Strip foundation design
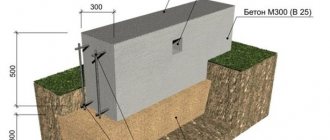
Purely structurally, a strip foundation is a strip (hence, in principle, the name), which is constructed under all the walls of the building. This is a continuous structure laid in the ground, for which formwork is erected for it, installed in a previously dug trench.
Strip foundation
Advantages of a strip foundation:
- high load-bearing capacity;
- ease of construction;
- high construction speed.
The design also has its drawbacks:
- the heavy weight of the structure, which can cause uneven shrinkage, so it is very important to first conduct a soil study and determine the level of groundwater;
- after pouring, you will have to wait 28 days for the concrete to gain its original strength, after which the foundation can be loaded.
Calculation of the number of reinforcement bars
At this stage, calculations are performed to determine the required amount of material. If the structure is 3 meters long, a rod with a diameter of 6 mm or more will do. For the frame, 4 rods are taken (2 working rods each, located in different places).
If the height of the strip foundation is 80 cm, transverse rods are chosen with a diameter of 3 mm or more. For numbers 80 cm or more - from 8 mm. The rods should protrude 2.5 cm from each part of the structure. This is necessary for fastening, a protective layer of concrete for working rods when performing concrete pouring work. To protect the concrete layer, builders use plastic clamps. They are convenient to work with. The use of such elements makes it possible to strengthen the structure. Information about the types and characteristics of such clamps can be found in specialized sources.
The rods are laid at intervals of 30–60 cm, across, based on the dimensions of the strip foundation. If the house is wooden, the foundation is not installed deeply, an acceptable step is 60 cm. For large buildings it is made small. Such a calculation is necessary to prevent the reinforcement used from spreading due to the pressure of the mass of concrete being poured. All rods that are used in construction work are connected with a special wire, it is called wire rod or knitting wire. Welding is also suitable for this purpose. It should be borne in mind that this method is important in construction on an industrial scale. Owners of low-rise buildings can use this fact at their own discretion or according to the recommendations of the masters.
Knowing the required cross-section of the reinforcement bars, their required number is calculated. This is easier to do after receiving the necessary information on the choice of material. Incorrect calculations can lead to significant overpayments, especially when it comes to large-scale procurement for large projects. Formula for calculating the number of rods: the number of rods along the frame is multiplied by the perimeter of the foundation along the strip. For a structural solution, multiply the total number of vertical and transverse rods along the length by the length of the perimeter. Then the number is divided by the pitch of the rods and 1 is added.
Important! When performing any calculations, pay attention to the units of measurement. They should be the same. A significant failure may occur when using meters, centimeters, etc. at the same time.
Some retail outlets sell material not in piece count, but in mass equivalent. Based on this, GOST tables are used, which have a column corresponding to the weight per meter of the product according to the diameter. Practical data indicate the need for a reserve (about 20%). Such a solution can prevent significant overpayments, and if there is a shortage of material, there will be no need to purchase it in addition. If errors were made in the calculations or changes in design solutions are required, this will cover a certain spare number of products. The necessary products are not always available for sale. If the required length of the rods is not available, they are extended by overlapping joints (additional 15 cm).
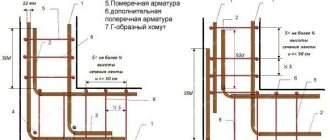
Reinforcing frame design
Purely structurally, a reinforced frame for a strip foundation is a three-dimensional structure of two or more gratings, which are installed vertically at a certain distance from each other and fastened together by crossbars made of the same reinforcement. The dimensions of the foundation are calculated taking into account the loads that the building puts on the foundation. And since it is the reinforcing frame that is the main one for containing loads, it is necessary to calculate it too.
Reinforcing frame design
Reinforcement consumption
On four external walls.
Reinforcing bars d = 16 mm – 11060 x 3 x 4 = 132720 mm (133 m).
Reinforcing bars d = 14 mm – 11060 x 7 x 4 = 309680 mm (310 m).
Wire d = 6 mm - 4540 x 21 x 4 = 381360 mm (382 m).
Knitting wire – 21 x 4 x 5000 mm = 420000 mm (420 m).
The reinforcement of the foundation of the internal walls will differ in that instead of reinforcement d = 16 mm, reinforcement d = 14 mm is used, as well as in the size of the clamps.
Reinforcement consumption for four internal walls.
Reinforcing bars d = 14 mm – 11060 x 10 x 4 = 442400 mm (443 m).
Wire d = 6 mm – 4300 x 21 x 4 = 361200 mm (362 m).
Knitting wire – 21 x 4 x 5000 mm = 420000 mm (420 m).
Weight of required metal
We use assortment
The weight of one linear meter of reinforcement d = 16 mm is 1.578 kg.
Required 133 meters, weight - 133 x 1.578 = 210 kg.
The weight of one linear meter of reinforcement d = 14 mm is 1.208 kg.
Required 310 + 443 = 753 meters, weight – 753 x 1.208 = 910 kg.
The weight of one linear meter of wire d = 6 mm is 0.222 kg.
Required 382 + 362 = 744 meters, weight – 744 x 0.222 = 165 kg.
The weight of one linear meter of knitting wire d = 1.4 mm is 0.012 kg.
Required 420 x 2 = 840 meters, weight – 840 x 0.012 = 10 kg.
Rules for calculating the reinforcement of a strip foundation
The calculation of reinforcement for a strip foundation is carried out on the basis of two documents: SNiP number 52-101-2003 “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures” and a design manual - “Reinforcement of elements of reinforced concrete buildings”. They clearly describe the requirements for the reinforced frame of a strip foundation. Namely:
- The total area of the longitudinal reinforcing bars should be equal to 0.1% of the section of the tape.
- The frame must fit completely into the body of the foundation so that there is a gap of 5 cm between its edges and the reinforcement. This applies to all planes: sidewalls, top and bottom surfaces.
- If the length of the strip foundation on one side does not exceed 3 m, then reinforcing bars with a diameter of 8-10 mm are used to strengthen it. If the length exceeds 3 m, then at least 12 mm.
- Vertical (aka mounting) and transverse reinforcement bars are not load-bearing. Their main task is to connect and fasten longitudinal reinforcement. Therefore, crossbars and vertical elements are assembled from rods of smaller diameter; smooth reinforcement can be used rather than corrugated.
- For longitudinal use of reinforcement, grade A3 material is used - hot-rolled corrugated steel. For vertical and transverse grades A1, A2 or A3.
- The distance between the vertical and also between the transverse rods is 20-40 cm.
- If the height of the reinforced frame does not exceed 80 cm, then reinforcement with a diameter of 6 mm can be used as transverse rods. If the height parameter exceeds the indicated value, then it is better to use rods with a diameter of 8 mm.
The main calculation is carried out on the basis of position number “1”. In this way the number of longitudinal rods is calculated.
General provisions
The reinforcement for the strip foundation serves as a kind of skeleton. Having assembled all the components of the frame, the foundation is poured with concrete mortar, which allows achieving maximum strength indicators. An important point in this matter is: selection of the necessary metal, and calculation of the cost of the frame material. Now there are many different online calculators that will help you calculate the number of reinforcement bars based on the dimensional data of your structure. It’s better to do everything yourself - this will help you better understand the structure of the foundation, and will also become a useful experience for you.
Characteristics of fittings
Although reinforced concrete mortar is considered to be a solid foundation, it also has its drawbacks. Like any other structure, the foundation can easily be affected by shifts of tectonic plates, as well as shrinkage. To protect your home from these external factors, it is better to initially strengthen the foundation structure. Metal fittings will cope with this task perfectly.
The main function of the metal rod is to reinforce the mortar. Concrete is not classified as a plastic material that has excellent elasticity. Such a solution is characterized by deformations that occur under increased loads on the base. Excessive pressure on the foundation can change its shape, up to the complete destruction of the structure.
To avoid deformations, the foundation must be properly strengthened. It should be taken into account that the foundation strip is subject to bending at two points. In these places, the structure is more susceptible to violations of the integrity of the surface due to compression and stretching of the hardened mortar. Such violations can only mean the following: either you made incorrect calculations and chose the wrong diameter of the rods; or the frame is assembled poorly.
The sore point of a strip foundation made of reinforced concrete is considered to be its low tensile strength. It was for this purpose that reinforcing elements began to be used, which increased the strength indicators of both the longitudinal and transverse parts of the base. The top layer of concrete pavement is most susceptible to deformation. That is why the frame is assembled in the shape of a parallelepiped. This form allows you to maximize the strength of the foundation due to metal rods located close to the surface.
Selection of fittings
Before starting construction work related to the assembly and installation of the foundation frame, it is necessary to correctly select all the binding material. If you take this seriously, your home will last you a long time.
One of the parameters necessary for the correct selection of reinforcement is its diameter. To correctly calculate this parameter, you need to accurately study the design of the future foundation. Pay attention to all aspects related to the expected load on the foundation. Very often little importance is given to this stage, which subsequently affects the deterioration of the performance qualities of the foundation.
To select the required reinforcement diameter for the frame, pay attention to the following parameters:
- If your house does not require a monolithic structure, and you use “shell”, aerated concrete or SIP panels as wall material, then a reinforcement rod with a diameter of 8 mm is acceptable for your foundation. Most often, such fittings are used in the arrangement of sheds and other small buildings;
- if you are building your own country house, and its design does not require a large number of floors, then using a metal rod with a diameter of 10-12 mm for the frame will be acceptable. Such reinforcement is well suited for one (or two-story) buildings with lightweight wall materials;
- to strengthen the foundation of a multi-storey monolithic building, reinforcement with a cross-sectional diameter of 14 mm and above is used. The main load carrier is the rods located along the tape, which also perfectly protect the base from stretching. Additionally, the foundation is reinforced with jumpers, which are mounted in vertical and horizontal positions. They are not subject to heavy loads.
For the construction of a strip foundation for a small country house, reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm is sufficient. To save a little money without losing the quality of the base, you can use reinforcement of a smaller diameter as jumpers. In addition, the material for the jumper can be used smooth. Unlike corrugated reinforcing rod, smooth reinforcement rod has a lower cost, but keep in mind that its use will somewhat reduce the strength of the foundation. If the building is small, then you can use a smooth rod; for a larger house, we recommend using corrugated reinforcement as all connecting parts of the frame.
Primary requirements
Before you start knitting a frame, it is necessary to identify all the basic standards of the material from which it will be made. Before determining certain requirements, the quality standardization service conducts many tests and inspections of the material. They help to identify all the strengths and weaknesses of metal reinforcement in order to avoid further damage and undesirable consequences.
Next, we will consider all the necessary requirements necessary for high-quality installation of the metal frame of a strip foundation:
- The minimum number of metal rods in the base must be more than 0.1% of the total cross-sectional area of the foundation. This data will help strengthen the base properly, without loss of quality.
- The minimum permissible distance from the edge of the frame plane to the foundation plane should not be less than 20-30 mm. Since metal and concrete mortar interact to some extent, this reserve is necessary for the protective layer.
- The number of rods in each row directly depends on the distance between them. Thus, for double-row reinforcement there is a rule according to which the distance between the rows should not exceed 30 mm. For a three-row, the distance should not be less than 50 mm.
In addition to the above requirements, there is one more that determines the cross-sectional size of the reinforcing bar.
In order to choose the correct reinforcement diameter, pay attention to the following indicators:
- For a section of foundation up to 3 m long, longitudinal pieces of reinforcement with a diameter of 10 mm are used. For a length of more than 3 m - diameter 12 mm.
- For curved or radius sections of the frame, a rod with a cross-section of at least 6 mm is used as transverse reinforcement.
- If high-grade cement is used for concrete mortar, the reinforcing bars of the top row should have a diameter of no more than 40 mm.
When starting preparatory work related to the calculation and selection of foundation frame material, carefully study all the features of this material. Correctly selected parameters will allow you to install a strip foundation quickly and without additional investments, and the quality will remain high.
Calculation of strip foundation reinforcement with an example
Input data:
- strip foundation length – 20 m;
- width – 40 cm;
- height - 80 cm.
First of all, it is necessary to calculate the amount of longitudinally laid reinforcement .
- The cross-sectional area of the foundation strip is 40x80=3200 cm².
- Total area of longitudinal reinforcing bars: 3200x0.1%=3200x0.001=3.2 cm². Or you can do it this way: 3200/1000=3.2 cm².
Now the resulting value must be divided by the area of one rod , thereby obtaining the amount of required longitudinal reinforcement. There are two ways to obtain the area of one rod. The first is to find on the Internet a table of the ratio of diameter and area of reinforcement. One of these is pictured below.
Table of the ratio of diameter and area of reinforcement
The second is to carry out the calculation yourself using the formula for the area of a circle: S=πD²/4, where
- "π" is the Archimedean number equal to 3.14,
- D – reinforcement diameter.
If the diameter of the longitudinal reinforcement was chosen to be 10 mm (1 cm), then: S= 3.14x1²/4= 0.785 cm². Now the total area of the reinforcing bars (3.2) must be divided by 0.785, resulting in 4.
The next stage of calculating the reinforcement of a strip foundation is determining the total length of the longitudinal rods . It should be noted that in the longitudinal direction the rods are laid relative to each other with an overlap of 5-10 cm. That is, the length of the rods, the standard length of which is 10.7 m, is reduced by the selected size. It turns out that the length of each after connection will be equal 10.6 m or 1160 cm.
Considering the length of the strip foundation - 20 m, you can calculate how many rods are required to lay one longitudinal element: 20:11.6 = 1.72 pieces. And since there are four of them, the total number is: 1.72x4 = 6.89 or, rounded, exactly 7.
Now it is necessary to determine the number and length of the vertical and transverse elements of the reinforcing frame of the strip foundation. Taking into account position number “2” of the requirements for assembling the reinforced frame, we can say exactly what length the transverse and vertical rods will be:
- for transverse ones: 40-10=30, where “10” is two by five distance from the edges of the foundation structure to the frame, “40” is the width of the tape;
- for vertical ones: 80-10=70 cm.
That is, in total, if both elements are made from the same type of reinforcement, then their production will take 1 m of steel material (30 + 70 = 100 cm). Next, you need to calculate the number of rods of this type used in the frame itself . If the distance between them is chosen within 30 cm, then the quantity is determined by dividing the total length of the foundation by the installation step: 2000:30 = 66.66 pieces. Round up to 67.
And since the total length of the two elements is 1 m, their manufacture will take 67 m of reinforcement. This indicator is multiplied by “2”, because in the reinforcing frame there are two pairs of transverse and vertical rods. The first are located at the top and bottom of the structure in a horizontal plane, the second on the sides in a vertical plane. This means that for their manufacture you will need 67x2 = 134 m.
The pitch of laying vertical bars does not always coincide with the step of transverse ones , as was discussed in the example above, because the crossbars mainly function as ties between the gratings. And their number can be reduced. For example, lay in increments of 50 cm.
Therefore, the calculation of the required reinforcement will have to be carried out for two elements separately.
Cross members are calculated as follows:
- 2000:50x30=120 cm or 12 m, where “20” is the length of the foundation strip, “50” is the step of installing the crossbars, “30” is the length of one transverse element.
Vertical rods like this:
- 2000:30x30=2000 cm or 20 m, where the installation step is 30 cm.
It turns out that the total length of the reinforcement required for the manufacture of vertical and transverse elements is 12 + 20 = 32 m. With a caveat, if reinforcement of the same diameter is used for them. Otherwise, each parameter will need to be taken into account separately.
It is necessary to indicate that the presented calculation of reinforcement for a strip foundation in terms of counting the number of rods is incomplete. Because in the corners of the foundation structure a special connection of frames located on different sides of the strip structure is used. Depending on the tying scheme of the mating corners, the total length of the reinforcement used may change. In the total mass, the addition is insignificant and can be up to 5 m. But it must be taken into account. Therefore, most often the total design length of the reinforcement is increased by 5-10%.
How to calculate reinforcement for the foundation of a house?
Calculation of concrete and foundation reinforcement is carried out at the stage of designing a house in order to obtain the volume of mortar to be poured, the length, cross-section and weight of metal rods and the spacing of their location. Its results are used in drawing up reinforcement schemes and preliminary estimates and are the starting point for purchasing building materials. The rules for calculating supporting structures are regulated by SNiP 52-101-2003, the type of frame is determined by the type and dimensions of the foundation being laid.
Specifics of calculating reinforcement for the foundation
The minimum permissible percentage of longitudinal reinforcing elements in a reinforced concrete monolith is 0.1%, provided they are evenly distributed. The second requirement is compliance with the cross-section of one rod specified in the building codes, including vertical and transverse ones. The initial data are the dimensions of the tape or monolithic slab. The recommended sequence of actions includes the following steps: drawing up a frame diagram taking into account SNiP and type of base → calculating the diameter of longitudinal, transverse and vertical reinforcement → calculating their number, taking into account launches at joints (separately for products with different profiles) → finding the length of the tying wire or number plastic clamps.
You might be interested in a review of bending machines.
The minimum permissible cross-section of the rods is determined by SNiP standards and depends on the dimensions of the foundation. For tape type:
| Dimensions of structures and type of rolled metal | Minimum diameter of metal rods, mm | Recommended range, mm |
| Longitudinal, with a continuous length of the strip foundation wall up to 3 m | 10 | 10-12 |
| The same, over 3 m | 12 | 12-14 |
| Vertical, with a tape height within 0.8 m | 6 | 6-10 |
| The same, for over 0.8 m | 8 | |
| Transverse | 6 |
In private and low-rise construction, the width of the tape is usually determined by the material and dimensions of the walls and rarely exceeds 50 cm, the height depends on the depth of the building. Standard schemes in this case contain at least two longitudinal rows with four or six supporting vertical rods. Any construction calculator will help you choose the right option; if you don’t have one, use the following requirements:
- The maximum permissible distance between longitudinal rods in one row is 40 cm. If possible, adhere to a step of 25-30 cm (but not less than 15); if the width of the strip foundation is over 50 cm, it is advisable to add another longitudinal row.
- The optimal distance between two horizontal lines is 60-80 cm.
- The recommended spacing of transverse reinforcement varies between 70-80 cm.
- The minimum distance from the side edge of the tape to the longitudinal rods is 5-7 cm.
- The thickness of the protective layer of mortar on the bottom side depends on the concrete preparation: from 40 mm - if present, 70 - if absent. It cannot be less than the diameter of the rods.
In addition to the above rules, a mandatory margin is provided for the length of the rods for the purpose of convenient tying or welding. If the total cross-section of the reinforcement exceeds the required minimum of 0.1%, there is no need for reinforcement; in private construction it is enough to adhere to the specified standards. When the deviation is smaller, thicker rods are used, but when a certain value is reached, this becomes impractical (it is cheaper to introduce an additional longitudinal row than to buy rolled products with a cross-section over 14 mm). The maximum value in this case is 40 mm, but such a thick profile is not used for various foundations.
When calculating the number of longitudinal rods, the total length of the walls, including load-bearing ones, is multiplied by the number of rows. The resulting value is minimal and does not take into account the need for metal reserves for joints. In reality, the length of the products does not coincide with the parameters of the monolithic slab or tape; in order to distribute the load evenly and eliminate the risk of sagging of the frame, the launch of the rod should exceed its cross-section by at least 30 times. For a profile with a diameter of 12 mm, it is 36 cm; builders usually round this value to 40. Calculating the number of joints is more difficult; for this you need to know the length of the purchased steel. When planning a scheme, it is worth using an online calculator.
Calculating the diameter of the reinforcement for a strip foundation allows you to obtain the optimal value in terms of price and compliance with expected loads. But you still shouldn’t deviate from the minimum specified in SNiP (the frame loses reliability), often this stage is simply skipped. The rental profile type deserves special mention. To improve the quality of adhesion when laying longitudinal rows, wire rod with a periodic (corrugated) section is used; for vertical and transverse rows, the use of cheaper smooth options is allowed.
It is advisable to knit the frame from rolled stock with the same quality, but when laying the foundations of private buildings, there are often cases of knitting it from leftovers. In this situation, the rods should be distributed as evenly as possible, with reinforcement with a large cross-section located in the bottom row, which is subject to maximum loads.
Features of calculating a monolithic slab
A typical frame for residential building foundations includes two layers of reinforcing mesh. The minimum thickness of the slab is 20 cm, the diameter of the rods is 10 mm. The recommended cell pitch varies between 15-20 cm; for light low-rise buildings, standard welded mesh can be installed. Calculating the total amount of reinforcement is simple; just add the number of intersecting bars along the length and width and multiply it by 2.
The main task is the correct spacing of these layers in height; it is taken into account that the minimum distance from the edge of the slab to the metal ends is 25 mm (and even more to the rods themselves). In this case, the upper and lower mesh should be equidistant from the surface of the slab and from each other (usually 10-12.5 cm). To ensure uniform load distribution, flexible clamps are used (rather than bonding or welding). These products are made from scraps of the same reinforcement with a diameter of 10 mm and are placed in increments of 1 m, in areas under load-bearing walls - every 40 cm. It is not recommended to calculate the total number of fasteners offhand; the only correct option is to draw up a diagram and mark them with dots.
You should find the total amount of reinforcement for a strip foundation 40 cm wide, 6 × 10 m with one additional load-bearing wall in the middle of the house and a monolith height of 70 cm. In this case, the optimal would be a four-rod scheme with a diameter of longitudinal rods of 10 mm, transverse ones - 6, vertical – 8. Using a regular or construction calculator, you can find:
- Total length of walls: (6×3+10×2)=38 m.
- The same for longitudinal rods: 38×4=152 m.
- The total length of the corrugated profile with a diameter of 10 mm, taking into account 10 pieces of overlap: 152 +10×0.4 = 158 m, with a 10% margin - 174 m.
- The number of supporting rectangles is 62 pieces, with a height of vertical rods of 60 cm, their total length reaches 62 × 0.6 × 2 = 74.4 m, longitudinal rods of 30 cm - 62 × 0.3 × 2 = 37.2 m.
To check the obtained values and the diagram, you can use an online calculator for calculating the amount of reinforcement. The above example does not take into account the need to reinforce the corners with metal (the recommended amount of outlet in one direction is 40 cm). The total cross-section of the longitudinal rods is 0.00785×4=3.14 cm2, which corresponds to the dimensions of the tape: 0.4×0.7×0.1%=2.8 cm2. The quantity for slabs or pillars is calculated in a similar way. The process ends with calculating the required length of the knitting wire: the number of joints is multiplied by 40 cm; due to the risk of it breaking, a margin of at least 10% is provided.
Reinforcement brands for strip foundations
There are several types of steel reinforcement on the market, and they are divided into construction and industrial. The first category includes several classes of material, which are marked with the letter “A” and a numerical designation. Today, builders use two types of designation: old and new:
- A1 is the old marking, corresponding to the new designation A240;
- accordingly, A2 is A300;
- A3 – A400;
- A4 – A600;
- A5 – A800;
- A6 – A1000.
Brands of reinforcement and their characteristics
Let us immediately make a reservation that the last two positions are not used in the construction of foundations. They have high technical characteristics, but are very expensive, which creates a high cost of construction. For longitudinal rods, class A3 or A4 reinforcement is used . Both brands are almost similar, the latter has higher strength and, accordingly, a higher price.
Class A1 fittings are easy to distinguish from others, because they are smooth rods. They are not used in longitudinal laying of the frame, because the rods have almost zero adhesion to the concrete mortar. They are used for fastening reinforcing bars to each other. Class A2 is corrugated reinforcement that can be used in low-rise construction, most often civil cottage construction. Material of this brand with a diameter of less than 8 mm comes out of production in coils, more than 8 mm in rods.
According to the production method, the reinforcement is divided into hot-rolled and cold-formed. For foundations it is better to use the first one, because it has higher strength characteristics. The difference between both types is that hot-rolled is made by pouring molten metal, while cold-formed is a finished steel rod that is passed through rolls with patterns printed on their surfaces. The latter form the reinforcement relief.
It should be noted that in the reinforcing frame, the reinforcing bars are connected to each other by knitting wire. Welding is not used for these purposes, because the high temperatures accompanying the welding process change the properties of the steel from which the reinforcement is made. These properties deteriorate. But this is not the only reason.
During the process of pouring concrete mortar, the reinforced frame is subjected to loads, especially at the joints. The knitting wire allows the rods to move relative to each other by a small distance, which is a restraining factor for these same loads.
Connecting the reinforced frame with knitting wire
As for welding, today manufacturers offer reinforcement that can be welded by electric welding without changing the characteristics of the metal. Such material is marked with the letter “C”. For example, A400C.
Basic requirements for fittings
Technical documentation and established practice determine that the minimum permissible amount of reinforcement in a strip foundation must be at least 0.1% of the area of the entire cross-section of the base.
For example, if a base 1 m high and 0.5 m wide is being reinforced, then the smallest wire area in this case should be 500 mm2.
Example of calculation of reinforcement.
How to calculate the diameter of the reinforcement (in mm):
- longitudinal rods with a side length of up to 3 m must have a cross-section of 10;
- longitudinal rods along a wall length of more than 3 m must have a cross-section of 12;
- transverse rods of knitted bending frames - at least 6;
- The diameter size of the reinforcement of the top row for heavy grade concrete should be no more than 40.
For ribs and beams with a width of more than 15 cm, at least 2 working rods with a cross section must be used. If the width is less than 15 cm, then 1 such element can be used.
The largest number of reinforcement in a row depends on the minimum permissible distance between them. This value cannot be less than the largest cross-section of the reinforcement:
- if reinforcement is carried out in 2 rows - no more than 30 mm for the top row and 25 mm for the bottom row;
- if the strip foundation is reinforced in 3 rows - at least 50 mm in the top row.
Additional strengthening, span calculation
Additional strengthening of single reinforced areas (areas of high overload and the presence of holes) is carried out with single iron rods with a length of 400 - 1500 mm, depending on the loads and span lengths:
- the lower part of the mesh is in the middle of the slab;
- the upper part is located on supports.
The rolled products used affect the relief of the ceiling; the fascias are placed in 2 or 1 directions. The advantage of openwork increase is the likelihood of reducing the thickness of the finished product near the same areas.
Supporting reinforcement protects the slab from cracking in wall areas.
The calculation of the reinforcement slab for the floor slab must be carried out with absolute accuracy, since the reliability of the entire structure as a whole will depend on this process. Some experts in the field of calculating reinforcement for a floor slab argue that the calculation should be made uniquely for almost every case, since many factors are different, including the dimensions of the slab itself.
It is worth considering that rolled metal will have a huge impact on the load-bearing capacity of the floor. And the advantage of the mesh used is the reduction in the thickness of the entire structure as a whole, but this is after all the “rough work” has been completed.
In absolutely any building, the best guarantee of quality work will be the correct and accurate calculation of the reinforcement for the floor slab. And when performing the calculation itself, it is necessary to comply with all the norms of technological progress, many of which are indicated above.
Calculation of reinforcement for a floor slab during deformation using steel reinforcement
a. Selection of cross-section, calculation data
Determination of maximum data using the formula:
M = g*l2/8 = 0.83 mn / m * (3m)2/ 8 = 0.93 t * m
Determination of the coefficient, where =1(m) using the formula:
A0 = M*y/ b*h02R6*y62 = 93,000 kg/cm * 0.95/ 100 cm*13cm2 * 117 kg/cm = 0.045, n=0.0975
Indicators of the cross-sectional area where the reinforcement has class A-500C according to the formula:
A2 = M*y/n*h0*R2 = 93,000 kg/cm * 0.95/ 0.975*13 cm* 4500 kg/cm2 = 1.55 cm2
The basic data at the bottom of the entire reinforcement is accepted: Ø8 A-500С, taking into account the step of 200 (As = 2.51 cm2)
b. Calculation of reinforcement for a floor slab during deflection
The presence of a constant load on the floor itself is equal to 0.63 t/m².
The presence of a temporary load on the floor is 0.2 tons/m².
Maximum values for these long-term floor loads:
Mdl = g*ll2/8 = 0.63mh/m*3m2/8 = 0.71 mh * M.
The maximum values for these temporary loads on the floor are Mxp = g*l2/8 = 0.2 mh/m*3m2 / 8 = 0.22*m.
Reinforcement of slabs depending on support
A coefficient that takes into account the type of load and loading pattern S = 5/48 - for a beam with constant uniform load data y = y = 0.
Design of various concrete and iron structures made of heavy materials.
The coefficient for determination is equal to – k1, k2, k3.
Mn = f2/b*h0 * Ea/Eb = 2.51 cm2/100 cm * 13 cm * 2*10 '6 kg/cm / 3.1*10 '5 kg/cm2 = 0.012.
k1 = 0.64, k1 = 0.43, k2 = 0.10.
Axle irregularities under the simultaneous action of constant, long-term and short-term loads, which are calculated by the formula: 1/p = 1/Ea*Fa*H02 = Mkp/k1kp + M – k2 *b*n2*Rbin / k1 = 1/2* 10'2 kg/cm * 2.51 cm2 *13'2 cm2 * 22,000 ru * cm/ 064 + 71000 kg*cm – 0.1*100cm * 16 cm2 * 14.3 kg/cm2 = 1/848380000 * 34 375 + 71000 – 36 608/ 0.43 = 0.000135 1/cm = 13.5*10′-5 1/cm.
The maximum deflection data in the middle of the span are: f = 1/p *S*l2 = 13.5 * 10'-5 1/cm * 5/48 * 300'2 cm2 = 1.27 cm. f = 1/200 = 300 cm/200 = 1.5 cm. Fm = 1.27 cm = f = 1.5 cm.
These conditions are met with the adopted reinforcement, where (Ø8 A-500С in increments of 200). Calculation of reinforcement for a floor slab during deformation using fiberglass reinforcement (AKP-SP).
The tile load and design data are similar.
Calculations are made based on deformations for some reinforcement options.
The initial data, as well as the characteristics of the materials, are presented in the initial data.
Calculation of the diameter of transverse and vertical reinforcement
Longitudinal reinforcement for a strip foundation should be corrugated, while transverse and vertical reinforcement can be smooth.
You can calculate the diameter of transverse and vertical reinforcement without complex calculations. It is worth focusing on the data in the table:
In our case, with a foundation height of 80 cm, smooth rods 6 mm in diameter can be used for transverse and vertical reinforcement. If you are building, say, a two-story cottage, then rods with a diameter of 8 mm will be sufficient for transverse and vertical reinforcement.