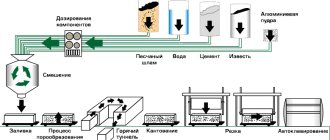
Wear resistance of concrete
According to regulatory documents, the durability of concrete or its service life varies between 50-100 years. It all depends on the proportions of the main components of the mixture and the additives used that improve the properties of concrete. But, as practice shows, premature destruction of concrete structures is a fairly common occurrence. Today, there are methods that make it possible to use the potential of concrete materials, significantly extend their service life, and maintain the durability of the surface in its original form.
What affects durability?
Before determining the appropriate method for strengthening the concrete surface and extending its service life, you should understand the parameters that influence this:
- Composition of the material. The strength grade, water resistance class and other indicators of cement greatly influence the strength and reliability of the future structure. The purity and clearly consistent fractional composition of the fillers is also important. For example, M150 cement cannot provide the necessary adhesion of all components, since its astringent properties are lower. Therefore, concrete surfaces made of this material will need to be repaired at least once a year. Therefore, it is recommended to use grades with a higher load resistance rating. Various unnecessary impurities also negatively affect the characteristics of building materials.
- Proportions of main ingredients. It is known that with an increase in the amount of the binder component, the strength qualities of the concrete solution increase, since the mixture is more dense, has fewer voids, and is compacted better.
- Filler type. The difference should be shown with an example. The service life of expanded clay concrete block material reaches 75 years, and wood concrete made from wood chips will require the first major repairs already in the fortieth year of operation.
- Concrete pouring method. It is easy to reduce the reliability of the design if the pouring technology and the ratio of ingredients to water are violated, weak compaction, too slow or accelerated drying, especially if heaters are used.
- Operating conditions. If the design and selection of materials does not take into account the conditions in which the structure will operate, then you should not expect durability from it. Excessive moisture has a detrimental effect on concrete. Constant exposure to water leads to efflorescence. Sudden temperature changes and frosts are also destructive.
- Vibration and soil movements.
- Wind erosion.
- Chemical corrosion of concrete and reinforcement. It is explained by the ingress of chloride ions into the concrete mixture when certain additives are used, for example, deicing agents, when used in a humid environment and in the presence of salt water sources.
- Human factor. Lack of knowledge, experience, and attention leads to mistakes being made during the preparation of the concrete mixture and at the construction stages.
How to extend the service life?
You can give concrete strength and increase its service life using different methods. Each of them is selected depending on the degree of influence of the factors listed above.
Correct pouring technology
Proper pouring of concrete guarantees its strength and durability.
An important step in this method is the selection of the composition and preparation of the concrete mixture. Ingredients and their quantities are selected according to the planned loads. The ideal option is to choose a brand of concrete and reinforcement with a safety margin. It is equally important to properly prepare the base. The soil should be fairly dense and inactive. This will allow you to avoid future deformations of the foundation and cracks in the walls.
The compaction of the material during pouring must be sufficient to remove all voids and air bubbles. The amount of porosity, and therefore the density of concrete, directly determines its moisture resistance and durability. Although there are exceptions. For example, aerated concrete has a long service life, despite the large number of voids. This is explained by the fact that a sufficient volume of air accumulates and circulates in the pores, which compensates for temperature deformations. Consequently, even frozen water in aerated concrete masonry is not capable of destroying the walls.
The drying period must be sufficient so that the cement has time to react and the structure does not lose its solidity. Natural drying under plastic film with periodic irrigation of the concrete surface is recommended.
In the cold season, the drying problem is solved by constantly heating the concrete solution and insulating the formwork.
Modifiers
To extend its service life, it is recommended to use specific additives that increase the resistance of concrete to various influences. A popular additive is fiber in the form of thin steel fibers. Such fiber fibers perform the function of reinforcement with the difference that they work not at the installation site, but throughout the entire volume of the mixture due to the uniform distribution of molecules.
Ferrous surface
Ironing of concrete is an improvement in the technological characteristics of a concrete base.
The concrete coating is treated with a special fluid or dry cement composition, the granules of which strengthen the weak surface layer of fresh concrete. Iron plating provides protection from high loads, mechanical and climatic influences. The method can be dry, when the cement mixture is applied through a sieve to the surface and leveled into a 2 mm layer after absorbing moisture from the concrete, and wet, when the finished compositions are diluted in water at the site of ironing.
Insulating impregnations
Silings are the most effective for processing masonry and monoliths. For their manufacture, fast-hardening polymers are used that are capable of penetrating deeply into the voids of the near-surface layer and isolating them. Impregnations increase the waterproofing of concrete, which significantly extends its service life.
But impregnation has negative sides. It blocks natural air circulation. Therefore, such compositions are recommended for treating floors, but are not suitable for use to strengthen concrete walls of residential buildings.
Timely repair of cracks
During the period of operation, it is important to promptly seal the cracks that have formed on the surface of the concrete. They will inevitably arise due to the natural expansion of the structure. If the defect is not repaired, a wide gap will soon form, which will be more expensive to repair.
Termoshov
Stages of seam repair work.
The joints are cut to a depth of one third of the concrete layer or a thickness of 5 mm. To do this, use a trowel, spatula or nail. It is more convenient to make cuts in freshly set mortar. If the concrete layer has hardened, then it is better to cut the seams with a grinder with an attachment for working on stone.
You cannot leave the seam open if the concrete surface is outdoors. To prevent it from filling with water and then freezing, the seam is filled with sealant, resin or bitumen. Indoors, you can use polyurethane foam for these purposes.
It is recommended to place thermal joints at perpendicular and parallel joints, near brick pillars, columns, and ceilings.
Ventilated facades
It is known that concrete masonry needs reliable protection from external influences. Ventilated facade systems cope with this task. For example, aerated concrete with a non-ventilated system will last only 50 years, and with a ventilated system - more than 100. This effect is achieved by ensuring natural air circulation, which removes excess moisture from the wall pores.
Water reducing compounds
A specific chemical additive can solve the problem of corrosion of steel in the reinforcement frame and concrete stone by regulating the content of chloride ions.
Conclusion
The main reasons that destroy concrete are:
- errors in design and pouring;
- low quality of mixture ingredients;
- exceeding load standards;
- reinforcement corrosion;
- fluctuations in the percentage of humidity inside concrete;
- sharp and frequent temperature fluctuations;
- aggressive impact and mechanical wear of the surface;
- natural deformation of the material.
Some of the listed factors can be influenced by the use of modern additives, impregnations, finishing and cladding technologies. This will be enough to increase the durability and resistance of the concrete structure, despite its natural wear and tear over time.
kladembeton.ru
Slow drying
If the solution was prepared too liquid, then when it hardens, cracks will appear on the surface due to uneven precipitation.
During drying, the solution precipitates. If the solution was too liquid, shrinkage occurs unevenly. As a result, cracks form. They are invisible inside, clearly visible on the surface.
A solution with an excess of water produces porous concrete, which subsequently actively absorbs atmospheric moisture and is destroyed by frost.
If you need to get a liquid solution, then for every additional liter of water you should add 2 kg of cement.
Many novice builders believe that three days is enough for complete hardening; after waiting this period, you can move on to the next stages of work. Complete hardening under natural conditions lasts up to 25 years. To reduce drying time, additives are added to the solution to speed up this process. Excessive additives will only reduce service life. The most durable and high-quality concrete – dried in natural conditions
The service life can be increased if high humidity is provided during drying, especially at high air temperatures, wind, or if the concrete is illuminated by direct sunlight. To do this, 12 hours after pouring, they begin to water it. At first, you need to water carefully, preferably from a watering can, so that strong jets of water do not destroy the top layer. The longer it stays wet, the longer its service life will be. To make work easier, concrete can be covered with a layer of sawdust, waterproof paper or film. You need to moisturize for up to 15 days. During this time, the solution gains 70% of its expected strength.
It is more expensive, but also more effective, to coat the top layer with a water-bitumen emulsion or ethinol varnish. Substances are applied with a brush or spray. They create a protective film. The film prevents the rapid evaporation of water. Milk of lime can be added to the emulsion. It gives the film a light color, which increases the reflection of sunlight and prevents the surface from heating up.
When it hardens, heat is released. If the volume of the solution is large enough, the temperature inside it can increase by ten degrees. Watering with water helps to cool and normalize the temperature.
Extending the service life of concrete
The service life of concrete or, in other words, its durability is the ability of this material to maintain the strength gained over a long period of operation of structures in contact with the external environment and to meet specified operating requirements.
If the solution is not prepared correctly, it quickly becomes covered with cracks and structures made from it become unusable.
Concrete does not rust or rot, and its strength is almost as good as natural stone. Therefore, durability should theoretically be between 60 and 100 years.
Practice shows that structures often collapse after several seasons of operation, or even after the first frost.
In order to increase durability, you need to find out what is causing its destruction.
The main reasons leading to destruction:
- errors made during the design and at the pouring stage;
- low-quality and inappropriate components;
- exceeding permissible loads on structures;
- corrosion of reinforcement structures;
- changes in humidity inside buildings;
- frequent and sudden temperature changes;
- presence of aggressive active chemicals in the environment;
- mechanical wear of structures under the influence of external loads;
- deformation of a material that occurs due to temperature changes.
Tools and materials
To increase the service life at the pouring stage, you will need the following tools and materials:
The water-bitumen emulsion should have a viscous consistency and dark brown color.
- brush;
- watering can or sprayer;
- Master OK;
- Bulgarian;
- disc on concrete or stone;
- waterproof paper;
- water-bitumen emulsion;
- ethinol varnish;
- milk of lime;
- protective film;
- ironing powder;
- polyurethane foam.
The first necessary condition in order to ensure durability is the correct choice of its components and their proportions: crushed stone, gravel, water, cement and additives.
The most important point when planning work is the choice of cement.
The most common cement is Portland cement grades 400-500. Hardens relatively quickly and has increased strength. Contains mineral additives.
When interacting with water, alumina cement releases a large amount of heat, which is why it hardens quickly.
Aluminous cement grades 400-600 is a type of cement that, when interacting with water, releases an increased amount of heat, so the solution made on its basis hardens faster.
Gypsum-alumina cement is rare; its main feature is its relatively large expansion during hardening.
Sulfate-resistant cement grades 300-500 is cement that is resistant to chemically active environments, including sea water.
Pozzolanic cement is indispensable when used in a humid environment; it has increased water resistance and, as a result, frost resistance.
Beginner mistakes
Many mistakes that reduce service life can be avoided at the design and pouring stage.
Concrete waterproofing W - 12
Many people are interested in the question of whether W-12 concrete needs waterproofing. Considering the properties and features of W-12 concrete, we can say that it is quite durable, but if it is covered with reinforcing components, its service life is much longer. The strength is so strong that even diamond drilling cannot make a hole. Concrete W-12 has high performance characteristics, allowing one to achieve good results when creating foundations designed for small structures that do not have high requirements for increased strength. The floor screed created using this brand is resistant to temperature changes, and with strengthening agents it has served for many decades without the formation of any defects or damage.
Durability of concrete and reinforced concrete
The durability of materials is characterized by the service life during which they remain operational.
Exhaustion of durability occurs when a limiting state is reached, after which further operation becomes either technically impossible or economically unfeasible. The durability of concrete (and reinforced concrete structures) depends both on its properties and on the characteristics of the environment in which it is used. Therefore, when designing concrete, its operating conditions must be taken into account.
Actual durability of concrete and reinforced concrete structures
Experience in the operation of concrete and reinforced concrete structures and structures provides examples of their high durability. The most famous is the Pantheon (temple of all gods) in Rome with a dome made of lightweight concrete with a span of 43 m. Its age is about 2000 years. Although reinforced concrete, unlike concrete, has existed for only a little more than 150 years, there are a number of structures of almost the same age that are perfectly preserved. Formulas have been proposed for calculating the durability of reinforced concrete, in which the factors influencing it vary widely. According to the formula of the All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Reinforced Concrete, at the lowest levels the durability was 5 years, and at the highest - 269 years. If the possibility of such high durability remains to be tested, then the minimum durability predictions are quite accurate. There are a significant number of cases of destruction of reinforced concrete structures after 2-3 years of operation. However, the situation has not improved at all in recent decades. Roads and bridges, exposed to the combined action of moisture, frost and chloride salts, and marine structures are very vulnerable. A number of structures operating in humid conditions with simultaneous exposure to frost also have insufficient durability. The durability of structures exposed to aggressive environments remains a problem. In particular, the number of cases of internal corrosion of concrete is increasing due to an increase in the alkali content in cement recently. One of the factors that has changed not in favor of the durability of concrete is the increase in the grinding fineness of cements. It is determined by the need to increase the early strength of concrete, improve the use of cement, and reduce the consumption of raw materials.
But this leads to a decrease in the clinker stock in concrete, which plays a significant role in ensuring its durability. Thanks to it, further hardening of concrete using conventional cement occurs after 28 days. At the age of three to six months, their strength increases by about a grade. The structure of such concrete becomes compacted, and its permeability decreases - the most important factor in durability. The ability of concrete with sufficient clinker stock to self-heal microcracks is also significant. Concrete based on finely ground cement practically does not have such properties.
www.uniexo.ru
Beginner mistakes
Many mistakes that reduce service life can be avoided at the design and pouring stage.
The most serious and common mistake when pouring: in order to make the screed easier to level and so that the solution completely fills the trenches, spills between the stones, they try to make it rare, and after setting it is diluted with water. The mistake is that the excess water does not react with the cement. When hardened, it forms voids, which subsequently cause microcracks leading to destruction.
Great Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
Page 1
| Strength requirements for coarse aggregate. [1] |
The durability of concrete depends on the quality of the materials. Portland cements without mineral additives with a C3A content of up to 8%, plasticized and hydrophobic cements should be used, or PVA should be added to concrete mixtures. Sand and coarse aggregate must be of high quality. [2]
The durability of concrete is its ability to maintain its operational properties for a long time, within the limits provided by the designs. [3]
Typically, concrete durability is defined as the resistance of concrete to alternating freezing and thawing. [4]
Increasing the durability of concrete (especially those with increased porosity) is primarily associated with their protection from water penetration. [5]
Ensuring the durability of concrete and reinforced concrete structures operating in aggressive environments is one of the main problems that requires rapid resolution, primarily for the construction of chemical industry structures. One of the important factors that helps to increase the durability of reinforced concrete working in aggressive environments is the correct choice of resistant materials for concrete. However, the use of highly durable concrete in highly aggressive environments of the chemical, petrochemical and metallurgical industries cannot always ensure the required durability of reinforced concrete structures as a whole and therefore, in some cases, additional special measures are required to protect structures from corrosion. [6]
The increase in the durability of concrete when polymers are introduced into its composition is explained by the complex action of two main factors [1]: firstly, the formation of a finely porous structure of concrete during the release of hydrogen with the rupture of the Si-H bond and the entrainment of air when using aluminosiliconates and sodium siliconates and, secondly , adsorption on the walls of pores and capillaries of polyorganosiloxanes, which impart hydrophobicity to concrete. [7]
Conditions for the durability of concrete and reinforced concrete. [8]
The quality and durability of concrete are determined by the main indicators of physical-mechanical and elastic-plastic properties, as well as the durability of concrete over time under the influence of adverse factors. [9]
Undoubtedly, the durability of concrete and concrete structures is associated with an increase in strength that compensates for the weakening effects. [10]
When determining the durability of concrete in an aggressive aqueous environment containing carbonic acid, one should take into account not only the durability of the cement batch, but also the durability of the filler, since rapid destruction of carbonate rocks can occur. [eleven]
To increase the durability of concrete (frost resistance, water resistance, water resistance and resistance in aggressive environments), the butt part of reinforced concrete supports and attachments is impregnated with bitumen and coal tar. [12]
When determining the durability of concrete in an aggressive aqueous environment containing carbonic acid, one should take into account not only the durability of the cement batch, but also the durability of the filler, since rapid destruction of carbonate rocks can occur. [13]
To increase the durability of concrete with the addition of chloride salts and slow down the setting of the concrete mixture, it is recommended to use plasticized cement and introduce air-entraining additives (abietic resin, p. [14]
Methods for determining the durability of concrete are much more complex, time-consuming and labor-intensive than determining strength. Nevertheless, it is necessary to be able to determine the durability of concrete both during the design and construction, and during the operation of buildings and structures made of concrete and reinforced concrete. Despite the desire to expand the study of physical and chemical mechanics, the rheology of the concrete mixture and the structure of hardened concrete, sufficiently reliable and quick methods for determining the durability of concrete have not been established. The wide variety of properties of materials and methods of manufacturing products from concrete and reinforced concrete or the construction of buildings and structures from monolithic concrete, on the one hand, and the variety of factors affecting concrete during its service, on the other hand, do not allow us to give an exact theoretical or experimental solution to the question of durability of concrete. [15]
Pages: 1 2 3 4
www.ngpedia.ru