Frost heaving of clays
Permafrost science is a branch of engineering geology and a very serious science, which, among other things, develops special methods for studying the characteristics of frozen soils and methods for high-quality construction on these extremely difficult soils.
Wet clay freezes in a rather complex way. The clay does not freeze as a whole at once, since it has pores, although you won’t notice it visually. First, water in large pores becomes ice and cements soil particles, as a result of which weak clay turns into rocky soil, which can only be mined with a pickaxe, or even with explosives. The increase in volume during freezing is about 9%. It is clear that in the spring this rock will turn into mud.
But the matter does not end with the freezing of water in the pores of the soil, since during the long winter there is a process of constant increase in the moisture content of the clay, due to the suction of groundwater from the lower horizon. And if the ground level is high and this water is nearby, the frozen soil can absorb so much of it that it forms entire layers of ice, and at the same time increases its volume so much that it can easily and simply lift a house, swell asphalt concrete road surfaces, deform railway tracks and the airfield runway etc. Tens of centimeters of heaving in winter is not uncommon.
And in the spring, the result of this phenomenon, called frost heaving, is obvious - the liquid melted soil becomes mud, the asphalt is destroyed, there are holes and potholes on the road, buildings have subsided, and the foundation has cracked. And repairs often won’t help.
Another “interesting” phenomenon is that frozen water-saturated soil tends to freeze with the foundation, including the pile, as with any underground structure. The pressure from frozen soil that arises in this case is so great that it breaks the piles. These forces act tangentially on the vertical surfaces of foundation walls, both destroying and pushing buildings out of the ground. One of the effective means to prevent all this is to arrange vertical waterproofing of the foundation using rolled materials; this will significantly reduce adhesion and force the frozen soil to “slide” along the surface, while the tangential forces of heaving will be largely leveled out.
But professional builders and road workers not only have a lot of troubles from the process of frost heaving, but they fight it quite effectively. There are different methods, sometimes using chemistry. But on your site, the best method of combating abyss is a simple remedy - drainage. If you managed to drain the water by arranging an effective drainage system, then heaving either will not occur or will be much weaker.
But before you fight, you need to recognize the enemy by sight. To build a permanent house on clay soil, geological research and design calculations are needed. Contacting a design organization in this case will be a practical solution, and construction in compliance with technology and according to a project carried out by specialists will save you from unpleasant surprises in the future.
In the case when a bathhouse, garage or small house is being built, it is possible to make a high-quality foundation on clay soil yourself, having studied the issue technically and being guided by building regulations.
Primer compatibility
The main feature of a pile screw foundation is its ability to work on such difficult soils:
- Swampy and clayey terrain;
- Soil with high groundwater;
- Heavily heaving soils, including those saturated with moisture;
- Peat bogs.
In addition to “difficult” foundations, piles with a screw tip can be used in more durable soils other than rocky ones.
In all cases, the accepted pipe length will be different, as will the diameter, because the bearing capacity of all soils is different.
Columnar foundation on clay soil
A columnar foundation, especially its pile variety, is also excellent for construction on clay soil. This option will not be the cheapest, but its reliability is quite high, which is completely justified. In the selected area, it is necessary to drill holes with a diameter of 200-250 mm, the depth should be below the freezing point. A layer of gravel is poured onto the bottom, after which an asbestos-cement pipe is lowered, which is poured using concrete mortar, compacted layer by layer. Such a foundation will need to be reinforced with metal rods. The installation step of support pillars should not exceed two meters; they are placed in the corners of the foundation, at the intersections of load-bearing walls.
To make a foundation, you need to prepare the following materials for work:
- drill for wells with the required diameter;
- asbestos cement pipes;
- gravel for embankments;
- reinforcing bars;
- concrete for pouring.
Scheme of a shallow strip foundation on clay soil.
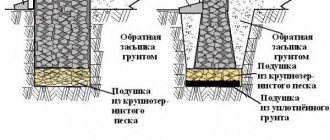
There is another option for the base device. This is the so-called prefabricated backfill columnar foundation, which is the simplest and cheapest. A similar foundation is used in places where there are water-saturated soils, rather dense clay-type soils. The technology for construction is as follows:
- the construction site is marked, after which the fertile soil layer is removed from it;
- in the places where the supports will be placed, you need to dig holes in the clay, the depth of which will be 50 cm, the dimensions will be 40 by 60 cm. After this, a layer of simple coarse sand or a mixture of sand and gravel is poured onto the bottom of each well. This pillow is moistened and then compacted manually. The filling is done up to the ground level in layers;
- Then the construction process continues by laying concrete blocks with dimensions of 20*30*50 cm on the cushions (you can also take blocks with dimensions of 30*30*50 cm). As a rule, the foundation requires the laying of two blocks, which are placed on top of each other. The lower trim is treated with an antiseptic, the upper one is covered with a layer of roofing material for waterproofing. The blocks are fastened together with cement mortar.
Technology for building a foundation on clay using screw piles
Construction of a strip foundation for a summer cottage.
Building a foundation for a house on clay soil is a rather complicated issue, since areas with such soil are not suitable for such work. It is not recommended to install a strip foundation in such a place; the benefits and reliability of slab foundations are also in great doubt. If another place cannot be found, you can limit yourself to installing a supporting columnar foundation for clay from screw metal piles. The process of installing such a foundation itself consists of several stages.
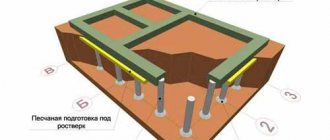
First, it is necessary to carry out geodesy of the area where the house will stand on clay. This will make it possible to most accurately determine all construction conditions, calculate the number and diameter of piles, and the depth for their safe installation. The depth of metal piles can be different; such a house can be erected even on a slope. The piles themselves should go in increments of 2 m along all load-bearing walls, including the corners of the house, joints, and intersections of walls. After the preparatory work is completed, it is necessary to separately check the load on each pile. If necessary, additional supports are installed. In this case, there is no need to try to perform the calculations yourself. The conditions for construction are difficult; only a specialist can calculate the foundation for a house.
After all the calculations are completed, it is necessary to prepare materials for constructing a foundation for clay. Another advantage of the pile foundation manifests itself here. The work will require very simple materials, the cost of which is much lower than for other construction options:
- metal screw piles of selected diameter and length;
- concrete solution for pouring piles;
- building level;
- pegs and rope for marking the territory;
- Bulgarian;
- metal beam for tying;
- anti-corrosion primer or paint.
To carry out markings, the most common rope, tape measure, and wooden pegs are used. They must be installed at the points where the piles will be located. At the foundation construction site, the fertile soil layer is removed.
Strip foundation on clay soil
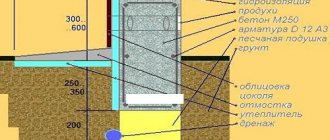
For the construction of country houses on sandy loam and loam, with deep groundwater, you can lay a strip foundation. On clay soil this will be a monolithic reinforced concrete strip under all external and load-bearing walls. as well as under the heaviest areas of the future structure. This is the only possible option if the house is supposed to have a cellar, underground garage or basement.
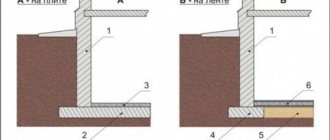
After transferring the markings from the plan to the “real life”, a pit is dug along the stretched signal strings, the depth of which is greater than the freezing level of the clay soil. In regions with cold climates it can be 1.5 meters. The bottom is carefully leveled and covered with layers of crushed stone (10-15 cm) and sand (the deeper the ditch, the thicker the sand layer). The walls of the trench are laid with waterproofing film or roofing felt.
The width of the pit is calculated as the thickness of the walls with finishing, plus 10 cm for the blind area and 30% for the base of the foundation. Concrete solution is poured into the bottom of the pit in a layer of 3-5 cm (this will be the base), and after hardening (about 14 days), formwork and reinforcement tied into meshes are installed.
The development of construction technologies has made it possible to use more expensive, but higher quality permanent formwork. It additionally insulates and protects the foundation from displacement.
Concrete is poured continuously, in parts of 15-20 cm, with the obligatory compaction of each layer. After 28 days, the concrete gains full strength and the formwork can be removed. The finished foundation is coated or sprayed with waterproofing materials. and if it is left to shrink for the winter, it is carefully covered.
- Sufficiently high load-bearing capacity.
- Durability (75-150 years).
- Possibility to build a basement or cellar.
- Great labor intensity.
- High costs for materials, and therefore the total cost of the foundation.
- Use only on loams and sandy loams, and in a deep-buried version.
Types of foundations for a house on peat soil
- When the peat layer is deep, it is necessary to completely remove it from under the house
. In this case, peat removal should be carried out over an area larger than the area of the house. In this case, the following types of foundations are used:- Shallow (with support on a sand bedding in place of peat, geotextiles are laid in front of the bedding);
- Foundation slab (supported by sand bedding);
- Deep foundation supported by a stable layer of soil;
- During partial peat removal, when the peat layer is no more than 1.5 m
, apply:- Monolithic strip foundation deep in trenches supported on solid soil;
- Reinforced concrete columns in pits (also supported on solid soil);
- No peat extraction
(when the peat depth is more than 3 m, it is not economically feasible to extract it):- Concrete piles (built in pits dug to solid ground);
- Drilled reinforced concrete piles (used without digging a pit with permanent formwork made of metal mesh and a cushion of 20 cm of crushed stone);
- Screw piles are the most economical, simple, but no less reliable foundation, erected on peat and without the involvement of additional earthworks and heavy equipment. Thanks to the metal of the pile and the special composition with which screw piles are processed, they are not afraid of the aggressive effects of peat soil.
The foundation of a house built on peat on screw piles will be strong thanks to the base and blades (which are compacted into the ground when screwed in), and due to the height of the structure, such a house will not be afraid of a low peat fire, since screw piles are fire resistant and are not subject to destruction when exposed to fire.
Another advantage of a pile-screw foundation is the ability to carry out work even in winter.
Typical difficulties with foundations on clay soils
Main reasons for base deformation
Clay consists of small particles that can be eroded over time by groundwater. Due to these properties, clayey soils are classified as highly heaving and subsidence.
If there is such soil on the construction site, then it is worth considering some factors that may negatively affect the integrity of the foundation. The main reasons for the destruction of foundations built on clays and loams include the following:
- Subsidence of the base. In this case, we are talking about the gradual immersion of the structure into the soil. Of course, when it comes to low-rise construction, subsidence is extremely rare.
- Bulging. Occurs when the foundation is installed above the freezing level of the soil. It mainly appears on heaving soils, which contain moisture-saturated clay and loams.
- Shifting the base to the side. Occurs when layers of earth move as a result of active movement of groundwater.
Preventing deformation of foundations on loams
There are several basic methods that are used by most builders. Among them:
- Installation of a metal frame made of reinforcement. It fits directly into the body of the structure throughout its entire volume. It is used to connect the upper and lower parts of the structure.
- Increasing the width of the sole. It is made slightly wider than the upper part of the structure. The walls are carefully leveled and covered with a sliding layer. It is made from machine oil or plastic film, which reduces the lateral impact of the soil.
- Strip foundations are fully connected with reinforcement. The connection must be rigid and reliable. This will prevent the base from moving to the side.
- To reduce the depth of soil freezing, the foundation is insulated along the perimeter with materials such as foam plastic or expanded clay.
- A shallow foundation is poured, which has a small lateral surface. This makes it possible to somewhat reduce the effect of the lateral heaving force.
Following these recommendations will allow you to build a reliable foundation for almost any structure. Of course, it is better to entrust the design of the foundation to professionals.
Determination of soil characteristics
First you need to decide on some characteristics of the soil on your site:
- The content of clay particles in the soil
- Soil moisture
- Soil freezing depth (SFD) for a given area
- Groundwater level (GWL)
Many people don’t need to be taught how to visually determine the composition of the soil; everyone who deals with the soil has a good understanding of what kind of soil is under their feet.
If you take a lump of wet soil in your hand, knead it and try to roll it into a sausage or make a “cord”, the sand will simply crumble, loam or “greasy” sandy loam will first roll into a sausage, but will quickly crack and fall apart into pieces. But if a whole and elastic “sausage” is rolled in the palm of your hand, it is clear that this is clay. That is, you have a soil foundation for construction of particular complexity.
Humidity can also be estimated without laboratory methods, although not in exact percentages. If you leave a lump of clay soil in the air and it takes hours to dry, the clay is wet. It is this kind of clay that can cause strong seasonal heaving and movement.
The groundwater level of the site is determined if there is a well. If not, you can determine it when drilling a well or pit. Information can also be obtained from neighbors, because during construction they often dig wells and drill wells.
Soil freezing depth
The depth of soil freezing is reference data; it is included in construction regulations, classified by construction area.
Table with standard freezing depth
| City | Standard freezing depth for loams and clays | Standard freezing depth for dusty and fine sands | Standard freezing depth for large and medium sands | Standard freezing depth for coarse soils |
| Moscow | 1,35 | 1,64 | 1,76 | 2,00 |
| Dmitrov | 1,38 | 1,68 | 1,80 | 2,04 |
| Kashira | 1,40 | 1,70 | 1,83 | 2,07 |
| Vladimir | 1,44 | 1,75 | 1,87 | 2,12 |
| Tver | 1,37 | 1,67 | 1,79 | 2,03 |
| Kaluga | 1,34 | 1,63 | 1,75 | 1,98 |
| Tula | 1,34 | 1,63 | 1,75 | 1,98 |
| Ryazan | 1,41 | 1,72 | 1,84 | 2,09 |
| Yaroslavl | 1,38 | 1,80 | 1,93 | 2,19 |
| Vologda | 1,50 | 1,82 | 1,95 | 2,21 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 1,49 | 1,81 | 1,94 | 2,20 |
| Saint Petersburg | 1,16 | 1,41 | 1,51 | 1,71 |
| Novgorod | 1,22 | 1,49 | 1,60 | 1,82 |
How to install piles and make a solid foundation
Foundation piles for clay need to be screwed in by at least two people, but heavy construction equipment is rarely needed here. Since the soil is clayey, the work will be difficult, so experts still advise using a special mechanism instead of a manual lever. This will make the work a little more expensive, but will make it better and faster.
A screw foundation on clay should be of high quality and reliable, so you should check the verticality of each support using a building level. Otherwise, severe distortion is possible, especially when screwing the pile by hand. And such deviations subsequently lead to a gradual distortion of the building, its deformation and destruction.
You should start screwing from the corner, constantly checking the plan. The pile is deepened to a specified depth. The only condition is that the location of its lower part must be below the levels of freezing and groundwater. If the length of the pile is not enough, it is necessary to build it up. After installing the foundation piles, the floor level of the first floor of the house is marked. For clay soil, it should be no lower than 50 cm from the soil surface; for outbuildings, 30 cm is enough. This point is marked on each pile, after which the remainder is cut off with a grinder.
Next, the supports are filled with concrete grade M 200. When pouring, which is done gradually, the solution must be constantly compacted. This can be done with a regular reinforcing rod. If a foundation on clay is being built as a temporary foundation, then pouring is not required; all supports can be reused after dismantling. After filling all the supports with concrete, you can begin tying. For this, a wooden beam or metal beam is used, which is simply attached to the surface of all supports. The choice of material depends on what the house will be built from. For example, for a foam concrete or brick house you need to use a metal channel, but for a wooden frame structure, an ordinary wooden rectangular beam is quite enough.
There are not many foundation options for clay. Clay is a type of soil that is not very suitable for construction. It is not always possible to install such a popular one on a clay site; preliminary geodesy is required during construction. The best option is a pile foundation for a house, which is made of metal screw piles.
Installation of screw piles for houses and baths on sand and sandy loam
Sandy and sandy loam soil directly on the surface is extremely rare in the Moscow region.
In the practice of constructing pile-screw foundations on clean sand, we installed piles only in gardening communities located in former sand quarries. A much more common situation is when sand lies under a thin layer of soil, earth or peat. Sand under peat is usually found in former peat mining areas. If the depth of the peat does not exceed 40-50 cm, we can say that the screw pile is installed in sandy soil, but if the peat depth is more than half a meter, we must consider this situation as installing screw piles on the peat bog (read more about installing screw pile foundations on see peat bogs). Due to the high density of the soil, installing screw piles by hand screwing in sand and sandy loam is one of the most labor-intensive. Moreover, the soil resistance in dry sands and sandy loams is lower than in watered ones. If it is necessary to install deep (more than 150 cm) screw-pile foundations in flooded sands, we recommend using the machine method of driving screw piles.
As when installing screw piles in clays and loams, before tightening the pile manually, we do leading drilling. True, if for the leading shaft in loams an auger (drill) with a diameter of 90 mm is used (an example is given for the most common screw pile in the construction of low-rise buildings and bathhouses with a barrel diameter of 108 mm), then for leading drilling in sand you can use a drill of a larger diameter, up to 200 mm. This is due to the fact that when the screw pile is twisted, it compacts the soil underneath. In loams, the walls of the leading shaft practically do not crumble, due to the viscosity of the soil. In sands, especially wet ones, the walls of the shaft crumble rapidly and literally after a few rotations of the pile, the shaft below the screw blade is completely covered with sand. And if the loam remains quite loose when shedding, then the sand, especially wet, immediately acquires almost its original density. The large diameter of the leading shaft partly compensates for the shedding of sand when tightening the screw pile.
Since sands and sandy loams, even partially watered, have a much lower expansion coefficient than loams, they are not classified as heaving soils. The depth of freezing, especially on dry sand, is minimal and with an average thickness of snow cover it is 20-40 cm. And there is nothing to freeze in dry sand. Therefore, the optimal depth of twisting of a screw pile on such soil is less than on peat bogs or loams and is 120-150 cm. Thus, on flat construction sites for installing a pile-screw foundation, you can use screw piles with a barrel length of not 250 cm, but 200 cm , thereby optimizing the consumption of materials and generally reducing the cost of a pile-screw foundation.
A solid foundation is one of the prerequisites for the safe operation of residential and industrial buildings. Its technical characteristics and consumer qualities largely depend on adherence to construction technology and competent design.
To build a reliable foundation for a house or utility room, it is necessary to correctly determine its depth. For a pile foundation, you will need to calculate the length of the supports.
Slab foundation
Another name for this type of foundation is a “floating” slab. This is an excellent option for clay soils, since the weight of the house is evenly distributed on the reinforced concrete foundation, and when the soil is washed out or moves, the entire slab will shift, and not its individual parts.
The concrete slab itself has a slight recess (depending on the weight of the future house), but it does not lie on clay soil, but on a sand and gravel substrate.
Under the entire base area, soil is removed to a depth exceeding the thickness of the slab by 30-40 cm. If the groundwater level is high, a drainage system of pipes is installed with a slope from the foundation. Now, the base can be covered with sand and thoroughly compacted or filled with “skinny” concrete. Formwork is installed along the perimeter of the foundation and its interior is covered with waterproofing film or roofing felt. The reinforcement bars are tied into a mesh, mounted in formwork and filled with concrete mortar filled with fine gravel. Filling is carried out as quickly as possible. "at once". Moreover, it is better to fill one layer over the entire base area on one day and finish it the next, than to fill the entire height in parts.
- Resistance to subsidence and erosion of soil, as well as seismic phenomena.
- Durability (up to 150 years).
- During the construction process, you can change the original layout of the house without additional changes to the foundation.
- Expensive materials and excavation work.
- The complexity of the process.
- Impossibility to build a basement without additional work.
Construction conditions
The depth of the foundation pile is determined on the basis of hydrogeological survey data carried out at the site of construction of the facility. This takes into account factors such as:
- physical and mechanical properties of the soil and the possibility of their change during the construction and operation of the house;
- location of groundwater;
- maximum probable level of precipitation during spring and autumn;
- the tendency of the soil to swell in winter;
- freezing depth.
In addition to the hydrogeological characteristics of the site, when calculating the level of the pile foundation, the architectural and design features of the objects being constructed are important.
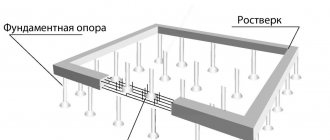
Installation of piles
Among them are:
- type of building, number of floors and presence of basements;
- level of occurrence of load-bearing structures of surrounding buildings;
- the magnitude and nature of the expected loads that will affect the foundation after the facility is put into operation;
- location of utilities.
After analyzing the hydrogeological and engineering-architectural conditions of construction, the type and material of piles are selected, their design is determined and the cross-sectional diameter, number and length are calculated.
Types and characteristics of soil
Since soil properties have a significant impact on the choice of building construction technology, when laying a pile foundation, attention is paid to the strength of the soil and its resistance to compression. When constructing a house or commercial structures, you can use traditional technological maps developed for a specific area. However, it is worth considering that they are relevant for industrial and civil construction projects. More accurate data is obtained by examining the soil directly on the site.
Another characteristic of the soil is the depth of freezing, which affects the level of foundation laying. It depends on the location of the construction, the type of soil on the site and the thermal parameters of the house. If the building being constructed is supposed to be heated, then the level of soil freezing is reduced by 20-30%. When constructing cold hangars and other similar structures, it increases by about 10%.
Errors in determining the basic parameters of the soil and possible subsidence can cause deformation of the foundation of the house, the appearance of cracks on the surface and damage to supporting structures.
Location of groundwater
An equally important parameter, along with the properties of the soil at a construction site, is the groundwater level.
Location of groundwater
If it is located low enough relative to the base, then its depth is determined taking into account the type and characteristics of the soil. When groundwater levels are high, all calculations are based on data on soil freezing. In addition, you should pay attention to the dynamics of moisture content in the soil.
If the groundwater level is unstable, which rises during heavy rainfall, it is advisable to construct special ditches on the territory of the facility. They prevent the negative impact of moisture on the foundation and serve to drain away its excess. Drainage systems or a complex of them will help reduce the high level of groundwater, which remains stable throughout the year.
As additional protection from moisture, it is necessary to provide waterproofing of the supporting structure.
Device Features
If you are selecting a foundation for a frameless house or bathhouse on clay soil or black soil, then a shallow strip foundation is best suited for you.
Types of strip foundations made from aerated concrete blocks or FBS slabs are convenient due to their design and method of transmitting forces. They directly take the loads upon themselves and transfer them to the soils that lie below. However, unlike foundations for a bathhouse with a solid slab, much less concrete and time are needed to produce FBS blocks from aerated concrete.
Let us give an example when a shallow foundation is mounted directly under the load-bearing elements of a house or bathhouse. If the house has a basement, then the loads are transferred between the block walls, floor slabs, and then the foundation.
If the house does not have a floor slab, and the floors of the house or bathhouse are filled with a regular screed over pebbles, then the structural loads are transmitted directly through the walls of the house or bathhouse. In any case, the shallow columnar foundation of the building is considered universal. Even SNiP recommends building standard low-rise buildings or bathhouses on strip foundations made of FBS aerated concrete blocks.
Purpose
Let's take an example when a shallow foundation made of aerated concrete blocks on clay soil or black soil differs from the usual one in that it has much smaller dimensions.
An example and calculation of a shallow strip foundation of FBS blocks made of aerated concrete shows that in this case the slab on clay soil will be buried by 60-70 centimeters, and the rest of its walls will serve as a plinth. Such a solution can aggravate the problem of installing the base of a house or bathhouse. After all, the entire floor slab will not cover a space of blocks 1-1.5 meters high. But the solution is very simple.
You just need to complete the missing part of the brick walls to the slab, and then insulate the shallow strip foundation made of aerated concrete blocks (ABC). At the same time, the use of combined fencing will help you avoid many problems that are associated with excessive rigidity of the foundation of the house.
Scheme-drawing of a shallow foundation
There are so many cases where in most cases they are not even taken into account, but houses made of blocks on heaving soils often face the problem of pushing out or shrinking of certain structures from the slab.
In this case, a reinforced rigid monolithic deep foundation made of FBS blocks can play a cruel joke on you. After all, its design will not allow it to absorb the load, but rather will lead to the appearance of cracks.
Shallow strip foundations are placed on clay, sand, soft and hard soil. You have almost no restrictions in this regard. But let us immediately note that if you plan to work on sandy soil or soil with a weak structure, then calculating shallow foundations does not recommend unnecessarily overloading the foundation by using too heavy a slab.
And in general, shallow foundations made of aerated concrete are ideal when you need to build a relatively light house with a single solid floor slab.
For large cottages, you should still select more reliable and expensive options from FBS blocks. However, an accurate calculation will most likely help you choose how much, so it’s better to turn to it. Let us turn to the main pros and cons of such structures made of aerated concrete. They also matter, and quite seriously.
Main advantages:
- efficiency;
- practicality;
- the ability to absorb loads from unstable soils;
- simplified calculation;
- construction is carried out using simpler technology.
Main disadvantages:
- not suitable for equipping large, heavy buildings;
- in some cases it shrinks due to unstable soil freezing.
Tape option
Typically, a strip foundation is considered suitable only for light frame or wooden walls, but this is not true; it can also be used for brickwork. This kind of foundation can be used on any soil, the only condition is that the groundwater level is low, since it is extremely vulnerable to any of their influences. In addition, strip foundations require greater labor costs, unlike other varieties.
Strip foundation diagram.
A conventional strip foundation is a concrete-filled trench 30 to 50 cm wide around the perimeter of the future structure, the depth is 50-70 cm below the groundwater level. This concrete monolith lies on a sand cushion. If there is a desire to strengthen this foundation, preliminary work is carried out to install special pits with support piles, which are installed in such a way that they rest on the ground below the freezing point and at a distance of about 2 meters from each other. These piles have a shape that expands towards the bottom to prevent negative effects from swelling soils. Moreover, the space around these piles is filled with compacted sand. It is on these piles that the strip foundation is laid.
In the case of constructing a concrete strip 90-160 centimeters below the groundwater level, it will be possible to build any house on such a monolith completely safely; it will withstand any natural movements of the soil. So in many cases, a strip foundation for clay soil is the best solution when building your house. But there are some situations when it is easier and safer to use other types of support for a building under construction, in particular pile or pile-screw foundations.
Choosing the right foundation for clay soil
Almost any foundation can be built on clay. The choice of foundation largely depends on the characteristics of the site and the wishes of the developer. Regardless of what kind of foundation will be built, experts recommend performing a number of necessary works.
This is especially true for areas in areas where the period of low temperatures is quite long.
When choosing a base, it is worth taking into account clay content and soil freezing depth. The level of deep waters is also important. In the case where groundwater is above the soil freezing level, it is necessary to arrange drainage around the perimeter of the base of the house. Drainage is carried out even before the construction of the foundation.
The following foundations can be built on clay soil:
- tape;
- slab;
- pile
The base is a reinforced concrete strip that runs under the external and all load-bearing walls. If the house provides for a basement or garage, then these areas are reinforced with a monolithic cushion. The advantages of the design include durability and high load-bearing capacity. Of course, building such a foundation will take quite a lot of time and money.
The slab is not laid on clay, but on a specially equipped substrate of sand and gravel. Such a foundation can last a century and a half. It very easily resists subsidence and erosion of the soil.
Of course, to build such a structure, it will be necessary to carry out labor-intensive earthworks. This will entail considerable financial and time costs. A pile foundation can last for several centuries. Of course, in order to achieve such results, it is necessary to carry out some calculations and also avoid common mistakes.
conclusions
As you can see, the depth of the foundation on clay soil directly depends on the clay component, the level of freezing and occurrence of groundwater, as well as the weight of the structure. During preparatory work for construction, it is better not to skimp on measures to study the composition of soils on the site. This will help you understand which foundation is better on clay soil in each specific case, because the price of the issue is the reliability and durability of a country house for many years.
Didn't find the answers in the article? More information on the topic:
- Assembling formwork for strip foundations on your own
- Step-by-step diagram for laying paving slabs
- Advantages and disadvantages of fiberglass reinforcement
- Types of foundations and common grades of concrete
- The best foundation for a country house
- Analysis and replacement of the foundation in an old house
Types of clay soils
Clay soils include:
Clay is a collection of small (up to 0.01 mm) particles with a small admixture of sand and dust. Characterized by flowability and high plasticity. You can build on clay if the soil is homogeneous and the groundwater is deep. But in any case, such a case is not at all suitable for independent construction.
Loam contains up to 10% clay. Depending on its specific volume, the soil can be light, medium or heavy. Loams are prone to frost heaving, so construction conditions on them are classified as difficult.
Sandy loam contains no more than 5 percent clay. These soils have another name - quicksand, as they have great mobility under the influence of groundwater. It is undesirable to build a foundation on sandy loam soils, but if there is no other choice, choose pile structures with a crushed stone base.
Clay as a natural material and its features
Clay soils come in different varieties. If the percentage of pure clay in the soil ranges from 5 to 10, then we have sandy loam. Loam is the name given to soils containing 10-20% pure clay. And if it is more than 30%, then the soil is called “clay”.
The main feature of clay is the ability to quickly erode under the influence of water, without letting it penetrate deeper. Layers of clay can lie at sufficient depth, and water that penetrates them freezes and swells the soil at low temperatures. Therefore, clayey soils are called heaving soils, and before starting construction it is strongly recommended to conduct studies of the composition and homogeneity of the soils on the site. Otherwise, the clay may behave unexpectedly, quite quickly turning a buried foundation into an above-ground one.
In general, a distinction is made between river (alluvial) and glacial clays. The first lies near reservoirs, in lowlands and has high plasticity. Construction on such areas is contraindicated, and in exceptional cases houses have a pile foundation. Concrete foundations can be confidently erected on glacial layers, but only if they are deep.
Foundation resource
The service life of piles, in addition to the correct choice of their load-bearing capacity, depends on the protective coating.
- Cold galvanizing peels off the metal already at the stage of immersion in the ground; such piles are not recommended for installation under a house; it is better to leave them for a fence or outbuilding.
- Hot galvanizing lasts for at least 75 years;
- Powder coating is only resistant to walking currents in the ground; it lasts up to 50 years;
- Coating with bituminous polymers protects the metal from getting wet and corrosion for 50-70 years.
After the warranty period has passed, the condition of the piles should be assessed through a professional examination for structural weakening.
Types of clay soils
Before you decide which type of foundation to choose, you need to know the type of underlying soil and its characteristics. For this purpose, engineering-geological surveys with laboratory soil tests are carried out. The geological report will describe which soils predominate in the construction area.
Sandy loam - soil with a clay content of 10 percent
The type of soil, its moisture content and the percentage of sand particles influence the choice of foundation. According to the regulatory literature, clay soil is divided into:
- Clay. Here its content in pure form is more than 30%. This soil can be used for the foundation if it is homogeneous in composition and the freezing point of the ground is located above the groundwater layer. It is characterized by high flowability and plasticity.
- Loam. It is sand with clay admixtures. Its content in the soil is no more than 30%. Loam is also divided into light, medium and heavy.
- Sandy loam. Here the presence of clay does not exceed 10%. This type of soil is almost never used in construction, due to the high probability of its movement under the influence of groundwater.
Depending on the origin and location, glacial and alluvial clay are distinguished. Glacial soils are characterized by high bearing capacity compared to other soils of this type. If the layer is large and deep, it can be used under the base. As the depth decreases, the plasticity of the clay increases.
Alluvial type of clay soil predominates in lowlands, near water bodies. Due to its high plasticity, its use in construction is very limited. Such soil can float, which will lead to the appearance of cracks in the building.
Determination of pile length
According to the provisions of SNiP 2.02.03-85 and its updated version SP 24.133300.2011, the choice of pile length is carried out in accordance with the soil parameters at the construction site and the level of the grillage base. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the available equipment and the technological capabilities of constructing the foundation.
The lower ends of the piles must be buried in solid soil by at least 0.5-1 m. The exact data depends on the characteristics of the soil and its fluidity indicators. When constructing foundations for industrial premises with inexpensive equipment, warehouses with low-value raw materials, wooden buildings and other Class III buildings, it is permissible to rest piles on silty-clay and sandy soils.
The length of the pile corresponds to the distance from the base of the grillage to the hard ground, adjusted for the terrain features of the site and the maximum permissible settlement. Its minimum value is:
- for seismically active areas - 4 m;
- in areas with moisture-saturated sands - 8 m.
In other cases, the minimum length is determined by the type of piles for the foundation of buildings and structures. Correction of design data is carried out using test driving, as well as statistical and dynamic testing methods.
What should be taken into account when constructing an MZLF
A very important factor is the type of soil on the site. The fact is that on soils of organic origin and on clay, the construction of a shallow strip foundation is prohibited.
The groundwater level is no less important. Their very close location can cause rapid destruction of a shallow concrete strip.
The terrain determines the degree of difficulty in constructing a shallow foundation. If there is a strong difference in height, it is better to build a different type of foundation. Previously, we wrote in detail about the construction of a foundation on a slope.
Features of installing a pile-screw foundation on peat soil
Important!
When performing any welding work on peat soil, fire safety measures must be observed, since peat is very flammable.
Due to the fact that dense layers of soil can be located at a depth of over 3 meters, the standard length of the pile will not be enough; it is built up and further screwed in. The process of installing foundation piles on peat looks like this:
- First, a 3-meter long pile is screwed in (it is not necessary to cut the piles to the same horizontal level at this stage).
The process coupling is welded on.
A so-called “extension” of 2 meters is inserted into the coupling.
All welds are cleaned and primed.
The pile is further twisted until it stops (when four workers with two three-meter levers cannot further twist the pile).
The usual installation stage takes place - all piles are cut to the same horizontal level, the pile cavity is filled with cement-sand mortar, pile caps are put on, the seams are cleaned and painted.
A pile-screw foundation built on peat is suitable for both small houses - cabins, bathhouses or gazebos, and for a full-fledged country house.
The complexity of building a foundation on peat soil requires that you choose a contractor with extreme caution and not resort to an independent method or a method “like your neighbor’s” in order to avoid negative consequences in the future, such as deformation and destruction of your structure.
A correctly chosen foundation plus a professional team of contractors is the key to success and many years of operation of your home.
If you have any questions, please contact our manager or request a call back.
The soils in the Moscow region are different. Sometimes, having bought a plot for a dacha or a country house, you can later during construction be faced with the fact that sandy soil predominates here. What to do in this case? Which foundation should you prefer?
First of all, you shouldn’t panic too much about this. It is quite possible to build a foundation on sand. This type of soil is not the most difficult - it ranks second after rocky rocks.
Below we will talk about some of the features of constructing foundations on sandy soil and what they are like.
Criterias of choice
Scheme of a columnar foundation.
In order to choose which type is suitable for clay soil, the specific characteristics of the soil are first determined, such as:
- specific gravity of clay particles;
- soil moisture;
- the depth of its freezing;
- ground water level;
- load of the building on the soil.
The presence of clay particles in the soil is determined in a fairly simple way. You need to take some earth and make a “sausage” out of it. If nothing happens when you crush a handful of soil, then the soil is sandy. The soil in the loam will initially take shape, but after a while it will begin to crack and fall apart into pieces. The presence of a plastic lump of earth that does not undergo changes indicates that we have clay soil.
Types of columnar foundation.
Soil moisture is determined by placing it in the air. If the soil takes a long time to dry out, the soil is wet. On cold winter days, such soil will be subject to frost heave, which can lead to destruction due to freeze-thaw cycles.
The depth of soil freezing is calculated using reference data. In the western and southern parts of the Russian Federation, the average level of soil freezing is 0.8 m, and in the northern it reaches 2.4 m. To reduce the effect of frozen soil on the foundation, it can be insulated with expanded clay or foam plastic.
The groundwater level is determined by drilling a hole or using a well (if it is located near a construction site). In the case where groundwater is located below the soil freezing level, it can be laid.
Otherwise, you should use the method of artificial drainage of groundwater. Drainage ditches and drainage systems are used for this purpose. If it is impossible to lower the groundwater level, it will be necessary to make a structure such as a foundation on piles.
Foundation layers.
The choice of foundation is also influenced by the load of the house on the ground. Installation of light frame houses can be carried out on any type of soil. For buildings that have walls two bricks thick and a complex gable roof, the foundation must lie deep and be of substantial size.
The foundation laid in clay soil must have increased resistance to soil transformation. The most suitable options for building houses on clay soils are to lay a strip or pile foundation.
For high-quality laying of one of the two types, we will need the following tools and materials:
Scheme of a homemade concrete mixer from a barrel.
- concrete mixer;
- mini-excavator;
- welding machine;
- hacksaw;
- hammer;
- Boer;
- winch;
- Bulgarian;
- nails;
- level;
- plumb line;
- square;
- buckets;
- shovels (scoop and bayonet);
- jackhammer;
- tamping;
- scrap;
- roulette;
- trowel;
- sand;
- crushed stone;
- gravel;
- fittings;
- boards for formwork;
- concrete solution;
- screw piles;
- beam;
- channel.
Sizes of different types of piles
In addition to the geological conditions and design features of the buildings being erected, the depth of the pile foundation also depends on the type of supports.
Screw
To determine the parameters of foundation supports for light, small-sized buildings, sometimes a superficial analysis of the site is sufficient. If in the lowest place of the construction site at a depth of up to 50 cm there is clayey or sandy soil of increased density, then the length of the screw piles should be at least 2 m. In other conditions, calculations are made taking into account the level of soil freezing.
For example, for the construction of various objects in the Moscow region, screw piles 2-3 m long are most often used. Structural elements of small diameter are in demand in the construction of fences and gazebos, and similar products with a large cross-section are used for the construction of a private house with several floors.
Bored
They are poured into pre-prepared wells, the number and location of which is determined by the building design and technical documentation. The drilling depth depends on the type of supports, which can be without widening, with a root-like base or a widened heel. When choosing a structure of a certain type, the characteristics of the soil and the loads affecting the foundation are taken into account.
The length of the bored pile in the ground must be at least 3 m from the base of the grillage or the surface of the ground. If structures without widening are used, they are buried at least 1 m into the supporting layer. The immersion of supports in cohesive soil with a widened heel cannot be less than 2 m or the value of its diameter. If construction is carried out in areas with a buried layer of peat, then the end of the piles is located 2 m lower.
The diameter of the shafts of bored supports is determined by their length and the height of the house, and is:
- for structures up to 10 m - 400 mm;
- for structures up to 15 m - 500 mm.
The strength of piles ranging in size from 15 to 30 m is ensured by shafts with a diameter of 600 mm.
Drivers
Depending on the type of materials used, driven piles are made of wood, metal or reinforced concrete. Structures made of wood or metal are treated with protective compounds before immersion. Watch a video of how driven piles are installed.
The minimum length of reinforced concrete supports does not exceed:
- for hollow ones - 4 m;
- for solid ones - 3 m.
The standard size can be from 3 to 16 m. If the installation depth of reinforced concrete supports requires a significant distance from the surface to the support point, then composite piles and a combined installation method are used.
Screw piles have become increasingly popular in recent years. They are actively used in the construction of low-rise suburban housing and in the construction of small architectural forms, when laying power lines, pipelines and constructing parking lot fencing, equipping berths, piers, etc. Moreover, the use of screw piles is possible on absolutely all types of soil, including peat and swampy soil, except for rocky soil. Undoubtedly, they have a number of advantages, but in order for these advantages to be fully realized, it is necessary to install screw piles correctly and efficiently. Meanwhile, the lack of special knowledge and inexperience of installers when installing screw piles contributes to a number of mistakes, which can subsequently lead to the destruction of the structure resting on these piles.
One common blunder is unscrewing the pile to adjust the height. The fact is that the high load-bearing capacity of a screw pile is ensured by screwing, in which the interturn spaces of the soil are not loosened, but rather compacted by the blade of the pile. Therefore, when screwing in and then unscrewing a pile, a layer of loose soil is formed under it and, as a result, the pile can, under the influence of load, sag to the height of unscrewing.
Another mistake is not installing the pile vertically. When screwed in, a pile in the ground may encounter underground insurmountable obstacles and, so to speak, “go sideways.” The maximum permissible deviation from the vertical according to the technology can be no more than 1.5 - 2 degrees. Exceeding these parameters will result in pile instability, even if the top of the pile coincides with the planned placement. In such cases, it is better to change the size of the pile, but achieve verticality, while separately strengthening the top of the pile to the plane of the superstructure. It is worth noting that a pile screwed at an angle exceeding the permissible parameters cannot be extended.
Another mistake is screwing a pile into a pre-dug hole for some reason. To ensure sufficient load-bearing structure, the depth of installation of the pile in the main (root) soil should be no less than 600-800 mm. This is a conditional value and can vary upward depending on specific conditions. For example, a screw pile 2.5 m long is screwed into the ground to a depth of at least 1.5 m for production. If the top layer of soil is unstable (peat), then the screw pile is extended to the required length and then screwed until it passes this unstable ground. In other words, the screw pile must have horizontal stability.
An error is also the case when a screw pile with a pipe (trunk) wall thickness of 4 mm is not concreted, which should provide the pile with an increase in bending rigidity parameters and prevent the pipe from rupturing under the influence of frozen soil. In addition, concreting the pile shaft not to the very top leads to internal corrosion of the shaft, and, consequently, to a reduction in service life.
It often happens that the site is not completely level and the soil is not homogeneous. Screw piles are installed at different depths. In order to save money, some installers may either not cut the piles “in level” or screw the piles to a depth less than required. This usually leads to uneven bearing capacity of the pile. When trying to level the level, inexperienced installers allow the pile to be unscrewed, which can result in subsidence of the pile. Uncut technological holes significantly reduce the durability and strength of the pile shaft. The welded head and weld seam should be painted to avoid corrosion.
Note that the service life of a screw pile is 80-100 years and failure to comply with the technology and relevant parameters for screwing the pile not only shortens the service life of the pile, but can also lead to the destruction of the structure being built on.
Video “Peat – which foundation to choose?
Pile-screw! The length of the piles is more than 5 m ":
A significant part of the areas of St. Petersburg, the Leningrad region, and Russia as a whole, is covered with swamps or was once swampy, so the problem of constructing a foundation on peat is familiar to many. Such soil is very weak, susceptible to frost heaving, cannot withstand loads, changes its characteristics over time, changes in size, since constant processes of decomposition of organic matter occur in peat, such soil is “aggressive” to metal and concrete.
A way out of the situation for building a house foundation on peat can be a complete or partial replacement of the peat layer, or the use of a pile-screw foundation, for the installation of which you do not need to remove the peat, even if its thickness is more than 3 meters and the standard length of the pile is not enough.
The SV-foundation company has extensive experience in constructing foundations on the most complex sites and unstable soils, including peat.
If you have a question or would like to know about the possibility and cost of building a pile-screw foundation on your site, contact our manager or request a call back.
The first mandatory step for constructing a foundation on any soil is a geological study. The peat bog often lies unevenly; it can be above or below dense layers of soil, or intruded from the side. The quantity, quality and configuration of its presence in the soil determine what type of foundation to place on peat soil under your object.