Functions of a sand cushion
Quartzite fractions are used to create a foundation and organize bedding during construction. In the latter case, sand copes with several tasks:
- levels dense soils, evenly distributing the load of the building;
- compensates for the increase in the volume of frozen water on heaving soils. The material eliminates deformation and reduces the risk of cracks;
- eliminates damage to organic rocks - peat bogs, increases the bearing capacity of the substrate.
A well-equipped layer will act as a barrier in conditions where groundwater is close and will absorb the weight of a multi-story building.
What is the need for an embankment?
A residential building must be built on a solid capital foundation. The monolithic structure located on a special bulk support has good strength indicators. After preparing the area (clearing debris, marking), determining the depth, and digging a pit, a cushion of sand is lined. When is the best time to build it? Sprinkling is recommended in the following cases:
- when constructing a dwelling on heaving soils. The sand layer prevents destruction and deformation of the structure during freezing and thawing;
- in the presence of uneven soil. The embankment provides distribution and leveling of the construction site;
- with increased dampness from passing groundwater. The layer acts as a barrier;
- with possible settlement of the building. The cushion resists compressive forces in the soil;
- when constructing a building of several floors. The topping is laid to cushion the structure.
Sand under the foundation is laid in even layers, to a depth of no more than 20 cm, followed by compacting and watering each layer.
What type of material is poured under the base?
Correct arrangement of the bottom of the pit in accordance with the norms and regulations of SNiP 3.02.01 - 87 “Earth structures, foundations and foundations” requires the use of a bulk mixture to ensure the reliability of the structure. It is worth choosing what kind of sand is needed for the foundation - river or quarry, focusing on the product range of modern manufacturers. The construction materials market sells sedimentary rock for foundation construction in 2 types: quarry and river. Which one is better to use for a pillow? In answering this question, you should decide on the nuances of using each.
Groups
When mixing concrete, much attention is paid to the composition of the sand, that is, its size.
| Group | Size | Full residue on the sieve with mesh No. 063 |
| large | 3,5 – 2,4 | 50 – 70 % |
| average | 2,5 – 1,9 | 30 – 50 % |
| small | 2,0 – 1,5 | 20 – 30 % |
| very small | 1,6 – 1,1 | 7 – 20 % |
| thin | less than 1.2 | less than 7 |
Types of construction sand, which one to choose: river or quarry, white or red.
Which one is suitable according to GOST It is important to know that very thin sands, the grain size of which is less than 0.7 mm, are considered unsuitable for solutions. It is not advisable to use a fine sand mixture for building a foundation. The medium grain size allows the material to be used as part of a concrete mixture.
To produce high grades of solutions, material of a medium or large fraction is used. And you can fill the pillow under the foundation of a building with a larger fraction, where the average grain size is 3.5 mm.
Quarry sand: characteristics, application features
The raw materials are extracted from a quarry formed through the destruction of rocks. It is of low quality due to large volumes of impurities from clay and other substances. It is used to construct pits, but not in its natural form. Before use for the construction base, it is washed, dried and sieved to remove impurities. The popularity is due to the low cost of raw materials. A pillow made from a quarry embankment must have an important factor that determines the reliability and strength of the future structure - moisture. Its percentage in raw materials should be 1-5%.
Dusty sand – a shallow foundation is suitable
The main characteristic for construction is load-bearing capacity, which mainly depends on the moisture content and compaction of the layers. So, the denser it is, the greater the load it can carry without much shrinkage.
But with an increase in moisture in it, it negatively affects the load-bearing capacity (this does not apply to gravelly soil and coarse sand). Sand containing larger particles is better suited than fine or silty sand.
As with any soil, as the depth of the rock increases, the compression resistance also increases accordingly, that is, the deeper the base, the less shrinkage will be.
Measures will be required to protect the base from moisture. Although sand does not retain water, it is impossible to do without waterproofing on sand.
Sandy soil is considered non-heaving, it does not retain moisture, and therefore does not increase in volume when it freezes. So, any type of foundation can be built on such soils. Even if groundwater is close, installing drainage and insulating the base around the perimeter will easily solve the problem.
Shallow tape is the cheapest type. Suitable for a house without a basement. Taking into account shrinkage, it is better to build such a foundation for wooden buildings. Can be mounted from prefabricated elements - for example foundation blocks. A foundation made of blocks stands well on sandy soil.
For buildings with a basement, a recessed tape is suitable. In this case, it is advisable to additionally create a complete drainage system and be sure to waterproof the walls and floor in the basement.
You can use columnar or pile foundations. They are simple, affordable, columnar can be built both for a bathhouse and for a massive structure.
Do not exclude construction on a slab foundation - the most expensive type of foundation.
Before construction, it is advisable to make holes 2 m deep in order to assess the nature of the soil on the site. If there is sandy soil on the site, you can save a lot on the foundation. Usually the groundwater level is low, and there is no need to think about changing the bearing capacity.
Freezing of the soil also does not pose a threat; sand is not a heaving soil. So, don’t worry about the fact that you have sand on your site, this is an excellent option for a foundation.
Fine and dusty sands behave differently - they do not let through, but absorb and retain water, forming, simply put, dirt. When freezing, this dirt greatly increases its volume, due to the large amount of water - typical frost heaving. Silty sands are a highly heaving base, and when choosing and calculating foundations and drainage systems, this circumstance must be taken into account.
Another possible factor complicating construction on fine silty sands and sandy loams is their tendency to turn into a quicksand state when the groundwater level is high, and sometimes the proximity of an aquifer. Quicksand is a serious matter, and in some cases it can become dangerous. A geological survey of the site’s soil is the best solution, especially if the soil is silty sand, sandy loam and loam, and there are wetlands nearby, or there is/was a body of water, even a very small one.
The exact location and thickness (layer thickness) of the quicksand needs to be clarified. If the quicksand is close to the groundwater level, it is possible to install a pile-screw foundation.
These soils are classified as complex, especially with high humidity in the area and high groundwater levels. For this foundation, a geological study of the site is required, and a foundation calculation is also required.
When choosing a strip-type foundation, it is necessary to provide conditions to reduce the effect of frost heaving. These forces act on the base from below, pushing the foundation out of the ground and tangentially to the foundation walls. Measures to reduce the effect of buoyant forces are to increase the area of the sole; for this purpose, the foundation is arranged with a widening at the bottom, or a trapezoidal section is chosen.
If weak soils or quicksand are detected at the base, the foundation is strengthened with piles resting on dense load-bearing layers of soil. The widening at the ends of the piles will provide resistance to buoyancy forces.
The question of what kind of foundation to build if the soil consists of coarse sand will not cause any difficulties, since the answer to it is quite obvious - any. Such soil perfectly removes moisture, preventing it from accumulating in the immediate vicinity of the foundation, is resistant to (seasonal) movements, and is not susceptible to frost heaving.
All work on its construction is divided into several stages:
- Cleaning, leveling and marking the site using pegs and rope. Columns are provided not only at the corners of the building and at the intersection of load-bearing walls, but also along external walls, especially those of considerable length.
- Trenches are dug for future posts, in which a gravel backfill is provided, which will eliminate capillary suction of water. A waterproofing layer of roofing material or polymer film should be laid on top.
- The actual erection of the pillars is carried out with the bandaging of all rows, while the number of bricks in one row depends on the desired dimensions, as well as on the thickness of the future walls.
- After this, all pillars are treated with polymer (bitumen) mastic to completely waterproof them, and an additional layer of roll insulation is laid on top.
On a weak foundation, which includes fine and dusty sand, a shallow strip foundation will be optimal. During its construction, it is highly desirable to take measures that will help reduce the influence of the forces of frost heaving, which negatively affects the base of the structure. For this, the most optimal way is to build a trapezoidal foundation (with a certain expansion downwards).
Tape base
In addition, such a strip foundation on sandy soil necessarily requires high-quality waterproofing using rolled fused materials. It won't hurt to insulate it either. This type of foundation is suitable for light buildings without a basement.
If you plan to erect a heavy building, you can use either a pile foundation or a pile-strip foundation. At the initial stage, after clearing the area designated for construction, a foundation pit is dug and formwork is installed along the entire height. It will need to be strengthened with spacers.
- Features of clay soil
- What is the best foundation for clay soil?
- Strip foundation on clay
- Columnar foundation on clay soil
- Why this type of foundation?
Soils on which the construction of a residential private house can be carried out can be divided into several different types. One of the most common ones is heaving soils, which are considered unfavorable for construction work. The fact is that its natural ability to retain moisture often leads to unpredictable pressure on the foundation, which can lead to deformation or even destruction of the entire structure.
Diagram of the strip foundation formwork.
But what to do if construction is only possible on this type of soil? You will have to not only take into account the characteristics of the soil, but also choose the right type of foundation. Of the soil characteristics on the site, you should pay attention to the following criteria:
- a type of clay soil;
- ground water level;
- soil freezing depth;
- weight, overall dimensions of the house, loads exerted by the structure;
- presence of a basement.
Scheme of a reinforced strip foundation.
- a mixture of clay, sand, small stone. This option is considered one of the best; it is a reliable base that is slightly susceptible to heaving and allows water to pass through well. Construction on such a site will be relatively simple, the structure itself will be durable and reliable;
- sandstone, for which the clay content is up to 10%. Such a base is perfectly compacted under the influence of the load from the structure and conducts water well. The best option for construction is soil with coarse sand;
- high clay content from 30%. It is already difficult to build a house on such soil, since the soil contains a large amount of water, which when frozen greatly expands, that is, swells. The soil begins to push out the foundation, breaks it, which causes problems with the structure of the house itself;
- sandy loam and loam are mixtures of clay and sand. Their behavior depends on the composition; before starting construction, it is necessary to conduct a geological study to determine the possibility of building a house.
Construction on clay soil is rarely carried out independently, as this is associated with numerous difficulties and costs. Therefore, most often they try to move the construction of a house to a more suitable site, but if there is no choice, then they turn to specialists.
For clay soils, two types of foundations can be used: strip and columnar, but the technologies for their construction differ from those adopted for ordinary soils.
They are not only more complex, but also more costly financially. What are the options for constructing strip and column foundations, which can be done specifically on clayey, rather complex, often water-saturated soils?
Types of material
According to the type of processing, quartz raw materials are divided into:
- washed. It is extracted using hydromechanical equipment from flooded deposits. The technology makes it possible to obtain a composition without impurities and various components. The alluvial type is used in the production of bricks, concrete, reinforced concrete products, paving slabs and roads;
- seeded Obtained as a result of technical and mechanical sifting from stones and large particles. It is used in casting stone products, preparing masonry mortars and for forming a mass of plaster;
- sandy soil. It is an unrefined mixture with many impurities. As a rule, they are used to fill trenches and level the topography of summer cottages.
Quarry crumbs offered on construction markets are of exceptional quality in accordance with GOST 8736-93. Materials extracted from quarries are inexpensive. To check the quality, i.e. humidity, it is recommended to weigh the wet sand and keep it in the sun for about 30 minutes, and then re-weigh it. Humidity is calculated as the mass of the raw material after heating, from which the mass of the container is subtracted, dividing it by 100. The optimal humidity indicator is from 1 to 5%.
Types of sandy soil
Sandy soils are a loose mixture of small fractions of quartz and other minerals with a clay content of no more than 3%. As a product of rock destruction, sandy substrate is divided by density into groups such as dense, medium density and loose. Depending on the composition and grain fraction, sandy soils are divided into 4 types.
- The kitchen sink is clogged, what to do - tips for cleaning it yourself
Read
Dusty
The substrate is very fine sand - more than 3/4 of the composition contains particles less than 0.1 mm - with a high content of clay inclusions. This mass does not allow moisture to pass through well, which causes instability of the thickness and a tendency to subsidence and swelling. On such an unreliable fine sand foundation, a strip foundation reinforced with piles is most often used.
Fine grain
This category of sandy soil contains 3/4 elements larger than 0.1 mm. The substrate is relatively stable as a support for the foundation structure if reliable waterproofing is used. The fine-grained layer absorbs moisture well and is susceptible to frost heaving. When laying the base of a building, a depth greater than the calculated freezing depth of the soil is required.
Large
Soil mass with coarse sand is a reliable base option for foundation construction. 1/2 of the total number of fractions have dimensions greater than 0.5 mm, the substrate has excellent water permeability, and frost heaving forces are minimal.
gravelly
Soil layers, 1/4 of the composition of which are grains larger than 2.0 mm, have a high potential for the construction of foundation structures. The gravelly substrate does not retain water, the soil layers are not subject to horizontal displacements, and there is no frost heaving effect.
River sediment is a versatile material
A universal type of quartzite raw material is mined from the bottom of freshwater rivers. The composition is considered a natural, pure product, designed for multi-purpose use in accordance with GOST - 8736-93. It rarely contains impurities and other organic compounds. Thanks to natural polishing, the river rock fractions have an ideal shape. Experts note the fact that it is better to use it for building foundations. The fine-grained product is relevant for interior and exterior decoration, for brickwork and wall plaster, as well as for creating a drainage system.
Breed gradation
Raw materials extracted from the river bottom are characterized by heterogeneity. When choosing the right size of pebbles for the base, it is worth understanding the factional diversity. There are the following types of river bulk material:
- Washed – represents grains of sand of medium size, gray or yellow. They contain silicon and iron oxides.
- Coarse-grained - mined in the beds of dry rivers. It has an unobtrusive neutral color. It is used for decoration and finishing of premises.
- Large – pebbles reach sizes up to 5 mm. It is obtained using specialized crushing and grinding equipment by splitting rock.
River bulk material comes in several fractions. Sizes range from 0.7 mm to 3.5 mm. The cushion, equipped with a mound of small grains of sand, is intended only for lightweight buildings. The fine-grained filling is strongly compacted and shrinks.
Positive characteristics of river sand
For residential capital buildings, it is better to use medium and large-sized chips - 2-3 mm, and for multi-storey buildings, only the coarse-grained type is used. River sedimentary rock has a number of positive qualities:
- meets aesthetic and technical requirements;
- has increased moisture resistance;
- is not exposed to aggressive environments and does not rot;
- characterized by excellent sound insulation qualities;
- environmentally friendly and safe.
It is popular not only on construction sites. Bulk rock is used for arranging playgrounds, for the manufacture of concrete products, landscaping, in decorating rooms and in landscaping work.
Sand material fractions
Quarry and river varieties are classified according to the size of the elements. Experts distinguish several fractions of quartz rock:
- very thin. Sand grains measuring 0.7 mm are unsuitable for foundation construction. They can be used in arranging children's play areas;
- thin. The grain sizes reach 0.7-1 mm. Loose sand is not suitable as a base component, but is not bad for creating lean concrete;
- very small. The elements are 1.5 mm, but it is not enough to fill the foundation;
- small. Characterized by the presence of fractions of 1.5 – 2 mm. The use of this type of material increases the consumption of the cement mixture;
- average. Grains of 2 to 2.5 mm in diameter are suitable as a component of standard concrete;
- large. Sand grains up to 3 mm in size are ideal for making high-quality concrete mixtures intended for large-scale construction;
- a composition of increased coarseness with grains of sand up to 3.5 mm is needed to cushion the foundation and distribute the mass of the structure over it.
For pouring, only particles with sharp edges are needed, which increase the adhesion of the concrete dough to the surface.
Rules for choosing sand for the foundation
Sand is one of the particularly important components of the concrete solution from which the foundation is made. You should know that sand is considered a sedimentary rock, but artificial production of this building material is possible. In particular, we are talking about crushing stone or crushed stone. For this reason, you should understand the question of what sand should be used when building a foundation.
Learn more about how foundation settlement occurs.
The main criterion when choosing sand for a foundation can be called the type of material according to GOST; based on this, recommendations for the use of sand have been created:
- High-fine sand has a particle size of 3-3.5 mm. This material is an excellent solution for creating foundation pillows.
- Coarse sand with a fraction of 2.5-3 mm is recommended for use in the manufacture of high-grade concrete and cushions for foundations.
- Sand of medium and fine fraction, from 1 to 2.5 mm, can only be used for preparing concrete compositions. The use of such material to create foundation cushions is not permissible, since the risk of shrinkage in this case is quite high.
We advise you to read the article “How to calculate the volume of a foundation.”
When choosing sand for the foundation and cushion, the purity of the material is of great importance. You should pay attention to the presence of the following impurities:
- Vegetation. The sand may contain small branches and grass, which can significantly affect the quality of the concrete for the foundation and the load-bearing characteristics of the foundation cushion. Therefore, it is recommended to sift the sand before use.
- Clay. High-quality concrete and a durable cushion can be obtained by using sand that contains no more than 5% clay.
- Gravel. The presence of this component is allowed in the range from 0.5 to 0.7 percent of the total volume, provided that the particle size does not exceed 10 mm.
By the way, in a separate article we talked about which foundation is best to choose for a house.
Features of the construction of a sand cushion
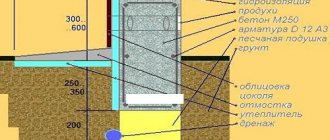
To build a reliable foundation, you must properly make an embankment and level the surface of the pit. The arrangement of the embankment implies the following indicators:
- The pillow is constructed 1/3 of the width of the foundation. The depth of the embankment layer should not exceed 20 cm.
- Before the flooring, geotextile sheets are laid on the bottom of the pit. It will provide additional drainage and protect the embankment from mixing with the soil.
- The embankment is laid in parts. After laying each layer of bulk material, it must be well moistened and compacted. It is better to compact sand using a vibrating plate.
- Compaction of sand under the foundation is carried out until then. Until there are no footprints left on the surface.
- Upon completion of filling, the surface level should be checked. It should be smooth. The correctness of the subsequent construction of the building depends on this indicator.
After filling the bottom, reinforcement is installed, formwork is laid and concrete is poured. To build a good and reliable foundation, you must first take care of the arrangement of the sand cushion. It plays an important role in the construction of the foundation, especially on heaving soils.
Article Rating
Which foundation to choose?
Strip foundation
It is often used in individual construction.
This is a thick “ribbon” of the same cross-section, running under all the load-bearing walls of the building - external and internal. Preparing a pit for a strip foundation A strip foundation is universal: it is laid for houses made of both light and heavy building materials on soils with very different bearing capacities. If you plan to build a basement or garage in the house, they also need a strip foundation. Its thickness depends on the thickness of the walls, the material used, as well as the load from the building. The technology is quite simple, but labor-intensive and requires a lot of material consumption. There are two types of strip foundation (LF) - deep and shallow.
Deeply buried LF is one of the most reliable for houses with heavy walls or ceilings. Here the entire monolithic “tape” is usually laid 20-30 cm below the soil freezing level. This ensures the stability of the structure on almost any soil, while simultaneously forming the space of a basement or basement floor, cellar or garage, but requires more material consumption.
The shallow-depth version of LF has become widespread due to its low cost and is a monolithic reinforced concrete “ribbon” on a sand cushion 20-30 cm thick and a brick superstructure. The depth of the tape is 50-70 cm. A shallow foundation is laid on slightly heaving and non-heaving soils . Sometimes, when constructing such a foundation, depths in the form of pits are drilled every 1.5-2 m or more often. The depth of the pits is below the freezing depth. Such a foundation allows the construction of any low-rise building with hollow reinforced concrete floor slabs. With good waterproofing, you can build a small basement or even a cellar inside the perimeter of the foundation. Strip foundation
Keep in mind : a shallow foundation cannot be laid on a frozen foundation and left unloaded during the winter. Otherwise, the foundation and the soil around it must be temporarily insulated with sawdust, expanded clay or similar materials that can protect the soil from freezing, and waterproofing must be applied to the surface of the foundation.
To make your own foundation, you will need a concrete mixer. You can choose suitable equipment in our market. Section Concrete mixers for summer cottages.
Concrete mixer Whirlwind BM-230 RUR 18,190
Gardener
Concrete mixer Whirlwind BM-140 RUB 13,490
Gardener
Concrete mixer Whirlwind BM-130 RUB 12,590
Gardener
Concrete mixer Whirlwind BM-100 RUB 10,990
Gardener