Types of lubricants
There are lubricants for dismantling foundation formwork by popular manufacturers:
- Formwork lubricant Emulsol EKS-A.
- Formwork lubricant Emulsol IM.
- ANGROL.
Emulsol formwork lubricant is especially popular in industrial applications.
Depending on whether this substance is used for industrial purposes or privately, it is customary to classify it according to the volume of the substance, so it can be either 20 liters or an EC barrel of up to 216 liters.
Types of formwork release agents:
- Aqueous suspensions. Typically presented as a mixture of water and lime or gypsum. The liquid product is applied to the mold, the water evaporates and a film of dry powder remains on the surface. The method is suitable for working with small volumes, pouring the foundations of dachas and private houses without vibration compaction. The use of mechanical means or intensive work destroys the protection, and lime and gypsum can deteriorate the surface of the concrete.
- Retarders. The idea of using retarders to separate formwork only works when pouring products without requirements for surface quality. The product slows down the hardening of concrete at the point of contact, but the depth of impact cannot be controlled. As a result, there is a chance of getting a not too smooth surface.
- Combined materials. Complex compounds that simultaneously repel water, slow down hardening, reduce porosity, and protect the formwork. The production of such products is too expensive, so combined formulations are not popular and are rarely found on sale.
- Water repellents. This is the largest group of products, which includes emulsol EKS-A, emulsol EKS-M and other lubricants based on salts of fatty acids. The composition is similar to machine oil with the addition of soap-like substances - the walls remain slippery for more than a day after treatment, the liquid has high adhesion to dry surfaces (wood, OSB, metal, plastic), and wet concrete material is separated without effort.
In fact, in the case of mass production of reinforced concrete products or high requirements for surface quality, the choice comes down to determining a suitable modification of the emulsol for lubricating the formwork.
Differences in lubricant composition
There are several types of lubricants based on their composition:
- Water based;
- With a combined base;
- With a substance that slows down the hardening of concrete.
- With a substance that repels water.
The first type is made from chemicals that are inert to concrete. They are relatively low in cost, so they cannot always effectively cope with the problem.
The second type is the most persistent. It does not delaminate within a week. Excellent adhesion to the surface. They are often reverse-purpose emulsions.
The third type introduces chemicals such as molasses or tannin. At the same time, complex regulation of the foundation setting process is noted.
The fourth type is made from a variety of oils, such as minsoal or salts of fatty acids, as well as the presence of the form lubricant EKS emulsol. They create a thin layer that repels water. At the same time, they may have disadvantages, such as overpriced.
Adhesive lubricant for high loads
How does adhesive lubricant work? Since this lubricant is intended for mechanisms to which it is impossible to force it during operation, the lubricant must have good adhesion (adhesion) to the lubricated surface. Once applied, it should remain on the surface for as long as possible and, ideally, not be erased from the surface at all during operation. It is also important that the adhesive lubricant displaces moisture and does not absorb dust and dirt - after all, often the mechanisms for which this lubricant is intended operate outdoors.
Special requirements are placed on its consistency. At the time of application, the lubricant must be liquid enough to penetrate hard-to-reach places, and after application it must thicken so as not to leak from the mechanisms that it is designed to lubricate and protect. This “duplicity” is achieved by using two components: the lubricant itself and a solvent, which gives the composition the necessary fluidity. When applied to the surface, thanks to the solvent, the lubricant penetrates into the most inaccessible places. The solvent then evaporates, leaving a lubricating compound on the surface.
Another requirement for an adhesive lubricant is temperature stability. The lubricant should not thicken excessively in the cold, depriving the mechanisms of mobility, and should not become too liquid when heated, so as not to leak out of the lubricated mechanism.
The annotation for the adhesive lubricant states that it has anti-corrosion properties. Does this mean it can be applied to rusty surfaces? Theoretically, there are no contraindications for applying adhesive lubricant to rust. However, the benefit of this is small. The lubricant will adhere less well to a rusty surface and will also begin to absorb solid rust particles. The lubricant does not contain special substances that slow down or stop corrosion that has already begun, and certainly does not contain a rust converter. In fact, protection against corrosion for an adhesive lubricant is just a pleasant bonus: since the lubricant displaces moisture and forms a fairly strong and durable film on the surface, it automatically protects the surface from moisture, atmospheric oxygen and other harmful influences.
What is meant by the high loads for which AXIOM adhesive lubricant is designed? In this case, high loads mean high intensity and long duration of operation. The lubricant adheres well to the surface, so frequent application is not required. It should be taken into account that the lubricant is not intended for use at high speeds of relative movement of lubricated parts, at high (above 200°C) temperatures and at very high specific pressures in the contact patch. There are special lubricants for these specific conditions.
Go to product →
How to apply formwork lubricant yourself, and what is the consumption?
Spray application of lubricant
Anyone can use lubricant, the main thing is to follow the application sequence:
- Application should occur immediately after the formwork has been assembled. This way you can reduce the consumption of substances.
- Previously laid concrete must be protected with film or tarpaulin from oil.
- The substance can be applied with rubber brushes or rollers, but then the consumption will increase. It will be more economical to use a spray gun for these purposes.
- To make the layer evener, it is worth using a gun at a distance of one meter from the boards; it is possible to use different nozzles.
Instructions for use of Protective Agent for Concrete Equipment BETAX-MK (BETAKS-MK) (Germany):
A protective product that dissolves concrete for concrete plants, concrete mixer trucks, concrete pumps, as well as formwork, scaffolding, and other construction equipment.
CHARACTERISTICS BETAX-MK protects concrete plants, concrete mixers, concrete pumps, construction equipment, formwork, crane buckets and concrete pavers from adhesion of concrete and mortar. By protecting work surfaces from concrete sticking, BETAX-MK also dissolves hardened concrete layer by layer. The process takes from several days to several weeks depending on the thickness and density of the hardened concrete.
EFFECT OF THE PREPARATION BETAX-MK forms a protective film on concrete equipment and machines. At the same time as anti-stick protection, BETAX-MK penetrates into the pores and destroys hardened concrete. Spraying continues until the concrete is saturated. Then the concrete becomes loose and is removed with water under pressure or with a spatula. At the same time, the surface being treated is lubricated. This prevents concrete, mortar and putty from sticking to metal and painted surfaces. Machines are protected from corrosion. The BETAX-MK protective film begins to work immediately after application and is water-repellent.
APPLICATION BETAX-MK is applied to the surface of concrete equipment by spray immediately after washing with water under pressure, directly onto the wet surface. The drug remains effective throughout the working day, even in concrete plant mixers. After applying the BETAX-MK film to the working surfaces of the equipment, concrete adhering to them can be easily washed off with a high-pressure washer. The protective film can last for several days, provided that it is not subjected to strong mechanical stress. For auto concrete mixers and concrete pumps, it is recommended to treat only the rear part of these machines, which is in contact with the concrete.
STORAGE CONDITIONS BETAX-MK can be stored in its original packaging for an unlimited time in an unheated room. Do not allow water to enter or add to the preparation, which may complicate its application.
SAFETY MEASURES If the drug gets into your eyes, rinse them immediately with water. Do not spray the drug near an open fire.
Capacity: - 10 liter canister.
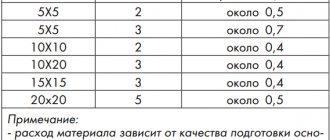
Approximate consumption is 0.2 liters per 1 square meter of surface.
Call tel., (909) 152-35-35 and.
zetolan-mek 3
Production of concrete fences
The production of such a widely demanded product in modern construction as concrete panels, the so-called “Euro fence”, is carried out using the vibrating cassette casting method according to 2 different technological schemes:
- Instant demoulding;
- Expositions.
Despite the seemingly minor differences between these casting methods, the difference in the end result is enormous. Since the instant formwork method involves the use of the most durable form-matrices, precise selection of the consistency of the filling mixture, mandatory uniformity of filler size and the presence in production of a large number of special formwork pallets.
The material for the manufacture of mold-matrices is fiberglass and a powerful metal frame, which makes this product as durable as possible with load-bearing capacity, practically unlimited working life and a weight of at least 50 kg. Despite the considerable weight, working with these forms is not particularly difficult, but requires the performer to be in good physical shape and a certain dexterity.
Production of Euro fences using the instant formwork method
Equipment for the production of concrete fences using the instant formwork method provides that the number of formwork pallets must be equal to the number of concrete sections produced per work shift multiplied by two.
The technological process of manufacturing Euro fences using the instant formwork method can be divided into the following stages:
- A fully prepared matrix mold is installed on a functioning vibrating table, into which the required volume of concrete mixture is loaded, after which the excess concrete is cut off using a special rule designed to level the pouring mixture and thereby bring its level to the same level as the edge of the matrix mold;
- After that, reinforcing elements are placed on the vibrating pouring mixture, followed by their recessing under the influence of gravity to the intended center of the product;
- Upon completion of the vibration compaction procedure, determined by the absence of air bubbles on the surface of the potting mixture, two physically strong performers with a deft movement turn the matrix mold with the finished product onto the stripping pallet for its subsequent setting and strength gain;
- Then the matrix mold is thoroughly washed from adhering concrete, lubricated no less thoroughly and placed on a vibrating table for the manufacture of the next product.
Release agent for polyurethane molds
Release agent is an anti-adhesive coating based on wax and silicones diluted in a mixture of solvents, intended for the production of polyurethane products in metal or polymer molds. Mold release agent forms an elastic, ultra-thin film on the surface of the mold with high adhesion to the base.
Features of the use of release agents
The use of lubricants allows you to quickly and without damage remove polyurethane products from molds.
One treatment is enough for several fillings of polyurethane foam systems, which allows you to speed up the production process and save money. Buying release agents for the production of products from rigid polyurethane is the optimal solution when working with substrates made of materials such as: 1 - metal; 2 - glass; 3 - gypsum; 4 - elastomers (rubber), etc.
Release agents are used to create an anti-adhesive coating on molds in the production of products from rigid polyurethane foam (sandwich panels, shells for thermal insulation of pipes), elastic products from polyurethane, automotive components and furniture. For the manufacture of a heat-insulating shell, Izolit-210 lubricant is used; when working with rigid polyurethane foam, MB-84 lubricant is used.
Release agents: benefits of use
The main advantages of these release agents are: •creation of semi-permanent coatings with the possibility of multiple recesses;
- easy application with a brush and spray; - wide range of operating temperatures - from 20 to 100: - small thickness of the anti-adhesive coating - about 5 microns. — products have clean, non-sticky surfaces.
The use of lubricants reduces the cost of products, because they do not need to be modified or thoroughly cleaned. Molds also do not require excessive cleaning due to the low thickness of the coating - order and see!
Description of supplied products:
— Release lubricant MB-84 is used in the production of products from rigid polyurethane foam, as an anti-adhesive coating applied to the surface of casting (metal and polymer) molds. Metal barrels with a volume of 50 liters and 200 liters. Weight: 35 kg; 150kg (net). — Release lubricant “MB-120” is intended for use in the production of polyurethane products as an anti-adhesive coating applied to the surface of casting (compression) molds, flanges, forming and locking equipment in the production of pre-insulated pipes, for application to vertical surfaces and surfaces with negative slope. - Izolit-210 SM-1 Lubricant is used as a separating layer in the production of heat-insulating shells. Spilling according to the customer's request (there are no standard spills); — Izolit-210 SM-3 Lubricant is used as a separating layer in the production of furniture parts and building decor. 50 kg in container; — IZOLIT-12 lubricant is intended for molding products from elastic polyurethanes, in particular, sealing rings for automobile air filters and products from elastic “integral” polyurethane foams. Supplied in containers of 35 kg and 150 kg (net). You can find out technical information about MB brand release agents here.
DESCRIPTION AND SCOPE OF APPLICATION OF LUBRICANT FOR CONCRETE MOLDS EMULSOL VK-1
Lubricant for reinforced concrete forms emulsol VK-1 (TU 0258-003-53855500-03) is an oil-containing liquid intended for lubrication of metal forms and formwork in the production of reinforced concrete products and structures. Prepared from purified waste oils.
VK-1& emulsols wet metal surfaces well and adhere to horizontal and vertical surfaces, ensuring ease of formwork removal and a clean, contamination-free surface of concrete products. Lubricants are non-toxic and do not have an unpleasant odor.
Depending on the viscosity of the oil, there are four options for emulsol VK-1:
- Emulsol VK-1 is a universal lubricant based on medium-viscosity oils of type I-20: for all types of shapes, molding and hardening methods.
- Emulsol VK-1A based on high-viscosity oils. For severe modes of forming (glass-type molds) or stripping (pressing), where a thick layer of lubricant is required.
- Emulsol VK-1Ch on low-viscosity oils. Designed as an analogue of imported low-viscosity lubricants, with the possibility of spraying through imported spray guns.
- Emulsol VK-1SV is prepared from the above emulsols VK-1 with the addition of “Emulsifier SV” (TU 0257-011-53855500-2016). The emulsifier additionally reduces anti-adhesive properties, improves the surface quality of reinforced concrete products and almost completely eliminates corrosion of the mold metal.