Choosing the type of foundation for a bath
The type of base depends on three factors:
- types of soil;
- material that will be used to build walls;
- financial opportunities.
If you plan to make a foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands, then you need to determine the type of soil. For this purpose, a hole is dug to the freezing depth. Soil consisting of peat or sand is considered weak . It requires a slab, pile or strip monolithic foundation. If the soil consists of stones and gravel, then any base design can be used. For clay soil, the best option is considered to be a strip or columnar structure.
The second factor is the weight of the walls , depending on the material from which they will be built and the area. A family does not need a bathhouse with several floors and an area of hundreds of meters. If the walls are made of timber, then the base structure can be pile or screw. For walls made of logs, a strip structure is preferable. If heavy materials (foam blocks, artificial or natural brick) will be used for the construction of walls, then the foundation should be presented in the form of a strip monolith or slab.
The last factor, financial, most often turns out to be decisive. The cheapest design is pile . In addition, its construction requires a minimum of time.
Existing options for foundations for a bathhouse
Preparing the site
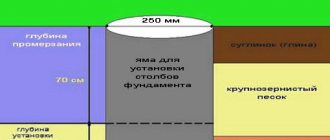
Once the foundation design has been chosen, it is necessary to carefully consider methods for strengthening it (if the soil is unstable or the groundwater is located very high). In addition, experts do not recommend erecting buildings on peat , fine sand or silt soil. If the choice of location is limited, then you have to build a cushion of sand and gravel 20 cm thick.
The next step is to determine the depth and width of the structure. The foundation should be 10 cm wider than the walls . The optimal depth of the foundation for a bathhouse is below the freezing level. Before starting construction, it is necessary to mark using pegs, a cord, a right triangle and a level.
The process should start from one of the corners of the future bathhouse. You need to drive a peg and put a triangle on it. On its two sides the length of two walls is measured , which will be located perpendicular to each other. In those places where they end, two more pegs are driven in. The triangle is then transferred to one of the new pegs to determine the location of the next wall intersection. It should be a rectangle. To make sure that the corners are even, you need to check the length of the diagonals - they must be the same.
Next, at a distance of 1-2 m from the pegs, it is necessary to arrange a cast-off of boards and posts . The boards are located at a distance of approximately 1 m from the ground. Cast-off boards must be packed parallel to the future walls. Then the axial parameters of the future structure are applied to the cast-off using small notches, into which nails should then be driven. The nails are connected with a cord (these are center lines), and the level is checked.
The next step is to take a plumb line and copy the center lines on the ground and put all the necessary dimensions on them. In accordance with the dimensions, you need to draw lines on the ground that indicate the internal and external contours of the foundation.
Determining the type of foundation
Based on the composition of the soil and its resistance to loads, the general recommendations look like this.
- On fluid and fluid-plastic soils (sandy loams, loams, clays flow down an inclined surface, do not roll out into a rope, stick) with a plasticity index JL from 0.75 to 1.0 or more: slab base.
- Tightly plastic and hard soils (sandy loams, loams, clays crumble upon impact or are difficult to knead). JL 0 – 0.5: strip, columnar foundation;
- On sandy soils - screw piles.
- On peat soil more than 3 m thick - driven or screw piles.
Where there is no soil and rocky, coarse rocks come to the surface, they themselves can serve as a foundation.
Engineering-geological surveys require financial costs; they are carried out infrequently for bathhouses specifically. They use the results of studies of their own and neighboring areas. If there is a gas pipeline, the operators have a survey report.
Before choosing, a preliminary calculation is carried out. The main quantities that are used are: the depth of the foundation for the bathhouse and the load.
Laying depth
Seasonal soil freezing is the main indicator that must be taken into account. Its dependence on the groundwater level and snow cover is standardized by SNIP 23-01-99 (Building climatology). Then the load, the depth of the foundation of the adjacent structure, and the location of utilities are considered.
| Depth of seasonal soil freezing, cm | |
| Omsk, Novosibirsk | 220 |
| Tobolsk, Petropavlovsk | 210 |
| Kurgan, Kusentai | 200 |
| Sverdlovsk, Chelyabinsk, Perm | 190 |
| Syktyvkar, Ufa, Aktyubinsk, Orenburg | 180 |
| Kirov, Izhevsk, Kazan, Ulyanovsk | 170 |
| Samara, Uralsk | 160 |
| Vologda, Kostroma, Penza, Saratov | 150 |
| Tver, Moscow | 140 |
| St. Petersburg, Voronezh, Volgograd, Guryev | 120 |
| Pskov, Smolensk, Kursk | 110 |
| Tallinn, Kharkov, Astrakhan | 100 |
| Minsk, Kyiv, Rostov on Don | 90 |
| Frunza, Almaty | 80 |
| Kaliningrad, Simferopol, Sevastopol | 70 |
A map and freezing tables for Russian cities will also help determine the required indicator, depending on the type of soil. Where frost heaving of the soil and its settlement during thawing is possible, to design the foundation one must be guided by Chapter 14 of SNIP 2.02.01-83. A bathhouse is a building with irregular heating. This must also be taken into account when making calculations: a shallow type with an insulated base and blind area will not help with heaving.
Loads
The prefabricated load consists of the weight of the base, the structure and its contents.
- The weight of a monolithic strip foundation is equal to the volume of reinforced concrete multiplied by its density: 2500 kg/m3.
- Weight of walls, partitions, plinth, stove, ceiling, roof, gables. Defined similarly.
- Temporary loads: people, water, snow on the roof. In areas with strong winds, this indicator should be added.
The resulting value is divided by the area of the foundation. This is R - the calculated resistance is 1.55 (conditionally) kgf/cm2, 15.5 tf/m2, 155 kN/m2, 155 kPa. It is multiplied by the reliability coefficient - 1.3.
The design resistance of a specific soil is determined using the tables in SP 22.13330.2011. So, for loam it is 1.8 - 2.8 kgf/cm2. Mixed sand – 3 – 5 kgf/cm2. If the calculated indicator is lower than the calculated normative one, the decision is correct. Above that, subsidence of the foundation, and with it the structure, is inevitable.
Construction of a columnar foundation
The most profitable in terms of financial savings are columnar structures: concrete, reinforced concrete, brick, stone, wood or piles. It is best to use them when building a bathhouse from wood materials on fairly stable soils.
Concrete, reinforced concrete and stone pillars are located at a distance of 2 to 3 m from each other at the corners of the building and at the intersections of walls. Dimensions 50x50 (60x60) cm. Depth - from 25 to 30 cm below the freezing level. Concrete and masonry have a significant negative quality - instability to tension . Therefore, the pillars must be perfectly vertical.
For a very small bathhouse with wooden walls, you can use wooden pillars, which are called chairs. Before digging, the wood must be burned so that a layer of charcoal protects it from rotting. This design is much cheaper than concrete or stone, but when properly executed, the strength is practically not inferior to harder materials.
On sandy and peaty soils, the best option is a type of pillar - drilled or screw piles. For drilled piles, it is necessary to make holes using a hand drill, install asbestos-cement pipes with a cross-section of 20 cm in them and fill them with concrete mortar to about a third of the volume. The pipes are then raised, resulting in an expanded base for the post. Next, the pipes are filled with the same solution approximately 10 cm below the ground level, the mixture is compacted using the bayonet method and supplemented with reinforcement.
In order for the future wall to be firmly connected to the pillars, anchors will have to be attached to the bottom of the walls, which should go into the unfilled parts of the pipe. Only after installing the anchors can the pillar pipes be filled with mortar to the top. A concrete or brick wall, called a fence, is mounted between the pillars. It is best to make a sand cushion 20 cm thick under it.
Arrangement of a pile-screw foundation
Installing a pile-screw foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands is even easier. This design is practically the only possible one if the bathhouse is built on peat or sand. The length of the pile should be approximately 2 m, the thickness depends on the area of the building. You can purchase screw piles with a thickness of 5.7−13.3 cm and a length of 1.65−3 m. They are screwed in manually and concrete is poured inside. The above-ground part of the piles is connected by a beam, a monolithic concrete slab or a grillage.
The pile-screw foundation has a number of advantages :
- this is the only option if the area for the bathhouse has a slope;
- can be arranged at any time, even in winter;
- to build walls there is no need to wait until the concrete is completely dry;
- such a foundation can last up to 100 years (repairs will never be required);
- this design does not require insulation.
Monolithic slab and its features
Type of monolithic slab
A monolithic slab for a bathhouse is a flat reinforced concrete structure buried a short distance into the ground. If, when constructing most types of foundations, a prerequisite is that the base of the structure lies below the freezing line of the soil base, then the monolithic slab does not have to be lowered to such a depth.
The slab foundation structure is not afraid of seasonal movements of the earthen base caused by the constant change of freezing and thawing cycles and heavy precipitation. A monolithic slab is a classic example of a floating structure, which is capable of rising and falling along with the soil base.
The sequence of installing a monolithic slab
The technological process of installing a foundation for a bathhouse in the form of a slab consists of sequentially performing a number of intermediate processes, such as:
- Preparatory work.
- Marking the foundation.
- Excavation.
- Installation of boundary formwork.
- Concrete pad and insulation.
- Assembly and installation of reinforcement cage.
- Filling the foundation structure with concrete mixture.
- Curing.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Carbon monoxide poisoning in a bathhouse: symptoms and first aid
You should pay attention to the quality of the materials used to perform the work. For pouring a slab foundation, it is recommended to use a concrete mixture of at least class B15.
Site preparation
Diagram of a monolithic foundation
In order to mark the configuration of the foundation slab, it is necessary to clear the site area. The top plant layer of soil is removed to a depth of 15–20 cm and removed from the site. You can do the work of removing the plant layer yourself using a shovel. If it is possible to use a bulldozer for these purposes, then this will allow the preparatory period to be completed in 1 - 2 hours.
Marking work
The foundation of the slab for the bathhouse is marked immediately along the entire perimeter of the structure. For marking, wooden pegs or cuttings of metal reinforcement rods are used. You will also need a strong rope or colored cord made of polyester thread. The site for the construction of a bathhouse is marked in the following order:
- The marking peg is driven 30–40 cm into the ground in the far corner of the future pit.
- In a straight line at a distance equal to the length of the building, a marking cord is stretched and a second peg is driven in.
- Next, sequential marking and installation of marking stakes are carried out, which are installed strictly at right angles.
This results in a regular rectangular or square linear configuration with right angles. In construction practice, a geodetic instrument, a theodolite, is used to construct right angles. Private developers do not always have the opportunity to use such a device and use the “diagonal rule” as a check.
Excavation
The monolithic slab for the bathhouse is made from 150 to 500 mm thick, depending on the class of soil, dimensions and weight of the building. In construction practice, it is customary to increase the size of the pit by 600 mm more than the linear dimensions of the foundation slab. The soil is developed manually with a shovel or small excavator.
Depending on the soil foundation, the minimum pit depth can be at least 400 mm. Typically, for a monolithic slab, the soil is excavated to a depth of 1500 mm, clay soil is selected, and the bottom of the pit is leveled to a horizontal level if possible. Instead of the removed clay, a gravel and sand cushion is poured, which is carefully leveled and compacted. Compaction is carried out using manual tampers or vibrating rollers.
Monolithic slab in formwork
A monolithic foundation slab must have clear geometric boundaries and smooth vertical side surfaces. In addition, when pouring, a plastic concrete mixture in a semi-liquid state is used, which can leak outside the foundation structure. Therefore, it is necessary to install restrictive formwork from separate panels, which is mounted along the edges of the pit 300 - 500 mm above ground level.
Formwork panels can be metal, planks or assembled from moisture-resistant plywood, OSB boards, flat slate sheets. During installation, the formwork is securely fixed from the outside with spacers resting on the ground. The upper above-ground part of the foundation forms the base of the bathhouse, which can be insulated with dense extruded polystyrene foam at the stage of installing the formwork.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to go to the bathhouse if you have a cold, flu or ARVI?
Sometimes inexperienced home builders have doubts about the advisability of installing a preparatory cushion for a “floating” slab foundation. When building a foundation slab for a bathhouse, making such a cushion will help to obtain an ideal flat horizontal surface for subsequent filling of the formwork with concrete mixture.
Before installing it, the bottom of the pit is covered with a waterproofing layer of roofing felt or geotextile and insulated with high-strength polystyrene foam boards. This structural “pie” allows a thin monolithic foundation slab to create a protective thermal barrier and make the floor in the bathhouse warmer.
Type of reinforcement cage
Reinforcement cage
The reinforcement in the body of a concrete monolithic slab serves to increase the strength of the structure and protects the concrete mass from cracking and the appearance of shrinkage cracks.
Often, a special mesh is placed on the top of the reinforcement belt for attaching a “warm floor” heating system, which will make the floor in the bathhouse warm and comfortable. The reinforcement frame is a spatial volumetric configuration of individual metal rods connected to each other by knitting wire.
The metal frame consists of working rods with a diameter of 12 to 16 mm of a periodic corrugated profile, and distribution (mounting) fittings made of smooth wire with a diameter of 5 – 6 mm. The working rods are used to make a reinforcing mesh with a cell size of 150 x 150 mm or 200 x 200 mm. In the spatial shape of the frame, reinforcing mesh is placed in the upper and lower parts of the monolithic slab.
Concreting the foundation slab
Concrete laying
Before starting concrete work, it is necessary to provide for the supply of utilities to the bathhouse. To do this, metal sleeves are installed in the formwork for the passage of plumbing pipes and electrical cables.
Before laying concrete, formwork panels are coated with waste machine oil or grease. It is best to lay the concrete mixture in one day as a whole mass. When laying concrete, it is necessary to compact it using a construction submersible vibrator or a bayonet shovel. The upper part of the monolithic slab is leveled and smoothed until a smooth horizontal surface is obtained.
Curing
After the concrete mixture has hardened a little, it must be covered with plastic film. During the hot season, the concrete surface must be moistened with water. If these simple protective measures are not taken, shrinkage cracks appear on the concrete surface, which can lead to a weakening of the bearing capacity of the foundation.
Detailed video instructions for constructing a monolithic slab: After familiarizing yourself with the technological chain of work on a monolithic slab, you can make a concrete foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands. The result is a reliable, solid foundation for a building that will last for decades.
Construction of strip foundations
Strip foundation is a monolithic slab made of concrete, rubble or reinforced concrete, slabs. A large amount of materials and a lot of labor will be required. The depth of occurrence is approximately 20 cm below the freezing level.
The first step is digging trenches in accordance with the markings. At the bottom of the trenches, a sand and gravel cushion of 15-20 cm is placed and compacted. Concrete strip has too low tensile strength , so it is preferable to use rubble or reinforced concrete.
If rubble stone is used, it is placed on a cushion and filled with mortar . Then another layer of stones is laid and also filled with concrete, etc. If the foundation is reinforced concrete, then installation of a reinforcing mesh is required, which should not protrude above the soil level. The ground part of the base (no higher than 20 cm) is constructed of brickwork or concrete. The second option requires installation of formwork.
Before erecting walls, it is necessary to carry out waterproofing and build a base . Suitable for waterproofing:
- roofing material treated with bitumen mastic;
- bitumen-polymer or bitumen-rubber coating;
- special waterproofing material in rolls;
- cement mortar with quartz sand and special additives.
The base is built from blocks, bricks or stones, which are filled with concrete.
Construction of a bathhouse foundation in the form of a slab
This design is used on unstable soils with shallow groundwater. To install a foundation in the form of a slab, a pit (depth of approximately 30 cm) and trenches (for installing a drainage system) are required. Geotextiles are laid at the bottom of the pit, then 15 cm of sand and 15 cm of crushed stone are poured.
After compaction, the formwork is installed , and roofing felt and polyethylene are laid on the crushed stone. Next, the reinforcing mesh is installed. If the bathhouse is wooden, then one layer of reinforcement is enough; for brick walls it is better to arrange a second mesh in the upper part. The reinforcement is filled with concrete mixture.
The construction of a slab foundation requires a large volume of concrete . You can't prepare it without a concrete mixer. In addition, concrete requires compaction, which cannot be done without a vibrator. A design feature is that the entire area must be filled at once to avoid the formation of cold seams. It is quite difficult to install a slab structure alone, so it is used only when absolutely necessary.
Advantages of an insulated slab foundation
And at the end of my story, I would like to once again dwell on the merits of choosing Swedish foundation technology. They are:
- An insulated foundation slab is a finished subfloor on which wooden joists can be laid.
- The stove can be installed anywhere.
- Heat loss through the floor is minimal.
- The labor intensity and time of the work are also very small (it took 2 days to build my foundation, excluding the time for concrete hardening. I worked alone).
- This type of foundation is suitable for any type of soil, even weak-bearing soil or with a high groundwater level.
If you just have to decide which type of foundation is most suitable for your bathhouse, I advise you to pay attention to the insulated slab. In operation, it has shown itself to be excellent: my bathhouse has been standing on this foundation for two years now, without sagging at all. The bathhouse is heated quickly and retains heat much longer than similar (but without an insulated foundation) neighboring bathhouses.
Tatarenko S.