Building a house often replaces buying an apartment. These types of housing are almost the same in cost, but in the case of building a frame cottage, the budget can be saved significantly. All work on the construction of the structure - from the base to the roof - can be done independently, knowing the technology. Building a foundation for a frame house with your own hands is not difficult even for a person who has not previously dealt with such matters. In this article we will look at the types, methods of construction and the advisability of using one or another type of foundation for each case.
What is a frame cottage?
The technology for building modern lightweight houses came to us from America. Another name for them is Canadian. In these countries, most suburban buildings are made using this technology, which is fully justified: the home is warm, reliable, lasts for many years, is cheap, and can be built quickly. In Russia, such objects appeared relatively recently (about 15 years ago), but are actively gaining popularity due to their qualities.
The technology for constructing frame and frame-panel houses is as follows:
- A vertical frame of walls made of wooden beams along the entire perimeter is installed on the constructed foundation.
- Fill the space between guide sandwich panels or panels made of OSB and insulation.
- The walls are sheathed with facade and finishing materials.
Thus, the construction of the walls is very light. Which foundation is better for a frame house? Definitely not powerful, it is not necessary. This allows you to save not only construction time, but also money on materials and labor.
Foundation calculator for a frame house
A frame house is one of the most popular designs for private housing construction in Canada, the USA, Japan, Scandinavia and Western Europe, but is still not recognized in the CIS. This type of structure has a number of undeniable advantages, including energy efficiency, lightness, ease of construction and the possibility of construction on almost all types of soil.
KALK.PRO construction calculators allow you to determine the most optimal parameters when calculating the foundation for a frame house . They will ensure reliable and durable operation of the building, and will also contribute to significant savings on materials, as they prevent overexpenditure, without loss in the quality of the structure.
Since structures made from sandwich panels (SIP) do not create a significant load on the ground, monolithic or shallow strip foundations . The base, in theory, should not differ in significant thickness, so many perform calculations by eye or rely on the experience of their neighbors, but this approach can lead to a fatal mistake.
To avoid deformation of the building, all initial parameters for working with calculators should be as close as possible to reality , first of all, this concerns the calculation of the mass of the house, in particular, the weight of walls, ceilings and roofing.
It is unlikely that you will be able to calculate the weight of the house with pinpoint accuracy, but it will not be difficult to find out approximately. There are special reference tables with average values of individual house structures, which we have given below.
Specific gravity of 1 m2 of wall
| Frame walls 150 mm thick with insulation | 30-50 kg/m2 |
| Walls made of logs and beams | 70-100 kg/m2 |
| Brick walls 150 mm thick | 200-270 kg/m2 |
| Reinforced concrete 150 mm thick | 300-350 kg/m2 |
Specific gravity of 1 m2 of floors
| Attic on wooden beams with insulation, density up to 200 kg/m3 | 70-100 kg/m2 |
| Attic on wooden beams with insulation, density up to 500 kg/m3 | 150-200 kg/m2 |
| Basement on wooden beams with insulation, density up to 200 kg/m3 | 100-150 kg/m2 |
| Basement on wooden beams with insulation, density up to 500 kg/m3 | 200-300 kg/m2 |
| Reinforced concrete | 500 kg/m2 |
Specific gravity of 1 m2 of roofing
| Sheet steel roofing | 20-30 kg/m2 |
| Ruberoid coating | 30-50 kg/m2 |
| Slate roofing | 40-50 kg/m2 |
| Roofing made of pottery tiles | 60-80 kg/m2 |
Having received approximate data on the weight of the house, it will not be difficult to find out the thickness of the foundation using our foundation calculator .
Is there a single solution?
There is no exact answer to the question of which foundation is best for a frame house. There are many types of lightweight structures, the use of which is optimal in a particular case. The basis can be:
- pile;
- tape;
- columnar;
- shallow;
- slab
Different materials are used for the foundation:
- concrete;
- reinforced concrete;
- tree.
Thus, there may be several options for constructing a foundation for a house. The choice is influenced by:
- house size;
- number of storeys;
- soil freezing depth;
- availability of groundwater;
- soil type: mobile, wet, viscous, hard;
- presence/absence of a basement.
The best foundation for a frame house is one that takes into account all the nuances of construction and geological conditions. A properly selected base will last a long time and help save time and money.
Determining the characteristics of the base
The first step is to determine the type of soil at the proposed construction site. The best way to do this is to order geotechnical surveys. Experts will determine:
- the exact type of soil and its characteristics;
- availability of groundwater and its nature;
- They will draw up a site plan taking into account elevation changes and terrain features.
True, such pleasure is expensive and takes a lot of time. Another option is to find a neighbor in the area who has already applied for such a service and has the results of an examination of his territory. As a rule, soil characteristics in one area have the same properties.
If there is no neighbor with a conclusion, you can try to determine the type of soil yourself. To do this, follow these steps:
- Dig a hole to the frost depth in the region. You can find it out using the map.
- Analyze a section of soil along the side wall of the pit.
- Rocky soils consist of rocky and gravel bases. They are strong enough, able to withstand any weight, and do not retain water (provided they do not contain a large amount of clay).
- Coarse sands and cartilaginous soils are also characterized by a low degree of heaving and a strong foundation.
- Fine sandy soils are not the best option for construction. They retain water, which solidifies in the upper layers and acts on the foundation by pushing and compressing. This property is called heaving.
- Loams and clay are the most unfavorable type of soil. Their mobility and buoyancy depends on the height of groundwater. But even in their absence, there is often enough moisture from precipitation. In areas with such soils, large puddles form because water drains into the ground very slowly.
The type and depth of the foundation for a lightweight frame house depends on the geological conditions of the area.
Choosing a foundation for building a frame house
The load-bearing foundation necessary for the construction of any structure is called the foundation. The durability of the structure and the required budget depend on its correct choice.
This design performs two functions:
- distributes the weight of the entire structure evenly;
- protects it from soil movement in any direction.
The choice of type of foundation for a frame structure is influenced by several factors:
- material, area and final mass of the structure;
- soil type;
- presence or absence of a basement;
- depth of groundwater;
- soil freezing level;
- seismic indicator of the area.
Before deciding on the choice of foundation for a building, you should remember that:
- the service life of the foundation and the structure should be approximately the same;
- if the construction of a frame house is supposed to be on loose soil, then a rigid space must be installed underneath it;
- correlate the costs of its construction with the features of the construction of the house;
- if groundwater is close to the surface, then it is better to abandon the basement equipment in the project. Otherwise, even high-quality waterproofing will not save you from excess moisture in the basement.
Features of the soil, design and size of the building
When designing the foundation, you should take into account the type of soil on the construction site, its freezing, the location of water relative to the surface, and the layout of the house being built.
Soil influence. Before starting to build a house, you should understand the type of soil on the site (to accurately determine it, you can use the services of surveyors). When independently determining the composition of the soil, a hole about 1.5 m deep is dug and a section of the soil is examined:
- rocky, gravel, sandy-stony without the presence of clay are considered the best options due to the fact that they do not retain moisture and do not swell at low temperatures, and also do not compress under load and there is no need to install a buried foundation. If the soil is dense enough, then it is possible not to build a foundation, but only to level the surface. But their significant disadvantage is the ability to freeze to great depths.
- Clay soil retains moisture and swells when it freezes.
- the presence of sandy soil is considered not a bad option for laying a foundation, but it also requires work to strengthen the walls of the foundation pit. But on the other hand, it does not freeze and can be easily compacted.
- It is not recommended to build a house on a peat surface. But if you still come across this type, then you should try to replace it with sand, make the base below this layer, or use piles.
Soil freezing . The type of soil directly depends on the depth of freezing. Rocky ones are resistant to freezing. They do not contain water and only slightly change their characteristics and expand at low temperatures. The amount of swelling affects the condition of the foundation. It may rupture or be pushed out of the ground.
The level of groundwater is of no small importance. If their indicator is less than 1.5 m, then the bearing capacity of the foundation decreases sharply. In this case, its laying depth is correlated with the amount of freezing. The presence of water affects the construction of a basement in a house.
To reduce its level, ditches are used to facilitate the release of water towards the slope of the water relief. The greater efficiency of their work is visible only with a temporary increase in level. If the water level is always high, a drainage system is used.
Type of building being built . The loads on the foundation of a frame house and, for example, a brick house with concrete floors differ significantly. Experts always advise that before making a foundation, you should decide what the new house will be built from. The frame structure itself, compared to other types, has a lightweight design. Therefore, when constructing a one-story and garden frame structure, non-buried or shallow foundations are constructed.
The selection of the foundation is influenced by the presence of a basement, cellar and their size. If they are expected to be present, it is possible to use the method of combining bases.
Material used . The most popular are:
- Concrete. Its foundation is very reliable. It is often used on sandy and rocky soils, but on clay soils it can easily crack.
- Reinforced concrete. It is cheap, strong and durable. With its help it is easy to make a monolithic foundation of complex configuration.
- Brick. Used only for the above-ground part of the foundation and the basement. In no case should it be laid below ground level for the reason that it is highly hygroscopic and easily destroyed in severe frosts when wet.
[ot-video type=”youtube” url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=72HJ-PaG0Js&feature”]
We take into account the depth of freezing
This aspect is relevant for soils subject to heaving. Rocks that do not retain water serve as a solid foundation in any season, unlike fine sandy and clay soils. If the latter are present, the depth of the foundation should be greater than the freezing value, then it will be able to firmly fix the building in one place and position. This is necessary to prevent uneven subsidence of the structure, which can lead to damage to the integrity of the house, its destruction or large investments in repairs.
It is also important to find out about the presence of groundwater. If they are present, you need to look for a way to deal with them or equip the structure in such a way that it is able to withstand a humid environment and conditions of severe heaving. The depth of soil freezing is not included in the calculations of a pile foundation.
Deciding on the design
Based on the work done to determine the type of soil and the depth of its freezing, you can decide which foundation design for a frame house is optimal in a given location.
- On clayey and fine sandy soils, a pile foundation is installed. It fixes the structure in durable layers below the groundwater level.
- Shallow slab foundations work well on heavily heaving loams and silty rocks. They play the role of a “boat”, capable of staying afloat and holding the house in one plane over the entire area of the structure.
- Rocky, coarse sandy, gristly soils themselves serve as a solid foundation, so they do not require a solid foundation - strip, shallow and columnar will be enough.
In the presence of groundwater, special types of waterproof concrete are chosen and additional waterproofing of the foundation walls is used. If the GWL is high, you should abandon the basement. In addition, it is advisable to install a drainage system throughout the area or directly next to the house: a trench is dug along the perimeter, through which excess liquid drains in a given direction.
We figured out the main stages. Next, we will consider in detail the principles of construction of different foundation designs and methods of their installation.
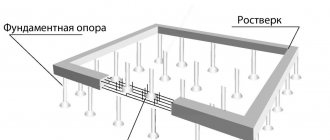
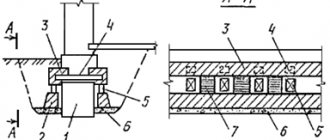
Pile-grillage foundation
This is a widespread type, universal in use. Since Russia is not rich in hard rocks, heaving soils of varying degrees of freezing predominate over most of the territory; pile foundations are used for the construction of buildings for various purposes and number of storeys. The pillars penetrate deep into the soil and are fixed with their lower ends in dense layers. Due to this, the structure resting on them is securely fixed relative to the ground surface.
To build a pile foundation for a frame house with your own hands, you first need to calculate the number of pillars for the structure. To do this you need:
- Look into the project, if there is one. If it is not there, see further.
- Draw the perimeter of the future house on paper to scale. Mark the installation locations of the piles with dots (in all corners, where walls meet, along the perimeter in increments of 1.5-2 meters). Since a frame house is light in weight, reinforcement of the structure will most likely not be required, so a simple arrangement will suffice.
- Count the number of marked points.
The next step will be to decide which piles to use: ready-made reinforced concrete or screw products from the factory or poured into ready-made wells on your own site.
- The finished pillars are buried using a special installation. They are hammered to the required level in the designated places, then the remaining ends are cut off to the level. For a lightweight building, it is enough to buy piles with a minimum cross-section.
- Screw metal supports are tightened with a special device.
- If a decision is made to construct piles independently, then first wells are drilled, the bases of which must be made wider for stability. The depth depends on the geological conditions of the area. You need to get to solid ground. Then a waterproofing material is installed into the cavity, for example, a hollow pipe or twisted roofing felt. After this, the frame is laid and concrete is poured. It is optimal to use a solution of the M300-M400 brand. It would be good if it contains special additives that give the stone water-resistant properties.
The piles are installed, now you need to arrange a grillage. In the future, the wall frame will rest on it.
The grillage can be prefabricated or monolithic. The difference lies in the installation method:
- The prefabricated one is mounted on reinforced concrete piles topped with a cap.
- Monolithic is installed at the construction site: formwork is installed, if necessary, a cushion of ASG is laid at the bottom of the grillage, waterproofed with roofing felt and a finished frame is installed, which is connected to the reinforcement of the pile pillars. After this, the concrete mixture is poured.
The foundation is ready. It is worth noting that this design does not imply the presence of a basement.
Calculation of a pile-screw foundation
All information regarding the piles, including their layout, depth, diameter, etc., must be indicated in the frame house design. In the process of designing the location of the future foundation, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Weight of the finished residential structure;
- Wind and snow loads on the building;
- Geological (including the depth of groundwater, the level to which the soil freezes, the characteristics of the soil at the construction site);
- Terrain.
Calculation of a pile-screw foundation allows us to draw conclusions that the structure can withstand up to 10 tons. The main advantage of such piles is the ability to carry out screwing in manually without the use of additional equipment. On average, the process of screwing one pile into the ground does not take more than 20-30 minutes. If it is necessary to increase the length of the pile, this is done by extending it using special couplings securely secured with a welding machine.
A set of piles for the foundation.
Installation of piles is carried out at the corners of the building, at the junction of internal walls with external ones, under external and internal walls. The distance between piles depends on the type of house structure. A pile-screw foundation is installed manually or using special equipment; the choice of method depends on the thickness of the pile.
Columnar foundation
Optimal for flat terrain in relatively stable soils. Similar to pile, but less buried.
You can build a columnar foundation for a frame house with your own hands using the following technology:
- Make markings on the plan. The supports are located in corners, wall intersections, and along the perimeter in increments of 2-3 meters. Next, these points are transferred to the site.
- They dig holes for the pillars. If the foundation is made of asbestos pipes or monolithic pillars, the recesses are made with a motor drill rented for the day. Holes are dug under the stone pillars with a shovel. The size of the excavation is 60x80 cm, and the depth should be 20-30 cm below the freezing level of the soil.
- Waterproofing for a monolithic element is carried out immediately - roofing material is laid in the hole. For stone, brick or rubble pillars it is arranged according to the finished product.
- For the concrete option, a reinforcement frame is installed.
- Install the formwork above ground level to the required height (minimum 40 cm).
- Pour in the solution.
A grillage is arranged on the finished pillars. This is done according to the same principle as in a pile foundation. It may not be there, then a wooden beam is laid on the tops of the racks, which will serve as a support for the frame.
The final stage is the installation of a wall that fills the space between the pillars. A trench 20-30 cm deep is dug between them, the base is filled with concrete, and after it hardens, a wall is laid out. If this is not done, then the lower ceiling will require additional insulation so that the floor in the house is not cold.
It’s not at all difficult to make a columnar foundation for a frame house with your own hands. It is important to remember that building a basement with such a design is a very problematic task, so this idea should be abandoned. On the other hand, the foundation is built quickly and is much cheaper than a pile or strip foundation.
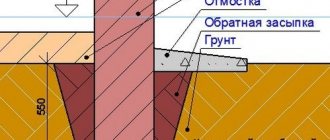
Strip foundation for a frame house
The most suitable one is shallow. But it can only be built where the soil is dense and moist. Since the tape is buried only 20-40 cm, these indicators are very important for the strength of the base. If the bearing capacity of the soil is low, it is better to make the tape buried. Here, the freezing point of the soil is taken as the basis for the calculation. The base of the foundation should be 20-30 cm below it. Then the heaving forces (and they are great at high humidity) will not have a destructive effect on the house and its foundation.
Stages of work on the installation of a monolithic concrete strip
Marking.
Diagram of the structure of the walls of a frame house.
- Before starting work on installing any foundation for a frame house, the construction site should be tidied up and leveled.
- Next, markings are made and the boundaries of the external and internal perimeters are determined. The distance between them should correspond to the width of the tape.
- Pegs should be used to mark the location of window and door openings. In these places, when pouring a concrete strip, more reinforcement will be required.
- A marking tape is stretched between the pegs. It must be strictly horizontal and determine the height of the foundation.
Formation of a trench and installation of a gravel-sand cushion
- To build a strip foundation for a frame house, they rarely rent construction equipment and tend to do most of the work themselves. Therefore, the trench is often dug by hand.
- During work, make sure that the bottom of the ditch is level; as you move forward, the soil is compacted.
- Then they begin to install waterproofing: lay sheets of roofing felt folded 2-3 times.
- After this, an even layer of sand (not river sand) 5-7 cm thick is formed. To make it easier to compact, water it with water. Then they compact.
- Do the same with the next layer of gravel or crushed stone. Its thickness should be 10-15 cm.
Installation of formwork and reinforcement.
Calculation of reinforcement for strip foundations.
- Inside the trenches, wooden panels are assembled and strengthened in a vertical position with the help of support jibs. If lumber will be used during the construction process, it can be protected from concrete by covering the internal walls with dense polyethylene.
- The mesh reinforcing the foundation is made of reinforcement. For horizontal rods you will need rods with a cross section of 10-14 mm, for vertical rods a diameter of 6-8 mm is sufficient.
- The reinforcement is connected to each other by welding or knitting wire.
- The mesh is assembled like this: horizontal rods are laid next to the formwork and welded. Vertical rods are cut to such a height that the reinforcing mesh is 5 cm above the bottom of the trench and 5 cm below the edge of the formwork. The horizontal rods are connected to each other by rods laid across them every 40 cm.
- When the mesh is ready, it is lowered into the trench. To prevent the lower metal rods from coming into contact with the ground, place stones or bricks.
Pouring concrete tape
Scheme for marking the area for the foundation.
- The best option is to buy factory-mixed concrete and finish the pouring job in one day. But if this is not possible, make the solution yourself. For this purpose, cement grade M400 and medium-grained sand are used. The amount of water should be such that the solution is viscous and at the same time plastic. Calculation of the amount of cement and sand: 1:3.
- When pouring yourself, do not rush and each subsequent layer is poured only after the previous one has hardened.
- The solution must be compacted to allow air to escape. This will improve the quality of the concrete strip.
- Until the formwork is dismantled, the concrete must be protected from drying out by periodically watering it with water and covering it at night in case of rain.
Wooden foundation
A kind of hybrid of pile and column. A wooden foundation is suitable for building a small frame house, but due to its comparative fragility, it is rarely used for residential cottages. It is optimal for country houses: the impact of minimal loads on the base, low cost of installation and material, high speed of the device. In addition, the tree has natural elasticity, which allows it to regain its original shape after minor deformations from soil heaving.
The lightest designs have seasonal frame-panel houses. The foundation for them can be very simple. It is in such cases that wooden poles are used. Although in Venice, high-rise buildings stand on such foundations for hundreds of years, so one can argue about durability in this case.
Certain types of wood are suitable for piles: beech, larch, oak, pine. Sections of wood with a diameter of at least 20 cm are suitable for blanks. The product can remain round or acquire a rectangular cross-section with a side of 20 cm. Piles are treated with special solutions that prolong the life of wood in unfavorable conditions. Before directly burying them, you should wrap the post with 1-2 layers of roofing material or other polymer material, then the soil will not stick to the product. This will allow the pile to slide relative to the base in a vertical direction when the soil is heaving, and will also preserve it for a longer period.
How to mount a wooden foundation for a frame house with your own hands:
- Markings are made according to the already known scheme: corners - intersections - perimeter in increments of 1.5-2 meters.
- Transfer the location of the pillars to the site.
- Holes are dug in the ground with a diameter 1.5 times larger than the pile. The depth must exceed the soil freezing level and reach dense layers. If they are not available, the pole should be placed 0.5 m below the level.
- Make a pillow of stones or a wooden cross.
- Pour 15-20 cm of concrete mixture and immerse the pillars in it. When the solution sets, it will fix the pile.
- The soil is backfilled and compacted.
Calculation of house weight
So, you need to calculate the approximate weight of the house. For this purpose, there are reference data with average values of the specific weight of house structures: walls, floors, roofs.
Specific gravity of 1 m2 of wall
| Frame walls 150 mm thick with insulation | 30-50 kg/m2 |
| Walls made of logs and beams | 70-100 kg/m2 |
| Brick walls 150 mm thick | 200-270 kg/m2 |
| Reinforced concrete 150 mm thick | 300-350 kg/m2 |
Specific gravity of 1 m2 of floors
| Attic on wooden beams with insulation, density up to 200 kg/m3 | 70-100 kg/m2 |
| Attic on wooden beams with insulation, density up to 500 kg/m3 | 150-200 kg/m2 |
| Basement on wooden beams with insulation, density up to 200 kg/m3 | 100-150 kg/m2 |
| Basement on wooden beams with insulation, density up to 500 kg/m3 | 200-300 kg/m2 |
| Reinforced concrete | 500 kg/m2 |
Specific gravity of 1 m2 of roofing
| Sheet steel roofing | 20-30 kg/m2 |
| Ruberoid coating | 30-50 kg/m2 |
| Slate roofing | 40-50 kg/m2 |
| Roofing made of pottery tiles | 60-80 kg/m2 |
Based on these tables, you can roughly calculate the weight of the house. Let it be planned to build a two-story house measuring 6 by 6 with one internal wall with a floor height of 2.5 m. Then the length of the external walls of one floor will be (6 + 6) x 2 = 24 m, plus one internal wall another 6 m long, for a total of 30 m. The total length of all walls on two floors is 30 m x 2 = 60 m. Then the area of all walls will be: S walls = 60 m x 2.5 m = 150 m2. The area of the basement floor will be 6 m x 6 m = 36 m2. The attic floor will have the same area. The roof always protrudes somewhat beyond the walls of the house (let’s say 50 cm on each side), so we calculate the roof area as 7 m x 7 m = 49 m2.
Now, using the average data from the tables above, you can make a rough calculation of the total load on the foundation. In this case, we will take the largest specific gravities in order to count with a margin. For comparison, the calculation was made for three house options: - a frame house with wooden floors with insulation with a density of up to 200 kg/m3 and a roof made of Ondulin type sheet material; — a brick house with wooden floors with insulation with a density of up to 200 kg/m3 and a roof made of sheet steel; - a reinforced concrete house with reinforced concrete floors and a roof made of pottery tiles.
In addition to the permanent load created by the weight of the house, there are temporary loads from wind and snow cover. The average snow cover weight is given in the table:
| For the south of Russia | 50-100 kg/m2 |
| For central Russia | 150-200 kg/m2 |
| For the north of Russia | more than 200 kg/m2 |
With a roof area of 49 m2 for central Russia, the load from snow cover will be 49 m2 x 100 kg/m2 = 4900 kg. We add it to the total load on the foundation.
| House | Wall weight, kg | Basement ceiling, kg | Attic floor, kg | Roof weight, kg | Snow cover, kg | Total, kg |
| Frame | 7500 | 5400 | 3600 | 1470 | 4900 | 22870 |
| Brick | 40500 | 5400 | 3600 | 1470 | 4900 | 55870 |
| Reinforced concrete | 52500 | 18000 | 18000 | 3920 | 4900 | 97320 |
Lightweight strip foundation
Widely used among developers due to its low cost and high installation speed. A lightweight strip foundation for a frame house is used on solid foundations, where there is no need for large depths and massive support.
The main difference between this design and the usual one is the reduced depth of the sole and the dimensions of the tape itself. This is acceptable for lightweight structures, in particular for residential frame houses.
Installation technology:
- Dig a trench or pit (affects the presence of a basement). In any case, the width of the excavation should be 0.5 meters greater than the specified perimeter for ease of work. The depth depends on the groundwater level, on average - 0.8-1.5 meters (taking into account the design of the pillow).
- Mark the perimeter of the foundation wall. It is important to correctly measure all angles and check the parallelism of the sides.
- Install the formwork. Its height is determined by the presence and size of the base, but not lower than 40 cm above ground level. The width of the future tape is calculated as the wall thickness + 100 mm. For a light frame house, you can make 200-300 mm.
- Fill with a pillow made of ASG (10-20 cm).
- Install the frame.
- Concrete solution M300-M400 is poured.
A lightweight foundation for a frame house is convenient because it does not require special preparation and installation of additional structures for the construction of walls.
Plate
Soils are not always conducive to standard construction solutions. There are many areas in Russia with clayey and highly heaving soils. But this is not a reason for them to be empty. Even for such cases, there are solutions.
If you happen to purchase a plot of land with floating soil, it is advisable for construction to arrange a slab monolithic foundation for a frame house. It is quite possible to do this with your own hands. The technology is similar to creating a lightweight tape:
- A excavation is made in the soil to the depth of the fertile soil layer and the upper exposed layer is compacted.
- Next, arrange a gravel-sand cushion about 20 cm thick.
- Roll out 2-3 layers of polymer waterproofing.
- Pour a preparatory layer of concrete up to 5 cm.
- Mount the frame. It must be solid, since the slab takes significant loads from the ground. For meshes, take thick reinforcement with a diameter of 12-16 mm, lay it in increments of no more than 40 cm in both directions. The rods are tied with wire. Make 2 planes and connect them to each other at a distance equal to the height of the slab (10-15 cm), minus the protective layer of concrete (up to 5 cm).
- Pour in the solution. You will need a lot of it; you should not choose low-quality concrete in order to save money. The optimal brand is M300-M400.
The monolithic slab is located at ground level, and involves the construction of a basement and a basement (it serves as the floor). A more massive and recessed one is not needed for a small house; this type is used for large buildings.
Slab foundation thickness calculation - principle and online calculator
UFP is essentially a strip foundation, inside of which a concrete slab is then poured on the floors along the ground, just like in UFP. The pros and cons are about the same as USHP. A columnar foundation is a column that is placed on top of the ground or buried in it like a strip foundation.
Essentially a mixture of MZLF and columnar foundation. Read more about the columnar foundation here with photos. It usually looks like this: A wooden grillage is often placed on top. Pros: Very cheap foundation Very easy to implement Can be done without helpers. Cons: Unreliable, only performed on good soil, otherwise the house may fall apart.
Well, this is an approximate picture of the market for foundations for a frame house. Choose according to your taste and color, or better yet, to suit your soil and home. If anyone has their own experience, it would be interesting to know about it, write in the comments what foundation you chose for your frame house and why. Or are you going to choose for future construction.
I remind you that you can contact me to select a team in your region. I have accumulated a large number of contacts of good builders who build the right houses. I independently designed and built a frame house with my own hands according to all the rules of frame house construction.
I write a blog about proper frame construction using Canadian and Scandinavian technology. I build and design frame houses.
Strip foundation
Email for communication: maximkazakovnn gmail. Communications laid in the underground are easy to repair and easy to replace, unlike in houses where they pass through rooms. Well, the planning possibilities are much wider, i.e. Of course, it is necessary to insulate the base. The disadvantages include the cost; the tape type is approximately 2 times more expensive than the pile-screw type.
But considering that with a cold underground you will have to insulate the floors, install a hydronic or electric heated floor, the costs of insulating the communications input, at the end of construction the costs for both foundations are almost equal. Yes, there is such an opinion. Although an uninsulated floor is still a kind of extreme.
I don't like the soundproofing in it. Do your steps echo around the house too much? The floors won't be hot, but I think overall it will be fine.
Frame house KD 6x6 24m 2 one-story t. Frame house KD 6.5x10 65 85 m 2 1 floor.
Typically, such conclusions are reached in cases where an assessment of the condition of soils on a site indicates their insufficient bearing capacity or a pronounced tendency to frost heaving. You can, of course, lay a deep tape, lowering its base below the freezing level of the soil, but this extremely complicates the project and leads to a large increase in the cost of its implementation. In addition, this may be hampered by the location of underground aquifers being too close. As an alternative, the option of constructing a shallow slab foundation is being considered. Let's take a closer look at this issue: slab foundation thickness calculation, depending on the conditions of the construction site, and on the specifics of the building planned for construction.
Frame house KD 8x9.3 12.3 74 98 m 2 1 floor. Frame house KD 7.8x11.7 91m 2 one-story??? Frame house KD 8x9.2 73 92 m 2 one-story t. Frame house KD 10x16.7 m 2 one-story duplex t. The price includes: insulation mm min. Two-story houses and houses with an attic from up to thousand. Frame house KD-1 6x10 m 2 with a warm attic etc.
Frame house KD-2 6x10.5 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD-8 8.5x9.7 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD-9 10.5x13 m 2 two-story t. Frame house KD 6x10 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 6x7 84m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 6x7.4 89m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 6x6 72m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 8x7.4 89 m 2 with a warm attic, etc. Frame house KD 8.4x10.5 m2 with a warm attic, etc.
Frame house KD 8.4x10 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 8.8x11.7 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 8.4x11 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 8x9 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 8x8 m2 with a warm attic t.
Frame house KD 8.8x9.8 m2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 9x9 m2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 9.5x9.5 m2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 10.5x13 m 2 two-story building. Frame house KD 9x10 m 2 with a warm attic??? Frame house KD 6x8 84 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 6x10 96 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 6x10 m 2 chalets with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 6x9 m 2 with a warm attic t.
Frame house KD 8.4x10 m 2 with a garage and a warm attic t. Frame house KD 7x10 m 2 with a warm attic t. Frame house KD 8.8x11.7 m 2 duplex with an attic t. Frame house KD 8x10.6 m 2 with warm attic t. Frame house KD 8.4x11 m 2 with garage t. Frame house KD 10.5x13 m 2 two-story with garage t.
Small architectural forms - bathhouses, garages, etc. Frame bathhouse KD-7 4x5 20m 2 including stove-fireplace, etc. Frame toilet KD 1.2x1.3 1.3m 2 beautiful and comfortable 10.5t. Frame garage KD 7x7 49m 2 garage t. Play complex KD 1.7x1.7 2.9m 2 with swing 16.2t. Frame house with bathhouse KD 6.5x10 65 85 m 2 1 floor.
slab foundation manufacturing technology
Frame bathhouse KD 6x6 36 44 m 2 with a terrace T. Frame bathhouse KD 6x6 72 m 2 with a warm attic T. Frame bathhouse KD 6 9 x8.7 52 78 m 2 with a terrace T. Frame bathhouse KD 5x6 30m 2 with a terrace T. B bath price included: insulation mm min. Scheme of reinforcement of a monolithic slab.
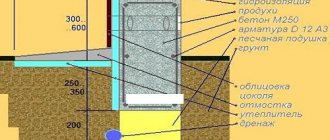
Insulation and waterproofing
The foundations of a wooden frame house require special finishing. Waterproofing is desirable for all structures below grade for any material. This way the elements are better preserved. This is especially true when the groundwater level is high.
Thermal insulation of the foundation and basement walls will ensure minimal costs for insulating the floor of the first floor. In those houses where there is no basement, the space between the ceiling and the ground can be filled with expanded clay and sand. These materials prevent heat from being drawn out from the lower room. To prevent them from getting wet, you can line them with a roofing felt sheet on both sides.
The walls of the strip foundation and grillage are laid on the outside with polystyrene slabs.
Depth of load-bearing structures: soil type
Before carrying out calculations, it is necessary to determine the structure of the soil, the depth of its freezing and the location of the groundwater level.
This will allow you to determine the optimal foundation depth. The supporting structure will be as strong as possible when laid on a homogeneous soil that settles evenly. The soil type is also taken into account.
Cartilaginous soil is a combination of stones and gravel. The minimum depth in this case is 0.5 m. Determining the exact indicator here is influenced only by the groundwater level and the weight of the structure.
In a rocky area where dense rocks predominate, the foundation is laid at a shallow depth, only removing the top thin layer of soil. Sandy soil absorbs water well, which does not stagnate on the surface. Due to this and slight freezing, the depth of the base can be about 50-70 cm. It increases to the freezing level in the case when the soil is dusty or fine-grained, and the location of groundwater is high. Useful: Exterior decoration of a house from facade and basement panels Sandy soils are also special features there is a risk of severe subsidence due to high compaction rates under load.
Therefore, the base must be high, and the depth can be increased to 70-100 cm. The foundation for clay soil must be laid below the freezing point. These recommendations must be especially followed when the groundwater level is high. Such soil is the most dangerous, as it contracts under heavy load and swells when frozen. To avoid cracks, a high-strength foundation is required.