Types of reinforced concrete slabs
When constructing roads, road concrete slabs are used that are resistant to various climatic conditions.
Cornice concrete slabs with increased density are used for the installation of balconies and loggias. They have a special type of support and additional functional holes. When installing balconies and loggias, such products are clamped into the brickwork of the walls and welded to the fittings of the lower floor.
Floor slabs, used in single-story and multi-story construction, are the most popular type of concrete slabs. This is a kind of semi-finished construction product, thanks to which the process of erecting building structures is accelerated and simplified.
The advantages of reinforced concrete floors are:
- fire resistance;
- sound and thermal insulation;
- durability and strength;
- ceilings are not subject to rotting and corrosion, and are not afraid of moisture;
- standard sizes;
- in each individual case, you can easily select ceilings of a suitable model and size;
- thanks to the flat surface it is easy to carry out finishing work on them;
The disadvantages of concrete floors include the need to use special equipment during construction. Concrete floors can only be laid using a truck crane.
For the construction of low-rise buildings, lightweight types of concrete floors are chosen, and for high-rise buildings, heavier types are chosen.
How to transport reinforced concrete products
Reinforced concrete products are considered the standard of strength. Even in everyday life, people, wanting to emphasize the inflexibility and perseverance of a person, say that he has a reinforced concrete character.
However, despite its excellent reputation, reinforced concrete is a rather fragile material. Therefore, when delivering it and performing loading and unloading operations, it is necessary to follow the established requirements.
Transportation, loading and unloading can be carried out in various ways, the most important thing is to choose the right technical means for this. It is preferable to use cranes for loading and unloading operations, and flatbed trucks for transportation. The following option is possible - using a truck equipped with a crane. In this case, there is no need to use additional units; all work can be performed using one piece of equipment.
Transportation of reinforced concrete products over long distances is usually carried out by rail. Universal gondola cars are used as trains. They carry out transportation of packaged concrete products, which do not need to be specially protected from negative external influences. In addition, platforms are used. They accommodate reinforced concrete products, which also do not need protection from various atmospheric influences.
Loading and unloading operations and transportation can be performed using any technical means. The most important thing is to achieve the main goal, which is to ensure that all products reach the customer safe and sound. It must be taken into account that if all requirements are not met, the strength of concrete products may deteriorate, which will lead to a reduction in their service life.
The main mistakes made during transportation
People involved in the transportation of reinforced concrete products make several basic mistakes, the consequences of which can be irreparable. Among them:
- Incorrect placement of products on the truck. The products must not be in close proximity to each other. Even slight shaking caused by slight unevenness in the road can at least lead to the appearance of small defects. But sometimes all transported products can be hopelessly destroyed. In this situation, even a perfectly flat road will not save you. Contact of products, and, consequently, their mechanical damage, will be almost impossible to avoid. As a result of such “savings,” there is a high chance of receiving a defective product.
- Shocks should be avoided during transportation. Although reinforced concrete products have excellent strength, they can be destroyed by impacts. The reason is that reinforced concrete products are manufactured in accordance with the loads that they will have to experience during operation. The impacts that the products may be subjected to during transportation are not included in the design. That is why, if they experience shock loads on the road, the result can be very negative. Concrete products may have cracks in the base, sometimes quite large, or chips. Reinforcement may be exposed. All this leads to losses. If such destruction occurred due to the fault of the supplier due to violations of transportation rules, the company should be required to provide material compensation for the damage incurred or replace damaged concrete products.
- Loading and unloading operations lead to unpleasant consequences if they are performed incorrectly.
It should be remembered that it is imperative to avoid impacts, since reinforced concrete products do not tolerate this.
Rules for transporting reinforced concrete products
To ensure that reinforced concrete products are delivered to the customer safe and sound, it is recommended to follow a few simple rules:
- Correct loading. This will be the key to successful transportation. When loading, it is advisable to leave all products in the position in which they are intended to be used. It must be taken into account that their longitudinal axis should be located in the direction of movement.
- To best protect the product from possible damage that may result from shock loads, it is recommended to use wood spacers. They are placed between products. When placing structures, you need to ensure that no unnecessary stress appears in them. It can cause further deformation of concrete products.
- On the road, it is necessary to ensure good protection of products. If transportation over long distances is intended, it is necessary to ensure that the conditions on the road are almost the same as during storage. A material such as reinforced concrete is sensitive to prolonged exposure to moisture. Water can cause the formation of fungi and mold, which have a destructive effect on the material and worsen its mechanical qualities. To eliminate this possibility, it is advisable to cover the products with some kind of waterproof film.
- Each piece of cargo must be approached individually. There are many reinforced concrete structures, the transportation of each of them has its own characteristics. Usually, the delivery of floor slabs does not cause any difficulties, but channel slabs are very sensitive and require extreme care. In order not to damage such cargo on the road, reinforced concrete channel slabs must be placed during transportation in pencil cases that are specially designed for
such a situation.
- Punctuality - delivery must be made strictly on time. It is necessary to organize transportation in such a way that the customer receives the products he needs no later than the agreed time. Clients' interests must come first.
- Accuracy, pedantry. During loading, on the road, and unloading operations, you need to remember the end result.
If all these rules are followed, the risk of damage to products is reduced to zero, and the cargo will be successfully delivered to the client.
Types of reinforced concrete floors
Concrete slabs vary in the types and quality of concrete they are made from.
Hollow core slabs are made of heavy concrete. Inside them there are longitudinal cylindrical holes (air chambers). They reduce weight, thereby reducing the load on the foundation and increasing the speed of building construction. You can hide means of communication inside them. The voids form an internal frame, which increases the strength of the slab and the durability of the entire structure. In addition, the transportation and installation of the slabs is simplified.
The disadvantages of hollow reinforced concrete slabs include their lower strength compared to monolithic slabs. Hollow slabs are used in the construction of cottages, garages, warehouses, and office centers.
Monolithic - the heaviest and most durable types of reinforced concrete floors. Their advantages are ease of manufacture and installation, as well as high load-bearing capacity. Disadvantages: high sound permeability and cost of the product. Such overlaps are difficult to produce in winter due to prolonged hardening.
Monolithic slabs are used for the installation of heating mains and the construction of massive structures.
Ribbed have longitudinal ribs. Their profile resembles the letter P. They do not form a flat surface, so they are not used in multi-story construction. The advantage of ribbed floors is their ability to withstand high loads, especially bending.
Mushroom-shaped concrete floors are slabs with a thickness of 15 centimeters, supported by edge and internal columns. Due to the thickenings around the column heads, this design resembles a mushroom in shape.
How to properly transport and store (store) reinforced concrete floor slabs?
Question: How to properly transport and then store (store) reinforced concrete floor slabs for building your house?
Quite often, the developer is faced with the task of purchasing large-sized reinforced concrete products, for example, floor slabs. Often, prefabricated reinforced concrete hollow slabs of the PC type are used to cover private residential buildings. Initially, factory-made reinforced concrete products (RCP) are distinguished by a high degree of reliability, comply with the declared strength characteristics and have high quality indicators. However, their transportation and storage can play an important role in preserving the integrity and performance properties of these products in the future. Also, the consumer does not always have the opportunity to purchase concrete products directly from the manufacturer and uses the services of intermediaries.
As practice shows, defects and damage to reinforced concrete products can often occur due to two reasons:
- violations of delivery rules;
- improper stacking and storage of slabs.
Transportation of reinforced concrete floor slabs
It should be noted that reinforced concrete products receive corrosion damage much less frequently than mechanical damage that can occur during their transportation. Transportation of reinforced concrete slabs is mainly carried out by trucks, taking into account the relevant transportation requirements. Floor slabs are stacked in the car body. Stacking more than four slabs is prohibited. Loading and unloading of products is carried out by lifting crane equipment. If the transportation of reinforced concrete floor slabs is disrupted, they can receive significant damage and become unsuitable for further use. The procedure and methods for transporting reinforced concrete floor slabs are prescribed in section 4 “Transportation and storage” of GOST 9561-91.
For reliable transportation of the slabs, it is necessary to transfer them with wooden blocks . The folded slabs must be loaded on top with concrete blocks. This, the safest type of transportation of reinforced concrete slabs, will ensure delivery of products to the consumer with the least number of defects. Definitely, this method of transportation will prevent the formation of cracks, chipping of the concrete slab and exposure of reinforcement. Suppliers with a good reputation often include delivery in the price of a floor slab and do not violate transportation rules.
Storage of reinforced concrete floor slabs
Before reinforced concrete slabs are installed in the designed position, they may be exposed to harmful environmental influences for a long time. Concrete is a porous material and can become saturated with moisture, for example, when storing products directly on the ground, or under direct exposure to precipitation. In this case, irreversible damage can occur when the concrete is saturated with moisture during alternating temperature fluctuations (freezing-thawing). Also, with periodic soaking of reinforced concrete products, a leaching process (corrosion of cement stone) may occur, which negatively affects the strength of the concrete slab and the load-bearing capacity of the product as a whole.
Therefore, if the slabs are stacked for long-term storage, then care should be taken to cover the top of the stacks of slabs with waterproofing materials:
- polyethylene film;
- roofing felt;
- used sheets of slate or roofing steel, etc.
When storing, the slabs should be stacked in stacks not exceeding 2.5 m in height, with the mounting loops at the top. According to its purpose and final position, the reinforced concrete floor slab must be stored in a horizontal position on a flat surface.
To prevent the formation of cracks in the body of reinforced concrete slabs, they should be laid with wooden spacers-bars. Wood blocks should be placed under the bottom row, as well as between the products, at the locations of the mounting loops. Thus, the pads must be placed directly under each other. It is this storage scheme that corresponds to the design scheme at the time of lifting the slab by crane, which the design engineer accepted when calculating it.
Before storing slabs, the following preparatory work must be carried out:
- choose the right location for stacks on your site. It should be remembered that stored structures should not interfere with the passage of equipment and excavation work. The slabs must be stored in such a way that a crane with a certain boom reach is able to move the slabs from the stacks to the design position from certain stops. The slabs should not be stored in close proximity to the boundaries of the pit or trenches (there is a danger of the soil of the walls of the pit and trenches sliding). You should also choose a fairly flat area with a slight slope; if the site has a significant slope, then the slabs should be stored across it. If there are a lot of stacks, then passages between the stacks should be about 800 mm wide. For the convenience of installers, the slabs should be stored so that the markings and signs are clearly visible (the slabs are marked on the longitudinal ends of the slabs);
- prepare a storage area. If necessary, level the area; ensure unhindered entry of a truck and a truck crane into the site;
- prepare linings for slabs of wooden beams.
When storing slabs, they should be properly sorted when stacked. Since builders build houses from bottom to top, and not vice versa :), it is necessary to store slabs at the top of the stacks, which will be installed earlier than the slabs laid in the lower areas of the stacks. This way you will be able to avoid additional financial and time costs that will be required when relaying the slabs at the time of installation.
Also, when storing, slabs of the same length and width should be stacked.
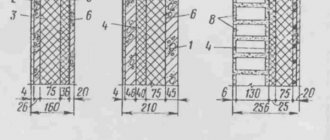
Let's look at violations of the rules for storing slabs and the consequences of such storage using a specific example.
Photo 2. Typical errors when stacking and storing floor slabs: 1 – the bottom wooden lining is insufficiently thick; 2 - the linings are not located one under the other; 3 – slabs of different lengths are stored in stacks; 4 - the stack is not covered with waterproofing material on top (this is done during long-term storage of slabs); 5 – no bottom lining made of wooden beams
Photo 3. A crack in the upper zone of a round-hollow floor slab that occurred due to improper storage. A damaged slab is unsuitable for further installation (another floor slab must be purchased and delivered).
We hope that this article will help you avoid mistakes when transporting and storing reinforced concrete floor slabs and you can easily build your dream home without extra costs.
You were advised by GIDproekt experts
Ismagilov Andrey Olegovich and Nechaev Kirill Vladimirovich
Marking
Even a superficial acquaintance with the technology of manufacturing floor slabs shows how different they can be. And for a full understanding of the essence of each product and its purpose, it is important to be able to read the labeling. It is by no means spontaneous; on the contrary, manufacturers are obliged to follow the instructions of GOST 2016. The usual notation is:
- type of structural element and product;
- length;
- width (height is always the same, so it is not written down);
- permissible load-bearing level (1 unit equals 100 kg per 1 sq. m);
- category of fittings;
- other parameters.
The last group includes information about:
- resistance to caustic and aggressive substances;
- seismic resistance;
- low temperature resistance;
- embedded elements or special holes.
The letters P, PTS or PP indicate a full-weight monolithic product. Behind the abbreviation PG or PR are hidden solid ribbed slabs. If a slab is marked as PV, then this means a continuous finned slab with ventilation openings. When preparing holes for lights, the designations PS or PF are used. The combination of PL symbols means that the ceiling is designed for an easily removable roof.
An easily removable roof made of arched and vaulted ribbed slabs can be labeled as POS, POV, POF, POL. As for hollow core slabs, they are marked by the number of points on which the slab rests. Products of class T rest on 3 sides, and products K - on all four. If there is no letter at all, this means that the structure is designed to be supported on both sides. PC and PG slabs differ from other hollow core slabs (PV) in their production method.
PG, PC - means pouring into the formwork structure. But PB means molding on a continuous conveyor. The result is smoothness and security at a very high level. In addition, the PB has no significant length restrictions. Therefore, such slabs can be used in places with atypical dimensions.
But the molding plate has relatively narrow openings. Drilling of such products is not allowed, therefore laying communications through them is impossible. In addition, the markings indicate the type of concrete. The letter C stands for increased resistance to seismic shocks, and the letter I stands for cellular materials.
Further:
- M - fine grain;
- C - dense silicates;
- L - lungs;
- F - resistance to heat;
- P - sand concrete;
- N - normal permeability.
In practice, there are no regulated grades for a series of hollow core slabs. However, their description may indicate some parameters.
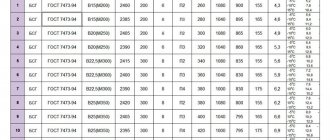
Thus, the marking PC 15-13-10 PC is a number of technical characteristics, such as:
- 15 is the length of the structure in decimeters.
- 12 - thickness in decimeters.
- The number 10 is the most important and indicates a permissible load of 10 kg per 1 dm2.
Types and features according to the method of support
Construction norms SNiP regulate the possibility of supporting floor slabs on walls on 2, 3 and 4 sides. But here everything depends on the type of reinforced concrete products and the design features of the reinforcing frame. Thus, reinforced concrete products of the PB brands can only be supported on 2 sides, while PCs are produced in several types depending on the number of supporting sides.
On both sides
The support for such products is provided by 2 opposing wall structures. Laying is carried out on the narrow sides, since the reinforcement is made in the longitudinal direction.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Shelf life of chicken eggs: Rules for storing homemade and store-bought eggs according to GOST at home at room temperature
Figure 6. Supporting reinforced concrete on 2 sides
On three sides
These slabs are designed to cover U-shaped spans in the corners of buildings. The possibility of installation on 3 sides is ensured thanks to reinforced end reinforcement.
Figure 7. Laying the product with support on 3 sides
On four sides
Precast concrete products of these types are usually used in complex structures where optimal distribution of increased loads is required, and in the construction of additional superstructures. Due to the presence of a reinforcing frame at all ends, hollow-core floor slabs can be supported on 4 walls.
How to buy floor slabs
1. Send your application for the supply of reinforced concrete to the supplier in writing and be sure to wait for the invoice to be issued. Check it for a list of items and item quantities. This will eliminate any misunderstandings when actually receiving the slabs. The wrong size or the wrong quantity can lead to additional delivery or exchange, which in the case of such large cargo will cost a pretty penny.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Installing a polycarbonate greenhouse: what you need to know
2. Be sure to ask the seller for the name of the direct manufacturer of the material. You can go to its website and check reviews about product quality and see its reputation.
3. Pay attention to the brand of concrete used to cast the slabs and its quality.
4. Request a quality passport for the goods supplied to you.
Quality certificate for floor slabs
5. When receiving the slabs, count their number and be sure to carry out an external inspection of them for possible defects, such as cracks, chips, etc. If there are any, notify the supplier about this and draw up a defect report with signatures of inspection witnesses. Perhaps this paper will be very useful to you in the future.
How to make
Hollow-core floor slabs are manufactured using different types and series of concrete. Among them:
- Silicate.
- Lungs.
- Heavy.
When producing hollow structures based on the listed types of concrete mixture, different technologies and methods are used:
- Without formwork. For the manufacture of such products, automated equipment is used that supports the vibration compaction function. The workpiece gradually passes along the line and is processed using automation, which gives it the correct geometry and overall dimensions of the hollow core slabs. In order to increase the density, the structure is equipped with reinforcing ropes.
- With formwork. The concrete mixture is placed in a standard metal formwork with metal rods and reinforcement. When hollow core slabs undergo the compaction procedure, they are treated in hydrothermal chambers. Upon completion of the steaming process, the products are removed from the formwork and left to harden.
The second method is considered more popular because it is performed without the use of complex equipment and technologies. In most cases, it is used in industrial enterprises where reinforced concrete hollow-core slabs are produced. The presence of reinforced elements increases the strength properties.