Reinforcement is a necessary procedure for strengthening crumbling banks and ravines. This especially applies to objects along roads and railways, to the banks of rivers and reservoirs, to lands with agricultural purposes. The construction of terraces and retaining walls with reinforcing material greatly facilitates construction and improves the efficiency of construction and excavation work. At different times, a variety of materials were used for reinforcement. With the advent of geosynthetics, work on reinforcing soil structures has become significantly easier and their service life has increased.
Functions and characteristics of geotextiles for foundations
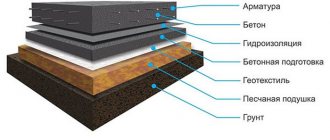
Geotextiles prevent erosion of the bedding and silting of the pit
The basis is polyester, polyamide, fiberglass or polypropylene threads; in mixed versions, cotton or wool blend fibers and viscose are added. They are used in various fields of management; in construction, they lay crushed stone on geotextiles or sand, and wrap foundations.
High-quality polypropylene material is placed in the soil during the construction of runways, railway and automobile tracks, and laid under blind areas and layers of paving slabs.
Does geotextile allow water to pass through?
In general, this fabric is hygroscopic, but each type conducts moisture differently. To determine throughput, the volume of water passing in a given time at a specific pressure is measured.
Permeability depends on the characteristics:
- type of textile (needle-punched allows more to pass through than thermally bonded);
- particle size and pore diameter;
- fabric density;
- surface structure (smooth or rough).
The method of laying geotextiles affects the permeability properties. Some species collect a mass of water along the surface, while others conduct moisture in only one direction.
Selection and installation of reinforcement
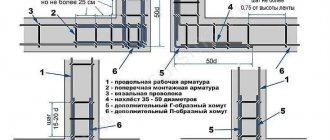
1. For foundations of this type, only ribbed reinforcement is used.
The frame is made of rods 12-16 mm with cells measuring 20 cm. When constructing outbuildings (baths, small country houses, garages), rods 12 mm thick are used. Heavier and more massive one- and two-house houses are erected on a foundation reinforced with rods with a thickness of 16 mm or more. 2. The reinforcement is laid in two layers. The upper and lower horizontal layers should consist of longitudinal and transverse rods. Vertical reinforcement connects both belts together.
Laying reinforcement
Advice.
The strength of the reinforcement at the welding site is reduced, so it is recommended not to weld it, but to tie it. In addition, if the rods are fixed too tightly on moving soils, the rigid ligament may simply burst. Therefore, they must have a certain degree of freedom, which is provided by the ligament. However, in order to avoid displacement of the rods during pouring, they must adhere to the reinforcement quite tightly.
3. The reinforcement should be fastened with binding wire
round section (at least 1-1.2 mm). It must be fired and bend easily.
Knitting reinforcement
4. To tie, fold the knitting wire in half, then wrap it around the reinforcement and twist its ends together with pliers, a special hook, a collet (a device with a sleeve for clamping) or a knitting gun. One knitting requires about 30 cm of wire.
Collet
Hook for tying reinforcement
5. To prevent the reinforcement from touching the formwork, it is better to strengthen it with plastic lugs
.
Plastic sockets for fittings
Types of geotextiles
The material is classified depending on the initial raw materials and production technology.
In construction they use:
- needle-punched non-woven material;
- needle-punched non-woven fabric with heat fixation on one side;
- non-woven needle-punched film with double heat setting.
Cushioning insulation is produced using high-quality equipment, each batch is supplied with technical data sheets and quality certificates.
By composition
Geotextiles are made from polyester and polypropylene
Polyester threads are obtained from recycled materials, then short fibers are bonded into dense layers. The particles are short in length, so the surface is linty.
Polypropylene textiles are produced from primary raw materials in the form of long continuous cords, which creates a durable geotextile for the foundation.
The color can be brown, beige, black, but white is considered the standard color. When wet, polypropylene does not separate into layers, has a dense structure and a smooth surface.
By structure
In woven types, the warp and weft lines are intertwined, and the density is adjusted by the size of the spaces between the threads. The structure provides high tensile strength, which is why high-density woven materials are used to reinforce embankments and airfield elements. Woven loose types are used for blind areas to strengthen the soil of shallow foundations.
Non-woven types are made by thermal or mechanical joining of polymer fibers. In this category, a distinction is made between thermally bonded and needle-punched material.
Application of geogrid for soil reinforcement
Geogrids are used when the destruction of the soil layer is significant and it will be necessary to fill it up to strengthen it. Laying geogrid makes this job easier. The newly applied soil is placed in cells and does not slide down the slope or slope. Geogrids also do not prevent plants from developing their root systems and allow precipitation to pass deep into the soil layers. Geogrids can be made of extruded polyethylene tapes or woven polypropylene. Their technical features are almost identical:
- rib height – from 50 mm to 200 mm;
- tensile strength – up to 22 kN/m for polyethylene and up to 100 kN/m for polypropylene;
- elongation at break – up to 30%.
Geogrids are used for large volumes of excavation work and when it is necessary to strengthen very large areas of slopes, cliffs and slopes. Together with other geosynthetics, geogrids can provide reliable protection for artificial soil structures and natural objects during road construction and landscape design.
Rules for choosing geotextiles for the foundation
Geotextiles for the foundation must be dense, strong, durable
Insulating fabric is used in many areas, but special selection criteria are used for construction. The separating layer of geotextile under the foundation slab must have high mechanical and physical properties.
To choose, consider the following qualities:
- versatility of use;
- density;
- affordable price;
- environmental friendliness;
- durability;
- strength.
The widespread use of geotextiles is explained by simple installation, which can be easily performed by people without special qualifications. The canvas weighs little and is cut with scissors.
When can you use a slab foundation?
Unlike strip foundations, a 25-40 cm thick slab is laid not under load-bearing walls, but under the entire building. When the ground moves, such a “cushion” will rise slightly at the same time as the house, without causing any damage to it. Shallow slab foundations are most often used in northern Europe for light-weight buildings
.
To make such a base, frost-resistant concrete M300
with W8 water resistance. If the groundwater is too close, it is advisable to use special sulfate-resistant concrete.
Advice
.
If the structure is heavy, to protect the slab from cracking, you can use structures equipped with ribs
directed towards the ground. Such ribs, like the base itself, are reinforced with metal rods.
Ribbed foundation slab
The most significant disadvantage of slab structures is the complexity of the construction of basements and ground floors. After all, during their construction, the cost of the insulation layer will be equal to the cost of the foundation itself.
Possibility of replacing geotextiles
Instead of geotextiles, you can use roofing felt, but it is less durable
The canvas performs special functions that are difficult to reproduce with other materials. In exceptional cases, builders advise using gaskets with similar properties, but the quality of protection may suffer as a result.
What can be replaced
If it is not possible to purchase and install geotextiles, builders use roofing felt. This insulator keeps the cushion from getting wet, but has a shorter service life (20 years versus 80 years for geotextiles).
Sometimes a small mesh made of galvanized or metal is installed. Such layers partially perform the functions of a geotextile. An analog material is Dornit, which is a type of geotextile material.
What useful functions does it perform?
- Soil strengthening. Correct use of geosynthetics is the key to success when solving specific problems of foundation arrangement. Geotextiles are laid in a dug pit. When mechanical reinforcement of the foundation is required, the area of the laid geotextiles must exceed the area of the house. An area covered with canvas should extend at least a meter from the wall in each direction.
It is reliable to use a cushion made of crushed stone wrapped in geotextile. Keep in mind that if you place geofabric exactly to the size of the foundation, the task of strengthening the soil will not be completed!
- Protection of the foundation from groundwater. The property of interrupting earthen capillaries makes it possible to reduce the seepage of water to the foundation.
- Increasing the strength of the concrete foundation. By preventing the seepage of liquid “cement laitance” from the concrete mortar into the ground, a geotextile bedding under the foundation allows you to preserve all the specified properties of concrete.
- Arrangement of drainage. Geotextiles have no equal in their ability to prevent siltation of the drainage system. Wrapping them around a drainage pipe increases its service life. To achieve even greater drainage efficiency, all drainage aggregate is completely placed in the geotextile. This is crushed stone with a drain inside. In this case, the filler may have a larger fraction - and therefore be cheaper.
Using geotextiles for different types of foundations
The insulator is produced in rolls with a width ranging from 2 to 6.5 meters and a length of 30 to 130 meters. The dimensions of the unit are determined depending on the scale of the work.
Density is selected according to the type of construction:
- for private housing construction, geotextiles with an index of 200 – 300g/m² are needed;
- unstable soils are drained with material 300 g/m²;
- simple landscaping work - 100 - 200 g/m².
When arranging the foundation, take material with a density of 150 - 400 g/m², the value depends on the type of foundation and the quality of the soil.
Tape monolithic
The use of geotextiles for strip foundations
The fabric is laid at the bottom of the trench to protect the layer of sand and crushed stone from getting wet. The edges of the geofabric are wrapped onto the pillow with a slight overlap. The material is placed inside the formwork so that after pouring it appears on the outside of the tape strip and protects it from moisture.
Install according to the instructions so as not to confuse the sides during installation. Thermally bonded type is used with a density of 200 – 250 g/m². The denser type costs more, but the results are similar.
Precast concrete strip
The use of geotextiles in the construction of prefabricated foundations differs in that the insulation is glued to reinforced concrete blocks using molten bitumen or special mastic.
The seams are treated with glue, and the edges are brought out, and after installation they are turned up. Seamless installation must be ensured. They use material with a density of 250 g/m², made by the thermopress method.
Pile foundation
Geofabric is placed in a pile foundation in case of construction of a basement floor. After driving the vertical posts, the top soil layer is cut off and a layer of canvas is laid. A sand and crushed stone layer is placed on it under cement mortar.
The material prevents soil heaving and earth movement. The canvas prevents the base from getting wet and the walls of the house from getting wet, which requires geotextiles with a density of 100 - 200 g/m².
Slab foundation
It is equally important to use geotextiles for a monolithic foundation slab. In this case, the bottom of the excavated pit is covered with insulation over the entire area. Choose fabric with a density of 350 g/m². Place the canvas again on the surface after installing and compacting the underlying cushion, take an indicator of 200 - 250 kg/m².
To reliably protect the slab foundation, thermo-pressed polymer types of textiles are used to protect the monolithic concrete slab from exposure to soil and rain liquid.
Blind area
When constructing a blind area, geotextiles are placed under a concrete strip
The blind area protects the foundation from rain and melt water, but is in an open state and interacts with groundwater. Its destruction is prevented by making a waterproofing lining, for which geotextiles are placed under a concrete strip.
The insulation is laid along the base of the open pit so that the outer ends can be folded over the underlying layer. The blind area often fails because... A large amount of water flows from the roof and moistens it. A separating layer with a density of 150 - 200 g/m² will protect the strip from vertical shifts.
Drainage properties of geotextile materials
Geotextiles in a closed drainage system
Only closed drainage can stabilize the groundwater level at a given level, in the standard version 30-40 cm below the base of the foundation. Restoring the functionality of the drainage system is an expensive and labor-intensive job, including excavation work, dismantling and cleaning drains from silt, and replacing the filter casing. You can increase the drainage life between repairs to 15 years if you use needle-punched geotextiles with a density of 150-200 g/m2 as the filter material.
If all the requirements of the installation rules are met, the funds invested in the arrangement of drainage and foundation waterproofing will be compensated by improving the microclimate in the basement, increasing the service life of the foundation and the entire structure as a whole.
High-density geotextiles have the ability to evenly distribute loads. Fabric reinforcement will increase the load-bearing properties of sandy soil. As a separator, the material eliminates the interaction of sand and crushed stone filling, thus eliminating the possibility of shrinkage of the foundation of the house and deformation of its walls. Sub-foundation crushed stone foundations equipped with a geotextile cover have the best efficiency and durability.
Popular types of domestic materials
GC "Polymerholding" produces the "Dornit" line. A popular brand name refers to all geotextiles used in construction. The company produces non-woven and woven varieties for home and garden use.
Geotext Group LLC produces geomaterials for individual construction and road work. Large-scale production provides heat-pressed types for drainage, construction of reservoirs, and sports complexes.
Nomatex LLC produces high-quality textiles for mass use and for individual orders with a density of up to 800 g/m². Rolls up to 5 m wide are used for seamless covering over a large area.
Avantex LLC produces needle-punched category, the density of the material is 100 - 600 g/m², and the roll width is increased to 6.3 m. The raw materials are primary products and secondary waste in the form of polypropylene and polyester.