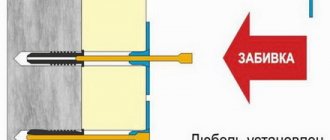
Currently, not a single construction or repair can be completed without the use of such a fastening element as an anchor dowel. This is a metal piece that is screwed, laid or hammered into a pre-prepared hole in a solid base.
These fasteners are as integral a part in construction and repair work as nails or self-tapping screws. The market is replete with various types of similar parts. What is an anchor, what types does it have and where is it used?
Rail fastenings - what are they?
These are the key elements of the VSP (superstructure of the track) - devices that connect metal structures to each other and/or to the base (that is, to wooden/reinforced concrete sleepers).
They are also in demand when creating a seamless road, when it is necessary that under the influence of external factors only the end parts of the strands shift, while the middle parts remain unchanged even with serious temperature changes. The quantity in which they will be used will directly affect the costs of construction and operation. It is important to remember that saving on them is not safe.
Types and classification of dowels
Anchor fasteners differ in purpose, types of installation, and materials of manufacture. The classification is quite simple. So, according to their purpose, anchor dowels are divided into two types. The first is purpose based on:
- For sheet materials (plywood, OSB, gypsum board, chipboard). Such dowels are popularly called “butterflies” because of their characteristic shape. Such anchor fasteners are convenient for installing lightweight structures on hollow walls. To fasten heavier structures made of sheet materials, it is necessary to use a dowel with an external thread. These elements are twisted into gypsum board sheets and subsequently securely hold any structures.
- For porous or cellular substrates. These are hollow bricks, cellular blocks, foam concrete, etc. These dowels are made of soft plastic materials. They have an extended spacer part.
- For dense, solid materials. These include concrete, solid brick, stone, etc. Types of fasteners for such bases can be made of both metal and plastic. They have a long, non-spacer part.
As for the purpose of use, according to it, furniture, frame and facade dowels are distinguished. Particularly worth noting are the elements for thermal insulation materials; in the jargon of builders they are called “mushrooms”. These types of fasteners are made of plastic. They have a wide head and are designed to connect thermal insulation boards to the base. Facade and frame dowels have an elongated, non-spacer part. They are designed for fastening heavy structures. Made, as a rule, of metal.
Why are rail fastenings needed: their purpose, types, description
In addition to connection, these elements solve the following tasks:
- reduce the level of vibrations that are transmitted to sleepers, ballast, and earthen bed;
- provide insulation on the canvas with electric traction and automatic blocking;
- maintain the integrity of the track, helping to withstand the maximum possible loads.
The key points for their use are: circuits in areas with traffic lights (shunting, entrance, exit, checkpoints), boundaries of block sections, electrified lines, roads with dispatch centralization. And these are quite diverse parts of the VSP, so we will consider the features of their classification in detail below.
They are divided into two main groups:
- butt - used to connect the links of I-beams to each other;
- intermediate – for fixing metal structures on supporting bases.
Rice. 1.1. Butt bonding
Photo of butt fastening type KD
Options for arranging joints - suspended, on one sleeper or double. A small gap is usually left between two fixed rolled products, thereby allowing for the possibility of elongation and expansion as the temperature rises. To move the ends, technical holes are made oval or round. In the latter case, their cross-section is larger than the diameter of the fasteners.
We will separately consider the materials used and the configuration of these VSP elements. Butt rail fastenings consist of a set of bolts with washers and nuts, as well as linings, but this is in the most general case. If they are insulating, that is, blocking electric current, then they either have surround linings - several layers and bushings made of polyethylene, fiber or textolite, or glue-bolt ones, when the fiberglass insulation is monolithically fixed to the rail using epoxy glue. If they are conductive, then they are plug-in and made of steel wire. They are welded to an unused face of the metal structure head. For reverse traction they are made of copper cable.
Intermediate elements, in turn, are:
- Non-separable - the I-beam railway profile is fixed on the supporting base along with the lining.
- Separate - the rolled product is first mounted on a lining, which is then placed on a sleeper (beam) and the joint is tightened with screws or bolts.
- Mixed - combined. The installation technology is the same as in the previous case, only with additional fastening of the textolite or fiber layer using crutches.
Each option finds its application depending on the expected loads on the line.
Rice. 1.2. Intermediate fastenings
a - inseparable; b - mixed;
c - separate (terminal - bolted for reinforced concrete sleepers):
1 - rail; 2 - crutch; 3 - lining; 4 - wooden sleeper; 5 - reinforced concrete sleeper; 6 — gasket under the lining; 7 — gasket under the rail sole; 8 — terminal clamping bolt; 9 - terminal; 10 - insulating sleeve; 11 - flat washer; 12 — double-turn spring washer; 13 – embedded bolt.
Dowels: purpose and types
There are only three varieties of these fasteners - a metal dowel (familiar to almost everyone since childhood), a mounting one with a plastic plug, and a spacer one, which is scientifically called a “Bierbach dowel.” Let's start in order.
- The metal dowel is the oldest of all types of fasteners. Designed for driving into almost all surfaces. However, it cannot be installed with a hammer into any material - as a rule, it is loaded into a pneumatic, electric or cartridge gun. They differ from each other only in length and diameter.
- Mounting dowel is the most common of all types. It is produced in two variations, differing from each other in the shape of the plastic stopper. In one case, the dowel is intended to be installed in a concealed position, but in the other case it is not (the plug of the last dowel has a mushroom-shaped cap). Mounting dowels are installed using a hammer drill and a hammer - first a hole is drilled, then a plastic plug is inserted into it, into which a steel nail with some kind of thread is driven. Such a nail can easily be unscrewed from the plastic cork with a screwdriver if the need arises. The diameter of such dowels can be 6, 8, 10, 12 and 14 mm, and the length from 35 mm to 250 mm.
Mounting dowels photo - Expansion dowel (Bierbach). Made from steel, it has proven to be excellent when used in concrete. It consists of two wedges, movably connected to each other by a washer of one of them. It is installed in a pre-drilled hole, into which it is wedged with one blow of a hammer. You can't think of anything better for fixing suspended ceilings.
Bierbach dowel photo
Photo mount type KB
The peculiarity of intermediate rail fastenings that they have excellent resistance to longitudinal movement deserves special attention. If separate elements are selected, then additional fixation is not required, which is convenient. Plus, such a structure will be naturally protected from “hijacking,” that is, from longitudinal displacement along the tracks, especially if the supporting base rests on crushed stone ballast. This is an elastic layer that will help to evenly transfer the load to the subgrade, and will also be able to effectively drain water from the VSP.
But a mixed or inseparable connection for protection against “theft” must be additionally equipped with anti-theft devices. These are spring brackets that are pinched on the sole of the I-beam railway guide with one end, and the other is latched on the opposite side of the sole. They can also be equipped with a pressure wedge, but are usually installed without it, since then they are as light as possible and there is nothing to break in them (there is only one part). Such devices have proven themselves well on narrow- and wide-gauge lines, on single- and double-track tracks. They are easy to maintain and operate for a long time, so their installation is economically justified.
Types of dowels for drywall
In addition to the “butterfly”, there are several other types of dowel-nails for plasterboard sheets:
- Molly. This fastener is made of metal, so it can withstand loads of up to 35 kg. It is similar in principle to a “butterfly”: the sheet is clamped from the front and back, which increases the contact area.
- Driva. Another reliable fastener for drywall. But it is often made of plastic, so it can withstand lighter loads - up to 25 kg. It is screwed in with a screwdriver, like a self-tapping screw. Due to the special design, it is securely held in the wall.
- Folding spring dowel. Most often used for plasterboard ceilings, you can hang a chandelier or flowerpot on it. But it should be remembered that this type is not suitable for punching bags and other heavy objects. It has plates that are held in place by a spring. These plates are inserted into the hole in the plasterboard, and the spring expands them, due to which reliable fixation occurs.
- An ordinary dowel-nail. This fastener is used if there is no free space between the wall and the drywall. A hole is drilled in the wall, a plastic part is inserted and a self-tapping screw is screwed in.
Important! The choice of fasteners for gypsum boards should be based on the weight that it can withstand. It should also be remembered that some types (for example, an umbrella) cannot be dismantled, so you need to correctly mark the holes before installation.
The most reliable is considered to be fastening to a metal profile on which plasterboard sheets are held. If possible, it is better to place it at the beginning of the repair in those places where fastening shelves and other objects will be required.
The butterfly dowel-nail is used to hang a TV, lamp, electrical wiring elements and other objects weighing no more than 20 kg on a plasterboard wall. This is the most common type of fastening, which is produced by various manufacturers. Metal dowel-nails with anti-corrosion treatment are considered the most reliable.
Classifications of rail fastenings
The following are widely used:
- Pandrol is an anchor unit, especially relevant in areas with high-speed traffic. It is distinguished by its ease of installation, which reduces the time required for the construction of the railway, as well as its low maintenance requirements, which minimizes operating costs.
- W30 (VOSSLOH) – is actively used for canvases that must stably withstand the heavy weight of passing locomotives (cars, loaded trolleys, etc.). Among its practical advantages are elasticity and high vibration resistance, which significantly extend the service life.
- Separate fastening of the reinforced concrete type - unlined and spring, its rigidity is specially reduced. In practice, it is in demand when laying reinforced concrete sleepers, as it ensures that the gauge is maintained and prevents attackers from removing individual rails.
- ARS – helps to ensure traffic safety and reduce operating costs on load-bearing sections of continuous continuous road fabric. After its installation, there is no longer any need to tighten and lubricate the bolts and nuts, so there is no need to waste lubricant (the savings are obvious).
- Mounting KB, KD, D.
- This is a lining mount and they are necessarily equipped with a layer of fiber, fiberglass, polyethylene, textolite.
- Unlined - mainly anchored, prominent representatives in this case are the already mentioned Pandrol and ARS. This category also includes reinforced concrete products and their varieties.
According to the design of the terminal, all types of fastening rails to sleepers are classified into:
- Rigid – the fixation is as reliable as possible, but over time it causes mechanical abrasion of the surfaces of the parts at the point of contact. The most common options here are CD and KB.
- Elastic - in turn, there are plate (ZhBR, ZhB) and rod (Pandrol-350, ARS, ZhBR-65). Here the design of the clamping element plays a role - flat and longitudinal, respectively - on which the uniformity of load distribution depends. In the first case, the contact surface is larger, as a result of which the pressure is distributed in all directions at once, but their cost is higher, which affects the overall costs.
All types of railway fastenings of rails and sleepers are also divided according to the type of installation - into the following varieties:
- Bolt-on - appeared earlier than the others and are a kind of current classic. Affordable and at the same time quite versatile. This subcategory includes brands KB, KD.
- Anchor - characterized by high reliability of fixation, therefore they are actively used when laying heavy canvases that need to withstand consistently high loads. They are pressed against the supporting base due to frictional forces, so they gradually wear out. This includes Pandrol-350 and ARS-4.
- Screw-dowel (another popular name is capercaillie) - a combined type. They are rods with a square or hexagonal head and an external thread, the pattern of which is compatible with the grooves in the hole. The most common options are ZhBR-65Sh and K2.
As part of the consultation, PromPutSnabzhenie specialists will tell you what products are needed specifically for your facility. We will move on to consider the supporting base, the material of which also plays an important role.
Fastening the butterfly dowel
Fastening this type of dowel-nails is not difficult; even a novice master can handle it. Stages of work:
- A hole of suitable diameter is drilled in the wall. There must be a distance between the wall and the plasterboard sheet that exceeds the length of the dowel.
- The dowel is inserted into the hole, but not all the way.
- Holding the dowel with pliers, screw in the self-tapping screw (not all the way).
- As soon as the butterfly’s petals open, insert the dowel all the way and screw in the self-tapping screw all the way.
If you are not confident in your abilities, you can watch training videos on the Internet about working with this type of fastener.
Rail fastenings for wooden sleepers
They are divided into:
- unlined - without metal linings;
- lining;
- indivisible;
- separate;
- mixed.
In case of inseparable connections, fastening is carried out directly with the support through the lining.
Separate - the rolled metal rail is bonded only to the lining, and the lining is independently connected to the support.
With mixed railways, the profile is connected to the support through the lining, and, in addition, it is independently attached to the support.
Currently, there are mainly two types of fastenings in constant use - crutch fastening D (Fig. 2.1) and separate fastening KD (Fig. 2.2, a). Fastening D4 is also used (Fig. 2.2, b).
Rice. 2.1. Crutch fastening D
1 – rail; 2 – crutch; 3 – lining; 4 - sleeper
It is customary to sew the lining to the sleeper with two sheathing crutches, and the railway metal to the sleeper on straight sections of the track - with crutches located diagonally. On curves, if necessary, the guides are additionally sewn to the sleepers with crutches. The main disadvantages are: the crushing of wood under the lining and the development of crutch holes, the possibility of snow and dirt being pressed under the sole, which causes a widening of the track and derailment of the rolling stock.
In the separate fastening KD, the metal lining is attached to the sleeper with four screws, and the rail beam is pressed against the lining with two rigid U-shaped terminals and terminal bolts. Unlike D, it provides constant pressure to the lining and allows for height adjustment up to 14 mm. This ensures track width stability and makes replacement easier. The main disadvantage of design design is its multi-part nature and high material consumption.
D4 type fasteners are distinguished by their multi-part nature and metal consumption. They clamp the rails harder than crutches and thus prevent theft. Can be used when laying continuous track. Spacers of different thicknesses are placed between the metal and the lining, which allows you to adjust the position in height.
Rice. 2.2. Split fastening for wooden sleepers
a – KD type; type – D4; 1 – double-screw washer; 2 – screw;
3 – lining; 4 – terminal bolt; 5 – terminal; 6 – under-rail platform; 7 – gasket under the lining.
The most common are inseparable, which can be of 2 types:
- Crutches - popular in the Russian Federation, China, Japan, USA, Scandinavia when creating a link web. Simple and therefore reliable, lightweight, which means they do not heavily load the path, simplifying the installation and dismantling of the grating. But they also have disadvantages, the main one of which is relatively loose fixation, due to the fact that over time, under the influence of moving loads, the parts are pulled, which results in increased vibration and accelerated wear.
A special case on post-Soviet and Russian railways is the fastening of D. (decoding of which: D - for wooden sleepers). It is distinguished by the presence of a wedge-shaped flanged lining and two models of mounting elements at once. It holds the metal structure not only from lateral shifting, but also from tipping over, but it has the same disadvantage that for all fasteners of this type, the strength deteriorates over time.
- Screw - relevant in Western Europe (in particular, in France, Holland, Great Britain, Romania, Hungary). They are also not without their drawbacks: they have little resistance to unplanned removal and allow the lining to vibrate. But the reliability of the fastening covers everything: they are used to connect rails with sleepers because their resistance to pulling out is one and a half to two times better than that of crutch sleepers. Add here the convenient spin rate - 40-50% less.
Briefly about the sizes: the diameter of the most common screws is 22 and 24 mm, with a length of 150 and 170 mm, respectively.
Attention, both options are tough: during their operation, the contact between the parts is gradually broken, which leads to accelerated wear between the VSP elements. To prevent premature failure of the canvas, it is necessary to ensure an elastic connection, which is being steadily improved by designers from different countries.
Dimensions and types of dowel Butterfly
The most popular fastening option, it is widely used by both private craftsmen and construction companies. The difference between this element and the first is that the spacer elements are much larger - this results in a better quality fastening. In addition, there is a double tongue inside the product, which increases the strength of the screw fastening. Option for installing drywall using a butterfly dowel
- The screw must be screwed in all the way, only in this way the elements of the dowel will expand as much as possible and be securely fixed to the plasterboard wall. The work is simple and takes a minute, especially if a screwdriver is used for screwing.
Drywall is increasingly used in apartment decoration, so many home craftsmen are interested in the possibility of attaching various types of elements to it. There are many fasteners, but there is the most popular one - the TNF butterfly dowel for drywall. This element is used for fastening small, lightweight structures, and is the smallest. Good quality products are sold everywhere, and the price is no more than 50 kopecks. This element is not used as often as the next one. If we consider the sizes, then there are a large number of them, the difference is in diameter and length, so choosing the option that suits you is not difficult. Universal elements are slightly lower in strength than special ones, so if you need to hang a kitchen cabinet on plasterboard, it is better to use a Butterfly dowel nail.
Rail fastenings for reinforced concrete sleepers
Fastenings for reinforced concrete sleepers can be:
- lining and unlining;
- hard and elastic;
- separate and inseparable.
The following types are relevant:
- KB-65 is the most common (88.8% of the total), captivating with its service life of 50 years. Here the metal structure is pressed against a pair of rigid clamps and secured with embedded bolts. There are 2 linings - a flat metal one, on a special platform, and an elastic rubber one, in contact with the concrete.
- ZhBR-65P – with spring rod holders and a steel layer that reliably stabilizes the width of the web. For electrical insulation, a plastic void former is used.
- ZhBR-65Sh - with screws screwed into dowels and acting as clamps. The main advantage is the absence of unnecessary parts that would have to be periodically tightened, which means a reduction in operating costs.
- ARS is an anchor connection that is in demand on main lines at high traffic speeds. It is distinguished by its reliability, low material consumption, and ease of assembly, but does not perform well on curved areas.
- Also used are KD-65, Pandrol (English) and VOSSLOH (German).
The most common intermediate fastening for reinforced concrete sleepers is the separate KB fastening with rigid terminals. Typical split terminal-bolt fastening has been operating in the main track for over 50 years. In this fastening, the rail is pressed against the lining with two rigid clamps, and the lining is attached to the sleeper with two embedded bolts. The main disadvantages of CB fastening are its multi-part nature (21 parts), material consumption (41.6 tons of metal and 2.1 tons of polymers per 1 km of track) and a large number of bolts (16 thousand bolts per 1 km). Bolt tension weakens quickly, requiring regular and frequent inspection, lubrication and tightening.
Unlined elastic non-separable fastenings of reinforced concrete reinforced concrete with a rod terminal have greater stability of bolt tension than that of KB. The disadvantage of such fastenings is high labor intensity during assembly and insufficient stability of the track width in curves. Varieties of such fastenings are fastenings ZhBR-65P and ZhBR-65Sh.
In the modernized lining fastening ZhBR-65P, instead of flat terminals, spring rods and a metal lining are used. The unlined screw-dowel fastening ZhBR-65Sh has two screws that are screwed into dowels embedded in the sleeper and press the terminals to the base of the rail.
Photo of intermediate fastening of reinforced concrete on a screw
Scheme of reinforced concrete on a screw
Boltless anchor rail fastening ARS can operate on main lines at any speed and load intensity. Its positive qualities are high reliability and ensuring track width stability and low material consumption (metal savings of at least 15 tons per 1 km), ease of assembly. The fastening is inseparable, the main fastening element is a frame-arch type anchor embedded in a concrete sleeper. Fastening modifications of ARS-4 (Fig. 3.1) allows you to adjust the position of the rail in height up to 20-24 mm.
The main disadvantage of ZhBR and ARS fastenings is the insufficient provision of a stable track width in curved sections of the track, especially in steep curves. The reason for this is the poor quality of the polymer fastening elements.
Rice. 4.4. Integral elastic anchor fastening ARS-4
1 – elastic terminal; 2, 3 – monoregulator-fixer; 4 – terminal block; 5 – anchor; 6 – insulating corner; 7 – rubber gasket.
Photo intermediate fastening ARS 4
We examined in detail the purpose of rail fastenings, their main types and features, and the photos will also help you decide. To make the choice even easier, contact PromPutSnabzhenie for advice.
_______________________
We sell elements for railway tracks throughout Russia. We sell sleepers, railway fasteners, track tools, provide drilling, milling, cutting, welding, replacement services, and manufacture specialized products. On other pages of our website you can also find out the sizes you are interested in.