In this article we will tell you about load-bearing walls. What is it and why load-bearing walls are so important.
Let's describe the picture from afar.
When a house is built, the walls perform two main functions in it.
- Divide the room into rooms.
- Serve as load-bearing structures on which other structures rest.
From this information it is clear that load-bearing walls are those walls that bear the load when other structures operate on them.
Load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls in the house
Building codes define load-bearing structures as those structures (walls and other building elements) that accept permanent or temporary loads from other components of the building.
Load-bearing walls are often also called capital walls, meaning that their structure must be strong and durable.
Load-bearing walls also include stiffening diaphragms, present in many residential building structures, which serve to absorb horizontal loads and ensure the stability of the entire building.
The concept of load-bearing walls can also include unloading walls, designed to partially take the load from the upper floor. Relieving walls are found in the construction of old houses with wooden or mixed floors.
Non-load-bearing walls are most often called partitions. They are designed to create boundaries of rooms and do not take the load, relying on the ceiling within one floor.
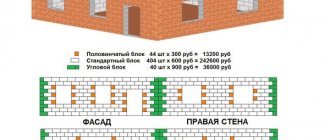
Strength of aerated concrete
First of all, it is distinguished by excellent load-bearing capacity and strength. Strength refers to the strength of a block when tested for compression, that is, its load-bearing capacity.
The strength level of the wall material of aerated concrete blocks depends on the amount of water in the cement mortar. The strength of aerated concrete decreases as the relative amount of water in it increases. Excessive amounts of water pushes apart the small pieces of cement. As a result, voids and pores are formed. An increase in the strength of materials is facilitated by a decrease in the ratio of water and solid components of the cement mortar, as well as the use of vibration and reinforcement technology in the preparation of mortars.
For example, when the strength index of an aerated concrete block of class B 1.5 is D500, it is prohibited to build load-bearing walls of a 2-story house from it. Using one of the most popular brands of aerated concrete block D500 with a range higher than B 1.5, it is possible to construct buildings whose height is no more than 3 floors, since the density is quite high and amounts to 500 kg/sq. m. Under these conditions, aerated concrete blocks will be able to fully withstand the load from the house structure and floor slabs.
Return to contents
How to determine whether a load-bearing wall is or not
Only its author can determine the location of the load-bearing walls of a house with absolute certainty. Fortunately, in most cases, general principles were used to create projects for apartment buildings, and standard projects are even intended for replicating buildings of the same design.
Due to the invariance of design principles in most standard buildings, the location of load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls is known in advance, and for buildings of old housing stock and houses built according to individual projects, they can be determined.
The main parameter that allows you to find out which wall is load-bearing is its thickness. A simple principle works here - the thicker the wall, the greater the load it can withstand.
The material from which the wall is made is also important - reinforced concrete and brick can withstand significant loads, but gypsum and other lightweight materials are not suitable for this.
The greatest difficulties in determining load-bearing walls are presented by wooden buildings and houses built before the mid-twentieth century with wooden and mixed floors.
Choosing a foundation for a house made of aerated concrete blocks
However, there are both positive and negative aspects when working with aerated concrete blocks. The opinion that since aerated concrete is classified as a lightweight material can save money on foundation construction is erroneous.
But choosing the right foundation for a house made of aerated concrete blocks is difficult. An excellent option would be to choose a slab foundation. This foundation is capable of rising and falling during periods of seasonal ground fluctuations. An excellent option that minimizes shrinkage deformation is reinforced concrete slabs. Before you start laying the foundation, according to the building design, you need to dig trenches. The trenches of this foundation must be protected to prevent water from entering there. For this purpose, adjacent areas must be developed and a water conduit created. The trenches where the foundation is laid must certainly be secured.
It is also possible to build a pile foundation for an aerated concrete building. However, it must be taken into account that a pile foundation for a building made of aerated concrete does not need to be created on moving soil, since it is not stable enough. The advantage of such a foundation is that it is possible to drill them using a regular hand-held construction drill.
It is also possible to build a pile foundation for an aerated concrete building. However, it must be taken into account that a pile foundation for a building made of aerated concrete does not need to be created on moving soil, since it is not stable enough.
A monolithic strip foundation is needed to minimize deformation during shrinkage and the risk of significant cracks in the masonry. The best option is a reinforced concrete slab. It can ensure uniformity and minimal parameters of shrinkage deformations. Creating a slab foundation is quite expensive. However, these costs are worth it.
You need to make the right decision about what kind of foundation you will create for a building made of aerated concrete blocks. Your choice will depend on the characteristics of the soil and the parameters of the building being constructed. will help protect the house from significant deformations.
To prevent floor slabs from cutting off aerated concrete blocks, you need to use a special reinforcing belt for the foundation. If this is not possible, it is possible to use reinforced concrete pads for support. You can use bricks that need to be laid using a special technology. But these additional components of the structure reduce the thermal insulation properties.
Return to contents
What are the load-bearing walls in a panel house?
Determining the location of load-bearing walls in a panel house is not difficult. Almost all panel high-rise buildings belong to different standard series and are built on the principle of repeating a single power circuit.
Unified projects have the same arrangement of structural elements, and complexity can only arise with any of the less common modifications of the standard series.
In 95% of panel houses, the minimum thickness of load-bearing walls is 14 cm. A wall less than 12 cm thick is most likely a non-load-bearing partition.
The fencing structures of the plumbing cabin are also non-load-bearing.
Even having understood how to determine the load-bearing wall in a panel house, it is important to take into account that the apartments in them, with rare exceptions, are distinguished by a large number of internal load-bearing walls, which significantly complicates the redevelopment.
Minimum wall thickness
One of the main characteristics of a brick house is the thickness of the walls. The size of a regular ceramic brick is 250x120x65 mm. Building codes and regulations accept a value that is a multiple of 12 (the length of half a brick) to determine the thickness of walls.
It turns out that the thickness of the wall is:
- in half a brick - 120 mm; in one brick - 250 mm; in one and a half bricks - 380 mm (10 mm is added to the thickness of the seam between bricks); in two bricks - 510 mm (10 mm per seam); in two and a half bricks - 640 mm.
The same building codes clearly define the minimum thickness of a brick wall.
It should be in the range from 1/20 to 1/25 of the floor height. A simple calculation shows that if the floor is 3 meters high, then the walls must be at least 150 mm thick. A brick wall less than 150 mm thick is suitable for simple internal partitions.
How to determine a load-bearing wall in a brick house
Brick four-story houses and five-story buildings built in the 50-80s of the last century, which do not even belong to the standard series, have similar structural designs: the load-bearing walls of the buildings are the external walls and the longitudinal internal wall separating the apartments in the house, as well as the walls of the staircases.
Typically, the minimum thickness of a load-bearing wall in a Khrushchev-era building, if the house is brick, is about 30 cm. All the thinner walls in these houses are partitions.
If we consider brick houses built after the 90s of the last century, the situation here is more complicated. Most of these buildings were built according to individual projects, so it is often difficult to determine the design “on the fly.”
An unambiguous answer to this question can only be given by the author of the house project or by an organization engaged in the technical inspection of buildings. Often, the management company that received the design documentation for the house from the developer may have information about the location of load-bearing walls.
Problems with the rising cost of a house made of aerated concrete blocks
Since the construction of buildings above the third floor requires high-density aerated concrete, such buildings are usually not erected, since this significantly reduces the thermal insulation properties of the house and increases its cost. This leads to a significant increase in the cost of constructing the structure.
Building a strong one can cost a lot of money. Therefore, in this case, it is not advisable to use aerated concrete.
Since the construction of buildings above the third floor requires high-density aerated concrete, such buildings are usually not erected, since this significantly reduces the thermal insulation properties of the house and increases its cost.
It is allowed to use aerated concrete in the construction of taller buildings. But in practice, construction companies rarely implement this. This is explained by the fact that in these cases the use of denser aerated concrete blocks is required. But, firstly, their cost is several times more expensive. Secondly, aerated concrete blocks of this type do not provide sufficient thermal insulation. In addition, it is often necessary to secure some massive structure to the material made from these aerated concrete blocks. But it's difficult. In addition, it uses much more expensive, special fastening technology. In general, if the average cost of the façade of an economical cottage is approximately 500 sq. meters, it will become more expensive by about 125 thousand rubles. This is almost half the price of aerated concrete blocks for this cottage.
Thus, we see that the use of aerated concrete, which initially has a low cost, in some cases requires additional costs. Moreover, aerated concrete is a rather fragile material. For example, it is so inelastic that it has the ability to break easily when bent. This property of aerated concrete cannot be ignored during the construction process. The slightest deformation of the foundation can cause massive cracks in the entire structure. The low elasticity of aerated concrete can be compensated by the hardness of the stone. Most often, autoclaved aerated concrete is used for this. It is produced using saturated steam technology. In this case, the pressure indicators should be much higher than atmospheric.
Load-bearing walls in Khrushchev and Stalin buildings
Unlike Khrushchev and houses of a later period, many Stalinist and pre-revolutionary buildings are built of brick, and the vast majority have wooden and mixed floors.
The rule regarding the thickness of load-bearing walls, as in most brick buildings, works in the same way in old houses and Stalin buildings as in Khrushchev buildings.
In such houses there are sometimes load-bearing walls, columns and crossbars of very considerable thickness, and in addition, there are unloading wooden partitions, which should be worked with in the same way as with load-bearing walls.
In “old-built” houses, often only a specialist can determine where the load-bearing walls are located through local openings of the finishing in the apartment and examining the condition of the apartment/house structures.
Even if the stalinka is built with reinforced concrete interfloor ceilings, it is not always possible to reliably understand the location of the load-bearing structures.
How to determine whether a load-bearing wall is in a monolithic house
Monolithic and monolithic-brick houses can be of very different designs, but they have one thing in common - all the load-bearing structures of such buildings are made of monolithic reinforced concrete.
Structurally, load-bearing elements can be external or internal walls, their individual sections, pylons, columns, crossbars, etc. Due to the fact that the principle of constructing monolithic houses does not imply “flow diagrams”, accordingly, each house is individual.
To the question of where to find out reliably whether a load-bearing wall is in an apartment of a monolithic building, there is only one answer - only from the organization that designed this residential building.
In addition, the developer’s documentation can tell a specialist a lot about the design of the building if it was transferred to the management company upon completion of construction.
However, here too there are some general guidelines - in most of these buildings there are no load-bearing walls inside the apartments, but there are often load-bearing columns or pylons.
Load-bearing walls on the drawings of the apartment redevelopment project in a monolithic building:
If an apartment in a monolithic building is rented without finishing, load-bearing walls and columns are easily determined. Unlike partitions made of lightweight block materials, all supporting structures are cast from concrete.
Aerated concrete production technology
Now, in the 21st century, the serial industrial production of aerated concrete is being revived again. Production volume is growing, and sales of this building material are expanding.
Aerated concrete refers to cellular concrete. There is no concrete filler in it, but there are through, artificially created pores created using cement, sand, and other components.
There is enough of this raw material on our planet. It can be easily mined without causing significant harm to the environment. Processing of these components in mixed form is carried out in an autoclave. Here, under specified conditions, the starting material is foamed. In this case, there is a reaction of corrosion of aluminum powder and the release of hydrogen, forming through pores. Next comes the process of hardening the composition. Depending on the method of pore formation, there are 3 types of cellular concrete. Among them are aerated concrete and aerated concrete blocks. The main components in aerated concrete blocks are virtually homogeneous. Only the foaming agent and hardening methods used in the production process of aerated concrete blocks differ.
In an autoclave, manufacturers obtain aerated concrete and aerated concrete blocks that have the characteristics necessary for building materials. In 2011-2012 Technical specialists in Russia carried out an examination of building materials in cottage villages. Based on their results, aerated concrete was highly praised by experts.
Return to contents
How to find out whether a load-bearing wall is in a block house or not
Determining what is a load-bearing wall in block houses is not difficult even for non-specialists.
Firstly, all houses of block construction are built according to standard designs, the structural features of which are well known.
Secondly, buildings of this type have a significant difference in the thickness of load-bearing (35-50 cm) and non-load-bearing (8-10 cm) walls, which simplifies the task.
Just like in panel houses, in block houses there are often load-bearing walls in the area of apartments, which complicates redevelopment.
Economic rationale for choosing wall thickness
Construction is absolutely impractical when the wall thickness is over 38 cm.
To preserve heat in this case, all kinds of insulation methods using insulating materials are used. Lightweight masonry is often used in low-rise construction. This method involves placing several walls in two rows at a distance of about half a brick from each other. The creation of an air gap in this case plays the role of an effective heat insulator. If necessary, the resulting cavity can be filled with any suitable insulating material.
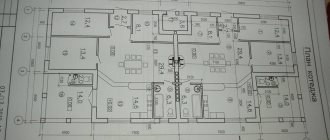
How load-bearing walls are indicated on the BTI plan
The floor plan of the apartment with an explanation for it or the technical passport contain a graphic reflection of the planning solution of the premises.
Plan analysis, considered as another way to determine a load-bearing wall, does not give a clear answer to this question, even in standard series houses.
BTI plans only indirectly reflect which walls in the apartment are load-bearing and which are not. The designation of load-bearing walls on the BTI plan has other purposes - to show the fundamental position of the walls and the planning solution as a whole.
However, upon closer examination of the plans, you will notice that load-bearing walls on them can be highlighted with thicker lines than non-load-bearing ones. The same applies, for example, to walls containing ventilation ducts.
But, as described above, this rule is not true everywhere and not always. Therefore, if there is a BTI plan where the wall is indicated with a thin line, this in no way means that it is necessarily non-load-bearing.
In the examples below you can see how the load-bearing walls of two identical apartments in a house of the P-44 series look on the BTI plan.
Two versions of the technical passport (extended and regular):
According to the technical data sheets given above, it is clear that the bathroom partitions are not load-bearing, since they are depicted with thin lines, but for all other walls this is not so obvious.
Even more questions are raised by the BTI plan with red lines recording redevelopment that has not been properly formalized. In this case, in order to understand where the load-bearing wall is, it is necessary to request from the BTI the original (archival) plan made before the changes were made. This will help determine load-bearing walls on the plan more reliably.
Even understanding where and how the load-bearing wall is indicated on the apartment plan, in order to avoid mistakes, it is better to make sure that the BTI information is accurate. The most effective way is to measure the thickness of the wall and drill through it, assessing the type of material from which it is made.
BTI plan with red lines and plan before redevelopment with the original location of the walls:
Redevelopment - what is it?
Redevelopment is a change in the configuration of an apartment. The Housing Code states that these changes must be made to the technical passport and approved by the relevant authorities. Redevelopment includes moving window and door openings, changing walls and partitions, dividing large rooms, moving a kitchen or bathroom.
Typically, redevelopment is limited to the removal of interior partitions. But you need to know exactly which walls are allowed to be demolished and which ones cannot be touched. Otherwise, demolition may change the impact of forces on the remaining surfaces below, and unsupported ceilings may collapse, unable to withstand the load. Do not forget that the walls not only divide the room into rooms, but also support the ceiling above similar structural elements.
Coordination of load-bearing wall redevelopment
In Moscow, any work affecting load-bearing walls, including the installation of doorways in them, as well as the dismantling of individual sections of them, should be carried out only on the basis of a project approved by the Moscow Housing Inspectorate, since the condition of load-bearing structures directly affects the safety of the building.
A project involving the redevelopment of a load-bearing wall must contain a calculation of loads and a section where the drawing shows the design of a metal reinforcement frame. A redevelopment project involving changes in load-bearing walls can be developed by an organization with SRO approval.
Also, for approval, a positive technical conclusion for such redevelopment is required. This document must be provided by the organization that designed the house, or the organization officially replacing it, if the author of the house project is unknown or has ceased to exist.
It is not always possible to make an opening in a load-bearing wall - on the lower floors the load on capital structures may be too high, even despite the reinforcement of the wall with metal profiles.
At the stage of planning renovation work, our specialists receive many questions from apartment owners. Below we provide answers to some of them.
Is it possible to demolish load-bearing walls?
A load-bearing wall cannot be completely/partially broken or moved - this threatens not only the appearance of cracks, but also the collapse of other building structures.
It is possible, although not everywhere, to make an opening or remove the end of a load-bearing wall by installing its reinforcement from metal structures according to a project approved by the Moscow Housing Inspectorate.
Is it possible to groove load-bearing walls?
The chipping of load-bearing walls is prohibited, which is indicated in a separate line in the list of prohibited activities in Moscow Government Decree No. 508-PP (clause 10.11 of Appendix 1).
If there is an air conditioner in the apartment, housing inspectors pay attention to the way communications are laid between the blocks, noting the chipping of load-bearing walls as a violation.
It will also be a violation to hollow out niches in load-bearing walls to install electrical panels.
These types of work can significantly reduce the load-bearing capacity of the structures of the entire house.
Is it possible to drill into a load-bearing wall?
In cases where making a hole in a load-bearing wall is required to install any fastenings, the work is not regulated, since the diameters of such holes are small.
If it is necessary to drill through load-bearing walls to lay utilities, it is necessary to install metal sleeves of the appropriate diameter, which essentially act as reinforcement of the walls.
It is important to remember that punching and drilling load-bearing columns, crossbars and pylons for laying communications is unacceptable.
Is it possible to make an opening in a load-bearing wall?
In the case where the load on the load-bearing wall is not too great, you can make an opening or cut a window in the load-bearing wall by installing a metal frame to strengthen it. As practice shows, it is very difficult to obtain permission to make a door in a load-bearing wall more than one meter wide.
In panel houses built according to the projects of JSC MNIITEP after 2007, it is difficult to coordinate the execution of an opening in a load-bearing wall with a crane - these houses have a copyright ban on this type of redevelopment.
In some of them, you can make a passage in the load-bearing wall between the kitchen and the room, using a design niche in the so-called “transformer panel”.