenic factors, moisture, temperature and temperature changes. Based on this, it is recommended to lay the foundation in dry soil, not prone to heaving, with a low groundwater horizon. Compliance with construction technology guarantees an average service life of a brick foundation of 30-50 years.
The main advantage of the brick base of the house is the absence of monolithic elements in its composition, the installation of which requires special construction equipment. Brickwork can be arranged alone. The absence of a monolith determines the mobility and flexibility of the foundation: soil movement does not cause destruction. If increased rigidity is required, this can be achieved by using reinforcement. If a section of the foundation is damaged, you can replace the damaged area without much effort. Among the disadvantages, water permeability due to the porous structure of the material can be noted.
Advantages and disadvantages of a brick base
The main advantage of a brick foundation is the absence of volumetric monolithic parts that need to be transported and installed using special equipment. You can even make a brick base alone. In case of damage, it can be easily restored by replacing individual sections of the brickwork.
The absence of monolithic components also determines the flexibility of the foundation. Thanks to this flexibility, the brick structure does not collapse when the ground moves, but only loses its rigidity. The latter can always be increased by means of reinforcement.
Another undoubted advantage of the foundation is its variability. It can have any shape without restrictions, since during its construction there is no need to prepare specific types of formwork.
The main disadvantage of a brick base is its water permeability. The structure of the material from which it is made is porous, and moisture easily penetrates into it. As moisture accumulates, it negatively affects the operational properties of the foundation, reduces its stability and leads to freezing of the foundation structure.
How to choose the right bricks
Diagram of a brick foundation for a greenhouse.
The foundation is a structure that bears the main load of the entire structure; so there are some peculiarities here. Plus, the material used is different from what is used in the construction of walls and other structures. What material is better to choose for constructing the foundation of a future building?
- The main element of the foundation is brick. Therefore, its selection must be approached with special care. Only red, ceramic stone will do. Silicate does not withstand prolonged contact with moisture and is destroyed. The required amount of ceramic brick depends on the depth, dimensions, and volume of the foundation. The first parameter is directly related to the freezing point, which is different in each region.
- To determine the required number of bricks, you need the volume of the foundation, expressed in cubic meters. m, multiplied by the number of bricks in one cube of masonry (approximately 400 pieces of single material, including seams). For good foundation masonry you only need solid brick. The one with voids inside has higher moisture permeability and lower strength, so it cannot be used to build a foundation.
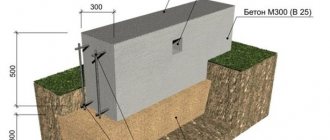
- Masonry must be done using a certain brand of brick. A stone with a strength of M300, M250 or M200 is best suited. You also need to pay attention to the frost resistance index F. It should be within 35-50 cycles. Water absorption should not exceed 15% (for bricks in direct contact with the ground). A single stone has dimensions of 250x120x65 mm, one-and-a-half - 250x125x88 mm. When purchasing, keep in mind that 1 pallet can hold from 300 to 350 pieces.
Main types of bricks
Sand-lime brick
Sand-lime brick is a material that is obtained by pressing a mixture of quartz sand, slaked lime and water, followed by firing in an autoclave. It has a characteristic light gray, sometimes white color, although with the addition of various pigments it can take on any other shades. This type of brick is not recommended for use in foundation construction, as it has a high degree of water absorption and can collapse over time. Experts recommend using it only for above-ground work.
Ceramic brick
Ceramic brick is a hollow or solid stone building material. It is made from clay with various additives and then fired in a kiln. Unlike sand-lime brick, this material is not so susceptible to the negative influence of groundwater and temperature changes, it has high bending and compressive strength. Therefore, provided there is dry soil and reliable waterproofing of the brickwork, ceramic brick is considered quite suitable for the foundation. For such work, red burnt solid clay brick is most suitable.
You can also use ordinary, thickened or modular ceramic bricks. An ordinary ceramic brick has indentations and weighs approximately 3.5 kg. The thickened one has a higher height, which is approximately 88 mm. And the last, modular brick, like a regular one, has a standard height of 65 mm, but is much larger in length and width 138x288 mm.
Clinker brick
Thanks to the technologies used in its production, this building material can rightfully be considered one of the most durable and durable. It is made from a special grade of clay with further firing in an oven at temperatures above 1200 degrees Celsius. Traditionally, clinker bricks are used for cladding building facades, as they have an aesthetically attractive appearance. But clinker bricks are also perfect for building a foundation, having resistance to external damage, frost resistance and, most importantly, low water absorption rates of 3-5%. The only drawback is that its cost is significantly higher than the cost of ceramic bricks.
Consumables for building a foundation
Foundations made of different materials.
First of all, it is a solution. It needs to be made from cement, preferably grade 500, and sand. Mix ratio – 1:3 (cement, sand). If you plan to lay the foundation of a house in places with a high groundwater level, then it will be better if you add special waterproofing additives to the solution. When laying the ground part, you can use cement-lime mortar, which has greater plasticity. When working below ground level, use only cement-sand mortar.
To strengthen the masonry, it is recommended to use masonry reinforcing mesh made of steel wire. For waterproofing, roofing felt laid in 1 or 2 layers is usually used. Waterproofing must be done twice; the first time when reaching the ground surface (between the foundation and the plinth), the second time - between the surface of the plinth and the wall. If the groundwater is too high, then additionally the surface of the foundation and plinth is coated with bitumen. In this way the waterproofing material is glued. In addition to consumables, you will need special tools and accessories:
- concrete mixer or container for preparing the solution;
- masonry trowel or trowel;
- a special hammer for splitting bricks (“pick”);
- building level, tape measure, plumb line;
- corner or profile pipe 25-30 mm for installing a vertical beacon;
- cord;
- shovels: shovel and bayonet.
Which brick is better to use for the foundation?
Recommendations on which brick is best to use when making prefabricated strip or column foundations from small-format materials are given in SP 15.13330 of 2012.
Masonry from red ordinary, facing solid ceramic bricks with a width of 51 cm or more or concrete blocks measuring 20 x 20 x 40 cm is allowed. With an unlimited budget, you can choose clinker stone with the highest possible moisture resistance.
For the basement part of the foundation, the requirements are much lower than for underground structures.
Types of bricks
Despite the variety of wall materials used for masonry, only red ceramic bricks and concrete wall blocks can be used in foundations. Foundation ceramics are classified according to the following criteria:
- dimensions – normal format (NF) 6.5 x 12 x 25 cm, double (2.1 NF) 14 x 12 x 25 cm, one-and-a-half (1.4 NF) 88 x 12 x 25 cm;
- appointment - front-line, private;
- frost resistance – F25, F35, F50.
Moreover, manufacturers guarantee the specified frost resistance values only for the basement part of the foundation masonry. Structures operating underground have a minimal service life (one and a half times less than reinforced concrete). The use of brick strip foundations is prohibited at a high (less than 1 m from the base) groundwater level (GWL) or the possibility of its seasonal rise.
Solid ceramic brick is the best choice.
The characteristics of solid concrete block vary. The strength of concrete is twice as high, frost resistance is F15 - F50, the format is much larger. Each block replaces 8 bricks, making masonry faster.
The dimensions allow masonry with a width of 40 or 60 cm to be laid without pinning. In the first case, you can save the construction budget.
The second option is more often used for deep belts, in which the walls of the underground floor experience serious lateral loads.
Solid concrete blocks
Attention! There are bricks measuring 6.5 x 8.5 x 25 cm (0.7 NF), made in Europe, single modules (1.3 NF) 6.5 x 13.8 x 28.8 cm, “three-quarters” 18 cm , “halves” 12 cm, “quarters” 6 cm.
For underground structures
The main criteria when deciding which brick is best to use for underground masonry are:
- strength - standardized only for grades M100 - M300 (2.2 - 4.4 MPa, respectively);
- water absorption – 6 – 14%;
- roughness – important in the manufacture of external waterproofing of masonry.
Ordinary stone is cheaper than facing stone; to reduce the construction budget, it is better to choose this option. The dimensions of the red brick solely affect the pace of construction of the foundation. Therefore, the format is not important.
When choosing a concrete block, the foundation construction time is reduced due to its large dimensions compared to even double stone. The disadvantages of brick foundation technology are:
- the spatial rigidity of a prefabricated structure is lower by default than that of a monolith;
- When waterproofing the outer edges of the tape and pillars, it is very difficult to ensure the tightness of numerous mortar joints.
Therefore, prefabricated columnar and strip foundations are often shallow or not buried. This is only possible on rocky, sandy or gravelly soils.
For plinth
With normal horizontal waterproofing of the foundation with 2 - 3 layers of rolled material, the load-bearing part of the base can be laid out of porous brick. Any materials are allowed in the facing layer, for example: silicate, hyper-pressed brick, slotted, hollow ceramics.
When deciding which brick is best to use, you need to consider:
- the base is an independent supporting structure;
- distributes uneven loads from main walls.
Therefore, it is still better to use solid concrete wall blocks or solid ceramic stone. Typically, standard NF sizes or one-and-a-half or double bricks are used to increase the productivity of masonry.
It is much easier to protect concrete blocks and brickwork from getting wet in the basement. It is enough to coat the surface with bitumen mastic and decorate the base with siding.
We recommend: How to make a brick plinth for a strip foundation.
What to look for when purchasing
When choosing bricks for the foundation, you need to pay attention to the accompanying documentation. The grade of stone must be higher than M150, frost resistance from F25, geometric dimensions must comply with GOST.
During transportation, unloading and storage, edges often break off, which is not a significant defect. In most cases, plaster waterproofing is used for brick foundations. Unevenness will only increase the adhesion of the protective layer.
When you tap a ceramic brick with a metal object, there should be a clear ringing sound, not a muffled dull sound. The ringing indicates the quality of the raw materials used, the correctness of the firing technology, and the absence of microcracks and voids.
Laying nuances
To increase the reliability of a brick foundation, several conditions must be met:
- whole brick - the masonry must be carefully tied by shifting vertical seams in adjacent rows, so it is necessary to select a whole brick, carefully transport it, store it in the building area, move it on site;
- reinforcement - in every 4th row it is necessary to tie the spoons/poke, use a wire masonry mesh with a cell of 2 x 2 - 5 x 5 cm;
- wetting - it is recommended to lower the brick into a bucket of water at the time of laying it on a bed of mortar;
- additives to the solution - a penetrating mixture will ensure moisture resistance of the seams;
- footing - unlike monolithic structures, brickwork is sensitive to unevenness of the base, the underlying layer of non-metallic materials, it is recommended to pour a 5 cm screed with a width twice the size of the strip or columnar foundation.
Experts recommend using an upper armored belt for all prefabricated foundations. It is poured into the formwork, after laying the reinforcement cage. The structure receives additional spatial rigidity.
Advice! Brick easily splits in any direction, so you don’t have to buy ¾, halves, ¼, which are more expensive. It makes more sense to use ordinary stone rather than face stone, which is not visible underground.
Thus, a brick foundation cannot compete with monolithic reinforced concrete structures in operational life and spatial rigidity. However, this option will save budget and construction time. It does not need to gain strength for 28 days; walls can be erected in just a week.
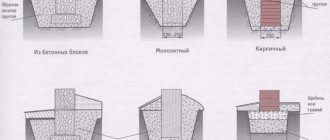
Main types of brick foundations
Construction of foundations from various materials: a – rubble; b – rubble concrete; c – brick on rubble concrete; g – brick; d – rubble on a sand cushion; e – brick on rubble; 1 – waterproofing layer; 2 – walls; 3 – lining.
- Columnar. It is a system of brick pillars installed in the corners of the future house, under the intersection of walls and load-bearing partitions. The pillars are tied, and a grillage is installed on top (these are beams that distribute the loads). This type of foundation makes sense when constructing relatively light structures: houses whose walls are made of panels, as well as wooden frame buildings without basements and ground floors. It is advisable to use a columnar base where there is a high probability of soil heaving in frost.
- Tape. This is a brick strip running along the perimeter of the future house. The strip foundation is laid under both external and internal walls. The thickness under load-bearing walls can be greater than under partitions. The strip base of the building allows you to create a basement or ground floor. This base design is successfully used in the construction of buildings with heavy load-bearing walls and reinforced concrete floors. When constructing a strip foundation in heaving soils, it is necessary to carry out reinforcement.
Tips for choosing bricks
Before choosing a plinth brick, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the general requirements:
- The material for the foundation plinth must be the same size and shape.
- The surface of the selected material must be smooth, without cracks or external chips.
- The color scheme of the basement brick should be the same.
- Availability of a certificate or technical passport indicating the brand of brick, the date of its manufacture and a list of technical characteristics.
With the correct selection of basement bricks, more heat will be retained in the house, and the building structure will be better protected from the penetration of cold air from outside.
Video example of the use of clinker bricks for a plinth: When choosing which brick is needed for a plinth, you should take into account the aesthetic component, that is, so that the selected material combines well with other wall materials of the building. For example, if you make a base from ceramic bricks, then the best combination will be walls with a smooth surface. All types of plinth bricks can be laid out with figured masonry, in which the brick itself will serve as a decoration for the plinth.
Stages of strip foundation construction
Construction of a strip foundation.
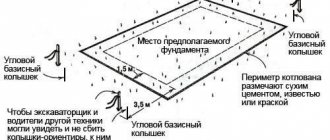
The tape type of base, due to its performance qualities, is most often used in the construction of country houses. To more accurately understand what type of foundation is needed, before construction begins, it is necessary to determine the depth of soil freezing and the groundwater level. Next, the site for the future building is marked. Taking into account the measurements taken, you can purchase the required amount of building materials.
- Preparatory work. They involve digging a trench for the foundation and arranging a 10 cm thick sand-crushed stone cushion. Next, you need to fill the bottom of the trench with concrete to prepare the foundation for future masonry.
- Bricklaying. You need to start from the corners. After the first row is laid, the cord is pulled from one corner to the other. Along the way, a reinforcing mesh is laid between the horizontal rows. Its end must be bent and inserted into a vertical seam. The cord helps to make the row evenly. After the foundation begins to rise from the ground, you can install a plumb metal profile pipe in each corner, or better yet, a corner. It is needed like a beacon to maintain the vertical position of the masonry. The standard seam thickness is 1 cm. Do not forget about waterproofing.
After the base is built, it is necessary to begin work on its cladding. The safety of the foundation, and therefore the service life of the entire building, depends on the quality of this event and the materials used. The ideal option is to insulate the basement and construct a ventilated façade.
The second no less important element is the blind area. Its construction is also necessary. The blind area prevents the penetration of external moisture to the walls of the foundation, thereby protecting it from destruction. If groundwater is close enough, it is better to make drainage to remove moisture from the base of the building. Measures to protect the foundation of the building, taken as a whole, will help ensure the long service life of the foundation, and therefore the entire house.
Features of the basement of a private house
When we are faced with the task of building a house, we need to think not only about what is meant to be used to assemble the structures of its foundation, but also about the base of the house.
The base of a house is a part of the wall that is located between the foundation structures and the load-bearing walls of the premises. The plinth may be partially recessed. Its upper part always protrudes above the ground by about a meter and a half.
The standard base is made of concrete. It is, in fact, a continuation of the foundation. However, the foundation is built exclusively from concrete, but not always the base. Sometimes it makes sense to build a basement out of brick.
It is easier to build a brick plinth with your own hands. It will take the same amount of time, if not less, to build. And the result will definitely please you.
Brick plinth also offers several advantages. It is worth understanding that in addition to the foundation, the house will most likely have a basement. An alternative to a basement is a basement. Making a basement floor with a properly selected foundation is quite simple.
Selection of base material
With a free choice of base material, priority is given to high-quality building ceramics. If ceramic brown brick is used as a consumable material, special attention is paid to the arrangement of moisture-proof cladding and horizontal foundation waterproofing.
In low-rise buildings, a standard building brick can serve as a consumable material for laying the basement part of the foundation of a house. The price per piece of this material, compared to special ceramics, is more affordable, which has a positive effect on the cost of the project as a whole.
The durability of the brick plinth is ensured by the effectiveness of external foundation waterproofing, the arrangement of the blind area and the creation of surface drainage, which prevents flooding of the foundation by melt water and rainfall.