An option for insulating a house without a basement along the perimeter of the structure. The goal of any house construction is a beautiful, durable, and most importantly warm structure where you can live for a long time and comfortably. The use of which will be required in the construction of various types of technologies.
The surface of the earth tends to freeze in the winter, so it makes sense to lay insulation immediately during the construction of the supporting structure. The easiest way to insulate the foundation from the outside is to use several types of insulation that are suitable specifically for your construction option.
In what case and how to use it, it is worth understanding in advance, at the initial stage of construction. It is better to carry out the work while laying the entire foundation and concreting the blind area. This can avoid unnecessary costs in the future, for example, on the development of soil around the perimeter. Let's look at all types of available materials and insulation step by step.
Leonid Zverev:
- Good afternoon. Well, first, let's figure out why there is no basement? Modern construction systems of modular or prefabricated houses do not initially include a basement
. From the heating engineering point of view, such a room, significantly deepened into the ground, is not required under current living conditions.
All communications are led into a specially designated room or annex, the so-called control unit, where the boiler, water filters or reserve tank are installed.
Let's return to the main question: there is a house, it stands on a foundation, why insulate it? In this case, the concrete base is in contact with the walls
, which are insulated and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
Concrete absorbs moisture in huge quantities. This does not harm the material itself; it does not collapse and retains its original strength. However, internally, the amount of heat from the walls and floor begins to transfer to the base, so to speak, trying to warm it up
. As a result, we get a problem: through the junction of the floor and walls to the concrete base, a significant amount of heat, so carefully accumulated inside the room in various ways, begins to escape.
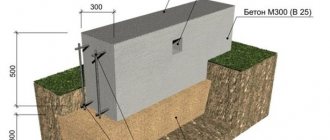
The most effective type of insulation is extruded polystyrene with a thickness of 5-15 cm.
installed outside the foundation. Such slabs are quite simple and quick to install and do not require special skills or professional tools. The joints between the slabs, as well as the unevenness of the foundation base, are filled with liquid foam in the required quantity.
If the building is located on a flat area and there may be cases of moisture accumulation under the base of the building, it is also necessary to take care of waterproofing. The hydrobarrier can be of several types: in the form of a rolled film coating, water-based cement materials, roofing felt or resin applied directly to the surface to be insulated.
Currently, a huge selection of liquid heat-insulating coatings
, so-called ceramic-based paints. Such materials simultaneously act as a heat insulator and prevent moisture from penetrating into the base.
In conclusion, I will say the following - an insulated foundation is not afraid of freezing during frosts, the floor covering will retain heat more effectively, and the lower part of the wall will never become moldy.
It is probably impossible to find a person who would not enjoy living in a cozy home. But after completing the construction of a home, many people have to deal with the problem of heat loss, both through the walls and through the foundation of the house. In this regard, the answer to the elementary question of whether it is necessary to insulate the foundation is obvious even if there is no base at the base. This must be done, and there are a number of good reasons for this.
There are several preconditions for which it is necessary to insulate the foundation even if it does not have a basement:
- climatic features of the region (due to sudden temperature changes, cracks may occur);
- maintaining heat inside the house;
- reducing heating costs;
- protection of utilities from moisture ingress;
- protection of building premises from penetration of low temperatures.
Materials for base insulation
Before you start insulating a house without a basement, you should figure out which materials are most appropriate to use in a particular case. Typically used as insulation:
- mineral wool;
- polyurethane foam;
- Styrofoam;
- expanded clay
There are two main types of insulation: external and internal.
External insulation of the base must be completed before the floor and walls of the future house are erected. The internal option is used only if the foundation and base cannot be insulated from the outside.
The need for insulation if there is no basement
When designing and constructing a strip shallow foundation, they are guided by the standards SP 50-101. In principle, there is no basement in the MZLF, but building rules allow the implementation of the project only if measures are taken to reduce swelling:
- ring drainage around the perimeter;
- replacing the soil under the belt base with non-metallic material;
- backfilling of the sinuses with crushed stone and sand.
However, even in this case, these technologies partially solve the problem - they do not allow heaving soils to become saturated with moisture. Therefore, the TSN MF-97 standards recommend insulating the blind area of the house with a horizontal layer of polystyrene foam 60–120 cm wide around the perimeter at a depth of 30–40 cm.
For all these construction cycle operations, access to the side edges of the MZLF tape is provided. Therefore, at the excavation stage, you can easily cover the outer edges with high-density extruded polystyrene foam. It solves several problems:
- eliminates the cold bridge - floors become warmer, heat loss is reduced;
- protects waterproofing from possible tangential swelling forces;
- prevents freezing of concrete - if there is no waterproofing or it is broken, the structural material will absorb soil moisture, which, when frozen, increases in volume by 9%, leading to the opening of microcracks in the foundation structure.
Attention! Taking into account the above, external insulation allows you to increase the service life of a strip foundation by 30 - 40%, regardless of the presence of a basement floor.
Permanent residence house
For constant heating, even if the building does not have a basement, there are several options:
- floor on the ground on top of insulation - sheets of high-density extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) completely eliminate heat loss; the ground under the cottage can freeze through the uninsulated foundation and base, which are cold bridges;
- floor on the ground without thermal insulation - the heat loss of the building through the ceiling is maximum, the ground under the house cannot freeze;
- overlap along beams - insulation is present between the rough and finished floors by default, ventilation vents are mandatory in the basement, the soil and the MZLF concrete strip are guaranteed to freeze;
- The floor slab is the option with maximum heat loss; all structures below the slab will always be cold.
Thus, if there are gaps in the outer layer of waterproofing, the concrete structures of a house operating underground (that is, in aggressive environments) can absorb moisture, which will freeze and create numerous small cracks inside the structural material. In addition, if the internal backfill is made with soil removed from the MZLF trenches, and not with inert material, there is a high probability of swelling of areas inside the MZLF tape. This leads to deformation and destruction of floating screeds, which are floors on the ground.
All problems for any specified case are solved by comprehensive thermal insulation:
- vertical - gluing the outer edges of the tape with polystyrene foam to the full depth + insulation of the base, inextricably linked with the thermal insulation of the facade;
- horizontal - insulation of the blind area 5 - 10 cm with a layer of polystyrene foam 0.6 - 1.2 m wide at a depth of 0.3 - 0.4 m.
Attention! Vertical and horizontal thermal insulation must be installed in a complex, since the base of the building is not only the foundation, but also the soil underneath it, adjacent to the MZLF on the sides.
Garden house without heating
In the absence of heating the house, most individual developers believe that it is impossible in principle to protect the foundation and adjacent soils from freezing. This is a serious mistake that reduces the service life of power structures by at least half. You can understand why thermal insulation is needed by considering the thermal contour of the house:
- geothermal heat – present in any area by default;
- horizontal insulation - allows you to retain the heat of the subsoil to prevent the soil from freezing;
- vertical insulation – protection of waterproofing + concrete structure from freezing.
Types of foundations and specifics of their insulation
In modern construction, different types of foundations are used, some of which have a base, while others do not. Each of them uses its own insulation technology.
Insulation of the strip base
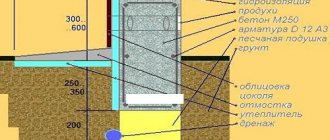
When insulating the strip foundation of a house, work should be carried out evenly along its entire length. For this, the design requires preliminary preparation. First of all, a trench is dug around the entire perimeter of the house, the width of which is 1 m, and the depth is identical to the depth of the base. Then the structure is thoroughly cleaned of dirt and soil residues. Neglecting this procedure is strongly discouraged. Since only a cleaned surface can provide good adhesion to the material. If necessary, the surface of the foundation can be leveled using a cement screed.
Before proceeding directly to the insulation procedure, it is necessary to ensure reliable waterproofing of the base. Why this is necessary is quite obvious - so that the insulation is not exposed to water and moisture. For this purpose, the surface of the base should be thoroughly coated with mastic. Alternatively, you can use any other waterproofing material. After all the preparatory work has been completed, you can begin laying the insulation boards. It is attached with special glue. If you want to achieve the best result, it is highly recommended to lay insulation material in two layers.
The procedures described above are performed along the entire perimeter of the base.
Insulation of columnar base
In order to insulate a column-type foundation, the first thing you need to do is make a base. Its main function is to protect the space between the base and the ground from the negative effects of moisture and freezing temperatures. To make a plinth, you will need to perform the following amount of work:
- dig a small trench under the house with a depth of 20 to 40 cm
- pour crushed stone or sand into the trench, the layer of which should be 5 cm less than the depth of the trench;
- attach special bars with grooves to the pillars of the base for attaching boards to them in the future;
- insert special beams into the grooves, on which the boards will then be attached;
- insert the boards into the grooves around the perimeter of the base;
- fill the lower part of the resulting structure with expanded clay.
By building such a base, you can be sure that your foundation is reliably protected from the cold.
Insulation of slab base
Insulating the slab foundation of a house is the most expensive procedure compared to those described. Most often, in this case , polyurethane foam is used to insulate the base.
, which is applied to the walls using a special device. It is most advisable to insulate the slab base before it is poured. To do this, a waterproofing layer is laid in a pre-dug pit (usually roofing material is used), polyurethane foam is placed, over which a screed is made. Next, reinforcement is laid and concreting is carried out.
Insulation of the pile foundation
A pile foundation is characterized by the presence of open space between the soil and the foundation, due to which heat loss can be simply colossal. There is no need to say that such a foundation should be insulated without fail, since otherwise dampness and cold will constantly reign in the house.
Such bases are most often insulated using polystyrene foam. The insulation technique itself occurs in several stages:
- the foundation grillage is waterproofed;
- laying a layer of insulation;
- carrying out finishing work.
When insulating the blind area is enough
There are many methods for carrying out such work; there is a more modern one. Spray liquid polystyrene directly onto the wall. If you decide to use this method, invite a company that has experience in this field. They will calculate all the insulation methods and choose the best option. They will draw up a project, find suitable material, and carry out all the necessary activities. A guarantee will be issued for all work performed.
Based on experience in the middle zone, where the winter temperature (average) does not fall below 20ºC, shallow insulation of foundations is carried out to 1.2 - 1.5 meters below ground level. If you need to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside, use the option of surface insulation of the blind area.
Such measures are quite sufficient, because the temperature of the earth itself at a depth of 2.5 meters does not fall less than 8º above zero. Based on economic considerations, basement insulation at such a depth is not carried out at all.
Insulation of the base from the inside
Quite often, those who are involved in building a house ask themselves why it is necessary to insulate the base from the inside if there is external insulation. There is no definite answer to this question, but if you want to ensure maximum heat conservation in your home, you should still do this.
The most commonly used materials for internal insulation are polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam. The latter option is the most preferable, since it allows you to obtain a monolithic thermal insulation layer, and the material itself has a long service life.
When drawing up cost estimates for construction work, individual developers often have the question of whether it is necessary to insulate the foundation of a house without a basement. The use of heat-saving technologies allows you to save a significant part of the cost of heating the room. Even if it is planned to build a house without a basement, insulating the base will help maintain a healthy microclimate in the house and protect the structure not only from temperature changes, but also from moisture.
Materials
For external insulation of the foundation of a house without a basement, modern materials are best suited:
- extruded polystyrene - slab;
- polyurethane foam - sprayed.
Each of the options and methods of thermal insulation has its own pros and cons. For example, to install slabs there is no need to hire qualified workers or purchase special equipment. And when spraying polyurethane foam, all the cracks and cracks in the concrete are filled. The layer is seamless, tightly adjacent to the surface of the foundation due to the high degree of adhesion (adhesion).
Both polymers have:
- good moisture resistance;
- durability;
- low thermal conductivity, which affects the small thickness of the insulating layer;
- high strength - when backfilling the insulation surface is not damaged;
- resistance to low temperatures;
- ease.
Although polystyrene and polyurethane foam are waterproof, they cannot replace waterproofing. Therefore, if there is a high level of groundwater in the area, the thermal insulation layer is additionally coated with bitumen mastic.
When choosing a material, it should be taken into account that if the permissible service life of the house turns out to be much longer than the durability of the insulation, then the owner will periodically have to change the thermal insulation. For this reason, experts do not recommend using foam plastic for vertical installation. It is, of course, cheap, but unreliable, as it can completely fall apart in 20-25 years.
What does foundation insulation provide?
Advantages of an insulated base:
- heat preservation in the house, warmer floors;
- gas consumption for space heating is reduced in winter;
- protection of communications;
- water will not freeze in the pipes.
When temperatures change, the material from which the house is built contracts/expands. This may cause cracks to form. Insulation helps to minimize the risks of violating the integrity of supporting structures.
External insulation helps protect the base from freezing; the dew point shifts towards the heat-insulating material, protecting the concrete strip from negative influences.
Why is insulation required?
To ensure that the atmosphere in the house is always comfortable and cozy, you should not abandon the thermal insulation of the foundation when constructing a residential building, even if it does not have a basement. We list several reasons explaining why it is necessary to insulate the underground part:
- seasonal temperature changes and periodic or constant soil moisture lead to the destruction of an unprotected foundation through the appearance of cracks and deformations;
- the freezing base of the house helps to cool the walls and floor, which is reflected in an increase in heating costs;
- thermal insulation protects communications from exposure to sub-zero temperatures;
- technological cold bridges lose their “efficiency”;
- due to the temperature difference, moisture may appear at the junction of underground and above-ground structures, and as a result, mold;
- Moisture-saturated heaving soils increase in volume when they freeze, resulting in frost heaving forces that have a destructive effect on the lower part.
From the above, it becomes clear that if the thermal protection of the foundation is not carried out in a timely manner, then no one will be able to guarantee long and problem-free operation of a house without a basement. There is no need to subject your household to the tests associated with cold floors and the appearance of condensation on the walls for the sake of momentary cost savings. Such frugality can result in large-scale and costly repair work.
If the foundation of the house is left without thermal insulation, then heat losses in winter can amount to up to 20 percent, even though the walls will be additionally insulated and the windows will be thoroughly caulked.
Insulation materials
The table shows the materials used for insulating foundations and their characteristics:
| № | Material | Characteristics |
| 1 | Expanded clay | It retains heat well and protects the foundation from moisture due to its porous structure that can absorb excess moisture. To achieve a better effect, insulation with expanded clay is carried out together with waterproofing of the base. |
| 2 | Expanded polystyrene | The most popular material for foundation insulation. Produced in the form of slabs, it is easily glued to the surface of walls and bases. Has high heat saving performance. Protects structures from destruction under the influence of moisture, temperature changes, and exposure to aggressive substances. |
| 3 | Polyurethane foam | Available in liquid form, applied by spraying onto the surface using a construction gun. After hardening, a monolithic coating with high thermal insulation characteristics is obtained. The composition fills all depressions, cracks, and pores on the base. Thanks to this method of application, it protects against the formation of condensation between the insulation and the foundation. |
| 4 | Bulk insulation from recycled materials | To save on insulation of a buried base, bulk insulation materials obtained from waste aerated concrete, foam concrete, and polystyrene foam are used. A waterproofing layer is laid on the outside, only after this the foundation is insulated. |
The choice of heat-saving material is influenced by many factors. You need to make a choice depending on climatic conditions, the proximity of groundwater, and the design of the house.
A good option for insulating the foundation is construction using permanent formwork made of polystyrene foam. It is quite expensive, but has a long service life and reliably protects the base from exposure to cold and moisture.
How to properly insulate
Before insulating the foundation, it must be reliably waterproofed. There are many ways to do this. Most methods are described in the article “Waterproofing the foundation.”
As soon as the waterproofing is carried out, they proceed directly to laying the EPS boards.
The diagram on the right shows what insulation looks like for a shallow strip foundation, which we discussed in one of the articles.
Laying the slabs begins from the bottom. They are attached to the foundation using bitumen adhesive or similar. Many manufacturers offer this glue, so it’s easier to check with the sellers.
The part of the EPS boards that will be located above the ground is additionally secured using special plastic dowels.
The part of the EPS slab located below the zero level is covered with plywood, boards or other similar material so that when backfilling the soil, the insulation sheets do not crumple under the influence of the earth.
Base insulation technology
The technology for insulating the foundation varies depending on the type of foundation and the heat-saving materials used.
Foundation insulation is divided into external and internal. The outer part of the base must be insulated before the construction of the base and walls.
If thermal insulation measures were omitted at the construction stage, insulation is done from the inside.
Thermal insulation of strip base
Many people ask the question why insulate the foundation of a house if there is no basement space. Moisture, penetrating through the pores of concrete, increases in size when freezing, which often leads to the formation of cracks.
The strip foundation is insulated with a uniform layer around the entire perimeter.
Step-by-step instruction:
- A trench is dug along the entire length of the foundation. Its dimensions should be: in depth, like a foundation, in width 80-100 cm.
- Clean the concrete strip from dirt, soil and dust.
- If necessary, the surface is leveled by making a concrete screed.
- Lay waterproofing from roll materials or treat the surface with bitumen-based mastics.
- The slab insulation is attached to a special glue.
When insulating the foundation with expanded clay, it is necessary to provide a drainage system to drain water from the base of the house. Expanded clay, due to its porous structure, is characterized by high moisture absorption, while it loses its thermal insulation qualities.
To install drainage, dig a trench at a short distance from the base of the house. The bottom of the pit should be located deeper than the base of the foundation. Cover the bottom with geotextile so that its edges touch the walls of the trench. Crushed stone is poured, pipes with a cross section of 10-20 mm are laid. They are covered with crushed stone on top. The protruding edges of the geotextile are folded so that they cover the drainage structure. A layer of sand is poured on top.
Expanded clay is poured to the level of the ground surface. It must be dry and clean, without foreign matter.
When using a material that is prone to increased moisture absorption as insulation, it is necessary to make a blind area. It will protect the expanded clay from getting wet during rain or melting snow.
Thermal insulation of pile foundation
In order to significantly reduce heat loss during the operation of the house, it is necessary to take measures for its insulation at the stage of construction of the pile-grillage foundation.
This type of foundation is characterized by the fact that there is a gap between the ground level and the floor of the house. In winter, the floor in such a house will be cold, and heating will be expensive. To reduce costs and create a favorable microclimate in the house, you need to insulate the grillage.
The grillage is a structure made in the form of a tape, connecting piles together. It takes on the load-bearing load from the house and distributes it evenly through the piles onto dense layers of soil.
At the installation stage of the piles, they are isolated from moisture. Roofing material or other material rolled into a pipe (with the rough side inward) is placed in the well. After this, the reinforcement is laid and the well is filled with concrete.
After installing the grillage, it is waterproofed and insulated. Most often, sheet polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam is used as heat-saving materials.
Insulation of slab foundations
The slab foundation has a large area, so its insulation is quite expensive. There is a lot of debate about whether it is necessary to insulate a foundation made in the form of a slab.
Heat-saving technologies make it possible to achieve a significant reduction in heat loss during the operation of the house. The investment pays off over time, and living in a warm home becomes more comfortable.
Insulation of the slab base is carried out after the bottom and walls of the trench have been leveled.
Step-by-step instruction:
- Lay strips of roofing felt overlapping by 150-200 mm.
- Sheets of polyurethane foam are laid on top.
- Fill the surface with cement screed.
- Install the reinforcement frame.
- The slab base is poured with concrete.
You must first carry out all communications, since after pouring the slab this will be problematic.
Thermal insulation of a columnar foundation
Before insulating the columnar base, a base is installed; it will prevent heat loss due to the gap between the floor of the house and the ground.
A trench is dug along the perimeter of the house, with a depth of 200 to 400 mm. Sand and crushed stone are poured into it so that the height of the layers does not reach the ground level by 50 mm.
They attach the bars to the posts and install the harness. After this, the surface is waterproofed and insulated.
Extruded materials
The use of extruded material for insulating the base of the house along the perimeter of the structure
. In cold climates, when the ground freezes to 1.5 - 1.8 degrees, there is a need to insulate all the concrete around the basement, as well as make surface insulation of the entire blind area. Expanded polystyrene fits all parameters, but it is not an economical option. But the service life is more than 50 years. Its density is 35 kg. per square meter, with a thickness of 50 mm, and moisture absorption is less than 3% per cubic meter, per day. Good parameters for insulating basements, semi-basements, plinths and concrete foundation slabs. It is also suitable for insulating blind areas. Work with it is carried out as follows:
- Prime the surface for insulation. Allow to dry for 24 hours.
- Coat the walls with bitumen mastic in 1-2 layers. The mastic must dry completely.
- Glue the sheets (standard size 0.5 x 1 m) at intervals using high-fix adhesive. After 2-3 days, holes are drilled for the fungi (a plastic dowel with a cap), and the dowels themselves are installed. Consumption of fasteners per 1 m² 7 − 10 pcs.
- Cover with a layer of mastic; the option of laying a special membrane is possible. The sinuses are backfilled, with layer-by-layer compaction of the soil. The sheets are installed above the zero level of the foundation, and subsequently the blind area insulation sheets are adjacent to it. Horizontal insulation under the concrete blind area is carried out to a width of 1.2 meters.
Important: Basement ventilation is a very important factor. If it is not properly arranged, the presence of capillary moisture from inside the basement or semi-basement is inevitable. Insulation of ventilation pipes is also carried out, but with rolled materials.
Blind area
Installation of the blind area is carried out after the completion of the main construction work on the construction of walls, roofs, installation of windows, doors, etc. It allows you to protect the foundation of the house from destruction as a result of frost heaving of the soil and exposure to humidity.
Markings are made and wooden stakes or steel rods are dug into the corners. A cord is pulled between them, which will serve as a guide during installation work.
Step-by-step instructions for installing the blind area:
- The area around the entire perimeter of the house is cleared.
- Remove the layer of fertile soil.
- Level the surface.
- Install formwork from boards. Supports are installed to prevent the structure from collapsing under the pressure of concrete.
- Pour a 5 cm thick layer of sand into the mold and compact it well.
- Cover with geotextiles, it will prevent concrete from seeping deeper.
- Rubble is poured.
- Mount the reinforcing frame.
- Concrete is poured into the formwork. It is advisable to fill in one go.
The width of the concrete path should be 200-300 mm greater than the roof overhang. An expansion joint is provided between the house and the blind area, which is subsequently filled with a mixture of sand and gravel.
You can watch the video on how to insulate the foundation of an old house with your own hands: To make living in the house comfortable and minimize the cost of heating the premises in winter, it is imperative to insulate the foundation. Materials for insulation are selected depending on the operating conditions of the building and the availability of funds in the construction budget.
Before you start designing the foundation, you need to decide on the structure of the basement. This is an important stage, since the type of support part and the depth of its placement depends on the decision whether to make or not to make an underground floor. Do-it-yourself foundation for a house with a basement is a responsible and costly undertaking, so the issue should be taken seriously.
The main factor that influences the decision to build a house with a basement or basement is the price. Most often, monolithic or is used for such construction. When doing work with your own hands, you may rashly decide that the cost will increase only due to the price of the material, but this is not the case.
Indicators that will affect the estimate:
- Excavation. The depth of the deposit increases. In addition, if there is a basement or ground floor, it becomes necessary to make a pit instead of a trench. When deepening the base of a strip foundation, it is necessary to take into account the angle of natural repose of the soil. This value shows what slope the walls of a trench or pit should have so that they do not collapse without additional reinforcement. The lower the angle of repose (internal friction), the more soil will have to be removed.
- Soil transportation. This factor follows from the previous one. The more material is removed, the larger the equipment and the more time it will take to remove it from the house construction site with your own hands.
- . The technology of this stage becomes more complicated. If there is no basement, it is enough to coat it with bitumen or use high-quality concrete. In the case under consideration, a waterproofing device made of more modern materials, such as linocrom, waterproofing, glass insulation, and membranes is required. To protect the waterproofing layer from destruction due to soil compaction and deformation, it is necessary to provide protection against mechanical damage. To do this, brick walls are erected or a layer of extruded polystyrene foam (penoplex) is fixed.
All these factors increase the cost of installing a strip foundation for a house with a basement with your own hands, so when making a decision, it is recommended to draw up a detailed estimate and reasonably assess financial possibilities.
Thermal insulation methods
There are two main options for protection: outside or inside. The first is implemented either when laying a new foundation before the installation of floors and walls begins, or is carried out on previously used structures when problems are detected. The second method is most often chosen when arranging basements, in order to achieve a good microclimate in them and avoid the accumulation of condensate. In other cases, there is no need to insulate the foundation from the inside; moreover, this practice is considered dangerous and leads to rapid destruction of the tape.
The method is selected based on the type of base:
- For columnar and pile structures, the section of the base (intake) and the blind area are subject to insulation. If there is a high risk of flooding, it is recommended to lay a layer of moisture-proof insulation under prefabricated supports made of concrete blocks.
- The Swedish slab technology is selected when laying a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation under the entire area of the house; in this case, it is based on a thick layer of Penoplex and can withstand any moving soil and does not depend on groundwater level. For obvious reasons, this is only possible when construction is carried out from scratch.
- When insulating the tape, several insulation methods are possible: vertical (for all external edges including the base), horizontal (arrangement of a blind area from 0.5 to 1.2 m wide at a depth of 30-40 cm along the entire perimeter of the house) and complex (combining these methods and guaranteeing maximum effect).
- When arranging unheated and rarely visited houses, all structures are subject to protection: blind area, base, sole, recessed part of the base and floors. Only such a scheme makes it possible to create a continuous thermal circuit and extend the service life of the foundation; in the absence of heating from the inside, destruction is possible even with reliable waterproofing of the tape and backfilling of the pit with non-metallic bulk materials.
It is important to understand the principle: when the foundation is not insulated, the degree of exposure to frost heaving and moisture increases. For this reason, areas of maximum loads are subject to protection - the base of the shallow belt, the outer side walls, and the blind area that receives precipitation. Internal insulation, with rare exceptions, is impractical, mainly due to a shift in the dew point and an increased risk of moisture accumulation in structures.
Not all materials are suitable for thermal insulation; taking into account the place of use, preference is given to durable, strong and maximum moisture-impermeable varieties: extruded polystyrene foam and sprayed polyurethane foam. The first is represented by slabs of a standard size, their thickness is determined by a calculation that takes into account the climatic conditions of the region (heat transfer resistance coefficient - tabular value), the width of the walls and the thermal conductivity of the insulation and the tape material itself. The recommended minimum for cellular types is 50mm.
If it is necessary to insulate the base and foundation that are already in operation, the work becomes more complicated; it is extremely important to carefully select the soil, without moving the base or damaging it. The scheme of action in this case is simple - the tape is released to the end or below the freezing level, insulated from moisture and cold, covered with finishing materials and filled back up. At the last stage, if possible, the blind area is insulated.
An alternative to cellular types are closed expanded clay granules, poured around the base or backfill and protected from mechanical loads by a layer of concrete. But this option is not recommended in areas with high groundwater level; if it is necessary to insulate the base, bulk materials are also poorly suited.
Optimal results are achieved when using sprayed polyurethane foam with a high cell density; it is not afraid of moisture and adheres to any surface; the only disadvantage of this method is its high cost.
The main enemy of the basement is water
In some cases, building a house with a basement with your own hands is impossible without additional measures that will protect the foundation from ground moisture. Before starting the construction of a house, you need to do detailed geological studies with the involvement of specialists. They will allow us to identify the exact level of groundwater location, the likelihood and frequency of its rise.
If the groundwater level (GWL) is located far from the surface of the earth, it is enough to provide the following types of protection from moisture:
- vertical (coating, lining with damage protection);
- horizontal at the level of the basement floor (closed with the vertical);
- horizontal along the edge of the foundation.
Important! The minimum distance from the groundwater level to the base of the foundation is 50 cm. If the water on the site lies less than 2-3 meters from the surface, difficulties will arise.
To protect the supporting part of the building from moisture at high groundwater levels, the following measures are provided:
- Gravity drainage is suitable for eliminating perched water in elevated areas. It is laid at the level of the sole or below and taken to the nearest body of water or to an open area.
- Forced drainage is used if it is necessary to lower water levels for flat or low-lying areas. In this case, the system is equipped with a well with two pumps (one main and one backup in case of emergencies). A device of this type of water reduction requires constant additional costs during the operation of the house.
- External insulation with pressure wall. It is a system of a vertical layer and a horizontal layer located in the structure of the basement or ground floor floor. The technology requires that the system be closed, that is, horizontal waterproofing is connected to vertical.
Important! The installation of drains of any type makes sense if the water rises during periods of heavy rain or flood. If the moisture level is constantly increased, the drainage system will not cope with the load.
How to insulate different types of foundations?
During the period of laying the foundation of a house, the question should not even arise: is it necessary to insulate the foundation?
If you are building “to last,” then, undoubtedly, the intended service life of the building will, first of all, depend on the strength of the foundation. And also - warmth and comfort in the house.
Let's consider how to insulate various types of foundations in order to protect the foundation from negative natural influences.
Shallow foundation
It is used in the construction of light frame buildings and has two types: strip and tile.
The insulation is placed at a distance of 1-1.5 meters from the foundation masonry, and between them a zone of non-freezing soil is formed.
Columnar foundation
To insulate this type of foundation, it is necessary to equip the so-called. a fence is a type of plinth, the main function of which is to protect the space between the soil and the foundation from moisture and freezing.
The process of installing the pick-up is labor-intensive , but during the operation of the building it will pay off.
This is done like this:
- You need to dig a shallow (200-400 mm) trench.
- Fill the trench one third with sand or crushed stone.
- Attach bars with grooves (slots, slits) to the foundation pillars.
- Insert special thin boards into the grooves.
- Fill the lower part of the structure with expanded clay and your foundation will be out of danger.
Monolithic foundation
An excellent basis for compact buildings without a high base, a very popular type of foundation among domestic developers.
The technology for insulating a monolithic foundation is the most expensive, as it is produced using polyurethane foam. But, despite the high cost of such insulation, it is used with the prospect that the costs will pay off in the future.
The cost of heating a house when using this type of insulation is negligible.
Pile-vital foundation
Buildings on such a foundation have one characteristic feature: an open space between the foundation and the ground, which always leads to significant heat losses. Insulation of the pile-vital foundation is mandatory, otherwise it will be very uncomfortable to live in the house.
Stages of insulation:
- Grillage waterproofing.
- Installation of the thermal insulation layer.
- Finishing work on the outer layer of thermal insulation.
Basement for the whole house
This option is the most common. When constructing, it is important to remember the following points:
- waterproofing (discussed in detail earlier);
- drainage system (installed even in the absence of the likelihood of flooding as a safety option);
- insulation (when laid below freezing is not required by standards, but is laid for additional protection);
- vapor barrier (provided jointly with waterproofing).
Penetrating waterproofing does not provide vapor control and is not recommended for new construction.
Basement under part of the house
An undesirable option that involves a lot of difficulties. You can’t do this without the professional help of a designer, so if you want to make a basement entirely on your own, it’s better to stick with the previous option.
There are two options for the location of the underground part of the house with a strip foundation:
- under an outbuilding, garage or protruding part of a building;
- under the construction site.
The construction of the first option should be given preference, since it provides greater reliability of the structure. In this case, one dangerous place arises: the connection of foundations laid at different elevations. Part of the main underground structure rests on developed soil, which differs in density from the existing one on the site.
Soils of different degrees of compaction are dangerous because they shrink differently. It is worth knowing an important thing: the house rests on the soil, and not on foundations. The structures simply transfer this load. If the density of the base differs in different parts of the building, cracks will appear, which are problematic to eliminate. The place where shrinkage cracks appear is the junction of the walls and foundations of the extension and the main part of the house.
To avoid unfavorable phenomena during the construction of a basement under an extension, the following methods are used:
- Creating a rigid structure that can withstand shrinkage. A detailed calculation of a strip foundation, like a cantilever beam, with the installation of additional reinforcement in the upper zone is required (usually reinforcement is installed evenly or with a larger diameter in the lower part). Only a designer can do this work. In this case, the location where cracks are likely to appear becomes unknown. They can form on any weakened area where errors (even minor ones) were made during construction.
- . To prevent the appearance of a crack at the junction of volumes with different depths, it is enough to make them independent of each other. An expansion joint is a gap, and the wall in its place can be either double or single. Double will require additional costs, but will be a more reliable solution. The gap width is taken to be at least 40 mm.
When designing a basement under a building site, not one weak point is formed, but several (the number of joints increases). A strip foundation is considered as a multi-span beam. To ensure reliability, perform the following actions:
- in the foundation along the entire building along the boundaries of the basement, a monolithic rigid belt is poured;
- perform thorough compaction of the soil backfilling the basement.
Important! The backfill soil must be identical in density to the existing foundation. Not more dense and not loose. If this condition is not met, uneven shrinkage will occur and cracks will appear.
Backfill compaction depends on the type of soil on the site. For sandy or loose substrates, sprinkling with water may be sufficient. If the house rests on dense soil, work is carried out in the following order:
- laying a layer of sand no more than 30 cm thick;
- its hydration;
- backfilling with a thin layer of crushed stone;
- compaction with a platform or weight;
- repeating steps from step one until the required thickness is achieved.
Height difference
It is worth talking about the weak point in more detail. When creating differences in foundation support marks, it is not recommended to do it in one go. It is better to divide the process into several stages:
- pouring a slab for the basement;
- raising the walls of the underground part by a third of the height (in a monolithic version or from prefabricated blocks);
- pouring a monolithic stiffening belt that will protrude beyond the basement walls by 60-90 cm;
- raising the walls another third of the height;
- pouring a reinforced concrete belt under the foundation strip (it is a continuation of the stiffening belt);
- production of tape (parts without basement);
- continuous reinforced concrete belt along the edge of the foundation.
The result is a stepped transition, which allows you to reduce soil compaction zones and better distribute the load. The foundation strip and basement walls can be made from either blocks or monoliths. In this case, it is important to perform shear calculations of the structure and lay additional reinforcement in the upper part of the cantilever protrusions.
Setting up a basement is a task that needs to be carefully considered. When deciding to arrange a room under part of the house, it is important to remember that the most reliable and less labor-intensive option would be the following: a basement under an extension separated from the main building by an expansion joint.
Advice! If you need contractors, there is a very convenient service for selecting them. Just send in the form below a detailed description of the work that needs to be performed and you will receive proposals with prices from construction teams and companies by email. You can see reviews about each of them and photographs with examples of work. It's FREE and there's no obligation.
Dreaming of building their own house, many people vividly imagine what it will be like in the end - how many floors, how many rooms, how much area it can occupy.
These kinds of questions are critical and the approach to construction directly depends on them.
One of these topics is whether the house needs a basement or a basement.
The basement gives many bonuses to its owner - additional areas for storing tools and pickles, and a boiler room can be installed there. And if you go deeper into the ground, you can even build a workshop, home theater or laundry room.
However, this kind of premises increases the cost of construction.
When choosing a building with a basement, you need to approach the topic of laying the foundation www.fundamenty-dlya-doma.ru quite seriously. After all, it is not only the basis of the house, but also heat and waterproofing. In this matter, you cannot save by using the cheapest option - you need to make a choice based on multiple factors, such as, for example, the type of soil, the severity of the proposed house or the proximity of groundwater. Details can be found on the website Fundamenty-dlya-Doma.ru
Which foundation is suitable for houses with a basement?
In the construction of low-rise housing, columnar, strip, slab and pile foundations are most often used. For the construction of premises with basements, columnar and pile options are not suitable due to the difficulties that may arise when constructing a basement.
Most often, in houses with basements, a tile or strip foundation is used.
When choosing from these two options, you need to evaluate the quality of the soil, as well as the proximity of groundwater. If the soil is not earthquake-resistant and water is close, then a single concrete slab is more suitable as a foundation.
What foundations can be insulated?
Due to the variety of designs, insulation of the foundation is possible for floating slabs, shallow and deep strips. The grillages do not have a base; the sides of the underground are decorated with a fence. Therefore, in buildings with a hanging grillage, foundation insulation is completely absent:
- the soil freezes completely under the base of the house
- There are no heat sources in the underground
- heaving forces have virtually no effect on piles
Attention: In the grillage, the outer edges of the underground structures are covered with insulation along the heads of the pillars. The fence is not insulated for the above reasons.
Depending on the design of the foundation, insulation schemes look like this:
- slab - side edges + blind area, under the sole polystyrene is laid only in an insulated Swedish USHP slab
- tape – blind area + outer surfaces MZLF + base part outside
- low grillage - similar to the previous case
When using a floor on the ground, insulation is usually included in the screed. By default, deep strips serve as the walls of basement floors. External insulation guarantees a shift of the dew point outward, after which there is guaranteed to be no moisture on the internal walls.
Tiled
The slab foundation is a single monolithic reinforced concrete structure, which is laid immediately under the entire building. Another advantage of this foundation is that it can support almost any weight of the building, and when groundwater rises, it rises along with the house.
The process of laying such a foundation comes down to the following steps:
- A hole is dug about half a meter below the expected level of the basement floor and filled with crushed stone or sand to a depth of 20-30 cm. The resulting layer is thoroughly spilled with water.
- Next comes a layer of concrete, preferably at least 5 cm.
- A layer of any waterproofing is laid (usually roofing felt)
- Another layer of concrete is poured.
- Another intermediate layer of iron reinforcement and thermal insulation material.
- It is covered with a third layer of concrete, but this time with a layer of at least 25 cm.
Having completed this work, you can begin to build the walls of the basement; they also need to be reinforced to increase strength and covered with waterproofing to avoid structural damage due to getting wet.
Why insulate the foundation, and is it possible not to insulate it?
Modern private construction involves the creation of a room protected from dampness and moisture. Therefore, even without a basement or plinth, foundations are usually insulated as profitably (cheaply) as possible. If you need a warm basement, then this question is not even worth asking. But when there is nothing below the first floor, they insulate it due to the formation of cold bridges.
Here's how it works. A proper private residential building is insulated over all areas, because these “bridges” can form where the walls meet the base. And destruction will begin due to temperature changes.
We come to the conclusion that as a stage in creating a personal home, this is a trifle. But a high-quality, thoughtful and durable residential building will be protected from moisture condensation, which accumulates at the joints, which leads to further destruction when freezing.
Tape
The strip foundation can be of two types - block, in this case the foundation is laid with ready-made bricks, or monolithic, that is, it is poured in the same way as a tiled foundation, but using formwork.
What is attractive about a block strip foundation is the speed and ease of assembly.
Monolithic strip foundations are most often used in the construction of private houses and other low-rise buildings with basements. During the laying process, a sand-crushed stone layer is first laid out, formwork is formed and concrete is placed into it. Next, the layers are repeated similarly to working with a monolithic foundation (waterproofing, concrete, reinforcement, thermal insulation and the final layer of concrete).
The strip foundation is quite reliable and its convenience is that it can be used in buildings of any shape and any size. Assembling such a foundation is much faster and easier than laying a tiled monolith. Although both methods are quite expensive and require skills and abilities from the performers.
It is worth noting that in houses with basements there is a danger of radon gas poisoning - it can accumulate in the lower underground floors of the room, getting there from the ground. To avoid this kind of poisoning, it is possible to bring the pipes out of the sand-crushed stone layer to the top during the process of laying the soil.