Before you start building a house, you will have to prepare the foundation, which is the basis for any structure. One of the stages of constructing such a structure is a foundation pit, which can have different shapes. This work is responsible and quite complex. Why? It is necessary to accurately determine the depth of the pit, determine the presence or absence of a wall slope, and prevent soil sliding. Such work includes not only preparation, but also performing some calculations.
Construction of a pit for the future foundation.
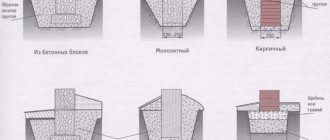
Types of pits
Schemes for laying out trenches, pits and embankments: a – pit; b – trenches; c – embankments on terrain without a transverse slope; d – the same on the slope; d – determination of the mark of the bottom of a deep pit.
Digging a foundation pit is a responsible task and does not tolerate errors. Today, all pits are divided according to the following criteria:
- presence or absence of slopes;
- the presence or absence of fastenings against soil shedding;
- inclined or vertical, stepped walls;
- pits or trenches (depending on the type of foundation, the presence of a basement, etc.).
To ensure that all work is completed correctly, the soil for the foundation is first excavated. This part of the work includes the following:
- carrying out an analysis of the characteristics of the soil, which is divided into rocky, clayey, sandy, etc.;
- analysis of the future structure (loads, weight of the structure, dimensions);
- calculation of pit depth;
- analysis of climatic and seasonal conditions.
Complicating factors
The most likely (and most serious) factor complicating the work may be groundwater, melt or rainwater.
If for a single pit or trench system it is enough to make a pit from which to pump out water as it comes in, then you can’t get enough pumps for a dozen separate pits.
To drain groundwater, the best option in such a case would be a drainage device.
If the bottom is filled with crushed stone, then the incoming water will not interfere so much
If this is not possible, the soil is removed below the mark by 20-25 cm, and crushed stone of fraction 10-40 or coarse sand is laid instead, compacting the backfill with a tamper. Now, even if water fills the pit, work can continue by pumping it out.
What calculations will need to be made?
Digging a pit with your own hands is a difficult job that requires preliminary calculations. To dig a recess under the future foundation correctly, you need to calculate the volume of soil and pit. The following formula is used for this:
V = H / 6 [(2a + a1)b + (2a1 + a)b1],
- where H is the total depth;
- a, b – side lengths;
- a1, b1 – lengths of the sides of the pit along its upper part;
- t – slope coefficient.
In addition to the volume of the pit, it is necessary to calculate the volume of backfill, which is obtained by subtracting the total volume for the underground part of the structure from the volume of the entire pit.
The depth of the pit depends on the type of soil; it is calculated not from the rough mark, but from the bottom.
Typical flow chart for constructing a foundation pit.
Before excavating the soil, it is necessary to determine the digging depth. This indicator will depend on the type of soil, but the total volume of all loads that are exerted by the foundation structure of the house is also of great importance. This pressure is calculated by the formula:
A=F/A(MH/m2), that is, the load divided by the area of the entire foundation base.
The sole area is calculated by dividing the load by the permissible level of ground pressure. Digging can be done with your own hands, without special equipment. This process includes several stages:
- removal of the fertile layer with a depth of approximately 40 cm;
- collecting groundwater and sediment (if any), organizing their rapid drainage to the side;
- excavation of soil to the depth of the calculated value. If the depth exceeds 1.25 m, then it is necessary to immediately install special support bars that will prevent the soil from sliding down the walls. If the depth is significant (from 5 m and above), then the stability of the steps in the walls is first calculated, but only a specialist can do this.
Excavation work when developing a pit.
Pits are temporary excavations
arranged for the construction of parts of a building or structure located below the surface of the earth.
The volume of excavation work when constructing a pit is calculated according to a project drawn up in accordance with the marks for laying the foundations and the bottom of the pit, the horizontal plan of the site and the accepted steepness of the slopes.
The stability of the vertical walls of the pit must be ensured by installing fasteners, or it is necessary to arrange slopes in accordance with Table 7.
Slope steepness - the ratio of its height to its foundation with a pit depth of no more than, m
Single-bucket excavators are most widely used for digging pits. (
backhoe, dragline, straight shovel
).
When choosing an excavator based on bucket capacity, you can use the recommendations in Table 8:
Monthly volume of soil processing, thousand m3
Excavator with bucket capacity, m 3
Backhoe excavator
develops soil below the standing level and therefore can develop pits and trenches in waterlogged soils. Work can be carried out in a dump or with loading onto transport. The disadvantage is the limited digging depth (up to 6.0 m). The use of these excavators is especially effective for developing trenches with vertical walls.
Excavator dragline
used for developing deep pits in dry and waterlogged soils. Working in a dump is especially effective. Cutting depth up to 20 m.
Excavator straight shovel
develops soil above the parking level and is used when developing pits mainly in dry soils. Due to the design features of this type of equipment, it is almost never used for working with dumping.
Excavator backhoe
and
the dragline
develops the pit using end or side penetrations. During end excavation, the excavator develops the soil on both sides of the axis of movement, depending on which side the machine is approaching from. With lateral excavation, soil development occurs on one side of the axis of movement of the excavator. When developing a pit with loading soil into dump trucks, end driving is more productive (Fig. 11).
A straight shovel excavator develops excavations by frontal penetration into vehicles that are placed directly in the face or slightly above the level of the bottom of the face.
Fig. 11. Schemes for developing pits of various widths with end
excavator penetrations, backhoe and dragline:
a – normal width; b, d – with longitudinal movement of the excavator by several penetrations; c – widened with the excavator moving in a zigzag; d – widened with transverse movement of the excavator.
2.1. Technological map for the development of a pit using an EO-4321 backhoe with a 0.65 m bucket
3
.
I. Scope of application
The technological map provides for the development of soil in a pit with a plan size of 37.41x17.17 m and a depth of 2.5 m for the construction of foundations (Fig. 12).
Construction is underway in Izhevsk. Climatic region I. Freezing depth -1.70 m. Soil – heavy loam, γ = 1800 kg/m 3, soil group II, slope steepness 1:0.5.
Fig. 12. Pit plan
The work is carried out in 2 shifts.
The work covered by the map includes: development and transportation of soil; cleaning the bottom of the pit.
P. Organization and technology of the construction process.
1. Before starting to excavate the soil in the pit, the following work must be completed:
Removing the plant layer of soil;
Layout of the site in the area where the pit is located;
Surface water drainage;
Construction of temporary roads;
2. Cleaning the bottom of the pit is carried out with a bulldozer and manually. When cleaning the bottom with a bulldozer, the soil is removed from the pit with an excavator, from the end of the pit.
3. Backfill soil is placed along one long side of the pit.
4. Excess soil is transported outside the construction site by KamAZ-5511 dump trucks to a distance of 3 km.
5. The pit is developed in 2 end penetrations.
6. Calculation No. 1. Determination of the volume of earthworks.
6.1. To calculate the volume of excavation work, the pit is divided into simple geometric shapes.
,m 3 (15)
where N
– pit depth;
– areas of the lower and upper base of the pit.
Also in volume V
= 0.5*2.5*(37.41*17.17+34.91*14.67) = 1443.07m3,
where H is the average depth of the pit;
F1, F2 – areas of the lower and upper base of the pit.
6.2.Scope of excavation work for constructing an entrance trench (for lowering a bulldozer):
,
where m` B
and
m
are the slope coefficients of the bottom of the trench and pit, respectively;
b
– width of the entrance trench along the bottom; H – depth of the pit, 30° – slope of the entrance trench.
6.3. Volume of soil when cleaning the pit:
, Where
S f
– area of the foundations at the bottom, m2;
h n
– amount of soil shortage by excavators.
With a bucket volume of 0.65 m 3, h n
= 0.15 m (with a bucket volume >0.65 m 3 we take
h n
= 0.20 m).
6.4.Volume of soil for filling the pit sinuses:
, where Vk is the volume of the pit; Vf – volume of foundations; Kor =1.07 – coefficient of residual loosening.
6.5. Volume of soil to be removed:
Pit volume Vk, m 3
Volume of soil when cleaning the pit V zach ,
m 3
Volume of backfill soil Voz, m 3
Sequence of work
Digging a trench or foundation pit is not an easy process. The most difficult part of the work is underground. When digging, you should be careful not to let the soil slide off the walls. The sequence of work will be as follows:
Scheme of types of trenches for the foundation.
- The fertile layer of soil must be completely removed. It cannot be considered load-bearing, since it is biologically active and can periodically change its volume greatly, that is, it cannot be used as a base for a foundation under any circumstances. The fertile layer is removed with your own hands using improvised tools or using heavy construction equipment - it all depends on the area of work and the depth of digging;
- if the foundation project includes a basement, then digging must be carried out over the entire area of the future structure. Therefore, it is impossible to do without special equipment. Of course, this will entail certain financial costs, but it is better not to use another method here. Excavation of earth must be carried out under the following conditions: construction equipment must stand from the edge of the trench at a distance of at least 70 cm, the entire volume of soil must be placed on the opposite side of the equipment.
- if the foundation is planned without a basement, then you can get by with a regular strip foundation. Then excavation is carried out only along the perimeter. A shovel is enough for the job; it wouldn’t hurt to have helpers. A similar design would be much cheaper.
Stage No. 4: Strengthening the walls of the pit
This is a mandatory measure for any pit, especially if the groundwater level at the construction site is high. The quality of the foundation, durability and safety of the building will depend on reliable strengthening.
The diagram shows the horizontal layout of the foundation.
The following methods are used to strengthen walls:
- – Cementing – used in dense buildings, if the structures are located in close proximity to each other. Thanks to this method, destruction of the foundation due to vibrations from nearby buildings is eliminated.
- – Sheet piling reinforcement – suitable for sandy and weakened soils, wetlands, on the banks of water bodies, and also if there is a high groundwater level. For this, a Larsen sheet pile is used, which is immersed in the soil before excavation and serves to strengthen the walls of the pit.
- – Bored piles are the most common and considered the most modern method. The role of enclosing and load-bearing structures is performed by prefabricated structures that are embedded in reinforced concrete or concrete. Thanks to this method, it is possible to construct the foundation at maximum depth.
- – The “wall in soil” method is similar to the previous method. Longitudinal reinforcement with an optimal cross-section is used, and reinforcement occurs using reinforced circles of small diameter.
After strengthening the walls, backfilling is carried out, which is necessary to prevent moisture from getting under the foundation and destroying it.
Stage No. 5: Backfilling
After constructing the foundation, the backfill process is carried out continuously. When the basement holes are filled, the floors are laid. The soil is laid in layers that should not exceed 10 cm. Backfilling can be done in two ways:
- Using mounted vibrating tampers or pneumatic tamping units.
- Manually, using hand-type rammers, hammers and carts for transporting soil.
It should be remembered that all work on the arrangement of the pit and foundation must include continuous quality control, corrective measures and careful reconciliation with previously approved documentation. This is the only way to build a building that will serve flawlessly for many years!
In this article, we examined the features and stages of working with pits during the construction process. We can conclude that this process is complex, responsible and labor-intensive. Therefore, in most cases, a reasonable decision is to contact a specialized company that develops and digs pits at a professional level. This will save you time, money and effort.
You can order the development and digging of pits of any level of complexity. Extensive work experience, a qualified team, the presence of powerful modern equipment, years of established work with the responsible authorities, prompt execution of the necessary documentation - will guarantee that the foundation pit will be equipped in the shortest possible time, and the quality of the work will not leave behind disappointments.
Features of digging a pit for a future foundation with your own hands
The foundation pit is a special part of the entire work that requires caution. The depth of the base will depend on the type of soil:
- for gravel and sandy areas – from 1 m;
- for sandy loam – from 1.25 m;
- for loam and clay – from 1.5 m;
- for especially dense ones – from 2 m.
Trench for the foundation.
To avoid shedding when digging with your own hands, you need to make the walls with a slight slope. For a wall height of 1.5 m, the following values are acceptable:
- for sandy soil: with a slope of 63 degrees the ratio is 1:0.5 and with a slope of 45 degrees - 1:1;
- for sandy loam: with a slope of 76 degrees – 1:0.25 and at 56 degrees – 1:0.67;
- for clay and loam: at a slope of 90 degrees - 1:0 and at 63 degrees - 1:0.5.
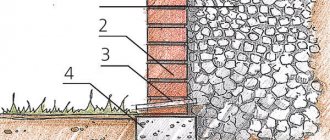
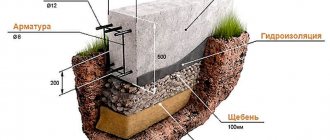
Often, builders use regular wooden supports before pouring. You can make them yourself; it won’t take much time. Such supports will help prevent the soil from sliding to the bottom. It is important to provide for filling the sinuses; it must be carried out in accordance with all requirements. Digging a pit requires strict adherence to all recommendations, but backfilling is also very important. It must be carried out so that the soil pressure is minimal. It is recommended to do backfilling in layers, the thickness of each layer should not exceed 25 cm. The soil should only be compacted manually, and starting from the foundation structure area towards the slopes. The blind area is carried out from the compaction point; at this stage, do not forget about waterproofing. Flat asbestos cement sheets are suitable for these purposes.
So, digging a pit for a future foundation cannot be done without preliminary calculations. First you need to determine what type of soil is on the site, what the digging depth should be, and whether there is a need to make the walls at a slope. Only if all conditions and preliminary calculations are met, the pit will take the correct shape and required depth. The work itself must be carried out in accordance with all standards.