Road slab foundation: advantages and disadvantages
There are many types of foundations that are suitable for the construction of various buildings, but it just so happens that in our country people are trying to save money at all stages of construction, starting with the construction of the foundation of the building.
If you lay a road slab on a prepared soil base (GOST 21924-84), it will withstand light loads and light buildings
One of the economical options is a foundation made of road slabs, the advantages and disadvantages of which we will examine in more detail.
Features and advantages of road slabs for foundations
Using road slabs to build a foundation is a rather non-standard approach, since this material was originally intended to create transport links. Due to the initially built-in indicators of wear resistance and strength, such products have proven themselves well in the construction of lightweight and medium-heavy buildings.
Road paved with reinforced concrete slabs
Road slabs, as a basis for the foundation, have a number of advantages:
- can be used to create monolithic, strip and other types of bases;
- there is no need for a deep pit;
- have good load-bearing capacity, especially when erecting structures on heaving soil;
- can be used for laying foundations on weak-bearing, horizontally mobile, permafrost and soils with high water levels;
- laying requires a minimum amount of specialized equipment;
- has good heat and water insulation characteristics;
- the mass of the structure will be evenly distributed over the entire area of the slabs.
Based on all these points, we can say that a foundation made of road slabs is an excellent solution for the construction of buildings, especially if the soil under the future structure has certain problems.
In fact, there will be no seams in the finished base, since the space between the elements will still be filled with concrete mortar.
The final monolithic design will provide maximum grip, which significantly increases load-bearing capacity.
Slab foundations have become especially popular in the construction of frame houses. They are relatively light in weight, and the type of structure itself contains maximum resource savings.
This material can also be used for the construction of temporary buildings (summer kitchen), extensions (sheds, garages) and many other types of structures. True, for each of them you will have to determine the thickness of the layer.
For lightweight structures, a layer of 15 cm is sufficient, for heavier ones (two-story or more) - from 25 cm.
About the disadvantages of road slabs
Even seemingly ideal road slabs have their own set of disadvantages:
- quite often during the construction of a foundation, used materials are used, but it is very difficult to find used slabs, therefore, most likely, you will have to work with completely new products, and in terms of price they are several times more expensive;
- if you are not familiar with a road crane, you will have to hire and pay hourly for the work of both the machine and the operator;
- for sufficiently large quantities, you will have to deliver in stages or rent transport with a high carrying capacity;
- difficulties may arise when creating basements and storage rooms that will be located under the main structure;
- Despite the high waterproofing characteristics, it is still necessary to lay additional layers of insulating material.
Stages of laying a foundation from road slabs
The process of constructing the foundation of a building from road slabs is similar in its scheme to laying a monolithic foundation:
- First, thermal and waterproofing protection is laid.
- At the next stage, the slabs are laid directly (as tightly as possible);
- The joints between the slabs are filled with concrete (don't forget about the formwork).
- After the joint fill has completely dried, the surface of the slabs is also covered with concrete mortar.
- In the summer, the screed should be periodically wetted (not watered), and also covered with polyethylene until complete setting occurs.
Road slabs are one of the best solutions for building a foundation.
Laying road slabs as a foundation for a garage
Laying the foundation of your future home with their help is quite quick and easy, and the costs mainly relate to the purchase of materials and the use of crane equipment.
Simple and versatile road slab foundation for home | Hearth
The construction of frame houses is increasingly gaining popularity.
Moreover, if several years ago this technology was used exclusively for the construction of suburban seasonal buildings, now it is widely used in capital residential construction.
In the process of planning work, the first step is to choose a reliable and inexpensive foundation. Of the wide variety of types of foundations for a frame house, it is worth highlighting the foundation whose basis is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. This option is characterized by efficiency, speed and relative ease of construction.
The article contains information about how foundation slabs are used: their sizes and prices.
general information
Road slabs are reinforced concrete products intended for the construction of roads, railways, roads for heavy tracked vehicles and airfield strips .
They are used for the construction of road surfaces on particularly difficult soils , on heaving, peaty and swampy soils, soils subject to horizontal seasonal displacement.
During the construction of a capital highway , being an element of a “cushion”, the slabs are laid under the asphalt roadbed, forming a reliable foundation; use for temporary purposes means laying the elements directly on the top layer of soil and tying them together.
A similar foundation made of floor slabs is similar in structure to a monolithic reinforced concrete slab , but there are also some differences. It is a plastic reinforced concrete base located on a sand and gravel bed with insulation and waterproofing.
In order to get full-fledged support for a frame house, it is enough to pour a cement screed on top and wait for it to crystallize.
A reinforced concrete slab is also used for a block foundation .
Road slab foundations for houses are used quite widely:
- Regions of the Far North and areas with permafrost.
- Construction of houses on heaving and sandy soils .
- When building on soils with strong horizontal displacement .
- They are used in mountainous areas , where digging into the ground and driving piles to build other types of foundations is impossible.
- In addition, it is possible to use it on ordinary soils, in any climatic zone, but it is not economically feasible .
As can be seen from the list, this type of support for buildings can be used on almost any type of soil and in any climatic zone.
Important! A monolithic reinforced concrete foundation slab differs in its performance characteristics. Therefore, when planning a construction, it is necessary to choose the right thickness and type.
Types of road slabs
The monolithic reinforced concrete slab foundation, which is discussed in this article, is produced for different operating conditions, and therefore has different characteristics .
The most common types of road slabs used in foundation construction are listed below :
- Road slab (PD) 2P-30-18-10 . Dimensions 300*175*17 cm. Designed for temporary installation, load capacity 10 tons;
- PD 2P-30-18-30 . Dimensions are the same, load capacity 30 tons;
- PD 1P-30-18-10 . For permanent styling;
- PD 2P-60-20-30 . Dimensions 600*200*140 cm, load capacity 30 tons.
In addition to these, there are other specific types of slabs, for example, PAG , they are intended for the construction of airfields and are not used in private installation.
Concrete fencing slabs can also be used as a foundation.
Road slabs differ in the degree of tension of the reinforcement and the shape of the side edge , which is also unimportant when building a foundation for a frame house.
When installing foundations for private buildings, you can use all of the above types of road slabs. It all depends on the material used to make the building itself and its purpose. For example, to build a frame house, it is advisable to use slabs 14 cm thick due to its low weight.
If you plan to build a structure made of brick or concrete blocks , you need to use slabs with a load capacity of 30 tons and a thickness of 17 cm. The necessary parameters for each specific case must be correctly calculated.
Foundation calculation
Exact calculations are carried out by special organizations, but in individual construction, with a building height of no more than two floors, it is quite possible to do it yourself.
The thickness of the slab depends on the mass of the structure, that is, directly on the material of manufacture. The groundwater level , the calculated soil resistance, the area of the structure and the thickness of the sand-crushed stone cushion also
For example, let’s calculate the thickness of the road slab required to build a one-story house made of wooden beams, measuring 8*8 m :
- Let's calculate the total weight of the house . The volume of wood will be about 50 cubic meters. Wood density is 700-800 kg/cubic meter. From here the weight of the log house will be about 40 tons. Let's add the mass of the roof and insulation, as well as interior partitions, and we get 70-80 tons.
- The weight of the house together with furniture and other household items will be no more than 100 tons.
- Let's calculate the mass of the load per 1 square meter of foundation. The total area of the foundation is about 70 square meters. It turns out that the approximate load is 1400 kg per square meter.
- We select the thickness of the slab according to the reference book. The simplest slab, 14 cm thick and 6 m long, can withstand a load of up to 30 tons with an area of 12 square meters. One square meter can withstand up to 2.5 tons of load.
- Let's draw conclusions . That is, in the case of using this type of slab, there is approximately a double strength margin of the foundation, with the required margin being 1.3 times. Therefore, this brand of plates can be used.
Important! The foundation is laid using a monolithic reinforced concrete slab with careful adherence to the technology of the entire “pie” of the support. There is no point in calculating the load on the slab and building a house if the entire foundation of concrete slabs “floats” due to improper excavation work.
Technology
1. Preparing the area . The area of the proposed construction is cleared of debris and grass; if there are trees, they must be uprooted. Free passage is provided for the delivery and unloading of slabs.
2. Marking the territory . First, the extreme corner point of the future foundation is marked. The required length of the future building is measured from it.
Metal or wooden stakes are driven in at both points and a construction cord is pulled between them. Next, using elementary mathematical measurements, the next angle is found, and then the last, fourth. We connect all the stakes with a rope.
The final measurement is made by measuring the diagonals of the resulting quadrilateral. They must be equal.
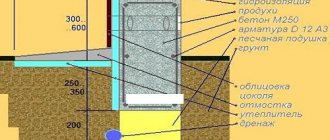
3. Excavation work . The first step is to dig a pit to the lower level of groundwater. This is approximately 1 - 1.5 meters, depending on the area.
The bottom of the pit is leveled and sand is poured on top in a layer of 40-50 cm. Every 20 cm of the layer must be watered and thoroughly compacted using a vibrating plate or tamper. At the same stage, all underground communications are installed .
A layer of geotextile is spread over the sand with a 20 cm overlap between the layers to prevent mixing of sand and crushed stone. A layer of fine and medium crushed stone , 30-40 cm thick, is poured onto the geotextile. It serves as a waterproofing agent and distributes the load from the slabs.
From above, the crushed stone is poured with cement milk until the gaps between the individual stones are completely filled. On top, the solution should cover the crushed stone with a layer of 2-3 cm. This is the so-called. footing.
4. After the concrete base has completely hardened, it is necessary to apply layers of waterproofing . Usually they use roofing felt in 2 layers, but other materials can be used. Strips of roofing material are overlapped by 5-10 cm and soldered with a torch or blowtorch.
Important! Waterproofing should be larger than the base area and extend beyond it by 40-50 cm.
5. Insulation is laid on the waterproofing layer . It is preferable to use polystyrene foam or penoplex. The thickness of the layer can vary from 10 to 15 cm, depending on the climate zone, but at the same time, the insulation should not be higher than the soil level. The joints of sheets of material are carefully coated with mastic or foamed with polyurethane foam.
Important! The heat-insulating material must have increased density, since it is the basis for laying reinforced concrete road slabs.
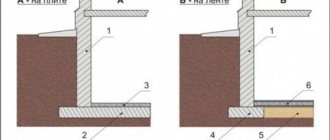
6. Installation of formwork . You can use ready-made formwork, or make it on site from boards at least 2.5 cm thick. The height of the formwork should be equal to the height of the slabs in the laid state plus 5 cm. Boards or panels are mounted along the entire perimeter of the foundation and carefully secured using self-tapping screws or nails
If desired, you can lay polymer insulation and the ends of the waterproofing remaining when laying it under the insulation inside the formwork. This will eliminate the need to carry out excavation work in the future to insulate the foundation.
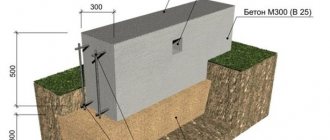
7. Laying road slabs . The slabs are laid on the prepared base using construction equipment. They are laid tightly to each other, a gap of 10 cm must be left only between the formwork and the edges of the elements.
8. After laying all the foundation elements, the surface is filled with concrete , grade not lower than M300. All joints between the slabs are carefully poured, a screed is made on top of the slabs, 5 cm thick using reinforcing mesh, with a cross-section of 5 mm and a pitch of 10 cm. The surface is carefully leveled.
9. After complete hardening (the reinforced concrete slab under the foundation hardens for about a month), the formwork is dismantled and is re-waterproofed over the entire area.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pros:
- Versatility . The foundation of road slabs can be constructed in almost any climatic conditions, on all types of soil, except for deep swamps. This is due to the large area of support on the ground, and, as a result, good stability of the entire foundation.
- Ease of laying the foundation . During construction, basic tools and a minimum of theoretical knowledge are used. The work is the same and uncomplicated.
- Strength and reliability comparable to the characteristics of a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation.
- Economical . With similar performance characteristics, such a foundation will be one and a half to two times cheaper than a monolithic one.
- The construction time of such a foundation is short and comparable to the labor hours required to build a strip foundation, with incomparably better characteristics.
Minuses:
- When purchasing used materials, there is no way to assess their residual quality.
- To deliver products to the construction site and place them in the pit, it is necessary to use heavy equipment.
- When using this type of foundation, it is not possible to equip a basement or basement.
- The impossibility of replacing or repairing the underground utilities of a house without significant dismantling of the foundation.
Photo
See what a foundation made of road slabs looks like in the photo below:
Check out the process of laying road slabs visually in the video below:
conclusions
The construction of a foundation from road slabs is a balanced, reasonable decision that allows you to build a relatively inexpensive foundation with impressive reliability characteristics in a relatively short period of time . This solution will be ideal when building a frame house in any area.
Pillows made of other materials for the base of the foundation
The maximum thickness of the sand cushion is taken to be equal to three times the width of the tape. And the usual thickness is about 20 cm. It is allowed to use other materials that are not heaving and resistant to shrinkage to fill the base of the trench under a strip foundation or foundation pit. A crushed stone pillow is good to use. it is much better quality than a sand pillow. The crushed stone fraction is much larger (from 20 mm) and better resists heaving and shrinkage of the foundation. To install a crushed stone cushion, you must first fill the trench or pit with a layer of coarse sand up to 20 cm. That is, first a sand cushion is made, and a crushed stone layer on top. The sand is compacted well, then crushed stone is poured in, its layer is up to 25 cm and is also compacted well. There should be a minimum gap between crushed stone fractions. Just like for compacting sand, a vibrating plate is used for crushed stone. The area of the crushed stone backfill must exceed the area of the foundation base by 20 cm in each direction. The crushed stone backfill should end at the zero level of the foundation; this is where concrete pouring begins. If a sand cushion is not always used, then for individual buildings a crushed stone cushion is used for any number of floors in the building and from any materials. A concrete foundation cushion is the most reliable and durable of those listed, but its cost is much higher. Its production occurs as follows: • On the previously prepared bottom of a trench or pit, covered with crushed stone, leveled and compacted, formwork is installed around the perimeter. Its height corresponds to the height of the concrete layer (about 30 cm). • The concrete foundation cushion is reinforced with rods up to 12 mm thick, for greater strength and reliability. • Upon completion of the preparatory work, the cushion under the foundation is poured with concrete, followed by compaction with an in-depth vibrator. The area of the concrete pad should exceed the area of the foundation by 20 cm in each direction. Tools used: • Level; • Cord; • Vibrating plate; • Deep vibrator; • Hammer; • Shovels; • Welding machine; • Bulgarian; A concrete foundation cushion undoubtedly has higher strength properties and is capable of supporting not only individual cottages of any number of floors, but also being a support for multi-apartment buildings.
Road slabs for the foundation - positive and negative features of construction technology
Monolithic type foundations are considered quite common, but their cost is quite expensive. In an effort to save money, many developers try to use ready-made road slabs for the foundation, which are laid along the entire perimeter of the property.
Experts are still debating how feasible and safe such a solution is, especially during the construction of large facilities.
Before building such a foundation, it is necessary to clarify the characteristics of reinforced concrete products and understand the scope of their application in order to eliminate possible errors when laying the foundation of a building.
Areas of use
The scope of application of such plates is very wide. It is a mistake to believe that they are used exclusively for laying the rough foundation of highways.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pJkLoqCvt1Y
Products are used in various economic fields:
- for the construction of roads in the northern regions and in areas with cold climatic conditions, where the temperature reaches forty degrees below zero. Such slabs are also laid in swampy areas, rolling a layer of asphalt on top;
- the base is made from slabs for the construction of temporary access roads for heavy equipment;
- road slabs are used in the construction of garages, sheds and bathhouses. In these cases, a high base is not suitable. In addition, the foundation of road slabs will become the basis for the floor and will contribute to uniform shrinkage of the entire object.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of road slabs for foundation construction is a non-standard solution, because from the very beginning such material was intended for laying roads. Due to the fact that the slabs have a good indicator of strength and wear resistance from the very beginning, the products have proven themselves to be excellent in the construction of light objects.
Slabs used as a foundation have certain advantages:
- They are used for the construction of monolithic, strip and other types of foundations;
- there is no need to build a deep pit;
- The slabs have good load-bearing capacity. This is especially true if the object is being built on an area with heaving soil;
- slabs are used when constructing foundations on weak-bearing, horizontally moving soils, in places with shallow groundwater;
- work is carried out using a minimum amount of special equipment;
- the slabs have good heat and moisture insulation properties;
- the weight of the structure is evenly distributed across all slabs.
It turns out that foundations on road slabs are a good solution when constructing buildings in areas with problematic soils. There will be no seam areas in the finished base, because the free space between the slabs will be filled with concrete mixture.
Particularly popular is the foundation made of road slabs for garages, frame houses, and outbuildings. Only for each object is determined the thickness of the slabs, which can vary from fifteen to twenty-five centimeters.
It is fair to note that slabs for road construction have certain negative aspects:
- Quite often, when arranging the foundation, slabs that have been in use are used. They are difficult to find, and they mostly work with new elements, the acquisition of which is quite expensive;
- You will have to rent a crane for installation. If there are a lot of slabs, they are delivered to the construction site using special equipment in several stages;
- difficulties arise when arranging basements and storage rooms planned under the base of the facility;
- there is a need for an additional waterproofing layer.
Technological features of construction
It is very important to complete the entire range of calculations and design work.
Having prepared the documentation and purchased all the necessary building materials, you can begin work. After preparing the construction site and arranging the entrances to it, the foundation is marked. At turning points, pegs are hammered along which the cord is pulled. The correctness of the geometry is checked by measuring the lengths of the diagonals.
The technology for constructing a slab foundation from road slabs is as follows:
- the sand base is poured onto the pre-compacted soil;
- a waterproofing layer is installed to protect the slabs from the negative effects of moisture. It is also recommended to install thermal insulation to retain thermal energy in the living space;
- slabs are laid on the prepared base, the joining areas are filled with concrete mixture;
- the final stage is a screed, which ensures the integrity of the entire structure and guarantees the reliability of the foundation. When it hardens, you should control the air temperature and humidity level by covering the concrete or periodically moistening it.
Work order
Let's take a closer look at the algorithm of actions when installing a strip foundation on road slabs.
Excavation
All construction work begins with site preparation and marking. In accordance with the design specifications, pegs and cords mark out the perimeter of the foundation base, check the correctness of the angles and the evenness of the diagonals.
After this, a pit is prepared to the required depth, for which you can use an excavator or do everything manually.
The bottom of the excavation is leveled, a sand cushion from twenty to twenty-five centimeters high is arranged, everything is carefully compacted.
Waterproofing and insulation
The sand is covered with waterproofing roll material, and thermal insulation material is laid on it to minimize the loss of thermal energy through the concrete base. The role of waterproofing is performed by roofing felt material, laid in strips with an overlap of ten to fifteen centimeters, the seams are filled with mastic and sealed with a gas burner.
The side edges of the roofing felt layer should extend onto the walls of the prepared pit to ensure good tightness.
Foam plastic material or extruded polystyrene foam is used as insulation.
With the help of roofing felt, concrete is protected from the negative effects of moisture and its penetration into the room. Polystyrene foam reduces heat loss.
Installation of slabs
Having poured a sand layer, covering it with waterproofing and heat-insulating material, they begin to lay road slabs. For this work, you will need to rent lifting equipment, since the slabs are quite heavy. During installation work, all elements of the supporting base are placed tightly to one another.
Concreting
Once the laying of the slabs is completed, perform the following steps:
- install the formwork structure, fixing its panels with stops. The boards are made from edged boards 25 mm thick, connected to the bars with nails;
- mix or order concrete mixture for delivery;
- all seam areas are filled with mortar;
- arrange a three-centimeter screed, leveling the concrete with rules and trowels. During the work process, the level of the rough foundation is controlled;
- As soon as the concrete has reached the required strength, the formwork panels are dismantled. Typically this takes at least four weeks.
If you prepare the solution yourself, then cement, sand and fine crushed stone are mixed in a ratio of 1 to 3 to 2. Mixing is carried out until a mass of homogeneous consistency is obtained. For additional strength, a reinforcing mesh is placed on top of the slabs, along which the screed is placed.
Recommendations from experts
To build a high-quality foundation for a house from road slabs, you must follow certain rules. Their practical implementation will provide the base with a long operational period.
Experienced builders advise:
- use high-quality materials when carrying out construction work;
- for the manufacture of formwork panels, take planed boards of the same thickness;
- the minimum grade of concrete mortar used for sealing joint areas is M 300. This will give the supporting structure additional strength and improve the adhesion of its elements;
- laying of road slabs is carried out under the entire building to minimize pressure on the soil;
- if bitumen is used to install a waterproofing layer, then it becomes possible to save a certain amount of money;
- a sand cushion is considered a mandatory element on clay or loose soils.
If you follow construction technologies and the advice of experienced craftsmen, you can build a reliable and durable reinforced concrete base from road slabs. In terms of strength, such a foundation is inferior to its monolithic counterpart, so it should be used for objects that do not create serious load effects.
From an economic point of view, a slab foundation is cheaper, and it does not take much time to equip it. The load must first be calculated in order to determine the thickness of the road foundation slabs.
These precautions and compliance with all technological features will help you avoid deformation and deformation of the foundation laid from road slabs.
Construction technology
To build a foundation from road slabs you will need:
- linear and water levels;
- Bulgarian;
- shovel;
- screwdriver or drill with attachments;
- hook for tying reinforcement;
- roulette;
- mason's trowel;
- pegs and construction cord;
- tamper
Before starting work, the site chosen for construction is prepared, during which garbage is removed and the area is cleared of excess vegetation. Further work consists of several stages. The video discusses in detail all the steps of constructing a slab foundation.
Marking the site and digging a pit
It is carried out using stakes and construction cord in accordance with the design features and overall dimensions of the house or garage. After marking, you need to make sure that the length of the diagonals of the outlined area is the same, and the angles of the resulting figure are equal to 90 °.
Then they begin to dig a pit using shovels or special equipment. Sand is poured onto a flat bottom in a layer of 20-25 cm and compacted thoroughly, periodically moistening it. The result is a sand cushion with a smooth surface.
The depth of the pit is calculated so that its bottom is 20-25 cm below the groundwater level. The value of this parameter depends on the region of construction and on average is about 1.5 m.
Waterproofing and insulation
Waterproofing is laid on top of the sand cushion, which can be used as roofing felt and other rolled materials. To ensure high tightness, it is laid out overlapping along the entire bottom, extending 10-15 cm onto the walls of the pit. After watching the video, you will examine in detail the entire range of waterproofing works.
Then a layer of thermal insulation is laid, which will help reduce heat loss through the concrete slab.
Preparing the base for laying road slabs
At this stage of foundation construction, formwork is prepared using boards more than 25 cm thick. Shields are assembled from them using nails and screws, which are installed around the perimeter of the pit.
To prevent the formwork from moving, it is additionally secured with struts or pegs. To insulate the ends of road slabs, a layer of thermal insulation should be secured to the inside of the formwork.
A frame is placed on top of the insulation, which is constructed from steel profiles with a ribbed surface and a diameter of at least 12 mm. The assembly of the reinforcement can be done using a special hook and binding wire or welding joints. The first method is labor-intensive, but allows you to obtain a flexible and durable frame. The use of welding helps reduce construction time, but the connections are less reliable.
Road slab foundation for home
The construction of frame houses is increasingly gaining popularity.
Moreover, if several years ago this technology was used exclusively for the construction of suburban seasonal buildings, now it is widely used in capital residential construction.
In the process of planning work, the first step is to choose a reliable and inexpensive foundation. Of the wide variety of types of foundations for a frame house, it is worth highlighting the foundation whose basis is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. This option is characterized by efficiency, speed and relative ease of construction.
The article contains information about how foundation slabs are used: their sizes and prices.
Foundation on road slabs
Road slab base
A road slab foundation is a cheaper analogue of a slab foundation. It is suitable for the construction of relatively light structures: small houses, garages, bathhouses, outbuildings.
Factory-made reinforced concrete slabs are laid completely under the entire structure in areas with different types of soil. Compared to a monolithic slab foundation, the construction time of the foundation is also reduced, but it cannot be done without lifting equipment.
Compliance with simple technology allows you to build a support structure with fairly good performance characteristics.
Scope and calculation of foundations made of road slabs
Road slabs are used as a foundation for construction in areas with soil that has low bearing capacity or is highly moist. Such a foundation is also suitable when there is significant freezing of the soil, or when there is a possibility of horizontal movement.
Road slabs
Ready-made road slabs are high-strength reinforced concrete products that are resistant to a variety of external destructive influences. They are used as a foundation for light structures:
- low-rise houses, dachas and cottages (up to 2 floors);
- garages;
- courtyard buildings (sheds, summer kitchens);
- baths
When they are used, pressure from the structure to the ground is transmitted evenly over the entire supporting area.
Before starting construction, it is necessary to determine the thickness of the base. It is determined by the magnitude of the future load on the supporting structure. So, for a garage or shed, a foundation with a height of up to 0.2 m is sufficient, but for a house this parameter should be more than 0.25 m.
When calculating the base parameters, take into account:
- the weight of the future building with all equipment, furniture and other items;
- snow load;
- soil properties;
- climatic features of the region.
Due to the large support area, the base of road slabs has a high load-bearing capacity. The individual elements are connected to each other using reinforcement, which ensures good structural rigidity.
The heavier the building, the more massive the foundation for it should be. The thickness of the supporting structure determines the stability of the structure being built. Road slabs produce a solid base that can withstand fairly large loads.
Pros and cons of the foundation
Road slab foundations have both advantages and disadvantages. They are presented in the table below.
No.AdvantagesDisadvantages
| 1 | simplicity and relative speed of construction | It is necessary to use lifting equipment during construction |
| 2 | high degree of strength of the erected supporting structure | it is problematic to determine the quality of used building materials |
| 3 | lower cost compared to a monolithic reinforced concrete base | limited weight of the structure being built |
| 4 | small amount of excavation work | the construction of a basement is often not provided for |
The popularity of the material is due to its relative cheapness and ease of installation. It is better to use new products with established quality for the house, and used building materials are suitable for outbuildings.
Laying slabs
Construction technology
The technology involves carrying out work in several stages. Initially, you need to stock up on the following required tools and devices:
- grinder;
- level (laser, water or construction);
- bayonet and shovel shovels;
- mason's trowel;
- crowbar;
- tamping;
- cord (rope), pegs;
- roulette.
Schematic representation of a slab base
The technology for constructing a supporting structure for a building from a road slab is similar to creating a monolithic slab. The pre-built area is cleared of debris, stones and vegetation.
Carrying out excavation work, waterproofing slabs and insulation
Construction work begins with marking the construction site. According to the plan, stakes and rope mark the perimeter of the foundation. In this case, the diagonals of the resulting contour must be equal to each other, and the angles must correspond to 90 °.
Laying insulation
After marking, they dig a pit with shovels or an excavator of the required depth. Then the following work is carried out:
- cover the leveled bottom of the resulting excavation with a sand cushion 0.2-0.25 m thick, which is carefully compacted, regularly moistening it;
- the sand is covered with a waterproofing coating on top;
- thermal insulation is laid on it to minimize heat loss through the concrete floor;
Roofing felt and other rolled products are often used as waterproofing materials. The strips are laid with an overlap of 10-15 cm, and the seams are sealed with a burner. At the same time, the sides also extend onto the walls of the pit. This ensures a high degree of tightness.
The insulation can be polystyrene foam or extruded polystyrene foam. The ends of the slabs are also thermally insulated.
The sand cushion, and accordingly the soil underneath it, should be well compacted to reduce the likelihood of subsidence during further operation of the building.
Waterproofing will protect concrete from the destructive effects of moisture and eliminate the penetration of dampness into the house. Insulation helps reduce heat loss through the concrete floor of a building.
Installation of slabs and concreting
After laying the sand cushion, waterproofing and insulation, the installation of the slabs begins. For this, different lifting equipment is used, since these reinforced concrete products are heavy.
Installation of slabs on a waterproofing coating
During installation, the elements of the supporting structure are placed tightly to each other. When all the foundation has been laid out, then do the following:
- install the formwork, fixing it with stops;
- prepare concrete solution;
- seal all the seams with it;
- make a screed layer of about 3 cm, leveling the solution using a rule and a trowel;
- periodically moisten the concrete (so that it sets evenly) and cover it with plastic film;
- After the screed has gained the required strength, the shields are dismantled.
- For formwork, lumber 2.5 cm thick is suitable. The boards in the panels are connected using self-tapping screws or nails.
A small gap is left between the formwork and the foundation structure for filling with mortar.
During work, check the level of the subfloor to ensure it is level.
The concrete will fully set in about a month (the time depends on the climatic characteristics of the region). Only after this they begin to build the building.
High quality material
You can prepare the working solution yourself or buy it ready-made. In the first case, you will need cement, sand and small crushed stone. The components are mixed in a ratio of 1:3:2, respectively. Stir the solution until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
You can lay a reinforcing mesh on top of the slabs, and make a screed on top of it. This will further strengthen the structure.
Pros and cons of the foundation
A foundation built from road slabs has both disadvantages and advantages.
The main advantages of a slab base include:
- Simplicity and relative speed of construction;
- High degree of support strength;
- Lower price compared to other building materials;
- Small volume of earthworks.
The disadvantages include, first of all, the use of special lifting equipment during construction.
An important disadvantage of using reinforced concrete slabs is the limitation on the weight of the structure being built.
In addition, during construction it is often difficult to determine the quality of building materials that have already been used. But when constructing small outbuildings, raw materials from other objects are often used. The increased popularity of this material is due to its ease of installation and relative cheapness.