Requirements for a concrete base:
Strength
The surfaces to be coated must comply with SNiP 2.03.13-88 Floors and SNiP 3.04.01.87 Insulating and finishing materials. This means that the surface of the base must be dry, strong, rough, and free of lime (cement) laitance, dust, grease and other substances that reduce adhesion. The peeling strength of the prepared concrete base must be at least 1.5 N/sq.mm (1.5 MPa). When the concrete strength is below this value, there is a high risk of the coating peeling off along with the concrete. The compressive strength of the base must be at least 20 MPa (M 200).
Humidity
If the concrete base lies on the ground, then it is permissible to use polymer floor coverings only if there is high-quality waterproofing under the concrete base that prevents the base from moistening due to capillary suction of moisture. The humidity of the concrete floor when laying the polymer coating should be no more than 4%. Otherwise, capillary rise of groundwater can lead to detachment of the polymer from the concrete base and its destruction.
Temperature
When applying coatings, temperature and humidity conditions are of great importance. The temperature of use should not be lower than that specified in the technical documentation (usually not lower than +15°C). Too low a temperature slows down the rate of chemical reaction and impairs flow, which can lead to increased material consumption and deterioration in the appearance of the coating. Too high a temperature accelerates the curing reaction, reduces the life of the composition and does not allow obtaining a flawless coating surface. High relative air humidity (more than 80%) with a decrease in air temperature can lead to unwanted condensation of moisture on the applied coating.
Preparation of bases for floors
Tweet
The most important factor in installing self-leveling polymer floors is very high-quality preparation of the base
.
Violation of technological regulations and failure to comply with surface preparation requirements can lead to peeling and swelling of the polymer layer. In approximately 90% of cases, the cause of destruction or peeling of polymer coatings can be attributed to improper preparation of the base. Self-leveling and polymer floors must be applied over any building materials: concrete tiles, metal, concrete, sand concrete, plywood, wood, etc.
Cement-sand screed and concrete floor
Such bases are porous and have good absorbency, which is why they require significant surface hardening and clogging of pores. The concrete base must be cured for 28 days, polymer-cement and cement-sand screeds must be cured until they gain strength, as well as until they dry, when the humidity is no more than 4%.
Before applying the material, the surface must be cleaned using an industrial vacuum cleaner; if there is water, it must be carefully removed from the pores, and then the base must be dried. Mandatory for porous bases is the stage of strengthening the base with the help of strengthening impregnations.
Freshly applied and wet concrete
The application of polymeric materials to various wet substrates is extremely undesirable, especially when the volume of the substrate contains water, as this can lead to blocking of water in the substrate. For priming substrates that have high humidity, Aquastone concrete sealer is used.
Before applying the topcoat, it is necessary to carry out a test application and make sure that the moisture of the base does not affect the quality of the coating.
Floors made from magnesite and anhydrite
Surfaces must be hard and clean. They should not contain fat or oil. If there are alkalis and efflorescence of magnesium chloride on the surface, they must be removed by an acceptable method (mechanically, with hot steam or water).
Coverings made from ceramic tiles
Old tile coverings are washed very thoroughly and then degreased using an organic solvent. The polyurethane primer PS-Grunt should be applied to the surface of the tiles in 1 or 2 layers, depending on the absorbency of the tile joints and the evenness of the floor. The tile must be firmly glued to the base. “Playing”, poorly attached tiles must be removed, and their seats must be well puttied and treated with PS-Grunt primer.
The presence of fats, oils and other contaminants that reduce adhesion in the coating is not allowed. If there are difficult-to-remove contaminants on the surface, a test application should be carried out.
Wooden bases
All wooden surfaces must be seasoned (humidity - 10-8%), dry, clean, free of grease and oil. Before application, you need to roughen the surface - sand and sand it. The surface treated in this way does not require priming.
Old polymer coatings
Very often there is a need to update old polymer floors. Before applying a new polymer, the old coating must be sanded with sandpaper or an abrasive disc. The choice of polymer coating usually depends on the requirements for chemical and mechanical resistance, as well as the influence of temperature, etc.
Requirements for a foundation made of concrete:
Strength of the subfloor
It should be noted that the compressive strength of the foundations must be at least 20 MPa (M 200), and the tensile strength of the concrete foundation must be at least 1.5 N/mm2. If the concrete strength is equal to or lower than this value, peeling of the concrete coating is possible.
Evenness of the
floor
Typically, polymer materials are self-flowing, which is why the surface of the floor must be very flat, without noticeable slopes (to avoid the materials flowing down).
Subfloor moisture
If the concrete base is on the ground, then polymer floor coverings are allowed if there is high-quality waterproofing under the concrete base. Waterproofing prevents the base from getting wet due to capillary suction of moisture. The humidity of concrete floors during installation of the polymer coating should be no more than 4%. Otherwise, capillary rise of groundwater will lead to detachment of the polymer from the base and its subsequent destruction.
Subfloor temperature
Temperature and humidity conditions are also of great importance when applying coatings. The main thing is that the temperature of use must be higher than the temperature indicated in the technical certificate (usually the norm is not lower than 15%). Very low temperatures can slow down the rate of chemical reaction and impair spreading.
Subfloor surface treatment
It is necessary to remove all factors that prevent the adhesion of the polymer to concrete. It is necessary to remove cement laitance, various contaminants, and oil stains; clean the surface from dust; repair potholes and chips; rub, embroider cracks; draw up the slopes required by the project and expansion joints.
Other useful articles:
Concrete floor repair
Preparing the concrete surface
It is necessary to remove all factors that prevent good adhesion of the polymer to concrete. Cement laitance, oil stains, dirt should be removed, the surface should be cleaned of dust, chips and potholes should be repaired, cracks should be opened and repaired, and the slopes and expansion joints required by the project should be completed.
The most effective methods of surface treatment are: sandblasting, shot blasting, and the use of mosaic grinding machines. After cleaning the surface, it must be treated with an industrial vacuum cleaner.
Strengthening the concrete surface
Concrete substrates are porous and highly absorbent, so they require plugging the pores and strengthening the surface. Therefore, it is mandatory to strengthen the base with the help of strengthening impregnations - concrete hardeners. It is this stage of base preparation that determines the quality of the resulting coating. It is impossible to obtain a high-quality coating (free from air bubbles) without completely closing the pores of the base.
“DSS” is an organic-based impregnation for concrete floors. It is used on old worn or new coatings using low-quality concrete. Particularly recommended for the rapid restoration of old concrete floors.
“PU-Grunt” is a primer for cement screed. Used on concrete of a grade not lower than M200.
“ET-AK” is a two-component water-based epoxy impregnation varnish. Intended for protection, strengthening and dust removal of cement screeds, concrete, asphalt concrete and magnesium floors.
All concrete hardeners have high adhesion, which allows them to be used as a primer for applying subsequent coatings.
Protecting Concrete Warehouse Floors
Concrete floors are often criticized due to their poor resistance to moisture and chemicals. Today, there are two methods for solving this problem: the initial selection of high-quality concrete and the subsequent strengthening of its top layer.
The following compounds can be used to protect concrete floors in warehouses:
- dust-removing, strengthening impregnations;
- dry strengthening mixtures (topping);
- polymer paint coatings;
- polymer highly filled self-leveling floors.
Polymer coatings for warehouse floors
The choice of polymer coating depends on the operating conditions of the floor in a particular warehouse. Most often, polyurethane compounds are used to protect floors in warehouses, which have excellent wear resistance. Polyurethane impregnation penetrates concrete to a depth of 2-6 mm, forming a concrete polymer in the top layer of the base. This increases the density of the floor and also seals it. Polyurethane self-leveling flooring has high tensile and compressive strength. It has high impact resistance and can withstand very high mechanical loads. In modern warehouses, self-leveling floors made using the two-component polyurethane material Polymerstone-2 have proven themselves to be excellent.
Self-leveling polymer floors are recommended for use in food industry warehouses , as they provide additional safety and hygiene for food storage. Such floors are also indispensable in warehouses for chemical products, as they are characterized by increased safety.
Instead of a self-leveling floor, epoxy or polyurethane based impregnation can be used. If a more budget-friendly option is preferable, then the floor can be painted with polyurethane enamel, for example, Polymerstone-1. It will give the flooring elasticity, as well as resistance to abrasion and various deformations. The undeniable advantage of paints for concrete floors is their low cost.
Concrete paints primarily perform protective functions. They prevent the penetration of water into the pores of concrete, reduce abrasion, and reduce the crumbling of the floor under the influence of physical activity. Floors in warehouses do not need spectacular decoration. For them, the main thing is not beauty, but protection. Although sometimes they are painted in bright colors to highlight work areas or areas for finished products.
Concrete paints in some cases can be applied directly to floors, but they must be dry and free of dust and dirt. However, paints will adhere much better and retain their properties if applied to prepared surfaces (cleaned and primed). For these purposes, special polymer primers and impregnations are used.
The maintenance-free operation time of any polymer coating depends to a large extent on the preparation of the surface of the concrete base. The adhesion of the polymer and concrete depends on the degree of roughness of this surface. Reliable adhesion of the polymer coating to the concrete base can be ensured by shot blasting the concrete or grinding with an abrasive tool.
Shot blasting or grinding concrete allows you to achieve a uniform surface roughness. With the help of these operations, the adhesion area of concrete and polymer is greatly increased, the layer of cement laitance is removed and the filler grains are exposed.
The technology for applying highly filled coatings consists of the following operations:
- processing of the concrete base by grinding or shot blasting (providing the necessary roughness, removing laitance);
- filling cracks and filling them with sealant;
- applying a low-viscosity primer in order to create the required degree of adhesion of the polymer coating to the concrete base;
- applying the main high-fill coating layer over an uncured primer;
- processing the hardened coating layer using a mosaic grinder;
- cleaning the floor surface from dust using a construction vacuum cleaner;
- application of colored protective and decorative coating;
- cutting expansion joints and filling them with polyurethane sealant.
This coating can be used 2-3 days after installation is completed. Pedestrian traffic is allowed every other day.
More details about the technology of installing concrete floors in a warehouse are described in the article Technology of installing warehouse concrete floors
Wet and freshly applied concrete
In any case, applying polymer compounds to wet substrates (especially when there is water content in the volume of the substrate) is extremely undesirable, since this will lead to blocking of water in the substrate.
For priming substrates with high humidity, epoxy impregnation-varnish “ET-AK” should be used.
For the finishing coating it is possible to use ET-2M or AQUABET epoxy paint, which is optimally suited for application to wet and freshly applied concrete.
Before applying the topcoat, be sure to conduct a test application of the material and make sure that the moisture of the base does not affect the quality of the topcoat.
General provisions
Concrete preparation for floors serves, like a cement screed, to level the floor surface. The difference is that it is made of concrete, and cement screed is made of mortar. In addition, there is a difference in strength characteristics, since the concrete base absorbs and redistributes large loads, depending on the purpose of the room.
There is a concept of “concrete floor”. Concrete preparation and concrete floor are very similar concepts. They are made of concrete using similar technology. The difference is that concrete preparation for floors implies the presence of a finishing coating (mosaic, ceramic tiles, etc.), but a concrete floor does not provide this.
Concrete preparation for floors is carried out on a soil base (in basements, when installing floors in private houses without a basement, etc.). If concrete preparation is carried out in workshops with increased load on the floor from equipment, intra-shop transport, in warehouses, garages, etc., then it must be reinforced.
Which self-leveling floor to choose?
The most important thing in the installation of self-leveling floors is the correct determination of the requirements for floors and the resulting correct choice of self-leveling floor.
The ProfiPol Group company offers you all the necessary materials to make self-leveling floors. The materials offered for the installation of self-leveling floors (polyurethane floors, epoxy floors) can satisfy any operational requirements. Sections of our website will help you choose a self-leveling floor, where detailed information about self-leveling floors is provided (how to make a self-leveling floor with your own hands, a description of floor installation technology, choosing a self-leveling floor, etc.). We ask you to call or write to us. The specialists of the ProfiPol Group Company will help you choose a self-leveling floor covering based on your technological specifications and will always advise you on the design and choice of coating. Attention!!! We do not carry out work in apartments and residential premises!!! Work in existing production facilities and warehouses by appointment only!!! Order work on floor installation tel. 8-495-227-78-10
to full list of articles
Main types
Each method of creating preparation has its pros and cons. There are four of them in total:
- concrete;
- crushed stone or gravel;
- membrane;
- sandy.
Crushed stone and sand
After completing the excavation work, backfill is made using inert components and compacted. The cushion of crushed stone, sand and gravel should have a thickness of 20-60 cm. If groundwater is located close, then the bottom of the pit is covered with geotextiles.
The first layer is coarse-grained fractions, which create drainage, and then a layer of medium grinding is laid. Sand is poured in last. The separation of layers makes it possible to increase the strength and rigidity of the foundation. Sand is used to apply uniform load to the lower layers.
There are some requirements for the quality of fine-grained filler:
- sand should contain granules of 2−2.5 mm; crushed gravel, which is light in weight and has good water permeability, is most suitable;
- impurities from limestone, clay and salts are contained in minimal quantities;
- there are no organic residues that contribute to a decrease in water permeability and the formation of silt in the sand.
A backfill of gravel, crushed stone based on limestone or granite is created under the foundation. The strength of the materials should be marked M800, and the fractional value should be 20−70 mm. After each 50 mm layer, compaction is carried out using a manual compactor or vibrating plate. The sandy surface is pre-moistened.
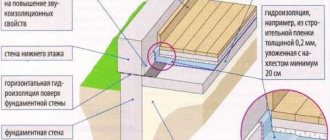
Concrete preparation
A cushion is formed under the foundation blocks and slabs using two technologies. In the first case, a layer of crushed stone is filled with a liquid solution of bitumen, in the second, a layer of 10 cm is created from cheap types of concrete M50-M100.
Preparation of the base for concreting is carried out:
- placing the formwork around the perimeter and forming the footing;
- pouring a pit without constructing formwork;
- sequentially lean and high-quality concrete is laid into the blank for the foundation.
The composition is leveled along the beacons, and it is compacted using a vibrating plate. The surface of the concrete base is protected from moisture by roll materials, films and bitumen.
Using a geomembrane
Polymer membranes have become a new element for preparing the base. Fiber helps protect buildings from moisture in the soil. The studded profile further strengthens the soil. Thanks to geomembranes, cracks from shrinkage are less likely to appear, and the load is distributed evenly over the entire base. The spaces between the concrete and the insulating material act as ventilation.
The preparation of crushed stone and sand is covered with geotextile, and a layer of fiber is laid on top. The seams of the membrane are connected by welding. This material can last a long time, withstanding temperature changes.