Recently, the building materials market has significantly expanded the range of products offered. The increasing pace of construction of individual housing and small private enterprises places demands on the construction industry to create lightweight, relatively inexpensive, easy-to-install materials. At the same time, they must meet all environmental safety requirements and have good strength characteristics, be moisture resistant, retain heat well, and have good sound insulation characteristics.
In the modern construction market of wall materials, aerated concrete has recently become widespread. Its most important property is environmental friendliness, which foam blocks do not have at all.
Traditional materials such as brick, reinforced concrete panels and wood have been replaced by fundamentally new wall structures - cellular concrete structures - such as aerated concrete or foam concrete. Comparison of these materials based on their strength characteristics, lightness and price ensured the interest of builders in the blocks made from them. To approach the issue of durability, let’s briefly consider how aerated concrete is processed.
Should be protected from moisture
At the same time, we should not forget that since this material appeared relatively recently, its durability can only be judged by preliminary forecasts. The service life of this type of cellular concrete is determined by factors that must be taken into account before choosing aerated concrete as the main material for the construction of a future home. First of all, these are, of course, weather conditions. Due to its porous structure, aerated concrete can quickly absorb moisture, which must be remembered when building a house and not exposing it to direct exposure to wind and precipitation. If, in order to avoid excessive hygroscopicity (the ability to absorb moisture), you use denser varieties of aerated concrete, there is a risk of losing one of the main advantages of this material - thermal insulation. From which it follows that this type of cellular concrete needs lining, but again, only on condition that moisture does not accumulate between the aerated concrete masonry and the lining.
Factors influencing the durability of a building
Let us dwell on the external factors influencing the service life of a foam concrete house in more detail.
Houses made of aerated concrete blocks are 2 times warmer than those made of foam concrete.
1. Increase in static and dynamic loads on the house structure in the event of disasters and bad weather conditions. If during the design the bearing capacity of the building frame and its foundation is correctly calculated and the necessary safety margin is provided, then neither hurricanes, nor seismic activity, nor other force majeure circumstances will significantly affect the durability of the structure made of aerated concrete blocks. 2. Frost resistance. With regular freezing and thawing, a house wall, even made of moisture-resistant foam concrete, can lose up to 15% of its strength and ability to resist compression, bending and shear. This is due to the presence of residual stresses and microdefects in the body of the blocks, which cannot be avoided even in a high-quality, factory-made process. production. 3. Mistakes when constructing masonry for a house made of foam concrete. For example, the use of low-quality cement mortars or incorrect calculation of the thickness of the mortar layer, changing the load distribution inside the blocks, which will certainly affect the service life.
Try to reduce risks
In order to increase moisture resistance and increase the service life of the house, it is advisable to make a ventilated facade. But we should not forget that, despite the high fire resistance of aerated concrete itself, the risk of a ventilated façade catching fire is quite high, especially if the necessary standards are not followed during its construction. In order to increase fire resistance, you should avoid using flammable materials, such as polystyrene foam (expanded polystyrene). In the event of a sudden fire, this material not only contributes to the rapid spread of fire, but also releases toxic fumes that can cause suffocation. It is also necessary to remember that a material such as aerated concrete bends very weakly. Therefore, you should not heavily load it with various heavy and cutting structures. That is why a house made of aerated concrete, by generally accepted standards, should not exceed three floors: above the third floor, aerated concrete is used only for various walls and partitions of non-load-bearing structures. If you have the desire and opportunity, there is the option of building a basement floor from the same material. The height of the base should not be lower than 80 cm. In addition to the main domestic purpose, the ground floor has a purely practical function - it forms, as it were, an air cushion between the soil and the main structure, preventing precipitation and groundwater from “getting close” to the house, which also increases the potential service life of the entire aerated concrete structure. In this case, a foundation made of ordinary “classical” concrete is required.
Durability issue
So, the advantages of aerated concrete and foam concrete are obvious.
But the question of the durability of houses made from these blocks still remains open, since most often the answer is based only on observation of the operation of a small number of buildings in Europe and America, built from foam blocks and gas blocks in the 50s of the 20th century.
If you are not building a temporary shed, and you are faced with the question of whether to choose a foam block or an aerated block, it is better to use aerated concrete.
The service life of houses made of foam concrete blocks and aerated concrete blocks declared to manufacturers is approximately 100 years, subject to major repairs after 60 years of operation. However, these terms are very, very relative, because the service life of a foam concrete house can be influenced by third-party factors, such as the correct calculations of the load-bearing structures of the house, compliance with construction technology, and the conditions under which the building is operated. If all these requirements are met, then the stated deadlines are correct. In other cases, it is premature to talk about such a long service life.
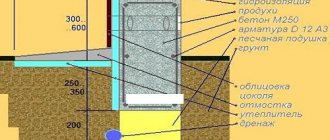
We make a strong foundation with metal reinforcement
In many ways, the durability of a building made of aerated concrete depends on how long the service life of its foundation is. When building a house, you should pay special attention to whether there are risks of soil erosion and how deep the soil is expected to freeze. When building a house from aerated concrete, it is better to use a strip foundation, and it is desirable that the foundation be as deep as possible. The strip type itself implies two methods of construction: prefabricated or monolithic. The monolithic method is usually used when the groundwater position is too high. Any type of construction is suitable for rocky or semi-rocky soils. The dug pit must be filled with crushed stone and sand to form a so-called “cushion” - drainage that does not allow the foundation to settle and protects it from the penetration of groundwater. If you save on the cost of construction by using a shallow type of foundation, the risks that the tape may burst increase. And this, in turn, can cause a variety of consequences - from cracks in the walls to the collapse of the entire house.
House made of aerated concrete: advantages and disadvantages, service life of aerated concrete blocks
Aerated concrete, among other similar materials, contributes to the fulfillment of these tasks.
Aerated concrete blocks The composition of aerated concrete includes cement, water, quartz sand, quicklime as a gas former, and aluminum powder. Composition of natural hardening aerated concrete During the production process, the result of a chemical reaction is the formation of pores inside the aerated block. There are two ways to produce aerated concrete blocks - natural hardening and baking in autoclave ovens under high pressure and temperature.
Composition of autoclaved aerated concrete During the production process, aerated concrete blocks are given different shapes. This can be a standard rectangular shape, U-shaped blocks or arched structures. U-shaped aerated concrete blocks Due to the porous structure, the aerated concrete block weighs little, so there is no need to bring special equipment to the construction site.
The construction of the house takes place in a short time.
So, conclusions:
Any qualified developer understands that not only the life and safety of many people, but also his face in the real estate market, as well as his authority in the eyes of competitors depends on how long his house stands. When choosing aerated concrete as the main material for a future home, there are certainly many advantages: the home will be warm and environmentally friendly; its construction will be economically profitable. And if all the above conditions are met, there is every chance that the life of the building will be from 80 to 100 years.
House made of foam blocks - characteristics
In the 30s of the 20th century, a new building material was invented - foam block, which belongs to the class of cellular concrete. For its production, cement, sand, water and special foaming agents are used, which come in two types:
- natural,
protein-based, the cost of which is high, but they are absolutely environmentally friendly; - synthetic
, having hazard class 4. The price of such additives is lower than natural ones, but the production process is considered toxic. At the end, the finished blocks are considered absolutely safe, because the percentage of dangerous additives in them is negligible.
The finished solution is poured into special molds of a standard size or hardens into a large monolith, which is subsequently cut into blocks. Finished houses are built from foam blocks, characterized by the following characteristics:
- Dimensions
: Length and height are always standard - 60 and 30 cm. Width varies from 10 to 30 cm. - Strength
. This parameter is marked with the letter “B” and is measured in the digital range from 0.5 to 60 kg/cm². The higher the indicator, the more weight one block can support. This is important to consider when choosing material for houses with several floors. - Medium density
, masked by the letter “D” and measured from 300 to 120 mPa. This parameter is important when choosing materials for load-bearing walls and partitions. - Frost resistance
should also be taken into account when constructing the external and internal walls of the block.
How long can it take to build a house from foam blocks?
The great advantage of a house made of foam blocks is the high speed of its construction. For 1 m² of wall it will take about 7 blocks of the largest size and about 17 of the smallest, so the construction of houses from foam blocks is carried out in record time. It is important not only to strive for speed of construction, but also to pay attention to the quality of construction. An experienced master with a sufficient level of qualifications will easily take into account both the importance of speed of work and its quality.
Service life of a foam block house
A distinctive feature of the solution used to make blocks is the increase in density over time. It is a scientifically proven fact that a country house made of foam blocks, which is 30-40 years old, is three times stronger than a new structure. It is believed that a standard foam block house has a service life of at least 150 years. This indicator is influenced by many parameters, such as the quality of the building material, its fire safety and compliance with all standards and technologies during construction.
Which foam block to choose for construction?
In order to build a high-quality house from foam blocks, it is important not only to determine the size, density and frost resistance of the required blocks, but also to choose high-quality material from a trusted manufacturer. You need to check certificates and other documentation and consider one of the blocks:
For reference:
For the first time, porous concrete (aerated concrete, cellular concrete) was obtained by the Czech chemist Hoffman by adding salts and acids to gypsum and cement solutions. Having received a patent for his achievement in 1889, but lacking a commercial vein, Goffman was unable to establish any worthwhile production. However, his followers, representatives of the New World, Dyer and Oulsworth, improved the method of their predecessor, replacing acids with zinc and aluminum. But the real birth of aerated concrete as a building material is due to the architect Yu.A. Erikson, who in 1929 established the production of this material on an industrial scale (in the first year, his company Ytong in the town of Ishult produced 14 thousand cubic meters of aerated concrete).
Durability of aerated concrete and what affects it
This is the reason that they treat aerated concrete without much reverence, simply as one of many modern wall materials. Their target is individual builders who need to make a choice of material for the walls of their future home. It is for them that this cocktail of truth and speculation about the properties of gas silicate blocks is designed. What is aerated concrete really like? What is true in the advertising of this material and what is not?
In what cases would choosing it be the right decision? To answer these questions, you need to use more authoritative sources than advertising brochures, that is, the requirements of GOST, which describes what characteristics aerated concrete blocks should have. So what do we learn? There are three types of autoclaved cellular concrete, namely thermal insulation, structural and a third, mixed type. Simply put, blocks with a density less than D are not intended for laying walls at all and can be used exclusively as insulation.
It remains to add that structural blocks are very expensive - not every construction company can afford to build with them, not to mention private developers. You will not see the above information in advertising. It is this dilemma that faces every buyer who decides to build with aerated concrete.
Another fact: blocks with density D on the verge of insulation and wall material are the most common and best-selling brand of gas silicate blocks. For some reason, advertising rarely mentions that if you do not equip an armored belt made of brick or reinforced concrete, then the masonry will not withstand the pressure at the points of its contact with the floor slabs. Let's not forget that aerated concrete is a fragile porous material. An armored belt is necessary, but it is worth considering that after its installation the masonry will be colder due to cold bridges.
Why are there so few people who want to build from durable and dense structural aerated concrete? It turns out that for walls made of such material, given their high cost, additional insulation will be required. More insulation means more costs.
Popular questions
What else are sellers of cellular concrete in no hurry to inform the buyer about? The fact that any vibrations in the foundation of an aerated concrete house will lead to a sad ending - cracks along all the walls. Do not forget: silicate blocks are a very fragile material that will only feel comfortable on a powerful, monolithic foundation - strip or plinth. Now the question is - what is such savings worth if for the sake of it you need to spend twice as much on the foundation?
In such a situation, a private developer has to rack his brains over a dilemma: building a small storey building on a huge foundation is stupid and unprofitable. And without such a strong base, cellular concrete cannot be used in construction - it is dangerous.
It remains to add that not everyone who wants to build their own house can simply pour a monolithic foundation like this. It’s not even a matter of money—it’s a technologically complex task that requires professional skills and knowledge.
The house is built, now you need to attach some massive structure to its walls - for example, part of the roofing system. An attempt to use ordinary fasteners for this will result in it simply being torn out of the wall. This is the same as hanging a huge kitchen cabinet with dishes on a plasterboard wall.
Here you will need special fasteners - screw-in dowels, or even better - anchors with chemical fixation. It remains to add that they are much more expensive than conventional fasteners for concrete and brick.
Feedback
Let's not forget that in addition to massive structures, there is also insulation, which also needs to be somehow attached to the wall. For example, for an average-sized cottage, sq. Their cost is rubles per piece.
You cannot use such dowels for aerated concrete; you need screw-in fasteners, which are five times more expensive. As a result, you will have to overpay thousands of rubles just for the dowels alone.
There is a story circulating on the websites of sellers of autoclaved cellular concrete that for regions located in the middle zone, aerated concrete walls of a house with a thickness of a millimeter are sufficient to meet thermal efficiency standards.
Specific numbers and citations from GOST, SNiP and other regulatory documents have a hypnotizing effect on an inexperienced buyer in construction - this is simply a win-win move.
Wall made of foam blocks
In addition to this scheme, there are also laws of physics, according to which the thermal insulation properties of materials in dry and wet states differ significantly. Apparently, advertisers confused central Russia with the Atacama Desert in South America, where there has been no rain for several hundred years. Let's leave the mm-thick wall to the conscience of the authors of this gem, and try to calculate the real thickness of the wall of a house in central Russia.
With such humidity of DD grade blocks, their thermal conductivity will decrease by 0. Now it remains to calculate the actual thickness of the walls: it should be at least mm, and at a maximum strictly according to SNiP standards - mm. Unfortunately, these calculations are not final. Humidity is a significant, but not the only factor that reduces the thermal efficiency of aerated concrete. Let's continue to figure it out.
I would like to believe that when purchasing aerated concrete, sales managers warn customers that ordinary cement-sand mortar cannot be used for laying it. This is not the only reason. Let us remember that lime is used in the production of aerated concrete. Under certain operating conditions, its content contributes to the formation of thaumasite and ettringite - minerals that contribute to an increase in volume, loss of strength and gradual destruction of the mortar and the masonry itself.
Conclusion - such material requires a special, sulfate-resistant solution. There are more than enough such solutions, or rather dry mixtures from which the solution is made on site, on sale, but not all of them have the necessary resistance to sulfates.
Only professional mixtures for aerated concrete provide optimal results - for example, some German quick mix solutions. However, it should be noted that products of this level are expensive. Whatever mortar mixture you choose, before purchasing, it makes sense to first compare its characteristics with the requirements set out in the Standard. In addition to the usual quality parameters of the mixture, frost resistance, adhesion, moisture resistance, etc.
But let's get back to calculating the actual wall thickness.
Let's consider an option in which the buyer of aerated concrete knows everything about its features and purchased a special, sulfate-resistant adhesive solution.
Have all factors leading to heat loss been taken into account? Unfortunately no. What happened? If you are planning to build a house from aerated concrete blocks in Moscow or the Moscow region, then the minimum thickness of its walls should be mm, and the maximum, strictly according to GOST, should be mm. Comments here, as they say, are unnecessary. This is where the restraint of professional builders towards aerated concrete becomes clear.
It is no coincidence that they consider it mainly as a material for interior partitions. For this, as card players say, you should hit with a candelabra. Aerated concrete is like a sponge: if you do not protect it from moisture, it will immediately absorb it.
It will be cold in such a house even with hot radiators. This means that one more column needs to be added to the construction estimate - vapor barrier of the masonry. Let's talk about aerated concrete. It is the only stone material against which panicky reproaches and assumptions about low possible service life are heard. But what really? The roots of the panic lie in the fact that aerated concrete has become the most popular wall material in Russia.
A lot of people, when deciding to build a house from any material, think about how and what to build it from. Some consult with friends and acquaintances who work in the construction industry, while others who are more advanced begin to search the Internet for thematic forums on a given topic, where would-be experts begin to give all sorts of advice based on rumors or a superficial review of the literature.
It objectively displaces other stone materials from the market. And representatives of the displaced do not want to be displaced. Analyzing the Internet, one often comes across statements about the low service life of aerated concrete blocks and gas silicates. The roots of these negative reproaches lie in the fact that this material has conquered the market of our country and has become the most common in the construction of walls, displacing other building materials.
Competitors of aerated concrete do not want to put up with this state of affairs. Autoclaved aerated concrete is an artificial mineral consisting mainly of calcium hydrosilicates.
Its physical aging consists of a decrease in the frost resistance resource. Chemical - carbonization of silicates is the process of converting silicates in a humid environment into chalk under the influence of carbon dioxide. The frost resistance indicators of gas silicates look very good, due to the high reserve porosity, which promotes the displacement of moisture from the capillaries into the pores, preserving their integrity. With the use of new technologies, the frost resistance of modern aerated concrete is much higher than that previously produced.
Because the average density of the brand is reduced without loss of strength. A decrease in brand density leads to an increase in reserve porosity with an increase in capillary viability. With this terrible word, competitors scare our gullible citizens who are thinking about building houses. Carbonization was studied very actively in the USSR.
Having studied the materials, two main conclusions can be drawn:. Low-basic hydrosilicate decreases in volume during carbonization, that is, it cracks and loses strength. Low-basic hydrosilicates are an example of the first low-strength aerated concretes produced in low-pressure autoclaves, which were mainly used for the manufacture of external wall panels. Practice shows that even such aerated concrete, after serving for years, does not reduce its tensile strength by much, approximately from 5 to 20 percent, depending on operating conditions.
The carbonization process occurs more intensely in a warm and humid climate zone than in a dry and frosty one. A chemical reaction requires a liquid phase and high energy of its own components.
How to protect a house made of aerated blocks?
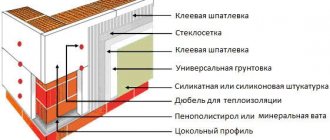
External factors aggressively affect the structure of the material. Unprotected blocks can absorb up to 20% of their own weight in moisture. When temperatures fluctuate, this effect becomes destructive. Therefore, it is necessary to provide external protection using plaster, facing bricks, tiles or other materials. When using a non-ventilated façade, the service life of the building reaches the stated 60 years, and when using a ventilated façade, it reaches the full 100 years.
The type of foundation has a direct impact on durability. The most commonly used is a strip foundation. Its depth must be sufficient, taking into account the characteristics of the soil in a particular region. If the foundation strip breaks, it will affect the integrity of the walls and the duration of operation.
When constructing buildings higher than one floor, a reinforcing belt will be required. It strengthens the frame and prepares the building for the load when supporting the floor slabs.
Extending the life of the material
To ensure the durability of aerated concrete cottage, the following actions should be considered:
- Cladding the building and external façade. For example, you can use tile or brick plaster for this. If the material is not protected in any way, then the outer layer of the wall can be destroyed after the first year of operation.
- Installing a monolithic strip foundation can save you from premature deformations and cracks in installation.
- If the building has two or more floors, then it is better to strengthen the frame with a “reinforced belt”.
It is important to note that all the rules and conditions for the construction of residential premises made of aerated concrete are prescribed in the “Building Codes and Rules” and “Interstate Standards”. If you adhere to the established parameters, you can extend the life of the building.
Durability of aerated concrete
It turns out that the durability of the structure depends not only on the characteristics of the material, but also on operating conditions. Let's talk about aerated concrete.
It is the only stone material against which panicky reproaches and assumptions about low possible service life are heard. But what really? The roots of the panic lie in the fact that aerated concrete has become the most popular wall material in Russia.
It objectively displaces other stone materials from the market. And representatives of the displaced do not want to be displaced.