Korovin Sergey Dmitrievich
Master of Architecture, graduated from Samara State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering. 11 years of experience in design and construction.
Foundation conservation is understood as a set of measures to protect building structures from adverse environmental influences during the cold season. The need for protection arises in the event of a forced stop in construction due to the impossibility of completing it before the onset of frost.
The main factors contributing to the destruction of the foundation in winter are:
- exposure to moisture;
- low air temperature and its sudden changes;
- deformation pressure from soil heaving.
The list of protective measures taken and work performed depends on the type of foundation, its size, lower support point, freezing depth, type and composition of soil.
Preservation of the foundation for the winter (methods)
Often, preservation of the foundation for the winter is carried out in situations where there is not enough financial opportunity to fill the foundation, install walls and roof within one season.
The main task of conservation is to ensure the protection of underground reinforced concrete structures from the effects of moisture and deformation forces that arise during soil heaving.
To do this, they use a waterproofing coating, insulate the soil next to the foundation, and carry out measures related to the arrangement of the drainage system.
Methods for preserving the foundation
The decision to pour the foundation before the onset of winter has its justification.
During the winter period, the foundation will gain the necessary strength, and with the arrival of spring it will be possible to begin building the walls.
When the construction process is frozen at the stage of foundation work, certain problems arise:
- There is no load on the power structure to compensate for soil deformation during frost heaving;
- Cracks open from frozen moisture inside the concrete coating;
- Rupture and deformation of reinforced concrete structures may occur as a result of soil swelling.
The occurrence of deformation forces can be observed in the presence of:
- High clay content in the soil;
- Large amounts of moisture;
- Low negative temperatures.
By removing any of the components, we can reduce swelling or completely get rid of it.
Based on the above, we can conclude that to preserve the foundation for the winter it is necessary:
- Insulate the perimeter of the building;
- Protect the concrete surface and soil from moisture;
- Replace heaving soil with non-metallic material.
What needs to be done to freeze construction work
In order to suspend construction work before spring, foundation work should be completed. It is necessary to install a drainage system around the perimeter of the foundation.
Waterproof the concrete surface using polyethylene film or rolled bitumen materials.
Insulate the foundation using expanded polystyrene.
Backfill the foundation with non-metallic material. The thickness of the insulating layer should not be less than 20 cm.
Provide an underground reservoir for the drainage system. It should be located below the foundation sole.
Protect the concrete surface from freezing from the sides. To reduce costs, you can use snow as insulation.
Insulation of foundations for the winter period
Since the most difficult operation to preserve the foundation of a house in winter is insulating it on each side, it is worth considering such work in more detail.
Such work should be carried out immediately after the foundation itself has dried, when the formwork is removed. Then you can not only leave the base of the house unloaded in winter, but also get warmer floors later, when the building is built.
The insulation process will look like this:
- polymer-bitumen mastic is applied to the vertical surfaces of the tape (supports, slabs) as a waterproofing layer - this will prevent moisture from spoiling the finished base;
- The vertical sides of the base are covered with expanded polystyrene slabs, using adhesive compounds for this - this will insulate the foundation and additionally protect it from damage;
- additional finishing of the slabs attached to the base is carried out using plaster - this will extend the service life of the foundation for many years;
- backfilling is carried out with non-metallic material in a layer of at least 18 cm with dense compaction.
Carrying out protective measures
Preservation of the foundation for the winter of a structure with a floating slab will include preparatory operations aimed at waterproofing the concrete covering and insulating the blind area.
Even if uneven swelling occurs after the soil thaws, the foundation slab will not be damaged.
It is much more difficult to prevent damage to the strip base. Moisture gets into the structure.
With uneven swelling, the strip structure is affected by forces that cause twisting and bending of the foundation.
Therefore, before preserving the tape base for the winter, the following actions should be taken:
Remove the formwork from the structure. Wood panels will not protect the concrete surface. They will absorb water and contribute to excess moisture in the concrete. There will be an additional risk factor when freezing.
Waterproof the concrete base using gluing, coating or plastering. Make and install a drainage system. Insulate the blind area.
Despite the work carried out, it is difficult to maintain the foundation structure in its original condition. The main structure is missing.
When using additional thermal insulation, it is impossible to achieve the desired effect. To protect the foundation structure from moisture and frost, the following methods are used:
- The perimeter of the construction site is cultivated. The soil near the foundation is plowed;
- Insulation is made using snow. Install snow-retaining shields;
- The foundation base is covered with natural insulation and polyethylene film.
After soil aeration, its density decreases and water saturation increases. When frost sets in, the swelling disappears.
The following natural insulation materials are used: straw, sawdust, bark shavings and various slags.
Methods for compensating for deformation effects on a strip structure
A strip foundation structure left for the winter is similar to the foundation of any unheated building structure.
In order to compensate for the deformation forces that arise during soil heaving, the following scheme is used:
- A polystyrene foam covering is placed under the entire base of the building;
- The blind areas are insulated with insulating sheets 5 cm thick;
- The thickness of the insulating material in corner areas, under the blind area should be 10 cm.
Frost protection used for long-term preservation
If construction is expected to be frozen for a long period, the facility should be re-opened upon the onset of spring.
Here is another addition to the article in the video:
As a result of this, excess moisture will evaporate and the foundation elements will dry out.
The structure is prepared for the next onset of winter as follows:
- Drainage sewerage is being laid;
- Engineering systems are being fastened;
- The grounding loop is extended;
- A waterproofing coating is laid on all concrete surfaces;
- Horizontal and vertical insulation is installed;
- Backfilling is carried out using non-metallic material.
Share this article with your friends on social media. networks!
Conservation of a construction site
For whatever reasons, the construction of the facility was suspended in the winter, it is necessary to carry out a set of necessary work to prepare for the conservation of the facility itself and the materials brought for construction.
Snow and frost can greatly damage the foundation
There are several reasons that can cause damage to prepared building materials and erected structures:
- Atmospheric precipitation - water from rainfall is absorbed into materials and accumulates in the cavities of building structures. With the onset of the first frosts, the water freezes and expands significantly, which can cause destruction of building structures and damage to materials.
- Low temperatures can cause deterioration in the properties of some building materials, which lose their properties and become very brittle. To prevent damage to material resources, it is very important to cover them correctly.
- Water and frost cause a phenomenon called soil heaving - frozen wet soil begins to push foundation structures to the surface of the earth. Shallow foundations suffer greatly from this phenomenon.
- Excessive snow load in winter can cause the collapse of building structures that are not designed to withstand a load of such force.
- The last reason in favor of conservation is not related to natural phenomena or the design features of the building. At a site unprepared for wintering, there is a danger of theft of materials that are not guarded by anyone during the winter period.
Related article: When to remove formwork after pouring concrete
Preservation of strip foundations
Since the main threat to unfinished construction is moisture, the entire range of conservation work is aimed mainly against its destructive effects. If the concrete poured under the foundation is excessively waterlogged, winter changes from positive temperatures to their low negative values lead to its cyclic freezing and thawing, which contributes to cracking and destruction of the laid monolith.
To protect against the penetration of moisture from the soil, the foundation is waterproofed using various rolled materials, namely:
- roofing felt;
- thick polyethylene film;
- waterproofing film with microperforation.
Based on the above, it can be noted that the market, in addition to the traditionally used roofing felt, is replete with films that tightly adhere to the surface when exposed to heat. However, with this method there is always a risk of penetration of wet precipitation between the foundation wall and the waterproofing due to poorly executed top covering of the structure. The trapped moisture, freezing and expanding, may well tear the protective waterproofing material, as a result of which all the work will have to be done again in the spring.
A better and more modern option for waterproofing would be to use micro-perforated polyethylene. Its main advantage is that the poured foundation gets the opportunity to “breathe” under such a film, without allowing moisture from the outside to pass through. In addition, the material is plastic and quite simple to install, which cannot be said about roofing felt.
The threat of precipitation penetration if the foundation is incorrectly covered can be avoided by using bitumen or other liquid mastic as waterproofing. However, it is important to remember that any coating insulation will need to be protected from damage when the foundation is backfilled with soil. For such protection, you can use fabric materials, such as burlap, or use insulation if the project involves their use.
Coating waterproofing of a strip foundation made of monolithic reinforced concrete should be carried out no earlier than a month after it is poured!
You can protect a strip foundation with prepared waterproofing from rain and snow falling on it for the winter with roofing felt or thick polyethylene film, laying it on top of reinforced concrete along the entire perimeter of the structure and pressing it down on top and on the sides with something heavy.
Stages of preserving an object for the winter
The optimal solution for preserving an object for the winter is to carry out measures at a certain stage of construction. The following building structures can be closed for the winter:
- Foundations with a basement or basement floor completed by construction.
- Walls of a one-story house with an attic ceiling.
- Second floor walls with attic ceiling.
- Finished building box with roof.
- The finished building box without finishing work.
Sometimes you have to leave a building with unfinished construction stages for the winter; such objects can be closed until spring in the condition in which they actually are.
Covering foundations
Actions to preserve foundations for the winter in most cases are aimed at carefully covering the foundations, especially if the support base is erected on heaving soils of deep freezing. If the soil under the foundation was not replaced, technically the issue was resolved only by making a sand cushion, there is a danger of destruction of the unloaded foundation belt in winter due to frozen soil. This structure cannot be left unloaded in winter.
Foundation cover
It is possible to prevent the destruction of foundations; for this it is necessary to erect a temporary shelter for the support. Materials for insulating foundation supports can be hay, straw, expanded clay, sawdust, slag wool and other materials.
To protect structures from the flow of rainwater and snow accumulation, you can insulate the foundation using film materials.
Each type of foundation is preserved for the winter with the implementation of certain measures. You can get acquainted with the technology of insulation of various foundation structures more closely, find out which foundations can be left without load.
Strip foundations: preservation for the winter
Before carrying out work on preparing the strip foundation for the winter, it is necessary to dismantle the formwork panels, but to do this you should make sure that 28 days have already passed since the day the structure was poured with concrete. The foundation must gain full strength.
Leaving formwork on the foundation structure in winter is dangerous, because unprotected wood quickly absorbs moisture, transferring it to concrete. When the temperature drops, water-saturated concrete will freeze, expanding as it freezes, and the water can cause irreversible damage to the supporting structure.
Insulation of strip foundations for the winter
The stages of conservation of strip-type foundation supports include the following work:
- Performing reliable waterproofing - for this you can use roofing material, waterproofing, reinforced durable film. Sections of waterproofing material are overlapped onto the strip foundation structure with sufficient overlap. The laid film or roofing felt is pressed down by heavy materials or structures.
- Providing insulation - polystyrene or foam plastic slabs can be laid on top of the foundation structures, covering them with reinforced film on top. In the absence of foam plastic slabs, you can use construction expanded clay, a layer of which is poured over the constructed foundation.
- Water drainage - to remove moisture from precipitation and soil water that has risen as a result of autumn rains, you can arrange an improvised drainage system. To do this, at a distance from the foundation of the house, you should dig a deep pit (at least 2 meters). Dig several trenches to the pit, which will serve as drainage ditches during rains.
It is very important to remember that only those foundation structures that have gained full strength after pouring the concrete mixture into the formwork can be insulated for the winter.
Preserving the foundation for the winter, especially the strip foundation, is a very important and responsible undertaking that must be taken seriously. Watch the video on how to cover a strip foundation for the winter.
Insulation of a monolithic slab
When preparing to preserve the foundation slab for the winter, it is worth remembering that the base of this structure is already insulated. Protection from frost and groundwater is provided by a sand-gravel cushion laid on the bottom of the structure before pouring the concrete mixture. A layer of waterproofing and insulation is laid on a sand layer, only after that work on reinforcing and concreting the slab continues. Based on this, the lower part of the slab foundation does not need to be insulated.
Protection from low temperatures and excess moisture must be performed only on the sides of the slab base. To do this, you can lay a layer of polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam, or cover the side edges of the slab with expanded clay.
A slab foundation cannot be left unloaded for the winter, therefore, after insulating the outer surface of the slab foundation from precipitation and insulation, the monolithic slab should be loaded, distributing the load as evenly as possible over the entire surface.
Preservation of screw pile foundation
When constructing a foundation on screw piles, especially in swampy areas and peat bogs, all construction work is planned for cold weather.
In winter, it is possible to screw piles into water-filled and mobile soils to a sufficient depth, which eliminates the risk of deformation of the foundation belt during further operation. Screw foundations screwed in in the summer do not need special protection from frost and atmospheric moisture; you just need to tie the piles with rolled metal (make a grillage), and also check that the internal space of all piles is filled with a concrete mixture, that the caps are installed on each pile.
How to prepare columnar foundations for winter
Columnar foundations do not require serious insulation measures in winter. These structures have little contact with the ground and open air. The foundation is practically not subject to winter buckling, with the exception of shallow columnar foundation structures; there is a risk of uneven buckling of individual supports.
To prevent damage, it is imperative to erect a grillage; it is advisable to complete the work before the onset of winter.
Preservation of slab foundation
Waterproofing of a shallow foundation slab is carried out before it is poured, which protects the structure from groundwater, especially in the autumn-spring period. Waterproofing materials and the required insulation are laid on a sand cushion or concrete screed, followed by the installation of reinforcing mesh and the slab being poured with concrete. It’s worth mentioning right away that such a foundation should not be left unloaded for the winter. Due to freezing of the soil, it heaves, which can lead to lifting of sections of the slab and cracking of the monolith.
If construction work still has to be stopped for the winter before even partial construction of the walls of the building begins, then it will be necessary to provide the maximum possible temporary shelter and insulation of the foundation itself, as well as some area around it. Expanded clay, waste slag, slag wool and even straw or sawdust are quite suitable for this.
The most optimal option for protecting the slab from precipitation would be to install a temporary roof. It is made from the cheapest building materials in the form of a sheathing covered with roofing felt. This, however, will require at least partial construction of the walls of the building.
Preservation of the foundation for the winter
The inability to complete construction before the onset of cold weather leads to the need to protect the concrete foundation from the negative effects of the external environment.
If this is not done, it may receive obvious or hidden damage. In the first case, we are talking about visible breaks, cracks, deformations and other similar defects. Even if you try to eliminate them, it will be impossible to achieve the previous integrity of the structure.
Related article: Do-it-yourself OSB formwork for foundations
A more dangerous situation is when the concrete base receives hidden damage. They can arise for the same reasons as visible defects (swelling of frozen soils, temperature changes, high humidity, etc.) - but they do not appear immediately, but after a certain time. Sometimes problems with the foundation become known only at the final stages of construction and even after its completion, which leads to the impossibility of operating the facility.
Is it possible to leave the foundation for the winter?
Preservation of the foundation for the winter is required regardless of the degree of its readiness. Otherwise, there is a high risk of losing already created foundation structures.
Low temperatures and high humidity have a destructive effect on the concrete base. The degree of negative impact depends on the following factors:
- climatic features of a particular region;
- type of foundation (pile, strip, columnar, etc.);
- the stage of work after which the foundation will have to be left for the winter;
- structure and other features of the soil (heaving, freezing depth, presence of groundwater in the immediate vicinity, etc.).
The most resistant to adverse weather conditions are pile (screw) foundations. Strip structures and concrete monolithic slabs are at greatest risk of destruction.
No less dangerous is the swelling of the soil due to its freezing. This phenomenon can seriously destroy the concrete base to the point of making it impossible to use further. Tears, deformations, distortions, and other defects appear. Strip foundations and monolithic slabs suffer the most from soil swelling.
Preserving the foundation in winter: options
To ensure that the foundation of the future house, previously poured and completely ready for further work, does not crack over the winter, it can be preserved in one of several ways:
- cover with thick construction film, sprinkle soil on top and press down with stones;
- protect from excess dampness and water using drainage;
- make additional waterproofing on all sides of the base of the house;
- cover the base of the building with one of the types of greenhouses;
- insulate the outer sides of the foundation with polystyrene foam, and backfill with non-metallic material in a 20 cm layer with mandatory compaction of the soil.
Of course, each type of base requires its own conservation. But these methods can be combined and used for any ready-made base . After all, the main reasons for the destruction and deformation of the flooded foundation of a house are increased heaving, the proximity of groundwater and the lack of load on the foundation.
Having eliminated one or more causes of damage to the foundation during the winter season, you can safely leave the foundation of the house for the winter.
Is it necessary to cover the foundation for the winter?
The need to cover the base depends on the degree of its current readiness. It is sometimes possible to keep the foundation open for the winter under the following conditions:
- concrete gained strength at positive air temperatures for at least a month (this rule is the most important);
- high-quality vertical and horizontal waterproofing was performed;
- tamping was carried out, the internal space and sinuses were filled;
- A hydraulic lock is made in the upper part of the backfill.
If it is necessary to fill the base at negative air temperatures, it is necessary to use special anti-frost modifiers. A more complex option is to heat the entire structure until it reaches the required strength.
Waterproofing is especially important for lightweight concrete. In other cases, its absence is allowed - if the soil is dry and the soil waters lie deep enough. But in this situation, when preserving the foundation for the winter, you can leave the foundation for the winter only under cover.
As for the backfill, it protects the created foundation from flooding by melt or rain water.
Concreting foundations in frosty conditions
Sometimes it is necessary to carry out work to create a foundation at a time when the air temperature is tens of degrees below zero. Or when concreting, the solution has not yet had time to dry, and frost is already setting in. In this case, there is no need to despair. You just need to perform a device called a heater, and calmly continue working as usual.
During winter concreting, the implementation of greenhouses becomes an indispensable operation. And although carrying out work in such a device is quite comfortable, the construction of the structure itself requires a lot of money.
Several types of greenhouses are used for winter concreting. Their difference is in the height of the structure. And the height depends on the degree of work performed.
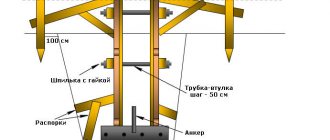
Actually, a warm house is the same temporary hut. A wooden frame is built over the unfinished foundation. It is covered with thick film or plastic. The resulting building resembles an ordinary greenhouse, with a door for entry.
It is important to remember that if you do not cover the frame tightly with film, warm air will escape from the greenhouse. And the building will not have the desired effect.
Heat guns are installed inside the greenhouse, which will maintain positive temperatures. This allows you to get a well-seasoned foundation when concreting in winter.
Is it necessary to load the foundation for the winter?
Leaving your foundation unloaded over the winter can be dangerous. One of the main threats to an unloaded foundation in the cold season is the risk of its destruction under the influence of such a phenomenon as swelling of the soil due to its freezing. First of all, shallow, monolithic and strip structures are susceptible to it.
Frozen wet soil pushes foundation elements out of the ground. This leads to their ruptures, deformations and distortions, violating the integrity and structure of the prepared base.
Thus, the absence of loads from the erected power structures of the building leads to the impossibility of compensating for buoyancy forces arising due to swelling of frozen soils.
Therefore, if you do not plan to load the foundation for the winter, it is necessary to take a set of measures to protect it from the negative impacts of climatic and geological nature. Otherwise, it may be subject to complete or partial destruction, up to the impossibility of subsequent operation.
Why insulate the foundation?
If the building being constructed is built on heterogeneous loamy or peat soils, then the shallow slab foundation will require mandatory insulation for the winter. The fact is that such soils are subject to heaving and deformation during freeze-thaw cycles. Regardless of the weight of the foundation, frozen soils are capable of pushing it upward, which is why the geometry and horizontality of the structure may well change, and cracks will appear in the body of the monolith.
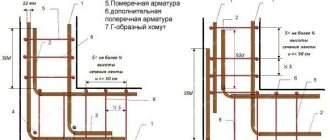
The soil from freezing of the slab foundation is protected by the insulation laid when it was poured. Thermal insulation of a strip foundation is carried out after its waterproofing at the depth of soil freezing. As a reliable insulating material, 10-15 cm thick slabs of extruded polystyrene foam or penoplex are used.
Foundation conservation work
The process of preparing a poured foundation for the upcoming winter period depends on its type and design. It is important to follow the sequence of steps and procedures, since even minor deviations from mandatory technologies can lead to devastating consequences.
Strip foundation
This type of foundation is one of the most susceptible to destructive effects from swelling soils, as well as high humidity and low temperatures. Therefore, preservation of the strip foundation for the winter is necessary, and in order to protect the foundation for the winter, several types of work should be performed, the main of which are:
- mandatory removal of formwork, since wood attracts moisture and then transfers it to concrete;
- waterproofing of the entire structure, for which different materials can be used: plaster, coating, primer, roofing felt, etc.;
- construction of a drainage system, and it is recommended to do it while working on the foundation (but it can be done immediately before conservation);
- insulation using polystyrene foam, polystyrene or other suitable materials, followed by covering with reinforced film.
In any case, it is necessary that before preserving the strip foundation for the winter, it must gain strength for at least a month at positive air temperatures.
Monolithic slab
This type of foundation, left without load, is most susceptible to deformation, erosion and displacement in winter. Its vulnerability is due to the fact that due to its relatively small thickness, the entire structure is actually located in the zone of soil freezing.
The presence of a sand-gravel cushion and a waterproofing layer protects against soil water and swelling, but in any case it is impossible to leave the slab foundation unpreserved for the winter. It is necessary that before the onset of cold weather, concrete gains strength for at least 30 days at positive air temperatures.
Before leaving the base for the winter, it is necessary to protect not only its surface, but also the surrounding area from moisture. You can use film, waste slag, expanded clay, etc. You must first provide insulation - polystyrene foam, polystyrene, dry sawdust or sand are suitable for this.
Screw pile foundation
This type of base is least susceptible to moisture, low temperatures and swelling frozen soils. Pile structures can be erected both in summer and winter. They are used on weak, crumbling, swampy, etc. soils, as well as in areas with high groundwater levels.
Special preservation of the pile foundation for the winter is not required; the preparation technology may only include tying from rolled metal. You should also first check that the internal space of the installed piles is filled with concrete, and that it is desirable to have a cap on top.
Columnar foundation
Structures of this type are used primarily for the construction of relatively light buildings, for example, frame, wooden, panel houses. The peculiarity of such bases is that they have little contact with open air and soil.
Related article: Which foundation to choose
They are practically not subject to destruction due to lifting forces from frozen soils. The only exceptions may be some types of shallow structures: in this case, uneven lifting of individual pillars is possible.
To prevent such damage, it is recommended to create a grillage. This will be the conservation process - but it should be borne in mind that this work must be completed before the onset of cold weather.
Is there a need to preserve the foundation?
The most optimal option for private housing construction is considered to be a phased construction of the building, when during the first year the development of the site is carried out with the laying of communications and laying the foundation, in the second year the box with the roof is erected, and in the third year the interior finishing is carried out. This is due to the specifics of a number of technological processes that can only be carried out at positive ambient temperatures. But it is precisely this sequence that allows the structure to be used for a long time without fear of shrinkage or cracking.
Moreover, some experts recommend leaving the finished foundation without load for the winter (until next spring) for its natural shrinkage and acquisition of the required design strength. Of course, modern technologies make it possible to carry out construction work even at negative external temperatures, but this requires the use of expensive grades of concrete or special additives, which leads to additional costs.
In any case, if you leave the foundation unprotected throughout the winter, then in the future there is a risk of encountering certain negative consequences.
- In the autumn-spring period, the underground structure can be washed away by groundwater accumulating in the pit.
- Atmospheric precipitation will probably fill the dug pit with water, from which it will be quite difficult to pump it out.
- Under the influence of negative temperatures, the exposed foundation can crack, after which its restoration becomes impossible.
- In addition, a frozen foundation loses its strength characteristics and gradually begins to collapse over time.
Thus, the question of the need to preserve the foundation is obvious and comes down, as a rule, to its thermal and waterproofing, as well as the creation of a drainage system for draining groundwater. It is worth mentioning here that pile foundations, in principle, do not require insulation or waterproofing. For the winter, slab and strip foundations are preserved.
When and how to prepare the foundation for winter?
Thus, the preparation of a concrete base left without load for the cold season depends on its design and engineering features.
The process of preserving the foundation for the winter must be followed in compliance with technology and using suitable materials. In the absence of the proper experience and skills, it is recommended to invite specialists, since even seemingly insignificant errors can lead to complete or partial destruction of the structure.
It is best if by the winter period the main structures of the building (walls, partitions, roof, etc.) stand on the foundation. This will eliminate the need for additional protection from humidity, low temperatures, swelling of frozen soils and other destructive influences from the external environment.
However, this is not always possible: most often, delays in building a house are due to lack of time or money. In such situations, proper preparation of the concrete base for the winter season allows you to postpone the construction of walls and other structures until spring without the risk of damage or destruction.
The type of foundation is selected taking into account the design of the house, the condition of the soil and other nuances. For any questions, please contact the specialists of Territory Group of Companies by phone or via the website.
How to preserve the foundation for the winter?
The final quality of the entire building will depend on how correctly the foundation is preserved for the winter. There are several ways to preserve the erected foundation of a building during the winter:
- Cover the foundation with one of the types of greenhouse.
- Drain the soil to protect the base from excess water. Additionally, waterproofing should be laid around the perimeter of the poured foundation.
- Cover with thick construction film, cover with a small amount of earth and press down with stones.
- Cover with polystyrene foam on the outside. Backfilling in this case should be carried out with non-metallic material, and compaction of the soil in this case is mandatory.
Naturally, each type of foundation requires its own conservation technology and this must be taken into account. The degree of concrete’s ability to withstand sub-zero temperatures is determined by the time period that has passed since it was poured and what types of work were completed before the onset of frost.
You can leave the support without cover only in cases where the pouring was done more than a month ago at a temperature above 0 o, and its sides and top are covered with waterproofing material.
Proper backfilling will protect the foundation from liquid that may get under the base during the spring melting of snow and autumn rains. Waterproofing is used only for concrete with low density, since it absorbs moisture well, which, getting into microcracks and seams, can break it when it freezes. But if you are the owner of a site with a low groundwater level and dry soil, then it will be enough to cover the base with any material that does not allow water to pass through.
Conservation by snow retention.
How to drain groundwater
In rainy autumn and especially in spring, groundwater rises, and the soil is saturated with moisture as much as possible. During frosts, wet soil hardens, expands and creates a certain pressure on the foundation. Frost heaving of the soil is quite dangerous for the foundation laid for the winter, therefore, to prevent its negative impact, a number of measures are taken to install drainage to ensure the removal of excess moisture. The simplest way is to plan the surface at the construction site. To ensure natural water flow, a slope is made in the direction from the foundation with the maximum possible addition of soil around and along the structure.
If construction is carried out in a lowland, then the only possible option would be to install a bypass trench and drainage system.
Along the perimeter of the laid foundation, a shallow bypass channel 30-40 cm deep is dug in the direction of the existing natural slope so that the accumulating water can move by gravity. If there is no such slope, it will need to be provided when laying a drainage trench leading to an dug reservoir for drained water. For normal functioning of the drainage, the bottom of the receiving pit must be located half a meter below the level of the bypass drain.
A responsible approach to preserving a concrete foundation for the winter allows you to preserve it as much as possible for further construction, acquire high strength and save funds already invested in the construction.
Conservation by foundation type
Tape
How to preserve a strip foundation? The main point before starting conservation is to dismantle the formwork, because it is made of wood and during the autumn rainy season it will absorb a significant amount of moisture, which the concrete will then absorb.
Next, waterproofing is installed using roofing felt, waterproofing and reinforced film. The material used is laid on the foundation with a margin so that there are no gaps. The waterproofing material is secured on top with stones or other weighty structures.
The strip support is insulated. To do this, the structure is covered with a slab of polystyrene foam or polystyrene, and then covered with a thick film.
Moisture removal. You need to dig a small pit at a distance of 3-5 m from the concrete base and dig a couple of trenches leading to this hole, through which water will flow.
Slab
The monolithic slab is a solid reinforced concrete structure. Such a slab ensures the stability of the house even on the most unstable soils and completely eliminates its possible deformations during soil heaving, since in this case the entire monolithic structure rises and falls back, and not its individual sections.
Insulation of a slab foundation requires minimal effort, since when constructing this type of structure, the base is already insulated with a cushion of sand and gravel mixture, and waterproofing is carried out even before concreting.
Therefore, work to protect against excess dampness and frost, using polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene, needs to be done only on the sides of the structure, sprinkled with expanded clay. The upper base of the monolith slab should not be left without load, which, at the same time, must be distributed as evenly as possible.
On screw piles
A pile foundation is installed in cases where construction is carried out on weak, crumbling rocks that are not able to withstand the heavy load of the house.
When using a pile base, the load is transferred to denser and more stable soil. Pile structures are especially often used in heaving soils with deep freezing levels (over 1.5 m). It is also advisable to install it in areas with high groundwater levels.
All construction work is carried out mainly at sub-zero temperatures. It is at this time that it is possible to install piles in moving soil.
Screw piles do not require additional conservation in winter, with the exception of performing a grillage (tying the piles with rolled metal) and checking all piles to ensure that their internal space is completely filled with concrete.
Preservation using insulation.
Stolbchaty
A columnar foundation is erected for wooden, panel and frame houses with light walls.
The base of the columnar frame does not actually come into contact with open air and soil, and therefore it is not subject to heaving (except for shallow structures). Therefore, in order to properly preserve the foundation for the winter, as well as to prevent uneven bulging of individual supports during the cold period, a grillage should be carried out.
For a more detailed study of the issue, we offer the following videos.