The part of the foundation that rests on the ground is called the base. Its area determines the amount of pressure on the ground: S more - P less. The structure of the soil significantly influences the choice of type and technology for laying the foundation. The strongest base is monolithic rocks, followed by hard or plastic clay layers, dense or loose sand. Where it is especially important, the soil is strengthened by pouring granulated slag, which tends to turn into concrete over time.
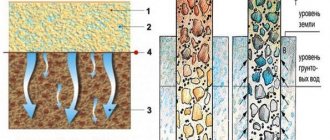
Foundation depth depending on groundwater level
All design features are described in SNiP 2.02.01-83*. In general, everything can be reduced to the following recommendations:
- When planning on rocky, sandy coarse and medium-sized soils, gravelly, coarse-clastic soils with sandy filler, the depth of the foundation does not depend on the level of groundwater.
- If there are fine or dusty sands under the base of the foundation, then if the groundwater level is located 2 meters below the freezing level of the soil, the depth of the foundation can be any. If the waters are above this mark, then the foundation must be laid below the freezing level.
- If under the base there are clays, loams, coarse soils with silty or clayey filler, then the foundation must definitely be below the freezing level (it does not depend on the groundwater level).
Table with recommended foundation depth depending on soil type and groundwater level
As you can see, the foundation level of the foundation is mainly determined by the presence of groundwater and how strongly the soil freezes in the region. It is frost heaving that causes problems with foundations (or changes in groundwater levels).
Why do you need to calculate the depth of the foundation?
How to calculate the depth of the foundation? How many calculations will this require? And most importantly, why and why should this be done?
To avoid many mistakes, you should know that the height of the strip foundation must be calculated based on the fact that it should be less than or equal to the part that is underground.
It is quite clear that in order for a house to stand firmly on the ground, good support is necessary.
It is this support that serves as the foundation. But why then carry out complex calculations and data analysis that will allow you to correctly calculate the depth and find out the required supporting area of the foundation?
According to the standards prescribed in SNiP, the depth of foundations should take into account the following factors:
Scheme of foundation deformation.
- Direct purpose and design features of the designed building, upcoming loads and their impact on the foundation. In other words, the supporting area of the foundation.
- Mandatory coordination with the depth of foundations of adjacent buildings and structures. It is also necessary to know at what depth all utilities are laid.
- The existing and projected topography of the territory where the development is taking place.
- Engineering and geological conditions of the construction site. That is, absolute knowledge of the physical and mechanical properties of the soil, the presence of layers prone to slipping, karst cavities, etc. features.
- Hydrogeological conditions of the construction site.
- The likelihood of soil erosion at the supports of structures that were erected in close proximity to river beds.
- Depth of seasonal freezing.
Perhaps the last three points are the most important, and therefore they are given a special role. Such close attention is explained by the fact that our country has several climatic zones. Accordingly, the quality and characteristics of the soil have their own characteristics. There are situations when on one site where a residential building is being built, it is necessary to take into account several types of soil at once. Therefore, it is very important to correctly select the area for laying the strip foundation and calculate the load on the load-bearing foundation slab.
Brief calculations that will need to be made during the planning process
Scheme of foundation types.
According to the rules, the standard depth of seasonal soil freezing is calculated based on observational data for a period of at least 10 years. If there is no such data, then special formulas are used for calculations. It is unlikely that it would occur to an ordinary person to carry out these measurements for 10 years or to calculate the freezing depth using complex formulas. Therefore, if you are not aware of the depth to which the soil freezes and the depth of groundwater, then it would be quite logical for you to contact the department of geology and hydrogeology in your locality. If you plan to hire builders to build a house, then choosing the dimensions of the area of the future foundation and calculating the required dimensions will be made by specialist designers.
If you yourself want to find out the actual freezing depth, then you will need to use the following formula: Dr = k*Dn, where Dr is the desired value, i.e. showing how much freezing depth there will be; Dn – standard freezing depth (data taken from the local geology department); k is a coefficient that takes into account the effect of heating a building on the freezing of the soil adjacent to the foundation. Indicators k are taken from the standards established by SNiP 2.02.01-83.
The depth of groundwater can also be determined independently. To do this, you will need to dig a hole in your area at least 2.5 meters deep and install a pipe in it. After some time, water will begin to seep into the hole and fill it. Your task is to find out how deep the groundwater is. Once you figure this out, you can easily determine the depth of the foundation.
Soil freezing depth
To roughly determine to what level the soils freeze in your region, just look at the map below.
But this is averaged data, so for a specific point the value can be determined with a very large error. For inquiring minds, we present a method for calculating the depth of soil freezing in any area. You will only need to know the average temperatures for the winter months (those in which the average monthly temperature is negative). You can calculate it yourself, the formula and calculation example are posted below.
Formula for calculating freezing depth
Dfn is the freezing depth in a given region,
Do is a coefficient taking into account soil types:
- for coarse soils it is 0.34;
- for sands with good bearing capacity 0.3;
- for loose sand 0.28;
- for clays and loams it is 0.23;
Mt is the sum of average monthly negative temperatures during the winter in your area. Find metrology service statistics for your region. Select months in which the average monthly temperature is below zero, add them up, find the square root (there is a function on any calculator). Substitute the result into the formula.
For example , we are going to build on clay. Average winter temperatures in the region: -2°C, -12°C, -15°C, -10C, -4°C.
The calculation of soil freezing will be as follows:
- Mt=2+12+15+10+4=43, find the square root of 43, it is equal to 6.6;
- Dfn= 0.23*6.6= 1.52 m.
We found that the calculated freezing depth according to the given parameters: 1.52 m. That’s not all; we need to take into account whether heating will be needed, and, if so, what temperatures will be maintained in it.
If the building is unheated (bathhouse, cottage, construction will take several years), apply an increasing factor of 1.1, which will create a safety margin. In this case, the foundation depth is 1.52 m * 1.1 = 1.7 m.
If the building is heated, the soil will also receive a portion of its heat and will freeze less. Therefore, in the presence of heating, the coefficients are reducing. They can be taken from the table.
Coefficients taking into account the presence of heating in the building. It turns out that the warmer it is in the house, the shallower the foundation needs to be buried.
So, if the temperature in the rooms is constantly maintained above +20°C, the floors are insulated, then the depth of the foundation will be 1.52 m * 0.7 = 1.064 m. This is already less costly than going deeper by 1.52 m.
The tables and maps show the average level for the last 10 years. In general, it’s probably worth using data for the coldest winter in the last 10 years in the calculations. Abnormally cold and snowless winters occur with approximately the same frequency. And when making calculations, it is advisable to focus on them. After all, it will not reassure you much if, after standing for 9 years, your foundation cracks on the 10th due to a too cold winter.
Sorry, the requested page does not exist.
Nothing found for this request. Try using the search to find what you need!
What can be done?
- Use the search
- Go to the main page.
You may also be interested
Greenhouse 0
How to store tulip bulbs in winter
Tips on how to preserve bulbs in winter at home After removing the bulbs, they are carefully sorted,
Processing 0
Bellarosa potatoes – variety description, photos, reviews
Bellarose potato variety - description and characteristics (with photo) Bellarose - early varietal potato
Processing 0
Auger snow shovel
Auger shovel For removing snow that has not yet been compacted, a manual unit is perfect
Growing 0
Description of the Levokumsky grape variety, characteristics of the variety, frost resistance
Description of the history of origin Not every locality can boast of a registered grape variety. Levokumsky
Diseases 0
Tomato Batyanya: description of the variety, reviews, who planted it, cultivation, photos
Features of cultivation and storage Since the variety is an early ripening variety, breeding occurs with the help
Growing 0
Tomato Amulet variety description, characteristics and cultivation with photos
Description of the variety This variety of tomatoes was bred a long time ago, because its popularity is due not only to the
Landing 0
Macadamia nuts benefits for women
How it grows and why it costs so much The area of macadamia plantations is increasing. But the quantity produced per
Trimming 0
Black radish juice effect on the body
Radish: benefits and harm to the human body, properties and contraindications Black radish has been around for many centuries
Landing 0
Apricots in the Urals are winter-hardy varieties, description of planting and care rules with photos
Features of planting apricot trees in the regions A biological feature of apricot is a short period of winter dormancy.
Growing 0
Cucumber Hector f1 description and characteristics of the variety, growing methods, plant care
Hector cucumbers: description of the variety This is a bee-pollinated, early-ripening variety of determinant type, recommended for cultivation in
Plants 0
Women's happiness flower why the leaves turn black
Possible reasons This indoor flower has a rather weak root system, frequent replanting for it
Processing 0
When to plant marigold seedlings
Types of marigolds and popular varieties There are more than 30 species of plants in the marigold genus. They
Landing 0
Boxwood planting and care in the Moscow region
Evergreen boxwood at home In the middle zone, in particular in the Moscow region, the most
Growing 0
Watermelons for Siberia: varieties, their descriptions and features of growing in a greenhouse
Astrakhan Famous variety, well known to Russians. Medium-late type, loves warm climates. Rounded
Processing 0
Soaked apples with rye flour
Which varieties are suitable for soaking? One of the main conditions for successful harvesting is the right choice
Contents 0
Corn for silage harvesting cultivation technology varieties and yield
The best varieties and hybrids of corn for silage The main indicators for choosing a variety: yield; energy
Growing 0
The most popular and productive eggplant varieties for growing in open ground and rules for choosing seeds
Does eggplant grow in open ground? We recommend reading our other articles: Feeding seedlings
Breeding 0
Tomato "Irina" f1: reviews, photos and yield
Tomato Irina: description of the variety The tomato variety Irina f1 was bred by Russian breeders of the research institute. The variety has been registered
Contents 0
What is an indeterminate tomato variety?
Determinate tomatoes The word “indeterminate” in botany is used to designate varieties of plants that are characterized by unlimited
Contents 0
Lemon tree care at home
Optimal conditions for growing Lemon care will not bring any particular difficulties if you create
How deep to dig the foundation
Armed with these numbers and the results of the site survey, you need to select several foundation options. The most popular are strip and columnar or pile. Most experts agree that with normal bearing capacity of the soil, their base should be 15-20 cm below the freezing depth. We described above how to calculate it.
Foundation depth is the level to which the foundation needs to be deepened
In doing so, consider the following recommendations:
- The sole should rest on soil with good bearing capacity.
- The foundation should be immersed in the load-bearing layer by at least 10-15 cm.
- It is desirable that the groundwater be located lower. Otherwise, it is necessary to take measures to drain the water or lower its level, and this requires very large amounts of money.
- If the load-bearing soil is too deep, it is worth considering the option of a pile foundation.
Having selected several types of foundations and determined their laying depth, an approximate calculation of the cost of each is carried out. Choose the one that will be more economical.
Also note that to reduce the depth of the foundation, you can use an insulated blind area. When constructing a shallow strip foundation, a blind area is required.
Popular designs for the basic foundation of a private house
Foundations used in individual construction:
- foundation slab;
- tape;
- pile;
- columnar.
The most reliable of them are tape ones, capable of rigidly connecting the entire base structure in all directions.
The most economical ones are columnar ones. They are indispensable for heaving soils and have a high load-bearing capacity. In addition, they require less material consumption and labor costs.
A pile foundation is a deep-laying option for support on denser, lower layers of soil.
Shallow foundation
Sometimes deep foundations are very expensive to build. Then consider pile (pile-grillage) or shallow foundations (shallow foundations). They are also called “floating”. There are only two types of them - a monolithic slab and a tape.
The slab foundation is considered the most reliable and easily predictable. It is designed in such a way that it can only suffer significant damage if there are gross miscalculations in the design. However, it can also be ruined.
However, developers do not like slab foundations: they are considered expensive. They take a lot of material (mainly reinforcement) and time (tying the same reinforcement). But sometimes a slab foundation is cheaper than a deep strip foundation or even a pile foundation. So don't write him off right away. It can be optimal if you want to build a heavy building on heaving or loose soils.
Shallow foundation
A shallow tape can have a depth of 60 cm. In this case, it must rest on soil with normal bearing capacity. If the depth of the fertile layer is greater, then the depth of the strip foundation increases.
With shallow strip foundations for lightweight buildings, everything is very simple: they work well. The combination with a log house or beam is an economical and at the same time reliable option. If there are kinks in the tape, the elastic wood copes with them perfectly. A frame house feels almost as good on this basis.
You need to calculate more carefully if you are going to build the rear ones from light building blocks (aerated concrete, foam concrete, etc.) on a shallow strip foundation. They do not react in the best way to changes in geometry. Here you need advice from an experienced and, of course, competent specialist with extensive experience.
Structure of a slab foundation
But it is unprofitable to install a shallow strip foundation under a heavy house. To transfer the entire load, it must be made very wide. In this case, most likely, slab will be cheaper.
How does a shallow foundation work?
This type is used when dealing with heaving forces is too expensive and does not make sense. In the case of shallow foundations, they do not fight them. They are, one might say, ignored. They simply make the foundation and the house rise and fall along with the swelling soil. That’s why they are also called “floating”.
All that is necessary is to ensure a stable position and rigid connection of all parts of the foundation and elements of the house. And for this you need the correct calculation.
Columnar foundations
Foundations of this kind are installed under light frame-panel structures made of wood that do not have basements.
The following types of such supports are used:
- reinforced concrete pillars;
- asbestos-cement or metal pipes;
- brick or building stone;
- logs
Regardless of the type, the pillars are placed in the corners of the future building and in the center, as well as in the gaps, at a distance of at least 2 meters. They should protrude no less than 30 cm above the ground surface. To install the pillars, they dig round holes (more resistant to collapse) up to 1.5 meters deep or drill holes to match the diameter of the pipes.
For greater strength, the pipes are filled with concrete from the inside, and the log posts are coated with bitumen or wrapped with roofing felt for waterproofing. Brick pillars are laid on a concrete screed, after it has dried, and covered with soil, compacting it.
To protect the pillars from the effects of lateral swelling and rubble, a grillage - a reinforced concrete monolith (log or beam frame) to distribute the load between the piles and as a basis for the walls being erected.
Construction of a foundation for a wooden house. Read an article about this here. And this article discusses a shallow strip foundation.
Calculation of foundation depth
This physical quantity that needs to be calculated for the foundation depends on many parameters.
The calculation of the depth indicator is influenced by the features of the relief surface, the location of the construction site, the design features of the planned building, the depth of soils that can be frozen, the level of groundwater in a given area, and others. Professional calculation, of course, is very important, but many who are building a private house cannot afford to calculate the depth of the foundation for a house in a construction company.
This article is for people who are building their own house, due to circumstances, cannot pay for the services of professionals and want to do this calculation themselves.
Approximate calculation of the required depth
Let's say we need to calculate the depth of the foundation in Moscow.
To begin with, the depth of the seasonal soil freezing rate is determined:
where d – has different values for different soil types:
- 0.23 m for soils containing a lot of clay;
- 0.28 m for soils consisting of fine sand;
- 0.3 m for coarse sandy soils;
- 0.34 m for rocky soils.
If the soil where it is planned to build the house is of a heterogeneous type, then d is determined as the average depth of soil freezing.
Mt is the sum of the average monthly soil freezing temperatures for the entire winter in the area where the house is being built. It is selected in tables published in reference books. There for the Moscow region there are such average monthly temperatures for all cold months: -7.8; -7.1; -1.3; -1.1; -5.6. Then the indicator M t is equal to the following value:
The freezing depth indicator for the Moscow region with clayey soil most commonly found here is equal to:
When the type of soil is unknown, you need to purchase a simple drill, which is sold in specialized stores, and make small holes in the center of the future site for the house and in its corners. This will allow you to determine the type of soil. Loamy and clayey soils are mainly common in Moscow and the region.
After the standard freezing depth has been calculated, another freezing depth is calculated.
where kh for the foundations of unheated buildings is equal to 1.1. In the Moscow region, the average annual temperature is +5.4 o;
kh for heated buildings is taken from the table, which can be found in the table of construction reference books. The calculated freezing depth is calculated:
- if the house under construction is not heated in winter, df = 1.1 * 1.1 = 1.21 m. When rounded, we get df = 1.25 m
- for a heated building without a basement, with heated basement floors: df = 0.7 * 1.1 = 0.77 m. It turns out df = 0.8 m
- if the house being built will be heated and have a non-cold basement df = 1*1.1 = 1.1 m.
The depth of the foundation is determined, taking into account the conditions for preventing heaving using tables of the dependence of the location of groundwater. Since such an indicator is difficult to guess, the worst option is most often chosen and d = 1.25 is accepted.
For a heated building without a basement with an insulated ceiling d = 0.8 m.
For a heated building with a cold basement d=1.1 m.
Approximate calculations of foundation depth
Two-storey house
The foundation depth of low-rise buildings is calculated as follows: Multiply the number of floors by 0.8, i.e. for a two-story house this value is 1.6 m.
It is also necessary to take into account the properties of the soil, the position of the aquifer and the depth of freezing. If the soil is sufficiently dense and not cavernous, and the depth of groundwater is less than 2 m, the foundation is laid at a depth of 1.6 m. Then the foundation is laid at a depth of 1.6 m.
On loamy or mobile soils, the depth increases to 2 meters or more.
Method for manufacturing wooden formwork for strip foundations: //6.//lentochnyi/.
Cottage
The depth of the base of a one-story residential building can be calculated using the formula: Hp=m*tm*Hh
- freezing point, m - coefficient of operating conditions (equal to 1.1), tm - coefficient of thermal impact on the soil (equal to 0.7-1).
For example, the soil freezes to a depth of 1.7 m, and the thermal effect coefficient is 0.7. After calculating the formula, we get the laying depth: 1.1 x 0.7 x 1.7 x 1.7 x 1.7 = 1.3 m.
This means that the foundation of a one-story house must be laid at a depth of 1.3 m on dense soil. The total load must be equal to that which the earth can withstand:
- Super - 2-3 kg/cm2;
- Gravel soil - 3.5-4.5 kg/cm2;
- Clay - 3-6 kg/cm2;
- Floor made of coarse shavings - 5-6 kg/cm2.
House made of foam blocks
A foam block is about half as heavy as a brick, so there is less load on the base. On hard floors under the house, make a flat foam strip foundation, provided the basement is intact.
If construction is carried out on an area with deep soils and a low groundwater level, it is necessary to follow the frost line - the foundation is deepened 30 cm below this level, as is the case with brick houses.
How the layout of the house affects the depth of the foundation
The calculation of the depth of the foundation is influenced by such features of the layout and internal structure as:
- presence and location of the basement;
- depth of foundations of neighboring buildings. If such buildings exist;
- underground communication routes and the depth of their location.
If the developer’s plans include a basement or pit, then the depth of the foundation must be laid at least 0.4 m below the floor level in them. It is recommended to lay sections of the planned foundation at different levels.
If it is not possible to arrange the foundation in this way, then it is recommended to make transitions from level to level in steps. The height of each step should be equal to the foundation block.
If the structure is planned wall to wall to the finished building, the level of the foundation must coincide with the level of the foundation of the neighboring building. If communication lines pass under the building being erected, the base of the foundation must be laid to enter them into the building.
This will save the pipes from the pressure of the foundation base on them, and the base itself will not end up on the loose soils used to cushion the communication lines.
Foundation depth - determining factors
When determining the type of future foundation, and making a decision about deepening the supporting structure, take into account the conditions in which the building will be operated.
It is important to pay attention to the following points:
- geological aspects;
- the impact of climatic factors on the depth of the foundation;
- the influence of the design features of the building on the level of the foundation.
Before starting calculations and choosing the type of foundation, you must:
- carry out soil analysis activities at the construction site;
- study the landscape and thoroughly clear the construction site;
- develop a building plan and calculate the mass of building structures.
At the stage of collecting information about the features of the construction site, a number of factors should be analyzed:
- the nature of the soil at different depths;
- average precipitation throughout the year;
- level location of aquifers;
- soil freezing depth;
- fluctuations in height and terrain features at the construction site.
Types of foundations according to the method of deepening
The decision on the type of foundation and the level of its laying is made taking into account the following points:
- features of the building included in the project;
- masses of the structure;
- presence of a basement;
- level of location of underground communications.
The average temperature in this area throughout the year and climate characteristics also affect the size of the foundation pit.
How to reduce the influence of frozen soils on the foundation
The condition of laying the foundation to the depth of the soil subject to freezing will eliminate the pressure of frozen soil on the foundation. But frozen soil will negatively affect the foundation design. This impact can be kept to a minimum. To do this you need to do the following:
- arrange drainage along the entire length of the foundation;
- narrow the foundation upward, giving it a trapezoidal shape;
- fill the foundation cavities with non-freezing soil;
- make a protective layer on the sides of the foundation.
One of the main mistakes when laying a foundation is neglecting the remains of the plant layer. It must be removed without fail. Approximately 15 cm of the removed layer is enough. And such work also needs to be taken into account.
Further, it is unacceptable to erect a building on black earth soil. Such soil is not suitable for laying a foundation on it and generally for constructing a building. The soft layer of soil must be removed.
It is unacceptable to build a foundation without reinforcement. The reinforcement will allow you to preserve the foundation and the building itself for a fairly long period. Reinforcement is performed closer to the upper and lower parts of the foundation.
Beginners in the construction business cannot always correctly and accurately calculate the correct depth of the foundation for their house. For this reason, if you have any doubts, it is better to seek advice from specialists. This will avoid problems in the future.
Slab base
A solid reinforced concrete slab is characterized by an increased safety margin, a high level of reliability and a long service life. However, it requires increased labor and monetary costs for its construction. A slab foundation reduces the impact of the building's mass on the ground and is popular on weak soils.
The depth level of a monolithic reinforced concrete slab is different:
- a shallow slab is laid on a pre-compacted gravel-sand cushion to a depth of 0.2–0.5 m;
- the distance from the zero mark to the lower edge of a deep foundation slab can reach one meter.
The decision on the depth of the foundation is made individually, taking into account the mass of the structure, soil characteristics and climatic conditions.
Calculation of the width and depth of the strip foundation: minimum thickness according to standards
Any foundation, regardless of type and design, is characterized by such parameters as the depth of the foundation and the width of the supporting structures. Many developers take the thickness of the load-bearing walls of the house as the width of the foundation, but this calculation is not always correct. They also calculate the depth of the sole by eye, taking into account personal experience and minimal knowledge in this area, but this should not be done.
In fact, the dimensions of the strip base depend on many factors; here the length of the strip is not taken into account, because these are the dimensions of the future house. But the width of the strip foundation and its depth are calculated separately, and this must be done for each building individually.
Common mistakes when pouring a foundation
When pouring a strip base, many people make common mistakes that lead to unsatisfactory results. Among them:
- Filling above the GPP level, which ultimately contributes to the formation of cracks and destruction of the building.
- Ignoring the load on the base of the foundation, which leads to the collapse of the house.
- Ignoring the level of groundwater - if they lie in close proximity, then upon contact with the foundation they will contribute to its destruction.
When determining the depth of the strip foundation, it should be remembered that this is an extremely important parameter, the calculation of which must be approached with all responsibility. Only by taking into account all the nuances, features and indicators can you build a reliable house that will last for a long time.
Determining soil type
Not only the depth of the foundation, but also the width of the load-bearing sole depends on the type of soil. Since there is a factor of soil heaving in winter, and this property of the soil can lead to irreparable damage to the foundation and house.
The type of soil can be determined not only with the help of specialists, but also with artisanal methods. To do this, just take the earth and moisten it with water, and then bend it into a ring. The clay will retain its structure. Loam crumbles into several parts, and sandy soil immediately crumbles into powder. This way you can determine the structure of the soil. Sandy soil with a fraction of 1.5 mm perfectly withstands heavy loads, it is optimal for the construction of strip foundations and does not contain much moisture.
Then, you need to determine the depth of groundwater. To do this, you can go to the nearest well and measure the depth of the water layer; this should be the maximum height of the soil horizon. Using a little math, the depth of the aquifer will be calculated.
You don’t have to do a soil composition analysis yourself. It is enough to contact the geodetic service. It will give a complete map of the soil composition, taking into account even the depth of soil freezing, and this parameter for choosing the depth of the sole will be considered key.
What determines the depth of the bookmark?
The following are factors affecting the depth of the base plate:
- Groundwater level;
- Soil composition;
- Permafrost content in soil;
- Total building load.
Groundwater level
The base of the strip foundation must be at least 0.5 m above the groundwater level. The close proximity makes basement and basement construction difficult, and the foundation is constantly wet and destroyed by moisture.
How to calculate the correct size of a strip foundation: //6.com///-.
If the groundwater depth is 2 m or less, additional drainage is necessary. If the groundwater level exceeds 2 m, the depth of the foundation does not change.
In order to independently determine the degree of occurrence of the aquifer on the site, it is necessary to create several wells with a depth of 2 to 2.5 meters using garden drilling. The best time for this is early spring, when the water rises to its maximum after the snow melts.
After 2-3 days you will be able to take measurements in the wells and find out how high the aquifer is. If the soil and walls remain dry after this, groundwater should not be taken into account when laying the foundation.
Caution: Do not walk through groundwater in adjacent areas as the aquifer is not evenly distributed.
Soil type
The density and composition of the soil are of great importance for the calculation, since the degree of subsidence and the strength of the foundation depend on them. All soils are divided into the following types:
What kind of concrete should be used for strip foundations? https://6sotok-dom.com/fundament/lentochnyi/kakoj-beton-ispolzovat.html
- Rocky. Rocky soil is not susceptible to the formation of bubbles, deposits and moisture accumulation. Belt and monolithic strip foundations on such soils do not require burial;
- Big chip. Large chunks of soil are made up of gravel, rocks and gravel, and the cavities between them are filled with clay or sand. In this case, the minimum laying depth is 45-50 cm;
- Glue. Clay soils are hard, freeze deeply, retain moisture for a long time and cause uneven shrinkage. The depth of the clay bottom must be at least 75 cm;
- Sandy. Sandy soil is characterized by increased mobility, so when laying the foundation, the hole is placed in solid soil. The maximum value is 2.5 m;
- Black earth. Black soil is unsuitable for construction, so during installation it is necessary to remove the foundation layer of black soil on a hard substrate.
Freezing level
The foundation depth of ½ corresponds to the freezing value for weakly aquiferous layers, but only on slightly curved and hard soils. This means that if the ground freezes at a depth of 1.5 m, the foundation trench will be dug to a depth of 75 cm.
On abyssal soils, the depth should be 20-30 cm below the freezing point. Under the influence of the blowing force, an insufficiently deep foundation is deformed, cracks form and the structure collapses. The table below helps to correctly determine the depth of soil freezing in a given region:
Advice! Heating the foundation reduces the depth of installation and, therefore, the cost of construction.
Building load
The weight of the building also affects the depth of the foundation. The higher the load, the deeper the earth. For light buildings in the form of sheds, single-storey half-timbered houses and bathrooms, the average installation depth is 50 cm.
Two-story houses made of wood or foam plastic require burial of a foundation of at least 1.5 m; for brick buildings (for example, for garage construction) this number increases to 2 m. However, this only applies to hard and loose soils, and on dense, hard soils the laying is done to shallower depths.
In order for the load to correspond to the bearing capacity of the soil, it is necessary to sum up the specific gravity of the foundation, walls of the house, floors, furniture, utilities and temporary loads caused by wind and snow. If the total load exceeds the permissible one, the width of the foundation strip must be increased.
How to calculate the depth and width of the base
As soon as the composition of the soil and the depth of groundwater are clearly determined, you can begin to calculate the size of the foundation. If the building is quite massive, tall and has several floors, then the immersion depth of the base should be large, right up to the soil freezing limit.
Developers who have the financial means try to deepen the foundation even lower, thus providing the foundation with greater strength and reliability. The height above the zero level should be up to 30 cm, sometimes more, for arranging the base and blind area.
So, the minimum depth of the strip foundation for massive buildings should be GPG + 60 cm. GPG is the depth of soil freezing. This tabular value is different for each region and soil composition. For light buildings, it is enough to arrange the foundation at a depth of the frost line or below up to 50 cm. In such cases, it is believed that due to the mass of the structure and the tape of the base itself, the soil will spread evenly under the sole, and swelling of the soil should be minimal.
The standard thickness of the strip is 40 cm, it can be increased as necessary, but it should not be less than the thickness of the load-bearing walls of the building.
Sequence of work
- Preparatory stage (features of the relief, bearing capacity of the soil are determined, the load of all piles, grillage, and floors is calculated).
- Marking the foundation (leveling the surface followed by marking corners, internal and external walls, places for piles).
- Excavation work (installation of pillars manually or using specialized equipment).
- Construction of a grillage (making formwork for pouring concrete. Removing sand from under a hardened structure (to obtain a gap above the ground surface).
At the same time, marking the contour is carried out with pegs at the corners of the designed object and cast-off boards (on the edge) for marking the axes. The cast-offs are removed after the base is completed. As an option: sprinkle sand along a cord stretched between the pegs or remove 10 cm of soil along it. The level of the relief is determined by the level.
In order for the foundation to have an aesthetic and finished appearance, after waterproofing work, the sinuses are backfilled in several layers with careful compaction from the outside, and, if there is a basement, from the inside. For insulation, they make a fence - a kind of plinth up to 50 cm high, made of wood or stone, sometimes with insulation, without mounting it rigidly to the pillars.
Next, they make a blind area , which, having a given slope, protects the foundation from the effects of precipitation. It can be soft fill or made of concrete and decorative tiles, have drainage grooves and outlets, and protect the walls of the house from the advancement of plants.
Calculation of the load on a columnar foundation. Read about it here. This article talks about laying bricks on the foundation.
And here you will find many informative articles about the foundation for your home.
Calculation of the area of the foundation base
The area of the sole is responsible for the uniform distribution of the mass of the entire structure along with the base onto the ground. Therefore, it will not always correspond to the width of the tape; in most cases it is larger. Moreover, the sole is also responsible for the following functions:
- Uniform distribution of building mass.
- Prevents local soil heaving due to seismic tremors or the impact of deep soil layers.
- Strengthens weak soils with its mass and presses them to strong soils.
- Ensures the uniformity of the structure of the building itself on a horizontal plane.
The area of the sole is calculated using the formula:
- k(n) – reliability coefficient, taken as 1.2. This coefficient means that initially the sole area will be 20% larger than the calculated one;
- F – Design load on the base. It consists of: the mass of the building, soil loads, the mass of the foundation;
- k(c) – operating conditions coefficient, taking a value from 1 for clay and rigid structures with stone walls to 1.4 for coarse sand and non-rigid structures;
- R – calculated soil resistance (this is tabular data). You can find them in reference books for all types of soils.
In fact, all the parameters are for reference, so all that remains is to calculate the load from the building itself.
Building load calculation
This parameter is calculated by summing up all the loads that the building creates on the foundation:
- Masses of load-bearing walls and ceilings (here the amount of building materials required for construction and their total weight are calculated).
- Coated roof masses.
- Masses of a snow ball that can be fixed on the roof and press with its mass, transferring the load to the load-bearing walls and foundation.
- The weight of all furniture, equipment and laid communications (this indicator is insignificant, it is often neglected or a coefficient of 1.1 is set).
- The weight of the foundation itself. This is where the difficulty in calculations arises, because the area of the sole also affects the mass of the base. Therefore, the width of the strip is assumed to be 40 cm, knowing from the design the length of the building, the density of concrete (2400), all this is multiplied and the weight of the foundation is obtained.
Estimated foundation height
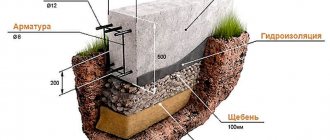
The height of such a foundation must be large enough to withstand horizontal ground movements and the influence of groundwater. Knowing the depth of soil freezing, it is also not difficult to calculate the height of the strip foundation. But when the construction of the foundation begins, the height will be completely different, and here's why. It consists of the following layers:
- First you need to make a sand and gravel cushion at the bottom of the trench, on which the foundation itself will lie. The thickness of the layer varies from 25 to 40 cm (depending on the type of soil), and this is an additional height of the structure.
- Soil freezing depth (reference data).
- You also need to make a base up to 30 cm, sometimes more, which depends on the type of soil and design decisions.
Now that we have all the necessary parameters for the future strip foundation, it is not difficult to calculate the required amount of reinforcement and concrete mortar for its arrangement. If you fill it strictly according to technology, then the base will last the longest possible period.
What factors influence depth
Figure 2. Strip foundation
When planning to make a strip foundation, the main attention is paid to depth, since this parameter is key and affects many characteristics. The higher the sole is located, the less money the owner will have to spend. However, strong savings are unacceptable, as they can lead to unsatisfactory results.
When determining the depth, take into account:
- GLP level;
- location of waters;
- heaving;
- structural features;
- type of soil.
Important: the upper layers are characterized by changes in properties depending on weather conditions, so it is advisable to bury the base in stable soils.
How to reduce the impact of freezing soil:
- create a sliding layer on the sides of the base using a material with a minimum coefficient of friction;
- fill the base in a trapezoidal shape, narrowing upward;
- protect the foundation with systems configured against waterlogging.
How to calculate the width of the foundation
The developer is always concerned about how wide the foundation of a strip structure should be. The greater the width of the foundation, the more labor and materials must be invested in its construction. Any excess in the consumption of building materials increases the cost of building a facility. To prevent this from happening, you need to accurately calculate the width and height of the strip foundation. Calculation of the foundation of the building determines the depth of the building, the height of the walls and the width of the foundation. It is also necessary to determine the amount of reinforcement and its diameter.
Methods for reducing depth
The depth of the strip foundation directly affects construction costs. To build a one-story house, a deep foundation is not required, therefore, the costs will be low. However, for heavier and more massive buildings, considerable costs will be required, which owners are trying to reduce by reducing the depth.
One of these methods is soil replacement - first, they dig a pit much larger than required and replace the heaving soil with non-heaving soil. This method is quite complex and difficult, as it involves large-scale work.
Another option is to use blind areas - concrete platforms to lower the GPP and prevent it from becoming waterlogged. The blind areas must have a slope of up to 10 degrees, and their width is determined based on the properties and type of soil.
It is possible to lower the boundary of the passage of groundwater passing under the object due to ditches equipped with outlets for liquid. Such designs are very effective and eliminate excess liquid in spring or rainy weather.
Types of strip foundation
Among foundations of different designs, the developer often chooses a strip foundation for his home. The strip base of the structure is mainly of two types:
- strip foundation made of precast reinforced concrete;
- monolithic reinforced concrete strip.
Reinforced concrete foundation blocks
Precast concrete
When installing reinforced concrete blocks in the design position, there is no need to arrange formwork. The block manufacturing technology includes vibration and steaming of concrete, which guarantees their strength.
When constructing a strip foundation from precast reinforced concrete on soft soils, the blocks are supported on concrete pads (wide slabs). Pillows increase the support area of the base of the house, thereby reducing pressure on the soil.
Foundation blocks of monolithic reinforced concrete are marked with letters - FBS. The main dimensions of the FBS are shown in the table: