If you plan to build a house on a site with significant differences in height, with a high groundwater level to the surface of the earth, as well as in an area where clay soils predominate, then it is preferable to use a pile foundation. In suburban housing construction, as a rule, they prefer to build screw-type pile-grillage foundations, which have a long service life, have good load-bearing capacity, and do not require large consumption of materials.
Waterproofing such a foundation is an obligatory stage in construction, since, despite the fact that pile manufacturers guarantee their durability, metal or reinforced concrete, under the influence of moisture and groundwater, undergo rapid destruction and lose their load-bearing qualities. The most vulnerable place of screw piles is the internal cavity, in which condensation forms under the influence of temperature changes and settles on the internal walls. As a result, after a few years, rust affects part of the foundation, distortion and gradual destruction of the building begin. Properly performed waterproofing will increase the service life of the structure and the house as a whole.
Preservation of the foundation for the winter
The inability to complete construction before the onset of cold weather leads to the need to protect the concrete foundation from the negative effects of the external environment.
If this is not done, it may receive obvious or hidden damage. In the first case, we are talking about visible breaks, cracks, deformations and other similar defects. Even if you try to eliminate them, it will be impossible to achieve the previous integrity of the structure.
A more dangerous situation is when the concrete base receives hidden damage. They can arise for the same reasons as visible defects (swelling of frozen soils, temperature changes, high humidity, etc.) - but they do not appear immediately, but after a certain time. Sometimes problems with the foundation become known only at the final stages of construction and even after its completion, which leads to the impossibility of operating the facility.
What are they doing now?
Waterproofing a brick foundation
The protective layer of the foundation slab is increasingly made from modern building materials that have adequate strength and reliability. First of all, stekloizol and rubemast are used, which are roll waterproofing devices.
They are based on fiberglass or fiberglass. The base, in turn, is impregnated with bitumen, which contains modifying additives. As a result, the material gains elasticity and good bending strength. Resistance to temperature changes is also at the same level.
Waterproofing under a roll-type foundation slab is convenient because it is simply laid on a backfill of gravel and sand. No additional screed is required at all. Using mastic, the joints between the strips of material are carefully glued.
The installation process itself is carried out very quickly. The only special equipment needed is a burner that will heat the mastic.
Coating waterproofing of a foundation slab using bitumen mastic is the most modern way to protect the base of a building from moisture. It is produced by applying modified bitumen to the foundation. The device required for such work can be a brush, roller or sprayer.
Waterproofing a monolithic foundation slab in this way involves applying a layer of cement screed to the sand-crushed stone bed.
A similar method is used to waterproof a penetrating type foundation slab. The cement screed is laid on a base of gravel and sand. After which it is covered with rolled materials.
After pouring, penetrating insulation is applied to all side and top surfaces. This protective layer of the foundation slab is the most high-tech and effective.
Is it possible to leave the foundation for the winter?
Preservation of the foundation for the winter is required regardless of the degree of its readiness. Otherwise, there is a high risk of losing already created foundation structures.
Low temperatures and high humidity have a destructive effect on the concrete base. The degree of negative impact depends on the following factors:
- climatic features of a particular region;
- type of foundation (pile, strip, columnar, etc.);
- the stage of work after which the foundation will have to be left for the winter;
- structure and other features of the soil (heaving, freezing depth, presence of groundwater in the immediate vicinity, etc.).
The most resistant to adverse weather conditions are pile (screw) foundations. Strip structures and concrete monolithic slabs are at greatest risk of destruction.
No less dangerous is the swelling of the soil due to its freezing. This phenomenon can seriously destroy the concrete base to the point of making it impossible to use further. Tears, deformations, distortions, and other defects appear. Strip foundations and monolithic slabs suffer the most from soil swelling.
Is it necessary to cover the foundation for the winter?
The need to cover the base depends on the degree of its current readiness. It is sometimes possible to keep the foundation open for the winter under the following conditions:
- concrete gained strength at positive air temperatures for at least a month (this rule is the most important);
- high-quality vertical and horizontal waterproofing was performed;
- tamping was carried out, the internal space and sinuses were filled;
- A hydraulic lock is made in the upper part of the backfill.
If it is necessary to fill the base at negative air temperatures, it is necessary to use special anti-frost modifiers. A more complex option is to heat the entire structure until it reaches the required strength.
Waterproofing is especially important for lightweight concrete. In other cases, its absence is allowed - if the soil is dry and the soil waters lie deep enough. But in this situation, when preserving the foundation for the winter, you can leave the foundation for the winter only under cover.
As for the backfill, it protects the created foundation from flooding by melt or rain water.
Is it necessary to load the foundation for the winter?
Leaving your foundation unloaded over the winter can be dangerous. One of the main threats to an unloaded foundation in the cold season is the risk of its destruction under the influence of such a phenomenon as swelling of the soil due to its freezing. First of all, shallow, monolithic and strip structures are susceptible to it.
Frozen wet soil pushes foundation elements out of the ground. This leads to their ruptures, deformations and distortions, violating the integrity and structure of the prepared base.
Thus, the absence of loads from the erected power structures of the building leads to the impossibility of compensating for buoyancy forces arising due to swelling of frozen soils.
Therefore, if you do not plan to load the foundation for the winter, it is necessary to take a set of measures to protect it from the negative impacts of climatic and geological nature. Otherwise, it may be subject to complete or partial destruction, up to the impossibility of subsequent operation.
Foundation conservation work
The process of preparing a poured foundation for the upcoming winter period depends on its type and design. It is important to follow the sequence of steps and procedures, since even minor deviations from mandatory technologies can lead to devastating consequences.
Strip foundation
This type of foundation is one of the most susceptible to destructive effects from swelling soils, as well as high humidity and low temperatures. Therefore, preservation of the strip foundation for the winter is necessary, and in order to protect the foundation for the winter, several types of work should be performed, the main of which are:
- mandatory removal of formwork, since wood attracts moisture and then transfers it to concrete;
- waterproofing of the entire structure, for which different materials can be used: plaster, coating, primer, roofing felt, etc.;
- construction of a drainage system, and it is recommended to do it while working on the foundation (but it can be done immediately before conservation);
- insulation using polystyrene foam, polystyrene or other suitable materials, followed by covering with reinforced film.
In any case, it is necessary that before preserving the strip foundation for the winter, it must gain strength for at least a month at positive air temperatures.
Monolithic slab
This type of foundation, left without load, is most susceptible to deformation, erosion and displacement in winter. Its vulnerability is due to the fact that due to its relatively small thickness, the entire structure is actually located in the zone of soil freezing.
The presence of a sand-gravel cushion and a waterproofing layer protects against soil water and swelling, but in any case it is impossible to leave the slab foundation unpreserved for the winter. It is necessary that before the onset of cold weather, concrete gains strength for at least 30 days at positive air temperatures.
Before leaving the base for the winter, it is necessary to protect not only its surface, but also the surrounding area from moisture. You can use film, waste slag, expanded clay, etc. You must first provide insulation - polystyrene foam, polystyrene, dry sawdust or sand are suitable for this.
Screw pile foundation
This type of base is least susceptible to moisture, low temperatures and swelling frozen soils. Pile structures can be erected both in summer and winter. They are used on weak, crumbling, swampy, etc. soils, as well as in areas with high groundwater levels.
Special preservation of the pile foundation for the winter is not required; the preparation technology may only include tying from rolled metal. You should also first check that the internal space of the installed piles is filled with concrete, and that it is desirable to have a cap on top.
Columnar foundation
Structures of this type are used primarily for the construction of relatively light buildings, for example, frame, wooden, panel houses. The peculiarity of such bases is that they have little contact with open air and soil.
Calculation of slab foundation parameters
Horizontal waterproofing of the foundation
Monolithic slab foundation is also called floating. This is explained by the properties of the slab to “float” during seasonal soil movements. However, to ensure such characteristics, it is necessary to accurately calculate the parameters of the slab foundation. Various factors must be taken into account.
When calculating the thickness of the concrete base, the following values are taken into account:
- The distance between the top and bottom rows of the reinforcement cage.
- The thickness of the concrete pour under and above the frame.
- Diameter of reinforcement bars.
In most cases, when adding these values, it turns out that the height of the slab is approximately 30 cm. The obtained result can be taken into account when constructing a monolithic slab foundation on solid and stable soil.
When performing calculations, you should take into account the material from which the main structure will be built and the number of floors. For example, 5-6 cm should be added to the obtained values if the walls of the house are brick. In addition, if there is a second floor in a brick house, the foundation slab increases by another 40 cm.
When calculating the depth of the pit, take the height of the slab as a basis and add to this the thickness of the drainage layer of 30 cm and a sand cushion 20 cm high. As a result, it turns out that 50-60 cm is added to the total height of the slab.
Based on the total height of the monolithic slab, the required amount of concrete, the total length of reinforcement and the load from the base to the ground can be calculated.
When and how to prepare the foundation for winter?
Thus, the preparation of a concrete base left without load for the cold season depends on its design and engineering features.
The process of preserving the foundation for the winter must be followed in compliance with technology and using suitable materials. In the absence of the proper experience and skills, it is recommended to invite specialists, since even seemingly insignificant errors can lead to complete or partial destruction of the structure.
It is best if by the winter period the main structures of the building (walls, partitions, roof, etc.) stand on the foundation. This will eliminate the need for additional protection from humidity, low temperatures, swelling of frozen soils and other destructive influences from the external environment.
However, this is not always possible: most often, delays in building a house are due to lack of time or money. In such situations, proper preparation of the concrete base for the winter season allows you to postpone the construction of walls and other structures until spring without the risk of damage or destruction.
The type of foundation is selected taking into account the design of the house, the condition of the soil and other nuances. For any questions, please contact the specialists of Territory Group of Companies by phone or via the website.
Protecting walls from moisture
Waterproofing to protect against capillary rise of moisture is laid on a plinth that rises 15-50 cm above the ground. The surface is first dried and leveled, after which it is covered with bitumen mastic. Roofing material is laid on the mastic in 2 layers. This technology is called continuous laying because it completely crosses the thickness of the walls and plaster.
The outside of the plinth must also be waterproofed to the level of the gasket. Moisture can come from both snow cover and rain, drops of which, bouncing off the blind area, wet the wall just at the distance of the base. Therefore, for its cladding it is necessary to use waterproof materials such as water-repellent tiles.
Protecting walls from capillary rising moisture
Insulation and preservation of a pile-grillage foundation for the winter
Recently, the question of maximum heat preservation in the house has interested almost everyone. There are many different ways to do this, and one of them is to insulate the load-bearing building structure, which takes on the main load of the entire building - the foundation. Let's talk about how to insulate a pile-grillage foundation.
Reinforced concrete slabs
Foundations of this type have high technical characteristics, which they acquire through the use of concrete of a grade not lower than M200. This is an excellent, high-quality material with good adhesion. When used, high reliability and durability of the building structure is achieved.
When planning a foundation, there are conditions where savings must be neglected in order to provide the most reliable foundation for a building. In these cases, a monolithic foundation slab is used, which in design can be:
- Solid base made of reinforced concrete foundation slab
- Base made of prefabricated panels united by a covering
- Lattice slab of cross beams made of reinforced concrete
- Box foundation
Is it necessary to insulate a pile-grillage foundation?
Let's now see whether it is necessary to insulate a pile-grillage foundation during construction. It is advisable to do this, and precisely because without good thermal and waterproofing, it is the grillage that can fail and crack during the shrinkage of the building, which will immediately affect the solidity of your building.
This is the only gap in such material, so we emphasize once again that insulating the pile foundation grillage during the construction of your building is extremely necessary.
Method of insulating the base of a wooden house
Some people believe that in wooden houses there is no need to insulate the foundation. But no matter what kind of wood was used to build the house and what treatments it was subjected to, it must be protected from all possible influences on it. To insulate this kind of house, polystyrene foam is used. Alternatively, the base can also be covered with brick.
Pile foundations are used in cases where the soil is quite weak and cannot withstand heavy loads. For the construction of modern buildings, screw piles are more often used. At the end of the construction process of such a foundation, it must be insulated.
Insulation materials: characteristics and cost
First, prepare materials for insulation. Which types of them to choose based on the characteristic data, determine after you make a calculation showing the conditions and intensity of penetration of frost and moisture to the foundation.
Natural insulation materials
- Paroc Linio 80, thermal insulation boards for plastering systems. These lamellas or strips of mineral wool do not allow the cold to pass through, but in order to prevent moisture from penetrating into them, additional waterproofing must be added.
- ROCKWOOL LAMELLA MAT, stone wool. Does not allow cold and moisture to pass through. Very practical and easy to use. Almost half the price of the first insulation.
- Steico Isorel, ecological, natural wood fiber insulator. Just as in the first case, it retains heat well, but to prevent moisture from entering, it is better to simultaneously waterproof the original material. Quite budget friendly.
- They also use simple sawdust, tow or plywood.
Stone wool for foundation insulation
Polyurethane foam
These are either cans that spray this material, or synthetic foam-like slabs. Quite good quality material, protects well from the cold.
Penofol
Innovative products consisting of mixed film and roll raw materials. Very easy to use thanks to the presence of an adhesive side. Waterproof and heat resistant.
Mineral wool
This is a textile that looks like cotton wool, in the structure of which glass, blast furnace slag and rock alloys are mixed. Not flammable. Easily tolerates changes in temperature. Excellent sound and heat insulation.
Extruded polystyrene foam
It is essentially polystyrene foam, but without many of its disadvantages. It has strong heat resistance and also resists chemical irritants well. The material is strong and durable. The truth is quite expensive.
Foam plastic (pressless polystyrene foam)
Perhaps the cheapest, but most successful insulation option. Shows a high level of protection against water and frost. Easy to install. True, it can also easily be damaged during installation, this must be taken into account. But it lasts for a long time.
Polystyrene foam protects the foundation from water and frost
We insulate from the outside and inside
Insulation of a screw foundation.
Insulating the base of a house with slabs of extruded polystyrene foam (penoplex) is beneficial due to the fact that it has high compressive strength (0.5 MPa) and its thermal conductivity is low. To insulate the base from the outside, we prepare the tools:
- shovels;
- buckets;
- construction knife for cutting insulation boards.
Materials:
- rolled roofing felt;
- insulation boards (from 50 mm thick);
- bitumen mastic;
- construction foam;
- sand, gravel, concrete.
We carry out the work in a certain order:
- We dig a ditch along the perimeter to the depth of the foundation, half a meter wide, and fill the bottom with a small layer of sand and gravel.
- After cleaning the foundation, you should level it, knocking down any uneven areas.
- We install waterproofing on the dried surface, fixing the roofing material on the foundation surface using bitumen mastic, applying it either to the entire surface or in dots (8 per slab).
- The insulator is placed from bottom to top, resting the first row on a rigid base in the form of a gravel-sand layer. Expanded polystyrene slabs are secured with mastic to the waterproofing, joining them with recesses into a “lock” and lifting them to a height of up to 40 cm.
- The joints of the slabs are covered with foam, protecting them from moisture.
- We cover the slabs on top with another layer of roofing felt.
- We pour a layer (15 cm) of sand into the ditch, laying the remaining insulation on top, then pour half a meter of gravel.
- The top is sprinkled with sand, earth, or a blind area is made by filling it with concrete mixture.
Options for foundation insulation.
If water easily accumulates in the soil, then below the floor plane, in a layer of gravel, you need to lay pipes for drainage. Plaster can be applied to the concrete surface and finished with ceramic tiles.
The basement of the house can be insulated with polyurethane foam (density 60 kg/cub.m), which forms a seamless layer, at the same time serving as a waterproofing agent, and is well attached to surfaces, forming a closed contour around the foundation wall. Let's prepare the tools:
- spraying equipment (with protective equipment);
- construction knife;
- putty knife;
- shovels.
Materials:
- polyurethane foam;
- primer and plaster solution.
We carry out work:
- We dig a trench along the foundation and clean its surface.
- We spray the cleaned polyurethane foam with the first layer (using special equipment) 15 mm thick.
- Let it dry for half a minute and repeat this technology several times to achieve a total layer of about 50 mm in thickness, avoiding tears.
- After hardening, we level the foam by cutting off the protrusions with a knife.
- We prime the surface, then cover it with plaster. Upon completion, the foundation is covered with earth.
Scheme of foundation insulation with polyurethane foam.
The foundation of the house should also be insulated from the basement side, if it is provided for by the design.
Tools:
- drill;
- putty knife;
- dowels with disc-shaped caps.
Materials:
- foam boards;
- plaster mortar;
- construction mesh.
We work in this order:
- We prepare the walls by cleaning them and leveling them with a plaster solution.
- After it has dried, the insulating boards are placed on the wall, starting from the bottom and pre-coated with glue (apply with a spatula).
- Additionally, the material is secured with plastic dowels, drilling holes for them in the wall (approximately 50 mm) with a drill through foam plastic boards. We hammer in the dowels.
- We lay a mesh on the slabs, apply a plaster solution, leveling it.
- Selected finishing materials can be stuck to the surface of the dried layer.
When the foundation of a house is insulated, it increases its service life, and a pleasant microclimate is created inside the premises. Thermal insulation must also be carried out from the inside if there is a basement compartment, and no expense or time should be spared in its implementation. Therefore, the question of why to thermally insulate the foundation receives a clear answer.
Insulation technologies
There are many ways to insulate a grillage; we will focus on the best of them.
Pile-grillage foundations
This option is designed to insulate the outer layer of the foundation from water and cold.
To insulate the grillage on piles in this way, the following steps are performed:
- First bitumen. It is poured in a layer into the ground floor, it fills all the sides of the grillage from the outside and thereby already creates a thorough safe protection for it.
- Next is polystyrene foam. The raw materials are glued onto the flat surface of the grillage itself or the bitumen with which you previously covered it. Reliable and for many years.
- Be sure to “blow out” all the seams with foam to block access to frost through them.
- Then it is advisable to cover the structure with reinforcing steel mesh to protect all preliminary coatings from rodents and prepare the base for plaster.
- And the final stage is the plastering of the base itself. Perform this only when the glue has dried and the mesh has tightened.
Pile foundation with intermediate grillage
Insulate the foundation with an intermediate grillage with thermal panels. Attach them either to the grillage itself or to the sheathing; there is no need to bury them too deeply in the soil.
There are many ways to insulate a grillage
We insulate the base of a pile-screw foundation with a high grillage
Since the pile-screw foundation is in greatest demand, we will tell you how to deal with its insulation. To do this, a false base is created from a wooden frame or brickwork.
Why do you need a grillage, description and features
Foundation waterproofing
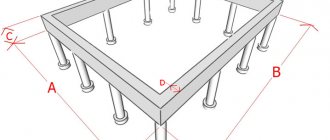
The grillage is considered one of the constituent parts of the foundation. It connects piles or pillars into a single whole. It will be needed in order to transfer the load from the walls to the piles and then to the ground. Iron beams are used as a grillage, but most often it is reinforced concrete.
Example of a grillage for a garage foundation
In the reinforced concrete version, it can be made as a strip or a solid slab. A tape or slab connects the pile heads in the foundation. The tape can certainly be recessed or not recessed.
What does a recessed grillage look like?
The foundation with a recessed grillage is considered the most popular. Its design is very simple. A shallow trench is dug along the perimeter between the pile heads. The upper part of the piles must certainly be covered with waterproofing. Sand is added to the bottom of the dug trench between the piles and compacted, then crushed stone is laid.
Recessed grillage for a country house
It should be placed at the same level with the top of the pile. Then, on top of the crushed stone, we put roofing felt. Then we install the formwork. We upholster it inside with roofing felt or glassine. The padding is required to prevent the concrete from sticking to the formwork panels.
We strengthen it from the outside with jibs and connect the walls of the formwork with transverse bars. This should be prepared so that the formwork does not collapse when pouring concrete. After this, a reinforcement cage is mounted inside the formwork. It is tied to the outlets of the reinforcement from the pile heads. After all the preparatory steps, concrete is added. When pouring, it is better to pierce it with an iron rod so that all the air escapes and the concrete becomes thicker and more durable. When the concrete dries, the formwork is removed and the grillage is ready.
Characteristics of a non-buried grillage
A non-recessed grillage is designed in exactly the same way as a recessed one. The main difference during its installation is that the trench is not dug. First, the formwork is installed and sand is poured into it. All the following work is carried out in exactly the same way.
A non-buried grillage made on screw piles for the construction of a house from Teplosten thermoblocks
Since it is not buried, a certain distance remains between the soil and concrete. To insulate such a structure, it is advisable to prepare a fence. It will be needed to insulate the subfloor and prevent the penetration of snow and dirt.
When the grillage is made, it is advisable to prepare its waterproofing. In addition, when creating it, you should not forget about ventilation holes - vents. They should be anticipated in advance, before pouring concrete. Further, after the construction of the building, it is finished with stone, brick or something else, using a variety of finishing materials.
Waterproofing insulation
Since water is present in the soil in any region, it is imperative to protect your insulation from moisture penetration, especially when it comes to preserving a pile-grillage foundation for the winter. It is quite easy to carry out waterproofing, using sheets, in the form of a spread, in rolls, as well as using spray cans and insulation.
You can combine them, this will give a better effect and lead to higher performance.
Can a strip foundation survive the winter without load?
The foundation for the bathhouse will be ready in mid-August. The main strip is 4x6 m plus a strip of 1.5x3 m, monolithically connected to the long side of the main strip (i.e. the entire foundation is laid in 5.5x6 m). Height 70 cm. Width 35 cm. Sand pillow 40 cm deep and 80 cm wide. Why is it dangerous to leave it unloaded for the winter? I’m interested in the question just in case - I still hope to start building in the fall.
No, soil heaving may even break it. Alternatively, insulate the foundation and the soil next to it; with the right approach, everything can be done.
I plan to make a shallow foundation - only tape, without pillars, because... I think the construction is easy (1-story log house). Our foundations don’t float too much, even though the soil is clayey (earth to the tip of a shovel, then dense clay; water doesn’t stand in large quantities). By the way, tell me how much it costs to bury it? I think see 15-20. This is right? Or maybe it’s better not to bury it at all?
Many sources indicate that the correct shallow foundation for MO needs 50-90 cm..
alpinist.ru wrote: Many sources indicate that the correct shallow foundation for MO needs 50-90 cm.
There is a popular opinion that with such deepening, the foundation will steadily stick out by several cm in the spring, i.e. Such foundations grow every year. There are experts who advise either burying it below freezing depth, or almost not burying it (10-20 cm). I definitely won’t do it below freezing depth.
alpinist.ru wrote: No, soil heaving can even break it. Alternatively, insulate the foundation and the soil next to it; with the right approach, everything can be done.
How can you insulate the foundation?
2gpav go around to your neighbors and see how they do it and just don’t repeat their mistakes
first, look at how fence posts behave
Fence posts of small diameter (pipes with a diameter of 5-7 cm), simply dug in at 0.5. 1 m, behave well. But concrete pillars, buried to the same depth, grow quite vigorously. I didn’t see any ribbons from nearby neighbors at all, only pillars made from shallow blocks. They have to be adjusted every few years. In general, of course, they crawl out and fall down, but not much and not quickly. There are ribbons on other streets. I'll take a look.
Any other opinions about wintering without load?
2gpav What does the load have to do with it? The force of frozen water is orders of magnitude greater than the weight of the foundation itself and the building standing on it. You are essentially creating a FLOATING foundation. If there is good concrete + tamping + tied reinforcement in sufficient quantities, everything should be OK. If not, it may burst due to uneven bulging in winter. insulate - don't insulate, load - don't load.
The strip will not bulge (IMHO) only when the foundation is deepened below the freezing point.
2sansan21 Yes, I understand that it is floating. But they don’t swim much in our area, judging by our neighbors. And the load is supposed to be not large at all - a one-story log house. Therefore, I believe that such a foundation will have a large margin and decided to do without digging below the freezing level. Naturally, I proceed from the assumption that everything will be done efficiently. Tell me, does it make sense to deepen it a little - 15-20 cm? Or is it better to pour directly from the surface of the pillow? I think that if you deepen it a little, it will float less horizontally. Right?
Radiofishka wrote: The tape will not bulge (IMHO) only when the foundation is deepened below the freezing point.
Don't forget about tangential heaving forces
If you fill both sides with good sand, see 40 cm (there is already a sand cushion), then the heaving will be much less. The main problem here is to prevent the foundation itself from bursting, and for a log house this is not a problem. And the log house weighs an order of magnitude less compared to heaving forces. As for the bulging of pillars, pillars of small diameter have a small lateral area and the soil slides along the pillar. If you make a sand backfill around the concrete pillars, and cast the underground part in polyethylene film (to obtain a smooth surface), then everything will be fine with them too.
2gpav You do not understand the term “floating” quite correctly :-). A floating strip foundation should work like a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. Those. in the worst case, if vertical or horizontal heaving forces