How to make a columnar foundation from concrete blocks?
For a frame or wooden structure, the most rational foundation is considered to be a columnar one.
The main advantage of arranging supports for a structure in the form of pillars is the simplicity of the technology and a minimum of preparatory excavation work. The most common and fairly reliable materials for constructing foundation pillars are small-piece solid concrete blocks. You can quickly build a columnar foundation from 20x20x40 cm blocks with your own hands; the technology is available for non-professional execution. An important factor in favor of using foundation blocks can be considered cost: the price of one high-quality product does not exceed 50 rubles.
Types of columnar foundation
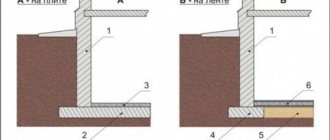
There are various classifications of foundation types made from columnar supports. Foundations are distinguished by the shape of the pillars: round columnar, a base with square supports, and pillars with a rectangular cross-section. According to the method of constructing the foundation, monolithic pillars are distinguished - with digging a trench, installing reliable formwork, pouring a concrete mixture, and a foundation using prefabricated technology made of bricks or blocks.
Let's learn more about the nuances of how to install a columnar foundation with your own hands; a video fragment is presented below.
Columnar foundations are classified by the depth of the pillars underground. The deeply buried type is installed on clayey or heaving soil areas, with the column located below the level at which the soil freezes in winter, about 1.5 meters.
Installation of a columnar foundation for a frame house with a slight depth is advisable at a depth of no more than 0.5 meters - it is installed on a sand bed. It can also be mounted on a gravel bed when there are sandy and heaving soils. Another type of columnar foundation, when the supports are not buried. This foundation is ideal for light-weight country houses, and is most often used on sandy soils.
Blocks for foundation pillars: basic requirements
The main criteria for self-construction of a house or other structure are considered to be the availability of understanding of construction processes, as well as the possibility of using simple, lightweight and small-sized materials. Wall blocks made of monolithic concrete are the most appropriate material for building foundations, subject to the following conditions:
- optimal dimensions: 400 mm length, 200 mm width and height;
- geometric shape - a regular parallelepiped with precise angles and dimensions;
- a monolithic concrete block should weigh within 35 kg;
- the structure of concrete can be rough, but smooth, without chips, growths, cracks and potholes;
- voids in foundation blocks are unacceptable;
- concrete must gain strength of at least 70% of the design value, that is, lie from production to use for at least 28 days to gain natural strength;
- a simple check of quality and strength: when a block is lightly hit with a hammer, it bounces off, and when dropped from a height of 1 m to the ground, the block does not receive damage.
Plan and layout of the building on the site
According to the rules, the breakdown of a building on the ground for the construction of foundations should be carried out along the axes of the building. But in practice, it is easier to arrange the dimensions of the building along the outer perimeter. You should not plan “by eye” or by drawing the outline of the building on the ground using the Pythagorean theorem for angles.
Hiring a specialist or renting geodetic instruments, theodolite, level, range finder and the like will be inexpensive, but will save you from troubles and additional costs during construction.
Foundation marking
It is recommended to mark the locations of foundation pillars according to generally accepted average norms and rules:
- foundations - pillars at the corners of the building are required;
- additional pillars are installed at the junctions of walls and partitions;
- the optimal distance between pillars is 2 - 2.5 m, maximum - 3 m, minimum - 1.5 m.
Do-it-yourself columnar foundation for a frame house
Initially, strictly vertical holes with a depth of 1.5 m or more are drilled to lay the foundation pillars. In the case of clay soils, such work cannot be carried out during the rainy season.
At the next stage, you can simultaneously pour both the pillars and the grillage, or alternately, but the concreting process as a whole should take no more than 24 hours for good adhesion of the individual layers.
This process is carried out in parallel with the connection of the reinforcement frame for the pillars, having decided on the reinforcement scheme.
The height of the reinforcement bars must necessarily reach the bottom of the pit, but free ends 50 cm long must remain. After installing this frame in the hole (it is desirable that the rods rest against the concrete solution to prevent the corrosion process), the pouring is carried out directly.
In this case, the ends of the reinforcement are bent at an angle of 90 degrees and are used to stitch the grillage.
Having installed the grillage formwork, you should tie up the reinforced frame of it, and insert it into the formwork, and then tie it to the rods of the pillars. This method of fastening is more reliable and rigid than using welding. Before pouring the grillage itself, install studs to secure the strapping beam.
If the grillage is low, you can strengthen it by backfilling; if it is high, you can immediately install the formwork.
The organization of embedded holes for the so-called vents is carried out using a regular 100 mm pipe.
Concrete should be poured in layers of 15 cm with each layer completely compacted. This is very important to prevent the formation of voids that are destructive to the foundation. The consistency of the concrete should also be uniform.
Please like (thumbs up) and support our channel. You can also subscribe to our channel SUMMER BUILDER so as not to miss new articles.
Construction of columnar foundations
Approximate step-by-step instructions for foundation work:
- When laying out a building on the ground along the external projection, marking cords are pulled.
- Along the entire perimeter of the structure, a layer of plant soil 15-20 cm thick and 50-60 cm wide should be removed, offset to the outside of the building. This is necessary for the subsequent device for collecting the base.
- The locations of the foundation pillars are marked with pegs in the center according to a pre-compiled sketch plan for the layout.
- The excavation depth for constructing shallow foundations is usually no more than 40 cm.
- With deep foundations (for example: below the freezing depth), the use of blocks is irrational due to the difficulties encountered in laying the blocks and the increasing volume of excavation work to facilitate high-quality installation.
- The soil, if possible, is removed in an area minimally larger than the cross-sectional dimensions of the pillar. Typically, a columnar foundation is arranged square with each side measuring 40 cm.
- The bottom mark of each hole must be the same for all pillars; the mark is checked using a level or other methods.
- The preparation or cushion for the blocks is usually made of a sand and gravel mixture. Only sand bedding can be used.
- Compaction of the underlying layer is carried out using a manual tamper made of logs. The sand layer can be compacted well by simply pouring excess water.
- The first (bottom) row of two blocks is laid directly on a sand-gravel bed or on a leveling layer of cement-sand masonry mortar.
- The gap between the blocks is filled with a solution about 1 cm thick.
- The laid row of blocks is covered with mortar and the next row overlapping perpendicularly is laid on it.
- Similarly, with overlapping, all rows are laid to the desired level.
- Cement-sand mortar is prepared at the rate of 1 part of M400-500 cement and three parts of sifted sand. Water is added in the amount necessary to create a plastic thick consistency of the solution.
- The top mark of the pillars is checked. It must be the same for the entire system. If necessary, it is possible to add leveling layers of mortar; in some cases, the top row can be laid out of red solid brick.
- An anchor bolt is sometimes inserted into the seam of the top row for subsequent fastening of the wooden frame
- The last stage is the installation of roofing felt waterproofing on bitumen mastic covering the top row.
Video: DIY frame house on blocks
How to do
So, all calculations have been completed, materials have been prepared. Now you can proceed to the actual construction of the columnar structure. This is not difficult to do and does not take long. In addition, this option is perfect for those people who do not have much experience in the construction industry.
Site preparation
Before building the foundation, it is necessary to carefully prepare the site itself. To do this you will have to use the following plan:
- Remove all debris and top layer of soil from the site . When performing the second point, it is necessary to remove a layer of soil to a depth of 18-20 cm.
- Level the surface.
- Mark the site according to the plan . For these purposes, prepare wooden pegs and drive them into the soil at the corners of the future house. Pull the cord through them and measure the accuracy of the markings according to the project.
- Mark the places where you will need to dig holes for tables . Recesses should be located at every corner of the future structure, as well as in those places where partitions and walls intersect. There should be a distance of no more than 1.8 m between each pillar.
- Using a special drill, dig holes.
The video shows how to make a columnar foundation for a frame house:
Foundation sole
If the construction of the foundation will take place on sandy and gravel soil, then level the bottom under each foundation and fill it with a cushion of small crushed stone. Next, compact it tightly. Fill everything with liquid cement. The thickness of the finished concrete base will be 20 cm. These measures are sufficient for the construction of a frame house. The formwork is installed even before the concrete base is completely dry. It is extremely important not to miss this moment.
On clay soils, it is necessary to prepare a bed of gravel or sand. In this case, it should be 40 cm wider than the body of the base. After laying out the material, it is watered with water and compacted. The thickness of the pillow will be 25 cm. The blocks are installed directly on the pillow. For a frame house there is no need to reinforce the base. But this article will help you understand what a pile screw foundation looks like, and how you can make it yourself.
The video shows the base of a columnar foundation:
Formwork
To reduce costs and speed up work, it is necessary to use inventory, ready-made panel formwork. Thanks to its prefabricated panels, it is possible to change the dimensions of structures and the degree of angles. In addition to boards, moisture-resistant plywood, iron and plastic can act as formwork. The boards should be narrow so that they do not crack and become damp. So before installing, moisten them with water.
Columnar foundation formwork
If the soil is dense and dry, and the walls of the recess are not crumbling, then you can forget about the formwork. Roofing material is laid along the perimeter of the recess so that water from the solution does not seep into the ground. There is no need to remove the roofing felt further, as it will act as waterproofing for the supports. Asbestos pipes installed instead of formwork should also be left in the ground. But what is the required consumption of bitumen mastic for waterproofing the foundation, and how it should be used, this article will help you understand.
There is also a simpler and more cost-effective option for constructing formwork. Using roofing material, form it into a pipe of a size that is equal to the size of the pillars indicated in the project. To prevent the roofing material from unfolding, it is necessary to wrap it with tape around the circumference from the outside.
Installation of the roofing felt slab is carried out vertically on the pillow. To prevent it from moving, it should be fixed with knocked down wooden planks.
Reinforcement and pouring of concrete
Reinforcement of the poured base is carried out by a frame. It is made from 4 steel stubbles, the size of which is 10-12 mm. Intercept them every 25 cm with wire clamps. This will prevent the reinforcement from diverging on the sides. You can replace the reinforcement bars with a pipe that is installed in the center.
Reinforcement and pouring of concrete
Fill the bottom of the formwork with mortar. Its thickness is 14-20 cm. While the solution has not yet dried, install a pipe core in the center. The frame is installed so that a distance of 2 cm from the walls is maintained between the reinforcement bars.
For filling, use M200 mixture. It includes sand, gravel of 3 different fractions and water. The mixture is laid in 30 cm layers and then compacted. When the pouring has been completed, you need to check the installation horizon. If the top edges of the pillars are not the same height, then you will have to balance the height using a grillage. To do this, use 1 part cement and 2 parts sand. The formwork remains intact for 7 days. It will also be interesting to learn how the framing of a frame house on a strip foundation occurs.
Waterproofing and grillage
After removing the formwork, it is fashionable to move on to insulating the pillars from moisture. For these purposes, coating or roll materials are used. The most commonly used materials are roofing felt, fiberglass, liquid glass and resin. To fill the spaces around the structure, it is necessary to use clay. It will be laid in a layer of 30 cm, and the loan will be compacted.
Waterproofing and grillage
A grillage is a lintel or belt that serves as a connection for the upper parts of the pillars. It is performed to give the pillars stability and protect individual bases from shifting. You may also be interested in learning about how to strengthen the foundation of a wooden house.
Pickup
This is a type of plinth that serves to eliminate the distance between the supports from the frame to the ground. Thanks to the fence, it is possible to protect the structure from the penetration of animals, precipitation, and is also an opportunity to maintain a stable seasonal temperature.
Picking up a columnar foundation
When building a frame house, a columnar foundation is often used. This is one of the simplest and cheapest ways to obtain a strong and reliable foundation. And although its construction is not that complicated, it is better to entrust this matter to specialists if a person has no idea how to make calculations, what materials to choose and how to directly carry out construction work. Read a separate article about a pile foundation with a grillage.
Columnar foundation made of blocks - where to use them
Of all the known construction options, the most inexpensive and reliable is the construction of a wooden house, bathhouse or utility structure, the basis of which will be a wooden frame erected on a columnar foundation made of blocks. It should be noted that this type of foundation does not imply the use of blocks or other reinforced concrete analogues that differ in significant mass. Let's talk about how to make your own block foundation from elements whose mass does not exceed thirty kilograms.
Advantages and possible disadvantages of a columnar foundation
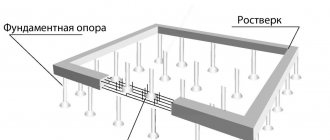
A columnar foundation is a simplified version of a pile foundation. The structure is a network of supports installed around the perimeter of the walls and in places of greatest load. The maximum step between supports is 2.5 m. All pillars are connected to each other by a grillage (horizontal strapping). Columnar foundations for frame buildings are used in 2 types: monolithic concrete (made by pouring into supports) and prefabricated (constructed from ready-made blocks or stones). Despite the fact that the structure is constructed without completely pouring concrete over the entire perimeter, such foundations have a number of advantages that make the structure reliable and durable.
Columnar foundation for a frame house
Advantages of a columnar foundation:
- Costs less than tape analogues;
- Can be made by yourself;
- Quickly erected;
- Its construction does not require heavy equipment;
- Easy to repair;
- The poles can be installed at any time of the year, including winter.
The disadvantages of the design include a large amount of manual work (if there is no drilling equipment) and the need for additional insulation of the floors, since the frame structure practically hangs in the air.
Blocks for columnar foundation
For this purpose, block material is used in the form of monolithic elements cast on a vibrating machine or press from a concrete mass of m100 - 150.
You should not try to make blocks yourself - purchasing them is much easier and cheaper. Moreover, you will need no more than five dozen pieces for the foundation.
To construct a columnar foundation made of blocks, elements with dimensions of 20 x 20 x 40 cm are used. And there are reasons for this:
- the parameters of the block indicate a small mass of material. Taking into account the filling component used in the manufacture, the weight of one stone can be 30 – 32 kg. This makes it possible to carry out installation work without the use of special equipment;
- A brick press and standard molds are used to make blocks. The result is a cast block, which is significantly stronger in strength than analogues produced by handicraft methods;
- the successful dimensions of the material create the opportunity for simple laying out of foundation columns and leveling the plane without trimming the supporting tops.
- Roughness is allowed on the block surface, but it must remain smooth and not have chipped areas, cracks, growths and potholes;
- void spaces in the block are not allowed;
- After manufacturing, the block must gain its design strength within four weeks.
Stage-by-stage execution of work
Step-by-step instructions for constructing a columnar foundation made of blocks are as follows:
Preparation
A plan for the future facility is being prepared, on which the locations for the pillars are marked. As a rule, they are located under each corner section and under the intersection points of the walls. In a straight line, the distance between two posts should not be more than two meters when the design solution includes a grillage made of metal or wood. For a reinforced concrete grillage, a distance between supporting elements of up to three meters is allowed. If this condition is not met, then manifestations of a deformation nature will occur.
According to the drawn up plan, the need for building materials is clarified using mathematical calculations.
Let's move on to marking work. To begin with, we outline the two most distant marks, which will serve as guidelines for the dimensions of the structure.
The diagonals are measured, the supports for the main and auxiliary purposes, and the columns for the partitions are marked. The markings are carried out along the axes of the future walls: the pegs are placed outside the building area.
Excavation
We continue to build a columnar foundation from blocks with our own hands. We begin to dig holes measuring 1.2 x 1.2 m and a depth of 1.5 to 2 m under each pillar. To speed up the process, you can rent a motor drill. The pits are prepared in such a way that after laying the blocks their upper levels coincide.
At this stage of work, it is recommended to install communications and dig trenches around the perimeter intended for arranging drainage and insulating the basement.
A pillow arrangement is provided. It doesn’t have to be done on sandy soil, but in other areas it won’t be superfluous to install a cushion. A twenty-centimeter layer of sand is poured onto the geotextile material, wetted and compacted. After this, a crushed stone layer of the same height is arranged. Having compacted the pillow, it is necessary to arrange a footing. If the groundwater is close, you should fill the crushed stone with a layer of forty centimeters, which will help maintain the geometry even with excessive moisture.
If a non-residential structure is being built, then the load-bearing platforms can be abandoned and the blocks can be laid on sand. But it should be remembered that the base of a columnar foundation made of concrete blocks must be at least 40 x 40 cm.
Sole device
To expand the base, the foundation is mounted on reinforced concrete slabs cast into formwork structures. At this stage there are certain nuances:
- the parameters of the slab must be twice the cross-section of the column in order to compensate for lateral impacts from heaving soil;
- the waterproofing layer of the sole will significantly extend the service life of reinforced concrete;
- It is better not to use crushed stone, as its sharp edges will break through the waterproofing material.
For this reason, many people prefer to build concrete bases from thin concrete mixtures.
To protect against groundwater, a drainage system of smooth perforated pipes is installed. They are placed in ditches, wrapped in geotextiles and sprinkled with crushed stone, then covered with soil.
Block laying, concrete pouring, waterproofing
When constructing a columnar foundation made of concrete blocks, a sand-cement mortar mixture is used. The posts are connected to the sole with a reinforcing rod running through the center.
Masonry work is carried out as standard. Dressing is necessary for each row. To do this, take several reinforcing rods, connect them with knitting wire, and place them in a hole. Concrete is poured in layers of thirty centimeters and compacted. A half-meter pin is installed at the top of each column.
When carrying out masonry work, it is necessary to control angles and horizontal lines.
If the design specifications provide for a grillage, then in the last row a reinforcement fill is installed, which is necessary for connection with horizontal beams.
If a non-residential building is being built, then the blocks can be laid without connecting them with mortar. In accordance with the technology, the pillars are laid out to a height of 0.5 - 0.8 m. For this purpose, formwork is arranged, into which concrete is then poured.
The blocks do not require time to settle; their edges can be waterproofed immediately. The surface of the stones is treated with bitumen or epoxy compounds. A carpet made of roofing felt or polyethylene materials is laid around the entire perimeter of the sole. The edges should be clamped so that when pouring the mortar mixture, the insulating layer does not move under its weight.
Grillage installation
This type of foundation is used on non-heaving soils, is buried less than a pile foundation, and is significantly subject to lateral movements. When building a light structure, the tops of the columns are not fastened together, but when arranging a residential building, you will need a grillage.
Its reliability improves the stability indicator by distributing the load effects between the support pillars.
If you need to create a practical monolithic grillage made of reinforced concrete, you will have to install a formwork structure and create a reinforcing frame. The concrete solution is poured at a time, and at the same time it is compacted with vibrators.
After stripping, the edges of the grillage are protected with a waterproofing layer.
Several types of grillage are known:
- slabs connecting pile heads;
- tapes holding the tops of the posts together.
Ground and buried grillages are easier to install, because the soil plays the role of the lower shield in the formwork.
Pickup
This is the final touch in arranging the foundation. The fence is a wall that hides the distance from the ground to the grillage. Concrete solution is poured into a ditch thirty centimeters deep and 10-20 cm wide. Subsequent construction work is carried out after the concrete has hardened.
At the end of the work, a layer of waterproofing material is laid. The roofing felt material used to cover the pillars is excellent for this.
Foundation for a frame-panel house
Question:
Hello! One company ordered a two-story frame-and-panel house measuring 6*4. In the basic configuration they have such a foundation. Reinforced tiles 40*40*5 and blocks 200*200*400 and they simply install the whole thing on the ground. As far as I understand, it’s better not to put it on bare ground, at least make a sand cushion. There are 12 points under this house, that is, 12 slabs and 12 blocks. Or make a pile-screw foundation? Or leave it as is and just add a sand bed? Please tell me what to do. The dacha is located in the Smolensk region, near the city of Gagarin. But I don’t really want to spend money on an expensive foundation. Thank you!
Maxim, Moscow.
Answer:
Hello, Maxim from Moscow!
It is difficult to unequivocally answer your question about the foundation for a two-story frame-and-panel house measuring 6/4 meters.
Everything ultimately depends on the place where the house is built and the characteristics of the soil underneath it.
The Smolensk province is large, the places in it are different, and I’m not talking about the soil at all, even on 8 acres it can differ significantly at a distance of 6 meters.
It is clear that everything comes down to the despicable metal. The cost of a point foundation made of tiles and concrete blocks is tens of times cheaper than a pile-screw foundation.
Let's talk about this topic together. First of all, about the input data. You write about 12 support points at home. Accordingly, 12 tiles and 12 blocks of the sizes you specified. Given the size of your home, this is clearly not enough. For a very light one-story frame-panel utility block, this quantity could be enough. For a two-story house - under no circumstances.
According to all building regulations, supports should be located at a distance of about one and a half meters from each other. Sometimes they are placed every 2 meters, but such gaps between them can no longer guarantee one hundred percent reliability of the stability of the structure. In your case, this is possible with a certain arrangement of the blocks, when along the 4-meter side of the house the blocks are laid longitudinally and not across.
That is, take a sheet of paper and draw a sketch of the foundation. With three support points along the 4-meter width of the house, it is necessary to have 5 support points along its 6-meter length. Consequently, there are 12 reference points along the perimeter of the walls. But don’t forget about the supports for the floor joists, and there will be at least 3 more of them. Otherwise, 4-meter-long joists will only rest on blocks under the walls and sag at such a length, not to mention 6-meter long joists.
In addition, when constructing your house, the corner support points and the intermediate 6-meter-long ones in the middle are usually made not in one block, but in two. And considering that the block has a height of 0.2 meters, this is completely insufficient for a home. The base of the foundation (that is, the part of it that rises above the ground) is never made as such. In a snowy winter, it will be covered with snow; the height of the snowdrifts near Gzhatsk, that is, Gagarin, can be up to half a meter. Your frame beam at home will get wet with all the ensuing consequences.
Yes, and support subsidence is very likely. More than once I had to observe this in houses that had stood for ten years, when they, having sunk the supports, simply lay on the ground with their foundation.
Therefore, at a minimum, the blocks must lie on top of each other to achieve at least 0.4 meters in height.
Let's skip all these calculations and just say that you need to have 15 tiles and 46 blocks. And not 12 and 12 at all.
And taking into account the blocks and tiles under the porch and the fact that some of them will fall apart during transportation, you will have to bring about 20 tiles and more than fifty blocks to the site. If something happens, there will always be somewhere to put the extra ones.
Next, we’ll talk about the construction site and the characteristics of the soil under the house.
To do this, you need to have the best possible understanding of these very important and significant things. Ideal soils are sandy and evenly distributed over the entire construction area, which has no slopes and is located at some elevation in relation to the surrounding land.
In such areas, the foundation is placed, which we discussed above. And it is placed as follows - they dig holes approximately to the depth of a spade bayonet in order to remove the top fertile layer of soil. The said sand is poured in a layer of at least 10 centimeters or a little more. It is spilled with water, compacted, leveled. The tiles are laid in such a way that their surface protrudes above the surface of the ground by 3 - 5 centimeters, that is, by the thickness of the tile.
Then, either one block is installed on the tile on top of another (more often using mortar than without it), or the first row of two blocks folded together, then the second row, with an overlap (the joint is perpendicular to the bottom one), in the corners and in the middle of a 6-meter wall. Waterproofing is laid on the upper surface of the support.
Sometimes it is possible to install a similar foundation on other soils. But without examining your site, I cannot speak about such an assumption. For more qualified advice and consultations, you need to invite a specialist builder. You can, of course, wander around the area yourself and see if there are similar foundations in buildings of the same type as your house. And how they behave for several years after construction.
As for the pile-screw type of foundation, today it is “all-weather” and is installed practically without any in-depth study of the soil characteristics. Especially on slopes. Of course, it must also be installed in compliance with the recommended technologies. That is, strictly according to the level, appropriate depth, priming of surfaces, pipes of a certain diameter, metal wall thickness, filling the cavity with concrete, installing upper brackets, etc.
If the contractor company (the one that is going to build your house) can guarantee you that for three to five years they undertake to accept claims from you in case of deformations of the foundation and the house, then agree to its cheap version of point supports made of slabs and blocks. Only they do not give such guarantees, and if they do, they are reluctant to comply with lawsuits, if by that time they do not cease to exist at all.
Many clients, of course, choose cheaper foundation options for “average lousy soils,” although after a few years they sometimes have to deal with some problems (but not always!). Correcting the distortions then most often falls on their shoulders.
So it’s up to you to decide on the type of foundation. If you still choose block construction, then in your contract with the company, include clauses on adding a compensation layer of sand under the tiles and increasing the number of supports and blocks. According to the above calculations. But this is in my opinion, and then you know.
Good luck!
Construction in Moscow and Moscow region
We work with a guarantee! Wide range of construction services.
Foundation, walls, ceilings, roofing, turnkey! +7 (905) 797-20-34
luxurycomfort.ru
Other questions on the topic of repairing house foundations:
- Repairing the foundation of a house on a slope
- Which foundation to choose for a stone house
- What kind of foundation for a 6 by 8 log house?
- The panel house sank along with the block foundation
- How to raise a foundation on a slope
- How to connect the old and new foundation
- Foundation creep: what to do?
- Repairing the foundation of an adobe house
- Waterproofing the log house from the foundation
- What kind of foundation for a house made of timber 150
- Pouring a new foundation and boulders
- Stability of a house made of crossbow stone on tires with concrete
- Uneven foundation under the log house
- Repair of a broken strip foundation
- Raw foundation
- Extension to a one-story panel house
- The pile foundation is walking
- Basement made of concrete
- Strengthening a columnar foundation on heaving soil
- Insulation of the veranda base
- How to fix blocks on a slab
- Foundation for part of a semi-detached house
- How to connect a basement and strip foundation
- Closing the base of a columnar foundation
- Filling the armored belt
- Completing the foundation for a wooden house
- Basement of a house on screw piles
- Distance from the ground to wooden structures
- Which foundation to choose for a foam block extension
- Dampness in the house on the foundation blocks
- Strengthening the foundation for the second floor extension
- Selection and orientation of the foundation for a house on a slope
- Waterproofing foundations in high groundwater
- Strengthening the columnar foundation
- Water seepage under the foundation
- Uneven gaps between the foundation and the frame
- Armobelt for a house made of wood concrete
- Column foundation problems
- Leveling the foundation for a timber house
- Cracks at FBS seams
- Why did the reinforced concrete piles bulge?
- Repair of the basement under a panel house
- New foundation on top of the old one
- Topping up an old strip foundation
- How to make a columnar foundation for an extension
- How to increase the width and height of the foundation
- Strip foundation for a timber extension
- Tire foundation
- What kind of foundation to make on a slope
- Strengthening the foundation
- Strengthening foundation blocks and waterproofing
- Choosing a foundation on sandy soil
- Ground floor on a slope
- How to raise a house in a hole
- The top of the brick foundation leaned
- Stages of pouring the foundation and plinth
- Strengthening the foundation of an old house
- The foundation made of asbestos-cement pipes is cracking
- The foundation burst
- The columnar foundation under the timber house was skewed
- Options for using brick fragments
- Concrete foundation in winter
- Replacement of the foundation and repair of a wooden house
- Recessing the basement floor
- Foundation for a house made of arbolite blocks
- Replacing the foundation under a timber house
- Increasing the height of the block foundation under the house
- Foundation for a two-story house with an extension
- Strengthening the grillage on bored piles
- Soil collapse under a house on a slope
- The block foundation under the timber house is sagging
- The pillars under the frame house were knocked out
- Raise a 2-story house from a cylinder
- The foundation for the timber is wider than necessary
- Cost of repairing a columnar foundation
- Strengthening the foundation of an old cinder block house
- Link the old foundation to the new one
- Strengthening bridge piles
- Strengthening the columnar foundation
- The foundation is smaller than the log house
- The gap between the foundation and the trim
- Raise the foundation under the finished log house
- Replacing a broken foundation in a swamp
- The foundation covered with slabs is crumbling
- Foundation for a cabin 3 by 6 m
- A new house on the foundation of a burnt one
- Inclined blind area
- Cracks in asbestos foundation pipes
- Replacing concrete blocks with sleepers in the foundation
- Strengthening concrete piles under the house
- Increasing the strip foundation under the frame
- Foundation for a timber house and frame veranda
- Choosing a foundation for a house made of wood concrete
- Foundation for a garage with an attic made of blocks
- Strip foundation for a frame house
- How to strengthen a pile foundation on clay
- Bathhouse foundation size
- Deepening the foundation for the basement floor
- Columnar foundation for individual housing construction
- Garden house on swampy ground leaning
- Foundation for a house made of shell rock
- Lay the foundation for an old extension
- Foundation at the drop
- Repair of old brick foundation
- Foundation for an extension made of reinforced concrete sleepers
- Is there a need for a blind area under the terrace?
- Strengthening the foundations of the house and extension
- The foundation of pipes is walking
- Gas connection to a 6 by 4 frame house
- Retaining wall as a foundation
- Complex foundation vents
- Raise the house
- Reconstruction of a strip foundation or pile
- The corner of a frame house sank
- Strapping on a foundation made of reinforced concrete piles
- Foundation for a house on pillars
- Foundation for a house made of polystyrene concrete
- Pour a strip foundation onto an old rubble foundation
- Pour a foundation for an adobe house
- Slab foundation on loam for a block house
- Is it possible to pour a new foundation on an old one?
- How to strengthen an old rubble foundation
- The FBS foundation subsided
- Repairing the foundation under a brick house
- Is a grillage required on piles?
- Foundation with a basement for a timber house
- There are no vents in the low base
- Replacement of the foundation and crowns of an old log house
- What is the best way to make a foundation for a house on a slope?
- Adobe foundation
- Screw piles for a two-story frame
- Repairing a sagging corner of the foundation
- FBS foundation
- Block foundation on a slope
- Make vents in the finished foundation
- Reconstruction of the foundation on quicksand
- Bundle of monolith layers
- The foundation is smaller than the size of a log house
- Screw foundation for a house made of wood concrete
- Foundation waterproofing FBS
- Blind area around a log house without a base
- The corner of the log house sank, what should I do?
- Foundation for walls made of permanent formwork
- Foundation for a garden log house
- Raise and slightly move the country house
- Raise an old wooden house
- Should I tie foundation piles under a log house?
- Screw pile foundation for a block house
- How many years will a brick foundation last?
- Foundation for a country toilet
- How to connect a bored foundation with a rubble foundation
- Foundation for a house on a slope
- House on a slope - problems
- Insulation of the foundation base with penoplex
- Foundation for a bathhouse base on screw piles
- How to repair a foundation
- Replacing the foundation under a house with an extension
- The armored belt of the foundation burst
- A pipe burst inside the foundation
- Insulation of the foundation base
- The foundation pile was squeezed out
- Foundation around an old house for a new house
- Foundation for the fifth wall of the log house
- Foundation for a heavy frame
- Forgot to waterproof the log house from the foundation
- Tying a pile-screw foundation
- Are vents needed under reinforced concrete floors?
- Top up the old foundation for a new building
- Walking veranda without a foundation
- What to make a high and economical foundation from
- Pile foundation made of asbestos pipes
- The foundation, two corners and the wall of the house sank
- Option for insulating an existing foundation
- Part of the foundation sank
- Joining the foundations of a house and an extension
- Waterproofing the foundation - forgot to do it
- The new strip foundation has cracked
- How to cut an opening for doors in a FBS foundation
- Unfinished foundation
- Expansion joint between foundations
- Leveling the foundation with a brick plinth
- Foundation for an extension made of arbolite blocks
- Horizontal waterproofing
- Log house larger than foundation what to do
- How to connect foundations at different levels
- Strengthen the foundation under a new house
- Foundation, crushed stone cushion
- The foundation of a timber house is cracked
- Foundation slab against dampness
- Lifting a panel garden house
- Replacing an old columnar foundation with a new one
- How to pour a foundation in water
- How to add a foundation to the middle of a house
- Brick pillar under a sagging beam
- The gap between the log house and the foundation is like a vent
- Step of the pile-screw foundation under the timber
- Used sleeper foundation for a bathhouse
- Foundation for a frame extension
- Foundation made of FBS blocks for a two-story brick house
- How practical is a 200 mm foundation?
- Foundation for a bathhouse made of sleepers
- The strip foundation collapsed
- Replacing the lower crown with a foam block and raising the foundation
- Foundation for a house made of aerated blocks
- Strengthening the foundation for an attic extension
- Pile-screw and shallow foundation
- Level the foundation from asbestos pipes under the barn
- Foundation for facing a finished house with bricks
- Find a foundation repair team
- FBS foundation joints are cracking
- Strengthening the brick foundation
- Squeezed out by FBS - how to fix it
- How to level the foundation surface
- Strengthening the old foundation of a cinder block house
- Adding asphalt chips to concrete
- Unburied foundation in the Far North region
- Reinforced concrete blocks or screw piles for a country house
- Foundation option for a wooden house
- Replacing the foundation under a garden house
- Foundation under an old house for a new house
- Foundation made of wooden sleepers
- Need advice on how to raise a house
- House partially without foundation
- Leveling the foundation level
- What kind of foundation is there for an 8 x 8 log house?
- How to lift an FBS block onto another FBS block without equipment
- Foundation with a plinth on a slope
- The log house turned out to be smaller than the foundation
- Asbestos pipe foundation for a panel house
- Strengthening a sagging foundation
- The foundation is collapsing
- Foundation for a bathhouse made of bolts 40 20 20 cm
- What kind of foundation is needed for a permanent residence frame house?
- How to use an abandoned foundation
- Reconstruction of the foundation of an old wooden house
- Different foundations for the house and extensions
- Air vents in a house under construction
- How to lay FBS for the foundation of a brick house
- How to level and build up a strip foundation
- Foundation and ground floor made of reinforced concrete sleepers
- Lay a foundation under an old log house
- How to strengthen a brick house
- Pile head foundation
- Insulation of the base and foundation
- Retaining wall on a sloped area
- Weak strip foundation
- Combining FBS and strip foundations
- Breathing of the foundation under a log house
- Plinth made of concrete slabs on a columnar foundation
- How to increase the width of a strip foundation
- Oak pile foundation
- Vents in the foundation in winter
- Coven tricks when building foundations
- Repair of the foundation under a panel house
- Foundation insulation
- The columnar foundation is moving apart
- Strip foundation depth
- Dimensions of the foundation for a timber house with a brick lining
- Lay a foundation under the walls of a burnt house
- Designing a foundation for a frame extension
- Bored foundation technology
- Step foundation for an extension
- Repairing the foundation of an old wooden house
- Shrinkage of strip foundation
- The rubble stone foundation is crumbling
- What kind of foundation is needed for a house made of wood concrete blocks?
- Foundation for a one-story house
- Repair of strip foundation under a panel house
- Waterproofing an already built foundation
- The foundation of an adobe house is crumbling
- Log house on an old foundation
- Brick country house without foundation
- Wall aerated blocks for the foundation of a house
- Construction on the site of an old building
- New frame house on old foundation
- Car tires instead of a foundation for a timber house
- Replacing the foundation under a house in three parts
- Shirt on the foundation of an old log house
- Reinforcement of a shallow foundation
- Drilling holes in the foundation for water supply
- Replacement of block foundation 20 20 40
- Skid foundation for frame extension
- Foundation made of reinforced concrete piles 1-2 meters
- How to pour a new foundation on an old one
- Need advice on strengthening the foundation
- Strengthen the old foundation under an oak frame
- How to top up a fresh foundation in height
- Foundation - wooden sleepers or concrete blocks
- Restoration of the old foundation of a brick house
- Set up a garage basement on heaving soil
- FBS blocks in the foundation are moving apart
- Foundation for an outdoor shower
- Foundation in water - should we raise the house?
- Old foundation for a new house
- Foundation on water - how to make it?
- Foundation for an extension to a cinder block house
- The strip foundation is crumbling
- Foundation for the internal walls of a house
- Foundation pillars of a frame house collapsed
- The columnar foundation sat on the ground
- Foundation for an extension
- Strengthening the foundation before building an attic
- How to insulate and waterproof a foundation
- Choosing a foundation for a log house
- Foundation conservation
- Plastering the old foundation and restoring the blind area
- Foundation piles subsided
- A new strip foundation is being layered
- How to cut FBS?
- The columnar foundation went underground
- Restoration of strip foundation
- The columnar foundation regularly protrudes
- Which foundation for a 4 by 6 m bathhouse to choose
- Finishing the base and blind area of a columnar foundation
- The use of reinforced concrete sleepers when pouring the foundation
- How to level the foundation
- Should I lay roofing felt between the timber and the foundation?
- When and how to pour the foundation for an extension
- Brick house is bursting at the seams
- Repair of strip foundation under a panel house
- The foundation piles next to the vegetable pit were squeezed out
- Choosing a foundation for a timber house with brick lining
- Pour a foundation for an old log house
- Strengthening the foundation under a cinder block house
- Strengthening the old foundation from broken rubble stone
- Foundation depth for a foam block house
- Construction of a new foundation for cladding an old house
- Restoration of the foundation plinth
- Is it worth using the old foundation for construction?
- How to pour a foundation
- Foundation for a frame-panel house
- Foundation for an old adobe house lined with bricks
- Replacing the foundation under a brick garage
- Renew old foundation before construction
- Brick plinth on a concrete foundation
- How to connect a strip foundation with a new floating one
- A strip foundation made of blocks collapses
- Is it necessary to raise a concrete plinth with bricks?
- Is it possible to vent the foundation vents upward?
- Strengthening the foundation for the construction of the second floor
- Log house sank on a slope
- Connecting old and new foundations with reinforcement
- Separate foundation for the second floor
- The columnar foundation is walking
- Foundation for lining a log house with blocks
- How to avoid foundation cracking
- The new foundation is crumbling
- Expansion of the old foundation for a new house
- Vents in the foundation
- Which foundation to choose for a log house
- How to get rid of weeds in the foundation
- How to make a foundation for an adobe house without a foundation
- How to expand a concrete block foundation
- Put an old house on bored piles
- Columnar foundation for a log bathhouse
- Barrel foundation
- Budget foundation for a house made of foam blocks 6 by 6 m
- Cracks in a brick house
- Blind area of a house on a slope
- Which concrete is better for the foundation?
- What to do with the foundation after flooding?
- The foundation under a wooden house burst
- The latest foundation repair technology
- How to build up an old foundation before building a house
- The corner of the house sank
- The house has settled and the foundation is cracking
- The foundation is three years old, how can it be updated before building a house?
- Make a brick plinth on a strip foundation
- The foundation is crumbling
- How to add a foundation under a cinder-cast house
- Block foundation repair
- Restoration of a strip foundation after a fire
- Repair of columnar foundation
- Foundation of adobe house
- How to properly add a foundation to an old clay hut
- The foundation crumbled
- The foundation piles were squeezed out. What to do?
- Strengthening the foundation in land with high groundwater
- How to choose a foundation for a brick extension
- To boot or not to boot
- Strengthening the foundation and walls of an old house
- Foundation made of tires for a timber house
- Strengthening the foundation of the dacha
- Foundation for a bathhouse on a peat bog
- The strip foundation burst
- How to pour a foundation in place of an existing old one
- Waterproofing under an existing house
- Sleepers as a foundation for a house
- Problem with the foundation of a one-story house
- Floating foundation for a timber house
- How to add a foundation to an old log house
- Pile-screw foundation for a bathhouse
- Foundation for a frame-panel house
- The foundation has burst! What to do?
- The foundation burst
- Restoration of an old brick house and strengthening of the foundation
- How to strengthen an old foundation
- Strengthening the foundation under a country house
- New foundation around an old house
- Add a finished foundation
- The brick of the false foundation wall is crumbling
- How to strengthen the old foundation?
- Repair of the foundation of a brick country house
- How to add a foundation to a house?
- Strengthening the foundations of country houses
Construction in Moscow and Moscow region
We work with a guarantee! Wide range of construction services.
Foundation, walls, ceilings, roofing, turnkey! +7 (905) 797-20-34
luxurycomfort.ru
Construction in Moscow and Moscow region
We work with a guarantee! Wide range of construction services.
Foundation, walls, ceilings, roofing, turnkey! +7 (905) 797-20-34
luxurycomfort.ru
Construction in Moscow and Moscow region
We work with a guarantee! Wide range of construction services.
Foundation, walls, ceilings, roofing, turnkey! +7 (905) 797-20-34
luxurycomfort.ru
Construction in Moscow and Moscow region
We work with a guarantee! Wide range of construction services.
Foundation, walls, ceilings, roofing, turnkey! +7 (905) 797-20-34
luxurycomfort.ru
Foundations
All questions to Semenych about construction
Semenych (author of materials)
Our site is regularly updated with interesting and unique materials and articles on the topics of lumber, building materials and works, the author's opinion and knowledge of a real coven with more than 15 years of experience are provided. There is a section - funny stories of shabashniks. If you would like to receive information about this, subscribe to our website's newsletter. We guarantee that your address will not be shared with third parties.
Apartment renovation in Moscow and Moscow region
We work with a guarantee! Wide range of repair work.
Professional craftsmen. +7 (905) 797-20-34
luxurycomfort.ru
| Country house | Bath |
| For the dacha | Tool |
| Materials | Tales |
| Foundation | Log houses |
| Roofs | Insulation |
| Walls | Siding |
| Floors | Cellars |
| Attics | Doors windows |
| Stairs | Extensions |
| Wells | Toilets |
| Balconies | Loggias |
| Condensate | Flooding |
| Fences | Kennels |
| Sidewalk | Birdhouse |
| Adobe | Carts |
| Garages | Barn |
| Greenhouses | Bath |
| Swing | Brazier |
| Shower |
| Horizontal bar |
What are the advantages of such a foundation?
Having certain skills and knowledge in the construction industry, you can build this type of foundation yourself within a few days.
Financial costs for the construction of a simplified foundation of a dozen pillars will not exceed three thousand rubles. But there is one condition here - blocks for a columnar foundation are purchased ready-made for fifty rubles per stone, and almost all work is carried out in-house.
For a small wooden building, you can’t think of a better way to arrange a foundation. The most difficult moment in such work is to maintain the geometry and horizontal levels of the supports.
Construction work is simplified if you have experience in masonry work using brick or cinder block material.
Scope of application of such a base
Such foundations are in most cases used in private construction. They do not have a high load-bearing capacity, which significantly limits their operational potential.
On soils that are not prone to heaving, one-story houses, bathhouses, and buildings for household purposes are erected on a columnar foundation.
If the construction is planned in an area with sandy, rocky or boulder soil, the load-bearing characteristics of the columnar foundation will be sufficient to build a full-fledged house from a log frame or a foam concrete block.
A columnar foundation does not imply the arrangement of a basement. If this criterion is important to you, you should consider the construction of other types of foundations.
You should not build such a foundation in the following cases:
- erecting a large house with heavy walls;
- on soils with a low level of bearing capacity, in areas with moving soils;
- on sites with a natural height difference of more than a meter. In this case, it is necessary to plan the site.
Manufacturing materials and technology
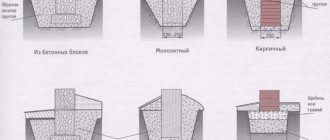
When making a columnar foundation for a frame residential building, the first thing you need to do is decide on the material. In most cases you can use the following:
- monolithic reinforced concrete;
- tree;
- rubble stone;
- brick;
- concrete blocks measuring 20x20x40 centimeters;
- rolled metal – channels, pipes;
- asbestos cement pipes.
Each of the listed materials has both pros and cons. For example, wood is the cheapest of all, but it is also the most short-lived, because even despite careful processing and impregnation with waterproofing solutions in the ground, it will rot very quickly. Rolled metal will last much longer, but its high cost negates the advantage in durability. Based on this, the most preferred materials for a columnar foundation are asbestos-cement pipes, blocks, bricks and reinforced concrete.
Columnar block foundation
Among all the known methods, it is relatively cheap and reliable to build a small wooden house, bathhouse or utility room on your country plot, the best option would be a frame building installed on a columnar foundation made of concrete blocks. It’s worth mentioning right away that the block nature of a columnar foundation does not mean the use of FBS blocks or other similar reinforced concrete products weighing a ton. We are talking about how to build a columnar foundation on your own from 20x20x40 blocks, each weighing about 30 kg, no more.
Characteristics of a columnar foundation
A columnar foundation for a frame house is made of successive load-bearing pillars, which are placed under the walls of the frame house. The supports of a columnar foundation are usually placed along the entire perimeter of the walls according to the construction project, and the lower frame of the frame house will be mounted on them.
Columnar foundation made of polystyrene foam blocks.
A foundation using columnar supports is necessary where the greatest load is expected on the elements of a frame house, at the junction of wall slabs, in the corners of a frame house and where spans will reach a height of 2.5 m.
Parameters of a columnar foundation
- If you decide to make a columnar foundation with your own hands for a frame house, then the optimal distance between the two supports will be from 0.5 to 1.5 m.
- Columnar supports of a frame house are installed in dimensions of 250x400x200-400 mm for rectangular shapes and 150-300 mm for round supports.
- The distance above the ground surface should be no more than 500 mm.
- The columnar foundation of a house with your own hands can easily lie at different depths - depending on the soil on which the frame house is being installed, the number of floors and the complexity of the frame structure being built.
A columnar foundation for a frame house can be placed in a single horizontal area, which will ensure the most optimal installation of the crowns of the lower frame of the house and create a solid structure.
Basics of columnar foundation technology made of concrete blocks
What is interesting about this version of the foundation:
- If you have the skills and certain knowledge about the construction methodology, you can build such a columnar foundation from blocks with your own hands within one, maximum two days;
- The cost of building a simple columnar foundation system of ten supports will be around 3 thousand rubles, provided that the blocks for the columnar foundation were purchased ready-made for 50 rubles apiece, and most of the work was done by hand;
- There is simply no simpler, faster and cheaper way to make a foundation for a lightweight wooden structure, and the most difficult thing in construction will be to maintain the geometry and horizon levels of the supporting surfaces of the columnar field.
Columnar foundation: step-by-step instructions
So, we have looked at the advantages of this construction technology, now we will look at how to make a columnar foundation with your own hands, step-by-step instructions will help you understand all the intricacies of the work. How to install a columnar foundation with your own hands, photo.
Step-by-step pouring of a columnar foundation made of pipes.
- It is necessary to begin preparing a summer cottage for the construction of a frame house, and to do this, we first level out all the large mounds in the excavated soil layer. The obligatory shallow recess must be made a couple of meters larger in area than the selected foundation design.
- The project for the future foundation of the house is transferred to the land plot with the help of pegs and fishing line. The future location of the supports is outlined, holes of the appropriate size are dug.
- The sand and gravel base is filled in and thoroughly compacted.
- If necessary, wooden formwork is installed to fill the future solution.
- Materials are laid out on the prepared surface - rubble, bricks, blocks.
- Installation of reinforcement and pouring concrete mixture. Metal reinforcing mesh consists of long rods, there can be three or four of them. The rods are fastened with wire reinforcement in different areas at intervals of 250 mm.
- Concrete must be poured gradually - in layers of 300 mm. with a mandatory puncture with an iron rod to seal and eliminate air bubbles.
- A columnar foundation made of blocks must be waterproofed with your own hands after removing the formwork. It is recommended to use sheets of reinforced roofing felt, liquid glass or a molten resin composition can be used.
- The role of the final fastening element is played by the lower frame of the frame house on a columnar foundation. It is recommended to do it from high-quality timber at a distance of at least 500 mm from the ground.
We build a columnar foundation from foundation blocks
Like any construction on a summer cottage, a block version of the foundation can be built several hours a day if you have free time and physical strength. The work is not hard and does not require a huge amount of digging of trenches or foundation pits. But there is one feature - the construction of a columnar foundation, first of all, will require very serious preparatory work. It is necessary to lay out the blocks, install beacons and landmarks along which the material will be laid on the cement mortar. The easiest way is to do this delicate part of the work right away, while the necessary details of how to mark the area are fresh in your memory. See how to seal and level a cushion under a columnar foundation of 20x20x40 blocks:
Two words about building blocks for a columnar foundation
For the construction of the foundation, in most cases, monolithic stones are used, cast on a vibrating machine or press from concrete grade M100-150. The easiest and cheapest way is to buy such material than to try to make it yourself. It is relatively inexpensive; during the construction of a summer house or utility room, you can buy leftover material from the owners, especially since you won’t need much of it, 40-50 pieces.
A 20x20 block with a length of 40 cm is most often used for the construction of columnar foundations for quite objective reasons:
- The size of the block determines its light weight. Depending on the filler used, the weight of one stone ranges from 30 to 32 kg, which makes it relatively easy to lift and lay out blocks without additional tools and devices;
- Most often, blocks are made on vibrating presses, in standard forms for foam concrete or cinder block. In this case, a cast stone is obtained with an initial strength that is significantly higher than an artisanal concrete casting;
- The successful proportions of the material make it relatively easy to fold the foundation column and level the plane, without using a grinder to trim the top of the support.
Marking the site and preparing the cushion for columnar supports
At the initial stage of preparation, you will need to correctly mark the installation points of the columnar foundation supports. For this purpose, the dimensions and shape of the frame of the dressing timber grillage, which will rest on the pillars, are used. Based on the project sketch, it is necessary to calculate the exact dimensions of the midline of the beam and transfer it to the ground using cords. In addition to observing the lengths of the sides of the future foundation with millimeter accuracy, you will need to check that a right angle is maintained between the adjacent sides.
The result should be four main installation points for corner column supports, between which a construction or marking cord will be stretched without sagging. In this case, the stakes on which the thread or cord is attached must be located outside the perimeter of the foundation.
In a similar way, you need to align the position of the marking cord in height so that the plane is perfectly aligned with the horizon.
The next step is to prepare the cushions for laying the blocks. It would be more reliable to bury the columnar supports into the ground by 20-25 cm, but in this case you will need to use an additional pair of blocks for each pillar, instead of laying three rows.
If you perform additional soil compaction within a radius of 50 cm around the support, you can get by with a non-buried version of a columnar foundation. In a pit dug to a depth of 30-35 cm, it is necessary to pour two layers of sand with the thickest layer of crushed stone in between. The poured material is carefully compacted layer by layer so that a small layer of spreading sand remains on the surface.
Installation of columnar foundation supports
Laying blocks at the base of a columnar support is carried out using the same technology as laying bricks. High mechanical strength is not required from the masonry mortar; the main thing is that it is plastic, but does not spread on the concrete. The sand base on which the block will be laid is moistened and immediately covered with a thin layer of mortar 1-1.5 cm thick. Blocks can be placed on the concreted layer.
The position of the block must be aligned with the stretched cords and the building level so that the supporting surface is well filled with the solution and there is no blockage along the horizon.
When laying the next pair of blocks, they are turned a quarter turn, thereby ensuring the ligation of the rows. If there is a third row, it also needs to be tied with the bottom pair.
In some cases, craftsmen make a cushion for laying blocks in the form of a concrete screed, which, after preliminary setting of the mortar, is cleaned with a lath and leveled horizontally. In this case, the top layer of sand is not poured onto the cushion, but the masonry mortar is laid directly on the crushed stone with liquid concrete poured over the gravel.
Finishing work and laying of strapping
After the masonry mortar has set, the base of the blocks in the columnar supports is cleaned, the cracks are filled with mortar, plastered and waterproofing is laid. If the pillars are installed correctly along the beacons, without blockages of the supporting surface, you can proceed to tying the foundation with timber.
The wooden frame of the grillage is made in carpentry in advance, most often in the form of two L-shaped elements. The lower part of the corner joint, which will rest on the columnar masonry of blocks, is reinforced with a metal plate. There will be an anchor pin running through a pair of metal flashings, embedded in the seam between the top two blocks.
Foundation for the construction of a frame house
Foundation for a frame house
The foundation is the basis of any house, which bears all the loads, the durability and strength of which determines the life of the housing itself. Therefore, it is so important to carefully understand the issue of preparing this foundation and make the right choice.
A frame wooden structure, due to the properties of building materials, is lightweight, so it is not advisable to form a deep and expensive massive foundation for your house. In this case, the depth of the foundation should not necessarily exceed the depth of winter freezing of the soil, but groundwater should be at a depth of more than a meter. Considering the above, we can conclude that a monolithic strip, column or pile option is suitable for a frame house. Each of these technologies has its own advantages and is used depending on future loads, the number of floors of the building and plans for future operation of the premises.
A strip foundation for a frame house is one of the most commonly used at the moment and is a foundation poured with concrete, which in the form of a strip repeats all the main load-bearing walls and support points, which takes on the main load of the structure. In addition to the recessed one, there is the possibility of forming a non-recessed strip base, which protrudes 0.5-0.7 meters above the ground level. It is better suited for flat areas and has the ability to “float”, that is, to evenly and smoothly raise the entire structure when the soil freezes in winter and also smoothly lower when the soil thaws in the warm season.
A columnar foundation for a frame house is a set of pillars buried to a certain depth and connected by beams. Asbestos pipes, concrete or brick can be used. This technology is more suitable for soil that does not freeze in winter; it costs the customer less, but the load on such a base is limited. Most often used in the construction of one-story, less often two-story wooden buildings.
Pile foundation is the simplest in terms of installation technology. It is a group of piles that are screwed into the soil to a freezing depth until they touch solid ground and form the basis of the building. This variety can be used in sloping areas and in almost any soil quality; its installation can be carried out at any time of the year, regardless of the condition of the soil. It can withstand heavy loads and is often used for the construction of low-rise buildings.
When planning the construction of a house and preparing the foundation of the house, it is important to correctly calculate the load on the foundation, which takes into account the dead weight of the future structure, the weight of people, furniture, house decoration, seasonal load on the ground of snow and moisture, and much more. It is quite difficult for an untrained person to carry out such a calculation correctly, so it is better to entrust the work to a specialist.
Building a foundation for a frame house takes much less time, effort and money than preparing it for heavy brick or concrete buildings. In most cases, this can be done by one professional construction team, without the use of heavy construction equipment and in a short period of time.
We should not forget that every little detail in the construction of your own housing ensures the durability and quality of housing, so you should approach each stage seriously and turn to professionals.
The construction company DomaSV is always ready to help, we know how to build a house correctly so that it stands long and strong.
Order a frame house cost estimate
Columnar block foundation
On this page you will learn where a columnar foundation made of FBS blocks is used and what advantages and disadvantages it has. The features of calculating this foundation will also be considered and the technology for constructing a columnar foundation with your own hands will be examined in detail.
Among all the types of foundations common in private construction, columnar foundations are the most rapidly erected and cost-effective.
Rice. 1.1 : Columnar foundation made of FBS blocks with a wooden grillage
If you need to build a garage, bathhouse, utility building or small frame house, and the construction project itself is limited both in terms of implementation time and financial capabilities, a columnar foundation is the best choice.
There are several types of columnar foundations - made of brick, concreted asbestos-cement pipes, wooden pillars and concrete foundation blocks.
Expert advice ! The best option in terms of durability and load-bearing capacity is a columnar foundation made of FBS blocks - expanded clay concrete or reinforced concrete products of factory production, made by vibration pressing.
Advantages of a columnar foundation
Despite the fact that a columnar foundation for a frame house does not require continuous concrete pouring of the entire perimeter of the base, it nevertheless has a number of advantages that make the entire structure durable and reliable. The benefits are as follows:
- Does not require long drying - can be installed with your own hands in one season.
- No special large-scale equipment or a large number of workers are needed.
- Saves a significant amount of money.
- Can be constructed at any time of the year and for any building.
- It is easy to repair and even replace some individual elements.
It is these advantages that push the owners of future frame houses to make their choice in favor of a columnar foundation.
Application area
The main area of application for columnar foundations made of FBS blocks is private construction. Such foundations do not have a high load-bearing capacity, as a result of which their exploitation potential is significantly limited.
On soil that is not prone to heaving or has low heaving, small frame, wooden or panel buildings can be erected on columnar foundations from blocks - one-story houses, bathhouses, utility rooms.
Rice. 1.2 : Wooden house on a columnar foundation
If construction is carried out in a region with sandy, dense rock or coarse-grained (gravel, boulder and pebble) soils, the load-bearing characteristics of a columnar FBS foundation will be sufficient for the construction of full-fledged houses from logs, timber or foam concrete.
Figure 1.3 : Scheme of a columnar foundation made of FBS
Expert advice ! A columnar foundation made of FBS blocks does not provide for the possibility of arranging a basement; if this criterion is important to you, pay attention to other types of foundations.
The optimal depth for laying a columnar foundation made of FBS (and any prefabricated structures) is up to one meter; if construction conditions (type of soil, weight of the house) require a greater depth of laying, it is more rational to equip columnar foundations from asbestos-cement pipes filled with concrete, since laying FBS blocks to a depth of more than 1 meter is an extremely labor-intensive process.
It is not recommended to erect a columnar foundation made of FBS blocks in the following situations:
- During the construction of massive houses with walls made of heavy materials (brick, reinforced concrete wall blocks);
- On soils with low bearing capacity - clayey, subsidence, moisture-saturated;
- On moving soils, a columnar foundation has low resistance to horizontal displacement loads;
- On construction sites with a natural height difference of more than one meter (preliminary leveling of the ground is required).
Rice. 1.4 : Foundation support pillars before grillage piping
Blocks used
Block structures used to create foundations are marked FBS (foundation building blocks). Their manufacturing technology is regulated by the provisions of GOST No. 13579-58. According to GOST standards, concrete of a grade not lower than M-100 must be used to create blocks. The FBS grid of standard sizes is quite wide.
There are large-sized reinforced concrete structures designed for mechanized installation using a construction crane (their weight can reach two tons). Such blocks must be reinforced with a reinforcement cage made of hot-rolled A3 reinforcement. The diameter of the reinforcement used depends on the size of the FBS; it can vary between 9-15 mm.
Expert advice ! Large-sized reinforced concrete FBS can be used for arranging slab and strip foundations for massive brick structures.
You can see the dimensional grid of reinforced concrete FBS in Table 1.1
Table 1.1 : Dimensions of reinforced concrete FBS blocks
Large-sized FBS are used extremely rarely in small-scale construction, since their weight does not allow manual laying of the foundation - for this you need to rent a construction crane, which negates the main advantage of a columnar foundation made of blocks - its low cost.
For manual masonry, FBS is produced from expanded clay concrete, a lightweight material with high heat-resistant characteristics.
The most common in private construction is FBS 20*20*40 cm, which weighs only 32 kilograms.
Technical characteristics of the FBS 20*20*40 block:
- Nominal strength – 150 kg/sq.cm;
- Dimensions – 200*200*400 millimeters;
- Frost resistance – at least 15 cycles;
- Moisture absorption up to 15% of volume;
- Maximum thermal conductivity – 1.16 W/mK.
Among the advantages of using FBS of this size, one can highlight the high speed of foundation construction - the laying of blocks is carried out using a special adhesive composition or sand-cement mortar, and all work is done with your own hands, without the use of special construction equipment.
Figure 1.5 : FBS foundation blocks 20*20*40 cm
The key disadvantage is the low hydrophobicity of the material - expanded clay concrete FBS has a porous structure, as a result of which it absorbs moisture from the soil like a sponge (up to 15% of its mass), which in the long term leads to the destruction of the block.
Expert advice ! This disadvantage is eliminated by waterproofing FBS, which must be carried out without fail during the construction of the foundation.