If there is no need to use the attic for living, insulate the ceiling in a house with a cold roof. Thermal insulation will affect the comfort of living:
- the air temperature in the interior will increase;
- humidity stabilizes;
- the cost of purchasing energy resources will be reduced;
- the speed of air movement will decrease (there will be fewer reasons for drafts).
Advantages of installing an unheated attic
Thermal insulation of the ceiling of heated rooms or the floor of the attic has a number of advantages:
- A buffer zone is created between the external environment and heated rooms. The gradual transition between cold and warm air has a positive effect on the service life of insulation and building structures. In winter, ice does not accumulate on the roof.
- The cost of purchasing building materials is reduced, because the ceiling area in most cases is less than the roof area.
- The requirements for the professional skills of a specialist are reduced, which makes it possible to carry out the work independently.
- The time a building is without a roof during insulation is significantly reduced, which is especially important in regions with frequently changing weather.
Let's start with calculations
During construction, it is necessary to take into account the weight of the insulation to be used. If the house has already been built, then when installing protection against heat loss, care should be taken to reduce the additional load on the load-bearing walls and foundation of the building. Calculations are carried out in 3 stages:
- determining the thickness of the selected insulator;
- calculating the weight of the resulting insulation;
- determining the possibility of using one or another isolation method.
Exceeding the permissible load on the floors, walls and foundation will lead to the destruction of the building either during the work or upon its completion.
Determining the thickness
To find the height of the insulating layer, you need to know two values:
– standard thermal resistance of floors for the region of residence;
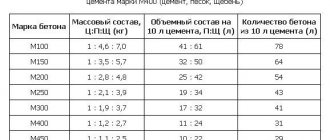
| Locality | Required thermal resistance of the ceiling R, m 2 °C/W |
| Anadyr | 6.0 |
| Arkhangelsk | 42829 |
| Astrakhan | 42828 |
| Barnaul | 42859 |
| Belgorod | 42889 |
| Blagoveshchensk | 42920 |
| Bryansk | 42950 |
| Vladivostok | 42981 |
| Vladimir | 42739 |
| Volgograd | 42889 |
| Vologda | 42770 |
| Voronezh | 42950 |
| Grozny | 42769 |
| Derbent | 42949 |
| Ekaterinburg | 42829 |
| Ivanovo | 42739 |
| Izhevsk | 42798 |
| Irkutsk | 42951 |
| Yoshkar-Ola | 42798 |
| Kazan | 42770 |
| Tver | 4.0 |
| Kaliningrad | 42828 |
| Kaluga | 42981 |
| Kemerovo | 42920 |
| Kirov | 42829 |
| Kislovodsk | 42797 |
| Komsomolsk-on-Amur | 42951 |
| Kostroma | 42739 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 42920 |
| Samara | 42739 |
| Mound | 42859 |
| Kursk | 42919 |
| Lipetsk | 42950 |
| Magadan | 42830 |
| Maykop | 3.0 |
| Makhachkala | 42980 |
| Moscow | 42981 |
| Murmansk | 42890 |
| Nalchik | 42797 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 42739 |
| Novgorod region | 42981 |
| Novorossiysk | 42918 |
| Novosibirsk | 42920 |
| Oymyakon | 42832 |
| Omsk | 42890 |
| Ordzhonikidze | 42797 |
| Eagle | 42981 |
| Orenburg | 42770 |
| Permian | 42829 |
| Petrozavodsk | 42770 |
| Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | 42770 |
| Pskov | 42950 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 42828 |
| Ryazan | 4.0 |
| Salekhard | 42891 |
| Saint Petersburg | 42981 |
| Saransk | 4.0 |
| Saratov | 42981 |
| Smolensk | 42950 |
| Sochi | 42796 |
| Stavropol | 42769 |
| Surgut | 42740 |
| Syktyvkar | 42859 |
| Tambov | 42981 |
| Tomsk | 42920 |
| Tula | 42981 |
| Tyumen | 42829 |
| Ulan-Ude | 42982 |
| Ulyanovsk | 42739 |
| Urengoy | 42983 |
| Ussuriysk | 42770 |
| Ufa | 42770 |
| Khabarovsk | 42859 |
| Khanty-Mansiysk | 42951 |
| Cheboksary | 42770 |
| Chelyabinsk | 42829 |
| Chita | 42771 |
| Elista | 42828 |
| Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | 42770 |
| Yakutsk | 42831 |
| Yaroslavl | 42950 |
- coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material used
| Material | Specific thermal conductivity coefficient, W/m K |
| Fibrous materials | 0,038 – 0,052 |
| Expanded polystyrene | 0,032 – 0,036 |
| Polyurethane foam | 0.026 |
| Expanded clay | 0.11 |
| Ecowool | 0,038 – 0,041 |
| Natural materials | |
| Felt (various types) | 0,031-0,05 |
| Foliage (dry) | 0,05-0,06 |
| Tow | 0,037-0,041 |
| Moss | 0.04 |
| Needles | 0.08 |
| Straw mats | 0,05-0,06 |
| cotton wool | 0.037 |
| Thin shavings (packing) | 0,05-1 |
| Campfire (various types) | 0,04-0,065 |
| Sphagnum (peat) | 0,05-0,07 |
| Wood sawdust | 0,05-0,08 |
| Straw (stuffed, cut) | 0.04 |
For example: To get the result you need to divide the first indicator by the second. The resulting number shows the thickness of the layer in meters.
The required thermal resistance for the ceiling in Saratov is 3.9 m2 K/W. It is planned to use polyurethane foam with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.026 W/m K. When divided, we obtain 0.1014 m. To obtain the required heat savings, it is necessary to apply 10.2 cm of insulation.
Calculate the weight
To determine the mass of a heat insulator, it is necessary to multiply its volume by its density. The volume is found by multiplying the layer thickness by the area determined by the product of the length and width of the thermal insulation.
We take the density of the main insulation materials from the table:
| Material | Density, kg/m 3 |
| Fibrous materials | 100 — 120 |
| Expanded polystyrene | 25 — 35 |
| Polyurethane foam | 54 — 55 |
| Expanded clay | 200-400 |
| Ecowool | 42-75 |
| Natural materials | |
| Felt (various types) | 100-150 |
| Foliage (dry) | 50 |
| Tow | 180 |
| Moss | 135 |
| Needles | 43 |
| Straw mats | 85 |
| cotton wool | 80 |
| Thin shavings (packing) | 140-300 |
| Campfire (various types) | 150-350 |
| Sphagnum (peat) | 150 |
| Wood sawdust | 190-250 |
| Straw (stuffed, cut) | 120 |
Fired clay
The use of pure clay as a heat insulator is hardly possible due to the need to use a layer up to 80 cm thick. Therefore, clay that has been heat-treated to give volume - expanded clay - has long been used. This is an environmentally friendly, non-flammable material. Quite light, with good thermal insulation ability. Can be used on both wooden and reinforced concrete floors.
The smaller the expanded clay fraction, the worse it retains heat.
Before installation begins, wooden structures are treated with septic tanks and fire retardants. A rough ceiling is installed from inside the room, which will take on the weight of the expanded clay.
Positive properties of expanded clay:
- does not generate dust during operation;
- has good vapor permeability;
- does not absorb moisture;
- does not require the use of protective membranes and films.
To ensure passage across the attic floor and use it for household needs, boards are laid over the joists or a subfloor is installed.
To insulate reinforced concrete floors, simply pour the required layer of expanded clay. If there is a need to use an attic, a reinforced cement-sand screed is installed on top of it.
Loose pulp
Ecowool is made from wood fibers and has many advantages:
- low fire hazard due to the use of fire retardants (refers to low-flammable, self-extinguishing materials;
- sufficiently low density even in compacted form, which does not create excessive load on the floors and foundation;
- quick installation of any thickness is possible;
- does not spread microorganisms, fungus and mold inside and on the surface;
- has a high vapor permeability;
- forms a continuous, unbreakable carpet without the formation of cold bridges;
- environmentally friendly.
Before installation, it is necessary to install a diffusion membrane, which will ensure insulation of the internal living space from the fibers of the heat insulator.
It can be laid in two ways: wet and dry.
When dry laying, ecowool is poured onto the surface of the ceiling, leveled and compacted.
Types of insulating materials for the ceiling in the house
Thermal insulation materials used to insulate the ceiling should not have a large mass so as not to create excessive load on the structure’s floors.
Minvata
Mineral wool is rightfully considered one of the most common materials used to insulate heat loss through the ceiling. It is necessary to lay insulation on the side of the living room or attic, since its characteristics are perfectly combined with this type of work.
This insulation material is produced from different types of raw materials - it can be sand, broken glass, blast furnace slag and even rock - basalt.
Slag
It should be noted that insulation produced by processing blast furnace slag and called slag wool is not very suitable for thermal insulation of residential premises. The attic is an area with high levels of humidity, this is especially true in spring and autumn. Slag wool has a high hygroscopicity rate, which is why its thermal insulation properties can be significantly reduced. The level of residual acidity of this insulator may not have the best effect on the building materials with which it comes into contact. This is especially true for ferrous metals.
Slag wool fibers are brittle and thorny, which is why it is not recommended for use in finishing premises intended for human habitation. Tiny fragments of material may become suspended in the air and enter the respiratory tract. The main advantage of slag wool is its price, which is significantly lower than that of other analogues.
Glass wool
This insulating material is made from molten glass, drawn into the finest threads. These fibers are used to create sheets of material that can be rolled or cut into blocks. The thermal conductivity coefficient of glass wool is lower than that of slag wool or basalt insulation. The moisture absorption rate of this material is at the level of 0.55÷0.8 kg/m².
Glass wool is successfully used for thermal insulation of ceilings on a cold porch. It is often combined with other types of insulation. But it is worth considering that it must be laid strictly from the attic side, since, like slag wool, its fibers break easily and can negatively affect the condition of the mucous membranes and skin membranes. Because of this, residential premises should be insulated from this type of insulation.
Basalt wool
Basalt insulation material is made from gabbro-basalt rocks and is considered the optimal choice for thermal insulation of the ceiling plane on the side of the room. Its fibers have greater ductility compared to analogues, and therefore their degree of fragility is lower. The material is sold in the form of durable mats made of tightly compressed fiber. It is little affected by the external environment, so it can also be used for installation from the attic side. You can also find insulation in rolls, the density of which is slightly lower than the slab version.
Basalt wool is sometimes covered with a layer of foil. If the installation is done correctly, the insulation coefficient will be higher, since the heat will be reflected into the room. All types of mineral wool have one significant drawback. It lies in the fact that formaldehyde resins are used as a binder of fibers, which are released into the environment and pose a danger to human health. Because of this feature, this type of insulator cannot be classified as an environmentally friendly type of raw material.
Expanded clay
Environmentally friendly materials include expanded clay, the raw material for the production of which is natural clay. It is perfect for thermal and sound insulation of attic floors. The material does not burn and does not form harmful emissions when heated. The backfill layer may differ in its density, since expanded clay is produced in the form of granules of various sizes. A smaller grain size allows you to obtain a coating of higher density with high insulation properties. The optimal size of expanded clay granules for insulating ceilings is from 4 to 10 millimeters.
Expanded clay does not generate dust and is safe for people with allergies. The service life of the insulation is quite long, while the material retains its original quality indicators throughout its entire service life. The heat resistance of expanded clay is high; it is often used to insulate chimneys from wooden ceilings. The method consists of pouring material into a metal box mounted around the pipe.
Ecowool
This type of insulation has not yet gained as much popularity as expanded polystyrene or mineral wool, but is becoming increasingly used for insulating walls and ceilings in a frame house. Ecowool consists of small cellulose fibers. The insulator can be laid “dry” or “wet”.
- The “dry” application method is carried out by scattering the material, which is then evenly distributed between the floor beams and compacted well.
- “Wet” installation is carried out using special equipment in which the insulator is connected to an adhesive compound and supplied outward under pressure.
Advantages of ecowool:
- If necessary, the material can be applied in any layer, since its weight is insignificant and will not create a load on the attic floors. The content of air bubbles gives it excellent thermal insulation properties.
- The insulation contains only natural materials that do not contain carcinogenic or toxic substances.
- Ecowool can effectively protect surfaces from the occurrence of mold and other pathogenic microflora.
- The service life of the heat insulator is significant and its qualities remain unchanged over time.
- If the need arises, you can increase the layer of material at any time without spending a lot of time on it
- Ecowool is non-flammable and has self-extinguishing properties. This is achieved by adding fire retardants during its production. The material does not smoke much and does not emit harmful substances into the atmosphere.
- The resulting coating does not contain seams and is completely sealed, thereby increasing the thermal insulation qualities.
- Cellulose wool is capable of allowing air to pass through, but does not retain moisture.
The payback period for this method of insulation is from two to three years. It depends on the installation method and the thickness of the material.
Styrofoam
Expanded polystyrene has been known as insulation for more than 50 years. During this time, it was possible to identify both the pros and cons of this material. Despite its shortcomings, it is still popular because it is quite cheap and easy to install. Expanded polystyrene is often used in combination with installation foam, which serves as a means of sealing the insulating coating. The advantages of expanded polystyrene include a low thermal conductivity, which can fluctuate depending on the density and thickness of the insulation.
The disadvantages of the material include a high degree of flammability, while it melts and emits a lot of smoke containing toxins. Because of this, in many European countries, polystyrene foam is prohibited from being used in the construction industry. Its replacement is extruded polystyrene foam, which is low-flammable and has the property of extinguishing on its own. Despite this, EPS is also a material with increased toxicity. Therefore, it is worth thinking carefully about whether it is worth giving preference when working on home insulation.
Polyurethane foam
This material is applied by spraying onto the insulated surface, which is impossible without the use of special equipment. If necessary, polyurethane foam can be applied in several layers. Thanks to this quality, it is often used in thermal insulation of residential premises located in regions with harsh winters. The applied material is able to fill all existing cracks, as well as smooth out unevenness. The result is a sealed coating that has no seams. After hardening, it becomes so dense that it can support the weight of a person. The thermal conductivity and water absorption rates are 0.027 W/mK and 0.2%, respectively. This is evidence that the insulating qualities will not be lost even in conditions of high humidity.
When the material has hardened, any excess can be easily removed with a sharp knife. Thus, adjusting polyurethane foam to the height of the floor surface is quite simple. Another advantage of polyurethane foam is that there is no need to install vapor and water protective layers, since the material itself has the qualities necessary for this.
Sawdust
Small shavings and sawdust are one of the most inexpensive materials that have long been successfully used for insulating ceilings. Most often, wood processing materials are used in tandem - sawdust provides the required level of density, and shavings are “responsible” for the porosity of the coating. The popularity of such insulation is due to its low price and completely environmentally friendly natural composition, which more modern materials cannot boast of. If the material is laid correctly, the ceiling will be well insulated. But in order to achieve maximum efficiency from the material, an accurate calculation of the required layer thickness will be required. It will depend on the climate in the region of application.
Lumber can be laid either in its pure form or as part of a complex with other materials for insulation. Pallets can be used that contain granules made from small compressed sawdust. The main disadvantage of sawdust is its increased flammability. Getting rid of this is not so difficult. Before starting work, it is enough to add fire retardant substances, clay or cement mortar to the composition. This processing method makes the material either non-flammable or slightly flammable.
When insulating the ceiling with sawdust, all wooden ceiling elements are pre-treated with fire retardants and insulated from the chimney. Electrical wires are separated using special tubes with a corrugated surface.
What we mowed down is how we insulate it
The possibility of obtaining a natural thermal insulator at a low price increases the attractiveness of using reeds and straw in this role. These materials are used in the form of pre-arranged mats, as well as in the form of finely chopped stems. When using mats, installation is carried out in several layers, taking into account that the top layer should overlap the joints of the bottom one. It is also used as the main filler using the technology of producing insulator from sawdust and cement (clay).
Purpose of ceiling insulation
Ceiling insulation in a wooden house performs the following functions:
- Many thermal insulation materials not only retain heat well in the room, but also dampen noise coming from the street. Therefore, such thermal insulation will increase the comfort of living in the house.
- In the cold season, the insulation will protect against significant heat loss, and in the summer heat it will not allow the room to become too hot from the roof heated by the sun.
- Also, a layer of thermal insulation will prevent the accumulation of condensation in building structures, thereby extending the service life of the ceiling.
From the bottom of the sea
Buildings located close to the sea and ocean coasts are insulated with algae. This natural, environmentally friendly material has some advantages:
- good thermal insulation ability;
- high vapor permeability;
- resistance to temperature changes and high humidity;
- low water absorption;
- resistance to biological forms of life (rodents and microorganisms);
- zero fire hazard;
- no need to use vapor barrier membranes;
- saturation of premises with iodine.
Used in the form of pre-prepared mats.
They made me from stone, slag and glass (insulation)
The use of natural materials with deep processing allows us to obtain materials for protecting premises with better performance at a lower price.
The use of fiberglass materials is associated with certain difficulties during installation and subsequent use. Glass dust and small fibers released during the production process can injure the human respiratory and vision organs. Contact with skin may cause lesions and allergic reactions. Work without sufficiently serious protective equipment is impossible. During operation, it forms fine dust, the inhalation of which is harmful to health. The extremely low environmental performance of the material makes it impossible to use it in rooms and buildings where people are constantly present.
Cotton wool obtained from furnace slag also has extremely low environmental test results. When water gets in, acidic fumes are released, which are dangerous if inhaled and destroy metal structures. Thin and brittle fibers can remain suspended in indoor air for a long time. They have an increased ability to absorb moisture.
The situation with environmental certification for slabs, mats, and rolls made from basalt fabric is almost excellent. Relevant documents allow for the insulation of floors in residential buildings, structures for long-term human stay, children's and medical institutions. Recommended for work on wooden floors.
Classification of insulation
Comparative table of characteristics, pros and cons of insulation materials.
| material | scope of use | pros | minuses | coefficient of thermal conductivity |
| sawdust | mounds in old attics, between walls | inexpensive material, easy to use, good air permeability, environmentally friendly | easily rots and burns | 0,070-0,093 |
| expanded clay | floors and attics of durable ceilings | does not burn, does not rot, holds heat well | very heavy | 0,085-0,160 |
| Styrofoam | walls, attics | inexpensive material, resistant to moisture and rotting | smoldering from fire with the release of toxic substances, creating a “greenhouse effect” | 0,047-0,065 |
| mineral wool | walls, attics | inexpensive, easy to use, holds heat well | unstable to moisture, shrinks and deforms | 0,048-0,070 |
| ecowool | walls, attics | breathes well, environmentally friendly material | not resistant to moisture | 0,032-0,041 |
NOTE. Artificial materials win in almost all respects. Their weakness is the greenhouse effect, as well as the toxicity of combustion products. However, these shortcomings can be compensated for by additional fire-fighting measures, as well as by constant ventilation of the room in winter.
Depending on the structure of the material, all ceiling insulation materials that are used in houses with cold roofs can be divided into several groups:
- Monolithic (massive) - these include artificial materials (foam plastic, polystyrene), which are laid on the ceiling in large blocks that reliably prevent heat loss.
At the same time, they block the removal of excess moisture from the air, as mentioned earlier. - Fibrous (porous) are materials with a developed internal structure, represented by numerous fibers. These fibers form large internal spaces that fill air bubbles that reliably retain heat in the house. A classic example is mineral wool.
Threads of mineral wool, as well as ecowool, are able to absorb and retain moisture, but at the same time the protective properties of ecowool are practically not reduced. At the same time, it has been experimentally established. that moistening mineral wool by even 1% of its mass leads to a decrease in thermal conductivity qualities by up to 8%. This is explained by the fact that loose fibers begin to disintegrate, so the material loses density. - Bulk insulation - for example, expanded clay and sawdust. They protect the house from cooling by creating a dense layer that retains heat well. The advantages of these materials are also that they allow the surface to “breathe” and do not create a greenhouse effect in the house.
Video review of some types of materials that are used to insulate walls and ceilings in houses with cold roofs
Core Technology
Insulation of the ceiling under the roof allows all work to be carried out efficiently without regard to external weather conditions.
High vapor permeability and the possibility of getting wet mineral wool insulation requires the mandatory installation of a vapor barrier membrane. In residential premises there is constantly air saturated with moisture, which tends to leave the room with excess humidity.
The presence of 20% moisture in the material by volume reduces the heat-holding capacity by 2 times. When 40% is reached, the insulation efficiency is zero.
The film is secured with a construction stapler. The strips are laid perpendicular to the laid and secured joists. The tightness of the connection is ensured by securing the edges of the strips with double-sided tape.
It is more convenient to file a rough ceiling or sheathing for finishing using screws.
The insulation is installed from the attic side. The width of the insulation should be 10 - 20 mm narrower than the distance between the joists. Otherwise, gaps will form that allow heat to escape. They must be filled with insulation scraps, or the orientation of the material must be changed, which will lead to excess material consumption. The height of the joist boards should be greater than the thickness of the heat insulator.
Pressing the insulation against the enclosing structures leads to its compaction and an increase in the specific thermal conductivity coefficient.
Boards are laid on top of the low-density heat insulator to make it possible to use the attic for technical purposes. High-density slabs can be protected by installing a screed made of cement and sand.
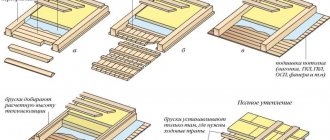
Do-it-yourself technology for laying a “pie” of thermal insulation
Laying of insulating material on the ceiling surface is carried out using one of the following schemes:
- Internal insulation - involves fixing the insulation to the surface of the wooden attic floor on the side of the living area. Often a plasterboard structure or suspended ceiling is subsequently installed. Please note that this method of laying insulator will reduce the overall ceiling height by 10-20 centimeters. It is important to choose a heat insulator with a high degree of vapor permeability. Basalt and mineral wool, as well as penofol, have this property.
- External insulation - consists of installing insulation in the attic area. This method is considered the most practical and profitable, since it does not require final finishing, except in cases where a residential attic is being installed. For this method, types of materials such as expanded polystyrene, mineral wool, penoizol and expanded clay granules are most often used.
There are a number of reasons why the internal insulation method is less preferable:
- The ceiling level is noticeably lowered, which in a private house may not be too high anyway and ranges, as a rule, from 240 to 260 centimeters.
- There is no possibility of laying insulating material in bulk.
- The dew point shifts to the area of internal floors.
- You will have to dismantle the old ceiling covering and refinish it.
With external insulation of the attic, the above disadvantages will be absent. But there are situations when it is not possible to resort to implementing this method. Below we consider two options for installing a coating for thermal insulation of a home by insulating the ceiling.
List of required tools
To carry out work on insulating the attic space, you will need to prepare the following types of materials and tools:
- the insulation material itself;
- wooden bars or metal profiles for creating sheathing;
- hardware;
- vapor barrier coating;
- construction staples;
- dowels;
- perforator;
- hammer;
- screwdriver;
- roulette;
- construction or stationery knife.
Styrene insulation
Polystyrene heat insulators produced using different technologies acquire qualities that are widely used in modern insulation systems:
- A heat-holding capacity unattainable for natural insulation materials (about 0.03 W/m K). This is achieved due to the presence in the volume of the material of a huge number of limited spaces with still air, which is an ideal insulator.
- A negligible degree of water absorption (from 0.4 to 4% of the volume at full immersion) and zero vapor permeability, which is especially important under unfavorable operating conditions.
- Increased resistance to compression, which determines the possibility of covering the insulation with heavy ties.
- A wide range of thicknesses allows you to select a layer close to the design one, thereby reducing purchasing costs.
- Standardized dimensions ensure ease of calculation and installation, as well as maintainability of the heat insulating layer.
- Low biological activity does not allow microorganisms and rodents to spread.
- Once the source material has been stabilized, the production process is environmentally friendly.
Application technology
How to properly insulate a ceiling under a cold roof using expanded polystyrene (EPS)?
Based on physical properties, it is recommended to use PPS when insulating structures made of metal and reinforced concrete. When working with wooden ceiling components, it is necessary to provide additional ventilation.
When laying it on the floor of the attic, it is enough to level the surface: knock down the protrusions, fill the potholes. For height differences of more than 10 mm, apply a leveling screed.
Diffusion membranes are not used in this case. Lay the slabs close to each other. The resulting gaps are filled with scraps or polyurethane foam. The slabs of the second layer are laid with a shift in relation to the first, overlapping its joints.
The insulation boards are secured with wide-headed dowels. The depth of the dowel is at least 60 mm. Its cap should be recessed into the plane of the slab by 1-2 mm.
Then the entire surface is covered with a reinforced cement-sand screed to ensure the safety of the insulation from mechanical, chemical damage, and natural phenomena.
Installing insulation between the guides
Lathing is used when cold ceilings are planned to be sheathed with plasterboard or clapboard. Insulation is preceded by marking the surface using a level. It is necessary to mark the lines along which the guides are installed. When using mineral wool, the distance between the lathing should be 3-4 cm less than the width of the insulation. This will allow the material to be tightly fixed between the guides. If polystyrene foam is used, the distance between the slats should correspond to the width of the insulation boards.
The wooden frame is fixed using self-tapping screws or dowels every 50-60 cm. Metal guides are secured using special hangers that allow you to adjust the height of lowering of the sheathing.
Then comes the installation of insulation. In order for the mineral wool to hold better, it is fixed with bent hangers. When installing foam plastic, gaps may form. They should be filled with polyurethane foam. When the installation of insulation is completed, they begin laying the vapor barrier. The film is laid on thermal insulation and secured to the wood with a construction stapler, and to the metal profile with double-sided tape.
After this, the ceiling is sheathed with plasterboard, which is attached to special screws every 15-17 cm. The joints are reinforced with sickle tape, and then the entire surface is puttied. When everything is dry, they begin finishing work.
Which insulation to choose and how to install it, everyone decides for themselves, based on budget, preferences and other conditions. It is advisable to choose a more environmentally friendly material that will not harm residents or cause allergies.
Liquid heat insulator
Polyurethane foam is delivered to the work site in a liquid state. This insulation is obtained as a result of a chemical reaction of two components under pressure. As a result, it acquires physical and chemical properties very similar to EPS. The big advantages are:
- the possibility of insulating any building materials;
- carrying out thermal insulation in hard-to-reach places;
- creation of a single thermal insulation layer on the entire insulated surface without the formation of cold bridges.
Application of polyurethane foam requires certain preparation and equipment. Failure to comply with the technology or the dosage of starting substances can lead to the receipt of a final product with properties different from the required ones.
In the case of thermal insulation of reinforced concrete floors with subsequent transformation of the attic into a technical room, it is necessary to install floor joists. In other cases, surface preparation is not required before starting work.
There is no need to use hydro- and vapor barrier. All subsequent processing of the insulated surface consists of arranging a subfloor or screed.
Expanded polystyrene and polyurethane foam
The most common polystyrene foam insulation is polystyrene foam. It has been used for insulation of residential and non-residential premises for more than 40 years. This popularity of polystyrene foam is explained by its ease of installation and low cost. This material is perfect for ceilings because it does not weigh down the beams. It has low hygroscopicity, so it is worth using if there is high humidity in the attic.
The disadvantage of polystyrene foam is its fragility. Over time, it can crumble, so it is better to use them to insulate a cold roof from the inside. When melted, the insulation releases gases that are dangerous to humans. For these reasons, owners are increasingly using penoplex rather than polystyrene foam for insulation. This heat insulator is more durable and is a type of self-extinguishing material. Both insulation materials have a low thermal conductivity coefficient.
Polyurethane foam is used in liquid form. It is sprayed onto wood or concrete floors in attics, so special equipment is required. PPU fills all voids, crevices and cracks, expands and forms a solid coating. Due to the fact that it can withstand significant loads without deforming, a cold attic can subsequently be used as a storage space or room. After hardening, if necessary, it can be cut with a knife.
There is no need to carry out hydro- and vapor barrier, because polyurethane foam has these qualities. And if it turns out that the applied layer is not enough, you can always add a new one, thereby increasing the thickness of the thermal insulation.