The main advantage of steel roof frames, in comparison with paving stones, is strength and durability. Metal, of course, can withstand much greater loads than wood. The main disadvantage of such farms is, first of all, their high cost and some complexity in installation.
In private housing construction, structures of this type are used extremely rarely. They are mainly installed during the construction of various types of industrial, warehouse and utility buildings of large area. In private households, such corner trusses are usually welded only when assembling some small metal architectural structures, for example, gazebos or canopies.
What are they?
The main structural elements of a metal truss are:
- top belt;
- lower belt;
- a grate located between them.
Elements of such rafter systems can be fastened by welding, bolts or rivets. There are truss units made from angles and pipes with direct connections and gussets.
The upper and lower chords of such metal support structures can be assembled, for example, from a profiled pipe. When installing roof frames for large industrial buildings, stronger channels are also used for this purpose in some cases.
Corners for the construction of roof support structures are also used quite often. Sometimes trusses are assembled from single metal products of this type. But in most cases, belts are mounted from corners connected by a tee. This allows you to assemble much stronger structures.
To weld the top flange of such systems, it is necessary to use angles with different flange widths. For the lower screed of the truss, material that is equilateral in the front plane is taken from paired corners. This technology allows you to assemble the most durable and durable structures. In the upper belt, in this case, the corners are connected on the smaller side.
Truss nodes from paired corners are designed on gussets. The lattice rods are attached to the latter with flank seams. The gussets themselves go around the corners. In this case, the node turns out to be the most reliable.
The elements of the angle truss lattice are:
- racks located perpendicular to the axis;
- struts mounted at an angle;
- trusses or auxiliary struts.
This part of the metal rafter system is assembled both during the construction of large buildings and small architectural forms, in most cases from a single corner. Sometimes a profiled pipe of small cross-section is used for this purpose.
Additional elements of angle trusses are usually load-bearing Z-profiles, onto which the actual roofing material is subsequently attached. Sometimes such elements are not installed when assembling the roof support structure.
When constructing small architectural forms, among other things, the simplest trusses without belts can be used, which are structures that form one plane. When manufacturing such systems, a triangular frame is first welded. Next, it is strengthened with stiffening ribs and struts.
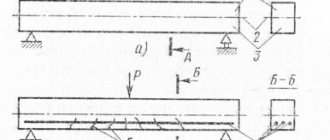
A truss is a rod system that remains geometrically unchanged after the conditional replacement of its rigid nodes with hinges. Trusses belong to the class of through structures, in which the chords are connected to each other not by a solid wall, like beams, but by a lattice consisting of individual rods - braces and racks. Trusses are used in coverings of industrial and civil buildings in cases where solid beams are not economically viable. The use of a lattice reduces the consumption of material on the structure, but increases the complexity of manufacturing, since nodes appear - the places where the lattice is connected to the belts. General types of the most common wooden trusses are shown in Fig. 9.1.
Triangular trusses are used, as a rule, for roofs made of materials that require a significant slope. The ratio of the height of the truss in the ridge to the span is taken to be no less than: for all-wood trusses 1/5, for trusses with a metal bottom chord 1/6. For trusses with a metal bottom chord and a glued top chord, this ratio can be reduced to 1/7 of the span. In this case, the slope of the upper belt and roof ranges from 1:2.5 to 1:4.
The upper chord of the truss can be made of glued blocks (laminated triangular truss) or beams (timbered triangular truss). It is recommended to make the lower belt metal from profile or round steel. The advantage of the latter is that, with equal weight, it has great fire resistance. It is also possible to use a wooden laminated or timber bottom chord, provided that it is made from carefully selected wood and well-developed gluing with joining along the length using a toothed joint.
To increase their industrial production, the lattice in triangular trusses should consist of a minimum number of elements. For this purpose, it is recommended to use four-panel (along the upper chord) trusses with two compressed braces and, correspondingly, one stretched or two compressed racks. Stretched racks are usually made of round steel.
When using timber trusses of larger spans, it is necessary to increase the number of panels of the upper chord to six and the lower chord to four, connecting the nodes of the upper and lower chords with a triangular lattice with a central stretched post
The solution of nodes in triangular trusses depends on the type of lattice adopted. For a four-panel truss with compressed braces and a central stretched post, the abutment of the compressed braces to the upper and lower chords can be made by resting on special metal shoes directly into the upper chord with appropriate trimming or on node bolts with a metal liner) similarly to the previously discussed trusses. Triangular trusses are also used for suspended ceilings.
In addition to the described solutions with one or another type of metal shoe, the support unit can have a different design, where the wooden element of the upper chord with a sawn horizontal plane receives the support reaction, and the vertical plane - the force from the lower chord with the help of a washer and nut.
In addition to trusses with a metal bottom chord (the main solution), in some cases trusses with a wooden bottom chord can be used, made in the form of a glued bag in glued trusses or from timber in timber trusses. The use of wooden belts from beams requires careful selection of timber. The selection should be made from sufficiently large quantities of timber by experienced graders.
| Rice. VI1.10. Details of the triangular beam truss TsNIISK. with support of the braces in metal shoes and with a lower belt that folds during transportation |
Calculation of trusses
The calculated normal forces in the elements of triangular trusses are determined in the usual way. A distinctive feature of triangular trusses is that when half of the span is loaded with a temporary load, the lattice on the unloaded half does not work. Therefore, the calculated forces in all elements of the trusses are obtained with a snow load over the entire span. One-sided loading with snow may be necessary in the case when it is necessary to calculate the connection of the cushion in the middle node of the lower belt to the belt itself. It is calculated on the difference in forces in adjacent panels of the lower chord, which occurs under one-sided snow load.
Upper belt.
In most cases, the panels of the upper chord, in addition to normal forces, are subject to bending due to internodal load and are designed as compressed-bending rods. The normal force in the upper chord, as in the considered trusses, is applied with eccentricity e.
If the upper chord is split, then the calculated moment in the panel
M = M0 - Ne,
where Mo is the moment of a simple beam from a given load at the middle of the panel span; Ne is the inverse moment of the normal force applied with eccentricity.
If the upper chord is continuous, then the calculation is made under two assumptions: a) the middle support has no subsidence and the upper chord works as a two-span continuous beam; b) the middle support sank by such an amount that the moment on it became zero and, therefore, the upper chord acts as a split beam with a span equal to the length of the panel.
Bottom belt.
The metal lower belt is calculated for tension, taking into account existing weaknesses in nodes or joints. Local lateral loads, for example from a suspended ceiling, causing bending moments in the lower chord, are unacceptable.
The wooden bottom chord is calculated for tensile strength over the net area at joints or nodes, where weakening from dowels is taken into account.
The joints of the wooden block bottom belt are covered with two overlays, usually wooden, the width of which is equal to the width of the belt, and the thickness is half the thickness of the belt. The wooden lower belt is connected to the metal support unit, as indicated, with strip steel plates on blind dowels. At this point, the wooden belt and metal linings are checked for tensile strength.
Lattice. The calculation of lattice elements - braces and posts in triangular trusses is no different from their calculation in the previously considered types of trusses: compressed lattice elements are calculated for longitudinal bending, stretched ones are checked for tension, taking into account existing weakening.
Farm nodes. The calculation of the nodes of triangular trusses is related to their design. In a glued truss with a split top chord and metal node liners, the design of the top chord nodes is similar to the design of similar nodes in segment trusses /
In a glued truss with the braces resting on the upper chord, it is necessary to check the wood collapse in the support and ridge units, as well as at the place where the brace rests on the upper chord and on the cushion of the middle node of the lower chord. In all cases, the calculated crushing resistance is taken taking into account the angle between the compressive silicone and the direction of the fibers of the crushed element.
In a cobblestone truss (see Fig. VII.10), in addition, it is necessary to calculate the connection to the upper chord of the metal shoe against which the brace rests. The dowels (or nails) connecting the shoe to the upper belt rely on the force tending to move the shoe along the belt. This force is the component of the forces in the brace in the direction of the upper chord or, what is the same, the difference in forces in the support and ridge panels of the upper chord. Dowels or nails work according to a single-cut connection scheme.
In modern construction, the following are used in the coatings of industrial buildings (Fig. 9.2...9.5):
— metal-wood trusses of MDF type (series 1.863-2, issue 1, 2);
— braceless trusses (metal-wood arches type AMD, series 1.860-6, issue 1);
— segmental metal-wood trusses (series 1.263-1, issue 1.2);
— plank triangular trusses with plywood overlays at the nodes (see Fig. 9.11);
— plank trusses with node connections on MZP of the “Gang Nail” type (“Gang Nail”).
Farm classification:
- according to the design scheme, they are distinguished: beam trusses (main type) and spacer trusses - arched (see Fig. 9.6);
- according to the outline of the upper chord: triangular trusses, trusses with parallel chords, trapezoidal, polygonal, segmental (see Fig. 9.1).
— by material: solid wood (roundwood, beams, boards), laminated wood, metal-wood, trusses made of plywood pipes, fiberglass-wood trusses;
- by type of nodal connections: on frontal notches, on steel cylindrical dowels, on cleestal washers, on toothed tenons on glue, on modern types of connections such as “Gream”, “Gang-Nail” (see Fig. 4.2, a, b) .
Design Basics
Wooden trusses are generally used in statically determined systems, both in terms of support fixtures and lattice design. The load-bearing capacity of statically determined trusses depends on the strength and stability of any rod, the destruction of which can cause loss of stability and destruction of the entire structure; as a result, increased demands are placed on the quality of materials for the manufacture of trusses. Farms are designed with the minimum possible number of nodes. The following types of trusses are used in modern construction:
- trapezoidal and segmental - for roll roofing;
- triangular - for roofing made of corrugated asbestos-cement sheets, steel, tiled and other similar roofs with slopes of 1/3, 1/4.
The spans of the trusses are: 9...21 m (45 m) - for triangular and 12...30 m - for segmental trusses. The pitch of plank trusses in low-rise housing construction is set from 0.5 to 2 m, the pitch of timber and metal-wood trusses in building roofs is from 2 to 6 m.
Rice. 9.1. Wooden trusses:
a - paving stones on the front cuts; b - plank on the MZP of the “Gang-Nail” type; c - metal-wood type MDF; d - braceless truss (metal-wood arch type AMD); d - paving stones with an upper chord from Derevyagin beams; e - trapezoidal pavement; g - segmental metal-wood with glued top chord; z - segmental plank
| Rice. 9.2. Metal and wooden triangular truss with glued top chord: a - load application diagram; b - general view of the truss type MDF 21-12 (Series 1.863-2, issue 2), for a design load of 12 kN/m |
The most common types of trusses by design
Most often, metal rafter systems are used as the roof frame of buildings and small architectural forms:
- triangular;
- arched
When constructing buildings, gazebos and sheds, in most cases the first type of truss from angle and pipe is installed. Such structures can be welded for both single-pitch and gable roofs.
Arched trusses are more difficult to install and are more expensive. To assemble them in a private household, among other things, you will have to purchase equipment such as a pipe bender. The main advantage of such trusses, in comparison with triangular ones, is their aesthetic appeal. In private households, such structures are most often installed when assembling canopies and canopies of attractive architecture and design, forged and carved, coated with polycarbonate, flexible tiles, and shingles.
Main types of farms
There are only 2 types of reinforced concrete frame structures:
- rafters;
- rafters
The design and construction of such elements must be carried out with the highest precision. If the frame collapses, the entire building will collapse.
Return to contents
Rafter structures
They can be made from the following list of materials: reinforced concrete, wood (timber), metal. The most popular are beams made of metal and wood. Reinforced concrete structures are made only in cases where no other material can provide the necessary protection and stability.
For wooden structures, the area on which the object will be placed is important. To prevent the structure from collapsing under its own weight, you need to correctly calculate the area and stability of the trusses. It should be noted that wooden trusses are difficult to securely secure (it is better to seek the help of specialists rather than secure them yourself).
Reinforced concrete beams are considered the most durable and reliable compared to previous ones. They are used quite rarely (due to their heavy weight). Most often they are used in one-story buildings in places with a fairly large area and a specific climate.
Return to contents
Rafter structures
This type of structure is used less frequently. Most often for the construction of attics and in cases where the size of the columns is larger than the size of the supporting structures. The basis of such trusses: a rafter beam about 12 meters long (its maximum length is 24 meters).
The reinforcement of the rafter beams has a beam shape. This reduces the weight and increases the reliability of the structure. They are installed on columns (rafter type) and connected with the necessary tools. For structures made of reinforced concrete or metal, additional welding should be used.
Such structures are used in cases where the building has transverse load-bearing walls (inside the building), or when both walls are transverse. Rafter beams are the only ones suitable for the construction of mansard roofs. To do this, you should insert racks directly under your feet (columns). The structure will put more force on the structure. At the same time, it remains reliable and stable.
Return to contents
What other types can be mounted
When constructing small architectural forms and small buildings, arched or triangular trusses are usually assembled from a single corner. When constructing large buildings, structures of this type can also be installed:
- with parallel belt (rectangular) - the most economical option, mounted from identical elements;
- polygonal - an analogue of a sloping gable roof;
- trapezoidal;
- segmental - similar in shape to arched ones, but at the same time having a more complex structure.
Shed corner trusses always have a triangular shape.
Types of gratings
Part of the truss structures located between the upper and lower chords, in turn, can be:
- triangular - the struts are connected to each other without racks;
- triangular with additional racks - vertical elements are mounted near each strut;
- cross - in the front plane it resembles a row of rectangles with diagonal struts;
- with ascending or descending braces;
- truss of complex shape;
- cross, in the front plane representing a series of diamonds, assembled without the use of racks;
- rhombic, similar to cross, but mounted with racks;
- semi-diagonal (herringbone lying on its side).
How to create a project
Before starting to independently assemble a truss from paired angles, single angles or pipes, you should decide:
- with roof configuration;
- slope angle.
The number of metal truss slopes may vary. Using such structures, it is also possible to build multi-gable complex roofs. However, in private farms, most often when constructing small architectural forms, single- or double-slope trusses are installed. Such designs are easy to assemble and at the same time reliable.
The angle of inclination of roof slopes with a metal truss is determined depending on wind and snow loads and some other factors. It is difficult to independently calculate this parameter for steel rafter systems according to all the rules, unlike wooden ones, without special knowledge. Therefore, in most cases, owners of suburban areas simply find a standard formula for a farm of one design or another. Next, the necessary indicators are substituted into it.
Scope of application of different types of trusses
- If the roof is planned to be built with a low slope, the best option would be to use non-braced trusses, in the upper chord of which additional racks are installed. Most often, such buildings are equipped with a large number of communication systems. The step for them is 6 or 12 m.
- When the building is single-span and its heating is not planned, the ideal option would be to use unbraced structures.
- Pitched roofs are equipped with a segmental non-slanted or slanted frame.
When covering one-story buildings with one or several spans with rolled materials, it is best to use standard reinforced concrete products.
There are currently many such options; let’s look at their designations:
- FS - diagonal products used on pitched roofs;
- FBS is a non-braced type of trusses used for pitched roofs;
- FP - products used as a slab covering, the length of which is similar to the span length;
- FPM - used on low-slope roofs without prestressing;
- FPN – for roofs with a low slope and prestressed posts;
- FBM – non-sloping products used on low-slope pitched roofs;
- FPS - found on pitched roofs;
- FT – trusses of a braceless type with a triangular outline.
Installation considerations
Before installing such structures, it is necessary to calculate the load-bearing capacity of the building as accurately as possible. Fastening is carried out to embedded parts located on the load-bearing wall or column.
Advice: you should not start installation without making sure that the quality of the elements, as well as their sizes, are fully consistent.
In addition, you will need the services of a welder who will need to connect the embedded parts and supports. Metal purlins are also welded to the former, thanks to which the optimal value of the longitudinal rigidity of the frame is achieved.
Depending on the shape, a reinforced concrete truss can be:
- Segmental.
- Arched diagonal.
- Arched, unbraced.
- Polygonal.
The entire process of manufacturing such structures is carried out in accordance with GOST for concrete or reinforced concrete structures.
The main characteristics are:
- the strength of the concrete used;
- its density;
- reaction to exposure to low temperatures;
- diameter of the layer enveloping the reinforcement;
- steel used for reinforcement and its grade;
- reaction to corrosion.
Despite the high levels of strength and reliability, such structures can rarely be found in private homes. This is explained by the complexity of installation and the significant mass of the resulting roof. But most often these concrete products can be seen on buildings whose span exceeds 18 m, and the pitch is in the range of 6-12 m.
If the span is less than 18 m, it will be more profitable to use beams, however, if there are a large number of communications located inside the frame, it is best to opt for reinforced concrete. But when developing buildings whose spans exceed 30 m, it is necessary to take into account the total weight of the roof, which will be significant. Therefore, it would be rational to split them into separate blocks, however, the price of the work increases significantly.
If we look from the point of view of the price/quality ratio, then the most optimal options will be segment or arched. On such trusses, there is practically no change in the forces on the chords, while the height of their support is small, as a result of which the total weight of the structure is minimized, as well as the height of the walls.
Examples of formulas
To calculate a truss made of paired or single angles, you must first determine the height and length of the structure. The latter indicator will correspond to the distance that the structure will cover during operation (the width of the building plus overhangs).
The optimal height of the truss can be determined using the following formulas:
- for polygonal, parallel and trapezoidal - H = 1/8 * L;
- for triangular ones - 1/4 * L or 1/5 * L.
Here H is the height of the truss, L is its length. The struts in the lattice of metal roof frames can be installed at an angle from 35° to 50°. In this case, a value of 45° is considered optimal. When using struts mounted in this way, the supporting structure is the most durable.
Manufacturing of reinforced concrete trusses
The simplest production process is for the arched braceless type, the nodes of which are reinforced very simply. All the resulting internal space can be filled with bends for various communication systems. Most often used when installing low-slope, flat or pitched roofs.
To produce such a material, concrete grade B30-B60 is used, which has high strength characteristics. Its lower belt can be made up of reinforcing ropes, high-strength wire or rod reinforcement.
In addition, lightweight wire frames are used, which prevent the formation of cracks during operation. To make the lower belt easier to crimp, it is recommended to use frame lengths less than three meters.
But to reinforce the elements of the lattice and the upper chord, welded reinforcement cages are used, which are installed in twos in support units. As a result, the strength of the frame along inclined sections increases. A set of transverse 6-10 mm rods, the pitch of which is 100 mm, makes up a welded frame used to reinforce the intermediate nodes of both chords.
To transport ready-made structures, specially equipped equipment is used, for example, the FKP-16 farm truck. Due to the growing demand for lightweight steel structures, the demand for precast concrete products is falling. However, according to fire safety requirements, reinforced concrete trusses are the best.
Calculation of a truss from the corners of an arched
In such structures, the required length of metal products for the lower chord is determined using the following formula:
- mh=pi×R×a×180, where mh is the length of the corner, pi=3.14, R is the radius of the circle, a is the angle between the radii of the circle drawn to the extreme points of the lower belt.
If the span length in a small architectural form is less than 6 meters, instead of a complex truss, it is permissible to use simply a single or double beam, bent to a selected radius. In this case, to assemble the supporting structure of the roof, it is usually not a corner, but a profile pipe that is used.
After completing the calculations when drawing up a roofing project, it is necessary to make a drawing indicating the dimensions of all elements, their angles of inclination, etc. According to this scheme, a truss is subsequently assembled from paired corners or simpler structures.
Calculation of an arched truss from a profile pipe
Let's consider a specific example of calculation for an arched canopy. The parameters of the proposed structure will be as follows: the trusses are located in increments of 1.05 m, the loads will be concentrated in the nodal areas. The height of the arch in our case should not exceed 3 meters. The recommended height of the truss will be 1.5 m - this parameter is considered more attractive both from an aesthetic point of view and for reasons of strength. A span of 6 m (L) is taken between the supports, the lower level boom is 1.3 m (f). The circle in the lower tier will have a radius of 4.1 m (r). The angle between the radii will be α=105.9776°.
The length of the profile from the bottom chord is calculated by the formula:
mн = π*Ra/180.
In it: mн – the size of the profile of the lower belt; R – radius of the circle; A – angle between radii; π – constant.
Eventually:
mn = 3.14 x 4.1 x 106 / 180 = 7.58 (m).
The step between the structural units in the sections of the lower chord should be 55.1 cm, while the steps between the outer sections are calculated individually. To simplify installation, the figure can be rounded to 55 cm, but you should not increase the pitch.
Calculation of a canopy of small dimensions allows for a number of spans in the region of 8-16. For the minimum number, the length of the rods will be 95.1 cm with a step between the belts in the region of 87-90 cm. For the maximum number of spans, the step will be 40-45 cm.
Installation rules
When assembling metal roof trusses with your own hands, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- It is better to make supporting vertical columns of large metal structures (sheds, buildings) not from a single corner, but from a profile pipe. This type of metal is more durable. It is advisable to make the trusses themselves from the same material. From the corners in such structures you can make a frame and braces.
- The truss structural elements must be fastened together using tacks and paired corners.
- In the upper chord, the parts should be joined using I-angles.
- In the lower belt, equilateral corners are used in mates.
- To join the main parts of the truss that are long, overhead thick steel plates should be used.
In order to eliminate the possibility of sagging of the belts, the roof is mounted on a metal truss so that its weight falls on the nodes of the truss from the corners.
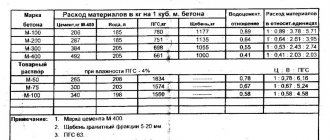
Reinforced concrete rafters
Reinforced concrete rafters are made with stressed reinforcement (wire, rope, rod, stretched over the stand stops) of the lower chord. Manufacturing is carried out on broaching stands, in multi-tier stand-chambers and in single-tier power forms and stand-chambers. Labor costs are about 10.4 people/hour to produce a cubic meter of trusses with a span of 18 m. Racks and braces are produced in cassette molds. The finished racks and braces are placed in a form for reinforcement. The lower chords are reinforced with string packages made of high-strength wire with a diameter of 5 mm. The upper chords are subject to reinforcement with conventional rods. The string packages are tensioned using hydraulic jacks. The concrete is placed using a concrete paver. A couple of hours after concreting, the products are heat treated. Stand turnover occurs within 2 days. In this way, it is possible to produce up to 8 trusses per day. The weight of a structure with a span of 18 m is from 6 to 7.5 tons, with a span of 24 m - from 11 to 12.3 tons.
Assembly order
The first step when installing metal rafter systems yourself, of course, is cutting out the corner and other metal products, according to the drawing. Further:
- assemble the truss structure on the ground;
- carefully check its geometry using a square and level;
- weld the assembled frame using overlay plates and corners where necessary.
The procedure for assembling a farm on the ground usually looks like this:
- longitudinal pipes or angles are laid (for paired trusses, the brands are first welded);
- weld the racks;
- Weld the braces and jumpers.
At the final stage of truss assembly, the quality of the welds is also checked. The design, of course, should be as reliable as possible.
After the first truss is ready, begin assembling the next one. In this way, all supporting elements of the rafter system of the structure are welded.
Frame assembly
At the next stage, the trusses prepared in this way are lifted onto the racks or box of the building. The upper frame of the structure and support beams are pre-assembled from a corner or pipe. The trusses are welded and then connected to each other with a ridge element and intermediate jumpers. The latter are usually mounted at a distance of at least 1.5 m from each other.
At the final stage, all truss structures made from a metal angle or pipe are sanded, coated with a primer and painted. After this, they begin to actually sheath the roof.
Requirements depending on the angle of inclination
All metal trusses used for the construction of roofs are divided into three categories:
- with slope angle from 6 to 15°;
- from 15 to 22°;
- from 22 to 33°.
It is believed that it is advisable to install roofs of the first type using trapezoidal trusses with a height of 1/7 to 1/9 of the span. If the construction does not intend to hem the ceiling in the future, the braces in such a structure are installed in the form of a triangular lattice.
To assemble roofs with a slope angle from 15 to 22°, trusses with a height of 1/7 of the span are usually used. This allows you to mount the most reliable structure. If a greater height is required (0.16-0.23 parts of the span length), the lower chord is made broken. Using this method, the weight of the frame can be reduced by 30%.
Installing trusses from steel angles with a broken bottom chord is allowed only on structures with a span length of no more than 20 m. Otherwise, it is necessary to install Polonso structures.
For trusses with a slope angle of 22-30°, a height of 1/5 of the span length is usually chosen. In this case, the structure will be optimally light and rain and snow will quickly drain from it. Triangular trusses made from corners are usually mounted on such buildings.
Roofs with such slope angles are covered in most cases with slate or metal sheets. For long spans from 14 m, trusses with downward braces are most often used. Such structures can withstand significant snow and wind loads well.
List of types of trusses made of profile pipes
Metal trusses from a profile pipe for a canopy are constructed from a profile, most often steel. The profile can have different cross-sectional shapes: oval, square and the most popular - rectangular.
Types of trusses are divided into two categories: trusses, where all elements are attached to each other in one plane, and structures with a suspended structure (includes upper and lower chords).
Structures are divided according to the following criteria: required load on the profile, system slope, type of floor arrangement, span length and degree of inclination. Depending on these factors, farms can be like this:
1. Structures with a slope of 22-30 degrees. The stability requirements for trusses of this type state that their height should not exceed 1/5 of the entire length. Typically, the height is calculated according to this principle, dividing the planned length of the hangar by 5. This slope is chosen when they want to achieve relative lightness of the system.
If the length of the entire structure exceeds 14 meters, then the braces should be positioned from top to bottom. In this case, a panel 150-250 cm long is placed on the upper tier. Ultimately, the result is a structure with two belts, the number of panels will also be even.
The shape of the trusses and their number depend on the type and size of the structure, as well as on the expected load on its roof
Helpful advice! If you plan to build a farm with a span of more than 20 meters, it is necessary to install rafter elements, which will be supported by additional columns.
Another frequently used variety of this type will be the so-called Polonceau trusses - triangular-shaped structures with a tie-shaped connection. A truss made from a Polonso profile pipe is considered very lightweight, since during its construction it is possible to avoid overly long braces.
2. Trusses with a nominal roof slope of 15-22 degrees. This option is being considered for structures that will not ultimately have a span of more than 20 meters. Types of farms with such a slope have a height of 1/7 of the total length. If it is necessary to increase the height, the lower belt should be composed of broken segments.
3. Structures with the smallest slope, not exceeding 15 degrees. With a planned truss angle of up to 15 degrees, trapezoidal structures would be the best option. The height calculation is carried out based on individual considerations; it all depends on the specific angle of the roof and the purpose of the hangar. The height can range from 1/7 to 1/12 of the length.
For trapezoidal trusses, the optimal length of metal panels should be 1.5-2.5 m. If the drawing does not include a suspended ceiling, the braces can be replaced with a triangular lattice.
When it comes to the shape of the structure, profile pipe trusses are of the following type:
- single-pitched;
- gable;
- straight;
- arched
The last type - arched trusses - are the most common. They are quite durable and can be sheathed with polycarbonate sheets. The calculation of the canopy of an arched structure must be very accurate so that the weight is distributed along the profile as evenly as possible. Arched trusses are built both from ordinary profile pipes and from welded ones.
The arched type of trusses allows you to make a semicircular roof made of polycarbonate
Twin trusses
Such systems are often mounted on racks and boxes when the span length exceeds 10-12 m. A solid truss in this case will weigh a lot. And this, in turn, will cause difficulties with its transportation and installation on the box. Therefore, for wide spans, the system is first divided into two fragments, and then connected at the top by tightening and welding.
When designing and calculating paired trusses, one should, among other things, take into account the fact that both parts must be absolutely identical. That is, the halves should not be divided into left and right. Otherwise, when installing trusses on the building box, confusion may arise.
When assembling such double structures at the top, it is advisable to use as many bolted connections as possible, in addition to welding. In this case, the knots will be the most durable.
What are Polonso Farms?
Such structures consist of two triangular parts connected by a screed. The main advantage of such trusses is that there is no need to use long braces. Thanks to this, the design is not only durable, but also lightweight.
Such trusses, as already mentioned, are installed for long spans. Most often they are used in the construction of large industrial buildings.
Wood-metal trusses
In order to save money in the construction of buildings and small architectural forms, combined support structures can be used, among other things. For example, the lower tie of a truss, racks and tie rods are often made from a pipe and angle, and the upper chord is made from a board or timber.
Lumber for such structures is chosen that is well-dried and with a minimum number of knots. The moisture content of timber or boards should be no more than 12%. Before using it to assemble combined support structures, it is advisable to dry the lumber for an additional several months. Otherwise, due to shrinkage, the wood in the finished frame may subsequently crack (the metal will retain its dimensions).
To make such trusses more durable, they are usually reinforced. In most cases, a steel rod is used for this purpose. Wood-metal trusses can also be reinforced with fiberglass reinforcement. The rods are usually connected to wood using epoxy glue. In this case, the reinforcement is passed inside the upper chord (in glued structures).
Reinforced concrete trusses
Reinforced concrete trusses
Reinforced concrete trusses are ready-made load-bearing structures that can withstand heavy loads on coatings thanks to frame-connected rods. Reinforced concrete rods, forming the lower chord of the truss, run along the lower edge, and the upper ones, respectively, along the upper, creating the upper chord. The inclined segments of the truss are called splits, the vertical ones are called posts. The reinforced concrete lattice of the truss is formed by nodes - the junctions of the racks and braces.
The material for the manufacture of reinforced concrete trusses is structural heavy and light concrete, reinforced with prestressed steel reinforcement.
At BLOK LLC you can order reinforced concrete trusses of various lengths 6m, 9m, 12m, 18m and 24m, as well as consult with our specialists to select the required truss designs. In our sales department you can find out in advance to clarify the price of reinforced concrete trusses and calculate the total cost of the order. You can buy reinforced concrete trusses and consult on general issues of purchase and delivery by calling the BLOK company: St. Petersburg: (812) 309-22-09 , Moscow , Krasnodar . Company operating hours: Mon-Fri from 9-00 to 18-00. The BLOK company delivers reinforced concrete trusses throughout Russia directly to the customer’s site or to the construction site, if infrastructure allows.
The classification of reinforced concrete trusses provides for the production of trusses and trusses, which, in turn, are divided into types:
- FS - diagonal segmental, used for the construction of pitched roofs.
- FBS - non-slanted segmental, for buildings with pitched roofs.
- FP - under coverings made of slabs equal in span length.
- FPM – for low-slope roofing without prestressing.
- FPN – for low-slope roofs with prestressed posts.
- FBM - non-slanting for low-slope pitched roofs.
- FPS – for pitched.
- FT - non-slanting triangular shape for pitched.
Application of reinforced concrete trusses.
Reinforced concrete trusses, depending on the purpose of the structure, covering material, method of supporting them, etc. may have different types and shapes. The possibilities for their application are quite wide:
- Buildings can have spans of up to 24 m or more
- Roofing - be both low-slope and pitched
- The covering of buildings can be either with or without lanterns
Advantages of using reinforced concrete trusses.
- high strength
- high rigidity
- high crack and frost resistance, which allows them to be used in aggressive gaseous environments
- good fire-fighting properties.
Production of elements of load-bearing structures from reinforced concrete.
Reinforced concrete trusses are made from structural concrete, heavy or light, mainly expanded clay concrete and aggloporite concrete. Precast concrete trusses are manufactured in single- or multi-tier stand-chambers. On each of them, several metal forms with a steam jacket are usually installed. The braces and racks are located on the vibrating table in special cassette forms; they are laid during the reinforcement process.
For the lower chords of the truss, string packages made of high-strength wire (ø 5 mm) are used for reinforcement, and for the upper chords, ordinary rods are used. High-strength wire is tensioned with hydraulic jacks and concrete is added with concrete pavers. After 2–3 hours, the product undergoes heat treatment. The quality of prestressed concrete trusses is regularly checked by loading as specified in the design drawings.
Marking of reinforced concrete trusses.
Farms are labeled using alphanumeric designations separated by hyphens. Letters are used to indicate the type and size, and all other information is used in numbers, such as length in meters, load-bearing capacity of the truss, class of prestressing reinforcement, grade of concrete, etc. The letters also indicate the permeability of concrete, that is, the possibility of using the structure in aggressive conditions:
- N – normal
- P – reduced
- C – 8-point seismic resistance
Reinforced concrete truss structures
A reinforced concrete truss creates a strong frame that creates the contours of the roof and the features of the floors. The structure of the trusses, which give the frame strength, rigidity and stability, has a rather complex design, containing a significant amount of reinforced elements and steel. The functions of load-bearing platforms performed by trusses require such strength and reliability that the stability of the building is ensured in extreme conditions.
The use of special lightweight grades of concrete in the production of trusses can significantly reduce the weight of the structure without loss of quality. High-strength reinforcing steel included in the internal structure has exceptional anti-corrosion properties. Therefore, the roof of a building based on reinforced concrete trusses is invulnerable to moisture and frost.
The outline of the truss is formed by its two belts, which work on bending, and the lattice is formed by braces and racks, which work on axial forces. Segmental reinforced concrete trusses are sometimes replaced with polygonal ones, in which the elements of the upper chord are straightened within the basic nodes. This is much more economical than using triangular or rectangular outlines. The following types are distinguished:
- segmental - distinguished by an upper contour belt and a diagonal lattice;
- polygonal - the belts in them are either parallel, have a trapezoidal outline, that is, they are distinguished by a diagonal lattice and a small slope angle of the upper belt;
- arched, unbraced – have rigid nodes;
- diagonal arched - characterized by curvilinear outlines of the upper belt and a sparse lattice.